Business
Russian Sanctions Snarl Shipping Even as Pandemic Pressure Eases

Russian ships banned from docking in Britain. Cargo containers piling up at European ports. Airfreight rerouted round Ukraine and Russia.
Simply as the worldwide financial system was on monitor to emerge from the coronavirus pandemic, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and international sanctions towards Moscow are rippling by way of logistics and provide chains, creating bottlenecks within the transport of products and commodities and threatening contemporary financial ache for international locations and companies close to the battle zone.
Transport firms, maritime insurance coverage executives and trade analysts say the two-week-old battle, mixed with uncertainty fueled by the sanctions, is inflicting backups of ships at some ports and will result in longer delays in shipments, particularly round Europe.
The price of transporting cargo delivered by sea, land and air, which had already jumped in the course of the pandemic, can be below stress as international oil costs surged previous $130 a barrel this week.
“We thought we skilled a bounce-back from Covid in January and February,” stated Detlef Trefzger, the chief government of Swiss-based Kuehne+Nagel, one of many world’s largest transport firms, which delivers cargo by ship, air, rail and truck. “However the Ukraine-Russia disaster is a big setback,” he stated, “and will probably be a long-lasting setback.”
Probably the most visceral blow is being felt close to the center of the battle zone, within the Black Sea.
Greater than 100 ships and their crews have been stranded at Ukrainian ports since Russia invaded Ukraine. Missiles have hit a number of industrial vessels, and an explosion on or close to an Estonian dry cargo vessel sank it 20 miles off Odessa, a Ukrainian port. The Russian and Ukrainian crew members all survived.
The chance has compelled shipowners to pay an extra insurance coverage premium of 1 to five p.c of a ship’s worth, stated Marcus Baker, the worldwide head of maritime and cargo at Marsh McLennan, an insurance coverage dealer and danger adviser. The insurance coverage trade’s Joint Struggle Committee widened its high-risk areas to the waters near Romania and Georgia this week after including Russian and Ukrainian waters final month.
The Worldwide Maritime Group’s secretary common, Kitack Lim, stated at an emergency council session on Thursday that there was severe concern in regards to the security and welfare of seafarers within the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov, and that seafarers couldn’t be collateral injury within the navy disaster.
The blockage has squeezed international grain provides from one of many world’s largest grain-producing areas, pushing wheat costs increased on world markets and fanning the specter of inflation. Russia and Ukraine collectively account for almost 1 / 4 of world exports of wheat.
Issues across the Black Sea are the tip of the iceberg, rippling disruptions all through the logistics trade and pressuring international commerce, analysts say.
Within the final two weeks, some European terminal operators have refused ships carrying cargo for Russia, and tons of of Russia-bound cargo containers have piled up at others.
Britain has gone additional, asserting sanctions that ban Russian vessels from its ports as a way to “limit Russia’s financial pursuits.” About 20 vessels have been diverted from British ports, stated Richard Ballantyne, chief government of the British Ports Affiliation.
International ports had been already going through bottlenecks in the course of the Covid-19 pandemic — particularly in america, the place scores of ships have been caught off California due to backlogged warehouses and a scarcity of truckers to fan cargo all through the nation.
Whereas the logjam in Europe’s ports isn’t as extreme, the sanctions, meant to punish Moscow with out devastating the European financial system, are shifting that calculus.
On the Port of Rotterdam within the Netherlands, the biggest seaport in Europe, some terminals have become “a car parking zone” for tons of of cargo containers destined for Russia, stated Tie Schellekens, a spokesman for the port.
Lots of the containers stacked on docks await endure time-consuming customs inspections to verify they don’t seem to be carrying blacklisted objects, like spare airplane components or semiconductors. The pileup shouldn’t be disastrous, Mr. Schellekens stated, however to stop additional congestion, some port operators are refusing to simply accept ships carrying any Russia-bound cargo.
On the identical time, he stated, some European firms will not be even attempting to ship items to Russia, for worry of breaching a listing of sanctions by Western allies that appears to develop longer by the day. Companies are additionally beginning to curb manufacturing amid worries that Russian purchasers gained’t pay them for shipped merchandise, partly as a result of monetary sanctions are gumming up fee mechanisms.
The Russia-Ukraine Struggle and the International Economic system
“It means the impact of the sanctions is wider than the sanctions themselves,” Mr. Schellekens stated.
