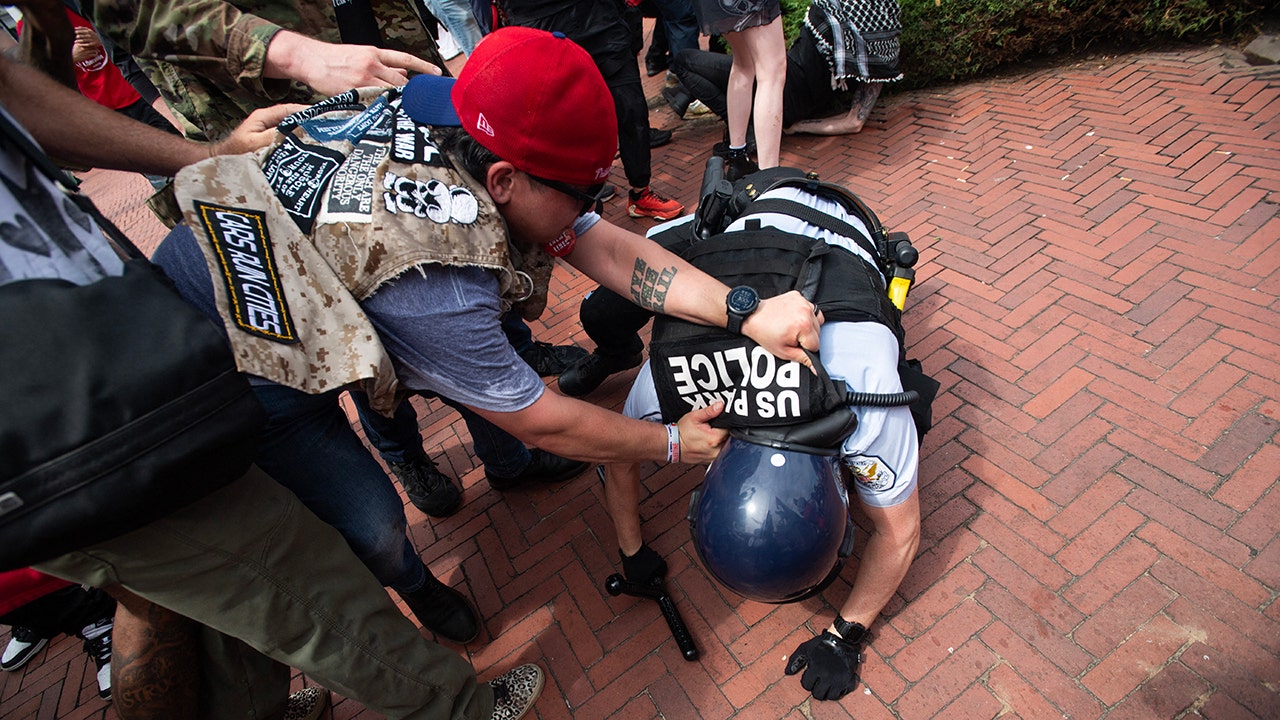Business
Column: With Democratic assent, House votes to open loopholes in crypto regulation

Money, as we all know, is the mother’s milk of politics in America. It can look even more nourishing if you can manufacture it yourself.
That’s surely what accounts for the solicitude that the cryptocurrency industry has been receiving from Congress.
The House on Wednesday passed a law reducing regulation of crypto, despite ample evidence that the asset class has been a haven for fraudsters, extortionists and worse.
The law will “make the United States safer for drug traffickers, for terrorist funders, for child and drug traffickers and those who buy and sell child pornography,” said Rep. Sean Casten (D-Ill.), listing a few of the documented users of crypto in recent years. “I did not know those groups had such proud advocates in Congress.”
The crypto industry’s record of failures, frauds, and bankruptcies is not because we don’t have rules or the because the rules are unclear. It’s because many players in the crypto industry don’t play by the rules.
— SEC Chairman Gary Gensler
Casten may find himself in the House minority in more ways than one. Crypto promoters have managed to peel several Democrats in the House and Senate away from the party’s strong opposition to reducing regulations on the asset class.