Mark O’Neil, president of Columbia Shipmanagement, a maritime companies supplier based mostly in Cyprus, stated the impression on the graceful movement of products was important.
“As quickly as you impose sanctions and embargoes, and firms themselves block sure commerce, then the knock-on results of extra checks inevitably trigger delays,” he stated. “The maritime logistical aspect is a really well-oiled machine, and it solely take a slight petal to be thrown into the pond for the ripples to be felt extraordinarily far.”
The bottlenecks will not be solely on the water. Sanctions towards Russia are placing contemporary stress on already tight air cargo capability, inflicting transport charges to spike. With Russian airspace off limits to most carriers, and america, the European Union and Canada banning Russian plane from their airspace, the worldwide air cargo market is being quickly squeezed, analysts stated.
Flights between Europe and Asia particularly need to be rerouted, including three to 4 hours to some routes and requiring extra gas simply because the battle pushes oil costs to file highs.
Russian carriers corresponding to AirBridgeCargo and Aeroflot Cargo — two massive gamers, flying round one-fifth of world air cargo quantity — have pulled again sharply. Whereas simply 3 p.c of world cargo travels in planes, air cargo makes up over a 3rd of world commerce by worth.
Floor transport can be being affected, because the battle disrupts key rail routes between the European Union and China, slowing commerce. Some firms have suspended rail freight between the areas over considerations about disruptions on the borders. The sanctions additionally imply European firms can not work with Russian railways.
Trucking isn’t being spared, both. Kuehne+Nagel stopped deliveries to Russia from Europe and China to keep away from violating the sanctions, Mr. Trefzger stated. However Europe’s trucking trade can be going through a contemporary scarcity of drivers, as tens of 1000’s of Ukrainian truckers head again to Ukraine to affix within the battle towards Russia, he famous.
That leaves many European firms extra dependent than ever on different means to get their items to prospects. However situations within the trade are more likely to worsen earlier than they enhance, executives and analysts say.
“Transportation hyperlinks are important to international provide chains, they usually have already been impacted by the worldwide pandemic,” stated Anna Nagurney, a professor within the Isenberg College of Administration on the College of Massachusetts.
“Now we have now an extra man-made catastrophe,” she stated.

Business
The Fallout From the End of the U.S. Steel Deal

The end of a troubled takeover bid
President Biden is set to officially block Nippon Steel’s $14 billion takeover of U.S. Steel as soon as Friday, most likely putting an end to an industrial megadeal that ran up against widespread political opposition.
But the decision could set off a cascade of consequences, including whether it would dissuade foreign investment in key industries, even from crucial U.S. allies like Japan. There’s one near-certainty: Expect a lot of litigation.
The deal’s demise seemed increasingly inevitable. In March, Biden said it was “vital” that U.S. Steel remained American-owned. The United Steelworkers’ union opposed the transaction from the start, questioning Nippon Steel’s commitment to maintaining the American company’s production and unionized employment levels. (That U.S. Steel is headquartered in Pennsylvania, a crucial election battleground state, escaped no one’s notice.)
Last month, the federal government panel, known as CFIUS, that reviewed the deal on national security grounds expressed concern that the Japanese suitor’s global business considerations could eventually outweigh any commitments it made to preserve U.S. Steel production levels.
President-elect Donald Trump also pledged to block the takeover once he took office.
Others have worried that blocking the deal could chill foreign investment. In recent days, some senior Biden advisers warned that rejecting the transaction could damage relations with Japan, The Washington Post reported.
Japanese officials pressed Biden to approve the deal. Rejecting it “will send a stark message that investment from Japan, regardless of lack of security concerns, is not welcome in the U.S.,” Takehiko Matsuo, a senior trade minister, wrote to Biden administration officials last month.
The matter will probably head to court. Nippon Steel has complained of the White House’s “impermissible influence” in the CFIUS process. That lays the groundwork for the Japanese company or U.S. Steel to sue over Biden’s expected move.
DealBook also wonders whether the companies would sue each other, perhaps citing a failure to do enough to win approval. (The deal agreement requires Nippon Steel to pay its American counterpart $565 million if regulators block the transaction.)
What next for U.S. Steel? The company’s C.E.O., David Burritt, has warned that the steel maker needs investment to upgrade its aging plants. Even CFIUS acknowledged that the company had a “history of inadequate attempts to improve its competitiveness.”
One possibility is another bidder — such as Cleveland-Cliffs, which had been previously rebuffed by U.S. Steel and whose stock has been under pressure — could swoop in. But there’s bad blood between Burritt and his Cleveland-Cliffs counterpart, raising the question of whether U.S. Steel investors would need to heap on the pressure to get a deal done.
HERE’S WHAT’S HAPPENING
Mike Johnson faces a nail-biter vote on Friday for House speaker. Johnson has the backing of President-elect Donald Trump and Elon Musk, but is hampered by a razor-thin majority and a fractious House Republican conference. Corporate America will closely watch the vote’s outcome for what it says about the chamber’s ability to pass legislation once Trump takes office.
The authorities identify the driver of the Las Vegas Cybertruck explosion. The man was an Army master sergeant on leave from active duty, who killed himself immediately before the rented Tesla detonated outside a Trump hotel in Las Vegas on New Year’s Day. The F.B.I. said it had found no link between the incident and the deadly New Orleans rampage hours earlier involving an Army veteran.
China places trade restrictions on dozens of U.S. companies. The Ministry of Commerce announced on Thursday that export-control limits would be put on 28 companies, including Boeing and Lockheed Martin. The move comes just weeks before Trump takes office, and will probably escalate a trade war between Washington and Beijing. More shots could be fired soon: The Biden administration is weighing a ban on Chinese-made drones.
Does Tesla sales stall matter?
At any other car company, the sales numbers announced by Tesla on Thursday would have been a catastrophe. Deliveries for the year fell slightly in a growing market, the first annual decline in the company’s history.
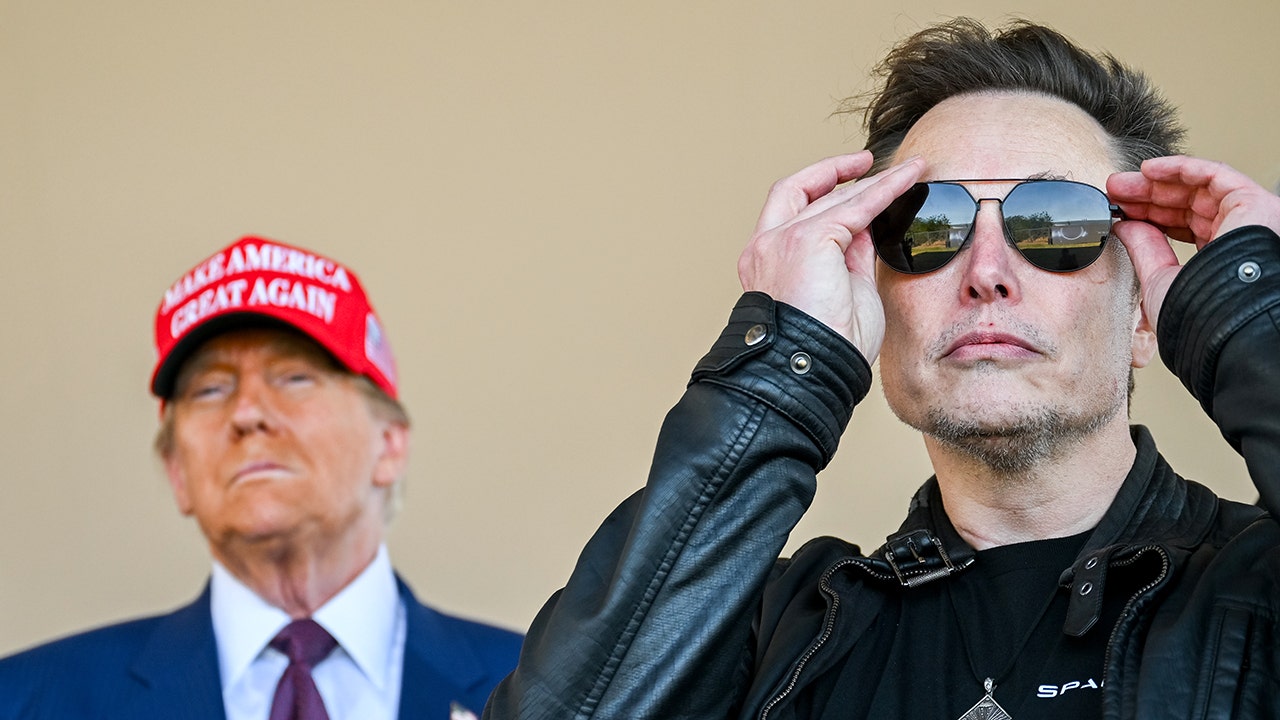
Yet the reaction on Wall Street was relatively muted when compared to the huge rally in Tesla’s share price in recent months, The Times’s Jack Ewing writes for DealBook. That reflects how much Elon Musk has sold investors on the idea that the cars are a piece of a much bigger vision that includes self-driving taxis and humanoid robots — and his close ties to President-elect Donald Trump.