Earlier this month, bipartisan majorities in both chambers voted to roll back a two-year-old Securities and Exchange Commission guideline for how financial institutions should account for crypto assets left in their care by customers. President Biden said he would veto the change, and the majorities in neither chamber were large enough to overrule a veto.
The congressional crypto caucus handed the industry another victory Wednesday, when the House passed the Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act, known as FIT21. The vote was 279 to 136, with 71 Democrats joining the Republican majority.
The measure’s fate is unsure in the Senate, which hasn’t yet taken it up. Biden has stated his opposition to FIT21 but hasn’t promised a veto, which the crypto gang and its supporters seem to think is a big victory. Biden said that he was willing to negotiate a regulatory system that protects crypto consumers and investors without unduly interfering with innovation, but “further time will be needed.”
If it becomes law, FIT21 would deliver to crypto promoters their most heartfelt desire: removing them from the jurisdiction of the powerful SEC and transferring oversight to the chronically underfunded and understaffed Commodity Futures Trading Commission.
Their goal is understandable, since the SEC has been explicit about its intention to regulate crypto as securities, subjecting the asset class to the disclosure rules and safeguards against fraud that have made the traditional financial markets in the U.S. the safest in the world.
During Wednesday’s floor debate, the bill’s advocates talked of the virtues of freeing an innovative technology from “overzealous regulators” — that was Rep. Cathy McMorris Rodgers (R-Wash.), mouthing words that could have been dictated to her by crypto executives — and relieving them of “regulatory uncertainty.”
SEC Chairman Gary Gensler put the latter claim to rest in a statement about FIT21 he issued Wednesday a few hours before the vote. “The crypto industry’s record of failures, frauds, and bankruptcies is not because we don’t have rules or because the rules are unclear,” he stated. “It’s because many players in the crypto industry don’t play by the rules.”
The bill’s advocates tried to pump up the importance of crypto as a financial asset with claims that 20% of Americans are crypto owners. There’s no evidence for this. On the contrary, the Federal Reserve has found that interest in crypto among ordinary Americans is weak and fading.
In its most recent survey of the economic condition of U.S. households, issued this month, the Fed determined that only 7% of Americans bought or held crypto as an investment (down from 11% in 2021) and only 1% had used it to buy anything or make a payment. That underscores the most important truth about crypto, albeit one its promoters seldom acknowledge: No one has yet identified a genuine purpose for crypto in the real world.
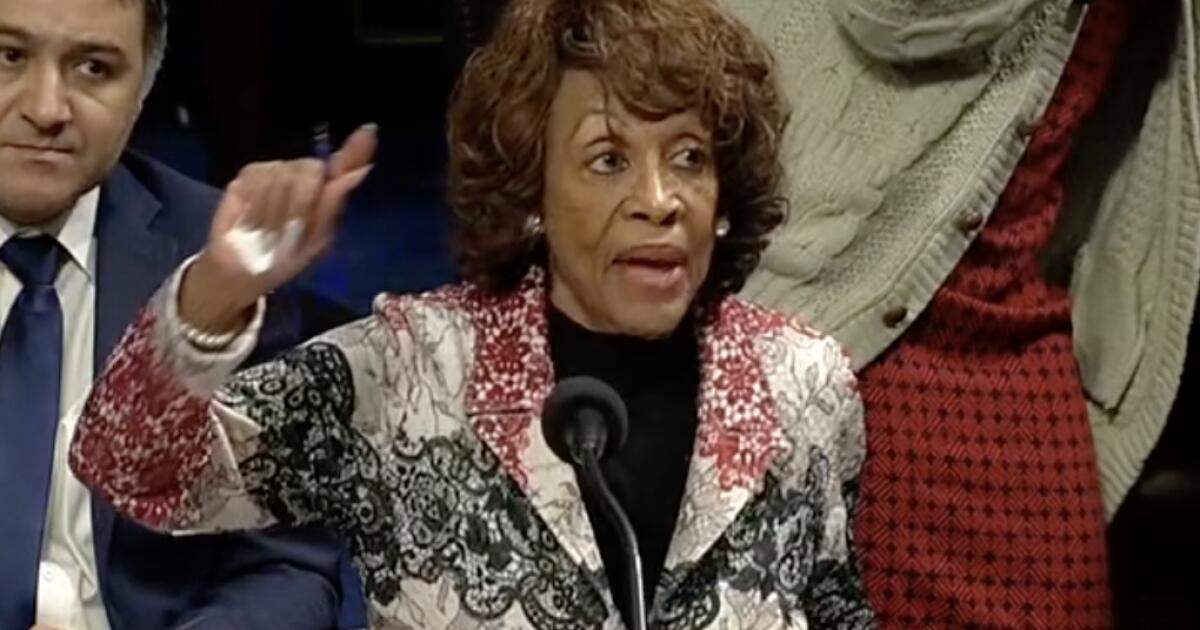
“The entities that stand to benefit from this bill are not ordinary investors trying to build wealth,” Rep. Maxine Waters (D-Los Angeles), the ranking Democrat on the House Financial Services Committee, said from the House floor Wednesday, “but rather the crypto firms. … They have already made billions of dollars unlawfully issuing or facilitating the buying and selling of crypto securities.”