Shares closed down but the stock is up more than 55 percent since Election Day. Musk’s relationship with Trump has given him a direct line to the White House that he can use to promote his business interests.
“Investors have shifted,” Erik Gordon, a professor at the Ross School of Business at the University of Michigan, told DealBook. “They thought of it as an E.V. company. Now they think of it as a technology platform. ‘What will Elon think of next?’”
Musk has revealed little detail about his plans. During conference calls with investors and analysts, he has focused on what he says will be trillions of dollars in revenue from self-driving taxis that are probably years away from mass production.
Yet Musk may find it difficult to realize his grand visions if the company keeps losing market share to rivals such as General Motors, BMW and BYD. (The Chinese car maker reported record sales in 2024.)
Does Musk need to accelerate plans for a lower-cost Tesla? He told investors in October that the company would begin selling a car this year that would cost substantially less than a Model 3 sedan, which starts at $42,500 before state and federal incentives.
But Musk has sounded ambivalent about the new vehicle, calling it “pointless” unless it’s capable of driving autonomously. And Tesla has not displayed a prototype yet.
That has led to speculation that Musk is not that interested in mass-market cars anymore. “What excites Musk is the technology for the day after tomorrow,” Gordon said. “An econobox E.V. just doesn’t ring his bell.”
One thing to watch in 2025: Musk’s reaction if car sales remain tepid and Tesla shares fall further. Would that prompt him to deploy more of the skills he used to build Tesla into the world’s largest maker of electric cars?
A blow to net neutrality
A federal appeals court has knocked down one of President Biden’s biggest tech policy accomplishments: the F.C.C.’s net neutrality rules on broadband internet providers that sought to safeguard consumers’ access to online content.
The dismantling comes as companies brace for the incoming Trump administration to usher in a new era of deregulation, and further limit regulatory reach.
The decision is a win for cable and telecom companies such as AT&T and Comcast, ending a two-decade effort to regulate them like utilities. It also shows the impact of a recent Supreme Court ruling that is expected to limit federal agencies’ power.
A recap: The regulations, which have been championed by Google, Facebook and Netflix, were put in place under the Obama administration amid concern that internet service providers could become de facto gatekeepers with the power to slow or block access to content. The rules were revoked during the first Trump term, only to be reinstated by the F.C.C. in April.
Brendan Carr, President-elect Donald Trump’s pick to lead the F.C.C., has been a vocal critic of the rules.
The ruling could inspire other legal challenges. It relies on the Supreme Court’s upending last year of the Chevron doctrine requiring courts to defer to federal agencies’ interpretation of ambiguous statutes. “The F.C.C.,” Judge Richard Allen Griffin wrote, “lacks the statutory authority to impose its desired net-neutrality policies.”
Tim Wu, a former Biden administration official who coined the term “net neutrality,” slammed the decision, calling it “blatant judicial activism that puts corporate interests over American democracy.”
What’s next? The fight over net neutrality isn’t over: The decision doesn’t affect state laws, including those in California, Washington and Colorado. And Democrats at the F.C.C. called on Congress to enshrine net neutrality into law. Still, many commentators note that net neutrality isn’t the hot-button consumer issue it had once been.
“The market no longer thinks it’s a big deal and hasn’t for a while,” Blair Levin, a former chief of staff to the F.C.C., told The Times.
A big reshuffle at Meta
In the latest sign of how Big Tech is repositioning itself for the new Trump administration, Meta has tapped a prominent Republican to head its global policy team.
Joel Kaplan, a longtime Meta employee and a deputy chief of staff under former President George W. Bush, will take over from Nick Clegg, as first reported by Semafor.
Meta has tried to take itself out of the political spotlight. Clegg, a former deputy prime minister of Britain, joined the tech giant when the company was facing fierce blowback, including for its handling of disinformation on its platform during the 2016 election.
He’s credited with smoothing relations with regulators, especially in Washington and Brussels.
Could his leftish politics have become a liability? Clegg may have been planning his exit before the election, but he didn’t hide his opinions. Last month, he warned that Elon Musk, whose X and xAI compete with Meta, could become a “political puppet master” and criticized Musk’s stewardship of X.