Waters accurately described the effect of FIT21 as placing crypto effectively into a regulatory “no man’s land.” She described the bill as “an extreme MAGA libertarian approach, where companies can operate without regulatory scrutiny, and consumers and investors are on their own on detecting and avoiding fraudulent schemes.”
What’s most striking about the push for FIT21 is that it comes so closely on the heels of major scandals in the crypto space. Sam Bankman-Fried, the founder of the crypto firm FTX, was sentenced in March to 25 years in jail for crypto fraud, after having been convicted in November on seven federal counts related to fraud.
During the heyday of FTX, Bankman-Fried appeared before congressional committees to promote a tailor-made regulatory scheme for crypto bearing close resemblance to the one embodied in FIT21.
Just last month, Changpeng Zhao, founder of the international crypto firm Binance, was sentenced to four months in prison on federal money-laundering charges; Zhao had earlier agreed to pay a $50-million fine, and Binance settled the government case against it for $4.3 billion.
The SEC is pursuing a lawsuit against the crypto exchange Coinbase for selling unregistered securities. In March, federal judge Katherine Polk Failla denied the firm’s motion to quash the case. Her reasoning effectively explains why FIT21 is not only unnecessary, but harmful: “The ‘crypto’ nomenclature may be of recent vintage,” she wrote, “but the challenged transactions fall comfortably within the framework that courts have used to identify securities for nearly eighty years.”
The counterweight to the arguments against FIT21 is cash — the green variety, not the notional type marketed by cryptocurrency firms. Three super PACs formed by crypto executives and investors have raised about $85 million to spend on 2024 political races.
The financial potency of this industry’s campaign spending isn’t in question. One of the PACs, Fairshake, spent more than $10 million over the last year in opposition to Rep. Katie Porter (D-Irvine) in her race for the Democratic nomination for U.S. Senate.
Porter was known as a strong critic of crypto. In 2022 she joined Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-Mass.) — the most vociferous crypto critic on Capitol Hill — in an investigation of how crypto “mining” by computer had affected the energy grid in Texas and raised energy prices for consumers.
Porter lost the Senate race. Her victorious opponent in the primary, Rep. Adam Schiff, has taken a much more indulgent position toward crypto, listing it on his campaign website among the “new developments in technology … we need to grow” in order to keep jobs and regulatory oversight in U.S. hands.
In the current congressional election cycle, Fairshake has made $702,300 in donations to Democratic campaigns and $551,700 to Republicans. Its largest single recipient is Rep. Patrick McHenry (R-N.C.), chairman of the House Financial Services Committee and sponsor of FIT21. His campaign has received $126,626 even though he has announced that he is not running for reelection this year and retiring from Congress.
In his statement, Gensler tried to strengthen the lawmakers’ understanding of the risks they were endorsing with the measure. The bill would “create new regulatory gaps and undermine decades of precedent” in the regulation of investment contracts, he wrote, “putting investors and capital markets at immeasurable risk.”
It would allow crypto promoters to “self-certify” that their products lay outside traditional regulations and give the SEC only 60 days to respond. By removing crypto trading platforms from the regulatory structure overseeing stock and bond exchanges, it would open the door to conflicts of interest by reducing consumer protections against the platforms commingling their funds with client funds.
The bill also exempts crypto promoters from rules requiring risky investments to be offered only to accredited investors—those with a net worth of more than $1 million, not counting their primary residence, or income over $200,000 (for couples, $300,000) in each of the prior two years.