The remarks came as many businesses worry about retribution from President-elect Donald Trump and Musk — and as Big Tech C.E.O.s have gone out of their way to curry favor with them.
Kaplan’s deep Republican roots could help Meta in the new Trump era. He joined Facebook in 2011, and later served as Clegg’s deputy. Before that, he clerked for Justice Antonin Scalia on the Supreme Court and is a close friend of Justice Brett Kavanaugh. (He appeared at Kavanaugh’s contentious confirmation hearings, and later apologized to Meta employees who thought his presence showed a political preference).
He has also been one of the loudest voices inside Meta pushing against restrictions on political content.
Mark Zuckerberg has largely turned away from politics. For years, the tech mogul publicly campaigned for liberal causes but has shifted after coming under sustained fire. Trump criticized Zuckerberg and threatened to put him in jail after accusing Meta of censoring conservative views.
But Zuckerberg, like other Big Tech leaders, has made efforts to court Trump, having traveled to Mar-a-Lago to meet the president-elect after the November election.
THE SPEED READ
Deals
-
Several prominent hedge funds — including Millennium, D.E. Shaw, Bridgewater Associates and Ken Griffin’s Citadel — reported double-digit returns last year. (Reuters)
-
Hindenburg Research, the activist short-seller, announced a bet against Carvana, accusing the used-car sales platform of accounting manipulation. (CNBC)
Politics and policy
-
President-elect Donald Trump picked Ken Kies, a longtime tax lobbyist for clients including Microsoft, as the Treasury Department’s assistant secretary for tax policy. (Bloomberg)
-
“How Silicon Valley won a powerful House committee” (Politico)
Best of the rest
-
The U.S. surgeon general, Vivek Murthy, called for cancer warnings to be placed on alcoholic beverages; doing so would require Congress to act, however. (NYT)
-
Richard Easterlin, an economist whose work challenged the assumption that more money always leads to more happiness, died Dec. 16. He was 98. (NYT)
-
“The Rise Of Big Potato” (The Lever)
We’d like your feedback! Please email thoughts and suggestions to dealbook@nytimes.com.
Business
U.S. Hits Chinese Cybersecurity Company With Sanctions After Breach

The Treasury Department imposed sanctions on a Beijing-based cybersecurity company on Friday, blaming it for helping Chinese hackers infiltrate U.S. communications systems and conduct surveillance across four continents.
In an announcement, the department said the company, Integrity Technology Group, had supported a Chinese state-sponsored hacking group known as Flax Typhoon in a campaign to break into foreign networks between the summer of 2022 and 2023, saying it found the group had “routinely sent and received information from Integrity Tech infrastructure.”
The action came after the Treasury Department revealed in a letter to lawmakers this week that a Chinese intelligence agency had breached its systems in what appeared to be an espionage operation, gaining access to the workstations of government employees and unclassified documents.
A spokesman for the department did not specify whether Flax Typhoon had been implicated in the attack on the Treasury Department’s systems, or whether the sanctions were merely part of a larger operation to disrupt China’s cybercapabilities.
The sanctions also follow the much more damaging revelation last year that a group linked to Chinese intelligence agencies and known as Salt Typhoon had hacked U.S. telecommunications networks, targeting the telephone conversations and text messages of an array of top political figures, including President-elect Donald J. Trump.
Like Salt Typhoon, Flax Typhoon is among a handful of groups that Microsoft has publicly identified as being linked to Chinese intelligence and responsible for a range of state-sponsored cyberattacks. The group has been active since 2021 and appears focused on targets in Taiwan and the United States, according to the Congressional Research Service.
“The Treasury Department will not hesitate to hold malicious cyberactors and their enablers accountable for their actions,” Bradley T. Smith, an acting under secretary of the Treasury, said in a statement. “The United States will use all available tools to disrupt these threats as we continue working collaboratively to harden public and private sector cyberdefenses.”
In September, the F.B.I. said it had taken down a network of 200,000 consumer devices in the United States and abroad that had been compromised with malware and weaponized by Flax Typhoon.
The sanctions announced on Friday generally prohibit financial institutions and individuals from transacting with Integrity Technology Group, and freeze any of its assets in the United States.
It was not immediately clear what the breach of the Treasury Department may have achieved, but the agency represents an attractive target for state-sponsored hackers because of its Office of Foreign Assets Control, which is responsible for imposing sanctions and determining which individuals represent a threat to national security.
Business
In labor-friendly California, 2025 ushers in more worker protections. Here's what to know

California lawmakers, by and large, are a labor-friendly bunch and, as in past years, they passed a host of new workplace protections that took effect when the new year struck.
Instead of breaking new ground, many of the changes represent expansions of existing protections, such as family leave and enforcement of workplace anti-discrimination laws.
And, while state legislatures typically produce fewer pieces of major legislation in years with big, national elections, Chelsea Mesa, an employment attorney with firm Seyfarth Shaw, said she expects legislative activity on the labor front to pick up speed in the coming months. “It’s going to be a very busy year,” she said.
Here’s what to know about new laws on the books.
‘Captive audience meetings’
A new law makes it illegal to penalize an employee who refuses to attend a meeting at which their employer discusses its “opinion about religious or political matters,” including whether to join a union.
Unions have long held that these “captive audience meetings” serve to intimidate employees and hinder organizing efforts.
But the law, Senate Bill 399, faces a legal challenge from business groups. The California Chamber of Commerce and the California Restaurant Assn. contend in a recently filed lawsuit that it violates companies’ rights to free speech and equal protection under the 1st and 14th amendments.
The suit asks the courts to block the law from going into effect. Business groups successfully challenged a similar Wisconsin law in 2010 but attempts to overturn Oregon’s law have been dismissed.
Digital likeness of performers
Unions backed a slew of artificial intelligence-related legislation, aiming to place safeguards around the rapidly evolving technology, with limited success. One big win was Assembly Bill 2602, which aims to protect actors and other performers by making it illegal for artificial intelligence to replicate their voice or likeness without permission.
Under the law, backed by performers union SAG-AFTRA, employers would not be allowed to use an AI version of a performer’s voice or likeness if that usage replaces work that the performer could have done in person. And it requires that workers be represented by their union or legal counsel in deals involving their AI-generated likenesses.
Another law sponsored by SAG-AFTRA, AB 1836, aims to prevent dead actors’ voices from being exploited by requiring a $10,000 fine for using their voice without consent from their estate.
Paid family leave
Workers taking leave to care for a new baby or for a sick family member will see a boost in benefits under Senate Bill 951, which passed in 2022.
Under the law, workers with incomes of less than $63,000 a year will now be eligible to receive 90% of their pay when taking leave. It’s a bump up from the previous 70% of pay these lower-paid workers were eligible for.
Workers earning higher than the $63,000 threshold will receive 70% of their pay.
Farmworker sick leave
Senate Bill 1105 allows California farmworkers to use sick time when environmental conditions prove too hazardous for work to be done safely.
“This law is critical as we adapt our policies to the impacts of climate change,” state Sen. Steve Padilla (D-Chula Vista), who was author of the law, said in a statement.
Freelance work
The Freelance Worker Protection Act requires that businesses hiring freelancers provide written contracts for services that pay the worker more than $250.
The law requires timely payments, on the date specified in the contract, or within 30 days of service completion if no specific date is set.
The law gives freelancers greater ability to enforce their rights if rules are not complied with. For example, a freelancer could sue and be awarded $1,000 if the employer refused to provide a written contract, as well as damages up to twice the amount that remained unpaid when payment was due.
Workplace discrimination
In September, Gov. Gavin Newsom signed Senate Bill 1137 into law, which clarifies that discrimination can happen based on a combination of protected characteristics. This layered approach to understanding discrimination is called “intersectionality” and it’s a policy change employers will need to take note of in their written policies, said Mesa, the employment attorney.
Mesa said, however, that it’s a concept that many companies already understand in theory. “My hope is that this doesn’t represent a dramatic change,” she said.
Another law, Senate Bill 1340, opened up the capacity for cities to enforce workplace discrimination laws on their own that previously was the domain of state agencies like the California Civil Rights Department.
Giving local agencies a chance to play a more active role in handling discrimination complaints could potentially result in quicker responses and remedies for workers. The Civil Rights Department in the city of Los Angeles, for example, is gearing up to take on such cases.
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoNew Year life lessons from country star: 'Never forget where you came from'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24982514/Quest_3_dock.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24982514/Quest_3_dock.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta’s ‘software update issue’ has been breaking Quest headsets for weeks
-

 Business5 days ago
Business5 days agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture5 days ago
Culture5 days agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics1 day ago
Politics1 day agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?