The cynical device FIT21 uses to neuter the SEC’s oversight of crypto investments is to turn that task over to the CFTC. As the regulatory watchdog Better Markets observes, the CFTC has a budget of only $365 million, versus the SEC’s $2.1 billion, and fewer than 700 employees, compared to the SEC’s approximately 4,500 staffers).
The bill “would heap a whole new set of responsibilities on the CFTC, making it the de facto regulator of countless new crypto exchanges and broker-dealers,” Better Markets wrote, even though the CFTC “does not have the funding to fulfill all its current statutory mandates.”
The debate Wednesday that preceded the House passage of FIT21 was typically tone-deaf and filled with fictitious and factitious assertions. Rep. Mike Flood (R-Neb.) invoked the FTX scandal, which saw billions of dollars in clients’ and investors’ crypto deposits illegally appropriated by the firm’s leaders. “We need to ensure that there are the protective rules that prevent anything like that happening again,” he said.
Flood asserted that, under FIT21, FTX would have been barred from registering as an exchange, and it would not have been able to commingle its funds with those of its clients. One wonders what he was talking about. FTX was barred from registering as an exchange, and didn’t do so. Why? Because Bankman-Fried, its founder, knew that to do so would have subjected the firm to SEC oversight, which no one in crypto wants to undergo.
As for commingling funds, it’s already illegal — it’s one of the practices that landed Bankman-Fried in prison.
The bottom line is very clear. There’s no justification for bestowing on crypto a hand-manufactured regulatory scheme all of its own. Its promoters have no argument other than to claim that they need regulation-lite to foster “innovation,” when the result will be to facilitate the cheating of customers, laundering money or lubricating ransomware attacks like the one that has disrupted the crucial operations of the UnitedHealth Group subsidiary Change Healthcare, which manages reimbursement processes for medical providers nationwide.
If there’s a corner of the financial world crying out for tougher regulation, it’s crypto. For Congress to even contemplate a slackening of the regulation that already exists is nothing short of absurd. But Congress doesn’t respond to practicalities; it responds to money. That’s the only driver of efforts like FIT21.

Business
After 57 years of open seating, is Southwest changing its brand?

Jim Kingsley of Orange County, who recently flew Southwest on a two-leg journey from Minneapolis to Los Angeles, likened the budget-friendly airline to In-N-Out Burger.
Both brands are affordable, consistent and more simplistic compared with competitors, Kingsley said.
“They’re not trying to offer all the things everybody else offers,” he said, “but they get the quality right and it’s a good value.”
Change, however, is in the air.
Southwest, which since its founding nearly 60 years ago has positioned itself in the cutthroat airline industry as an easygoing, egalitarian option, upended that guiding ethos this week with word that it would get rid of its famous first-come, first-seated policy in favor of traditional assigned seats and a premium class option. They will also offer overnight, red-eye flights in five markets including Los Angeles.
Experts say the changes, especially the switch to assigned seating, are a smart move and will appeal to many as the company tries to stabilize its precarious finances that included a 46% drop in profits in the second quarter from a year earlier to $367 million. But it remains to be seen whether Southwest will pay an intangible cost in making the moves: Will it be able to hold on to its quirky identity or will it put off loyal customers, and in doing so, become just another airline?
“You’re going to hear nostalgia about this, but I think it’s very logical and probably something the company should have done years ago,” said Duane Pfennigwerth, a global airlines analyst at Evercore.
“In many markets away from core Southwest markets, we think open seating is a boarding process that many people avoid,” he said.
That is all well and good, but “I didn’t ask for these changes,” Kingsley said. “Cost and quality is what I care about.”
Open seating has its pros and cons, Kingsley said, though he’s generally a fan. On his trip to Los Angeles, his group wasn’t able to get seats all together. But he likes that preferred seats are available on a first-come, first-served basis, instead of being offered for a high price.
Eighty percent of Southwest customers and 86% of potential customers prefer an assigned seat, the airline said in a statement.
“By moving to an assigned seating model, Southwest expects to broaden its appeal and attract more flying from its current and future customers,” the airline said.
An even bigger draw of Southwest, according to Kingsley, is its policy of including two free checked bags per ticket. This perk often makes Southwest a better bargain, especially for longer trips or bigger groups, he said.
The free bags are a big deal to customers, experts said, and contribute to the airline’s consumer-friendly brand. The airline hasn’t indicated they plan to change their bag policy.
“Southwest has always had a really good, positive vibe,” said Alan Fyall, chair of Tourism Marketing at the University of Central Florida’s College of Hospitality. “It’s free bags, good prices and point-to-point routes. That’s what they stand for and that’s what people love about them.”
Southwest’s change to assigned seating doesn’t mean they’re no longer a budget-friendly airline, Fyall said, but it does differentiate them from the lowest-cost, lowest-amenity options such as Frontier and Spirit.
The move will also require Southwest to update all or a portion of its fleet to include first-class seats. Currently, all seats on a Southwest flight are identical. Fyall said it’s worth the investment.
It’s an appropriate time for Southwest to make adjustments, said Chris Hydock, an assistant professor at Tulane University’s Freeman School of Business.
“They’ve not been profitable the last couple of quarters and they’ve had some activist investor pressure to increase their revenue,” he said.
Costs such as wages and maintenance have risen across the airline industry even as travel increased after the pandemic. Southwest saw a net loss of $231 million in the first quarter of 2024. Wall Street analysts estimate that assigned, premium seating could boost revenue by $2 billion per year.
“This is one of the options where they could potentially increase their revenue and do something that a lot of consumers have a strong preference for anyway,” Hydock said.
For Southwest’s changes to pay off, it has to stick to its roots when it comes to its culture and brand, experts and travelers agreed.
“I love Southwest being different,” Kingsley said. “If they’re trying to be like the other airlines, I think they’re shooting themselves in the foot.”
Business
Column: 99 years after the Scopes 'monkey trial,' religious fundamentalism still infects our schools

Almost a century has passed since a Tennessee schoolteacher was found guilty of teaching evolution to his students. We’ve come a long way since that happened on July 21, 1925. Haven’t we?
No, not really.
The Christian fundamentalism that begat the state law that John Scopes violated has not gone away. It regularly resurfaces in American politics, including today, when efforts to ban or dilute the teaching of evolution and other scientific concepts are part and parcel of a nationwide book-banning campaign, augmented by an effort to whitewash the teaching of American history.
I knew that education was in danger from the source that has always hampered it—religious fanaticism.
— Clarence Darrow, on why he took on the defense of John Scopes at the ‘monkey trial’
The trial in Dayton, Tenn., that supposedly placed evolution in the dock is seen as a touchstone of the recurrent battle between science and revelation. It is and it isn’t. But the battle is very real.
Let’s take a look.
The Scopes trial was one of the first, if not the very first, to be dubbed “the trial of the century.”
And why not? It pitted the fundamentalist William Jennings Bryan — three-time Democratic presidential candidate, former congressman and secretary of State, once labeled “the great commoner” for his faith in the judgment of ordinary people, but at 65 showing the effects of age — against Clarence Darrow, the most storied defense counsel of his time.
The case has retained its hold on the popular imagination chiefly thanks to “Inherit the Wind,” an inescapably dramatic reconstruction — actually a caricature — of the trial that premiered in 1955, when the play was written as a hooded critique of McCarthyism.
Most people probably know it from the 1960 film version, which starred Frederic March, Spencer Tracy and Gene Kelly as the characters meant to portray Bryan, Darrow and H.L. Mencken, the acerbic Baltimore newspaperman whose coverage of the trial is a genuine landmark of American journalism.
What all this means is that the actual case has become encrusted by myth over the ensuing decades.
One persistent myth is that the anti-evolution law and the trial arose from a focused groundswell of religious fanaticism in Tennessee. In fact, they could be said to have occurred — to repurpose a phrase usually employed to describe how Britain acquired her empire — in “a fit of absence of mind.”
The Legislature passed the measure idly as a meaningless gift to its drafter, John W. Butler, a lay preacher who hadn’t passed any other bill. (The bill “did not amount to a row of pins; let him have it,” a legislator commented, according to Ray Ginger’s definitive 1958 book about the case, “Six Days or Forever?”)
No one bothered to organize an opposition. There was no legislative debate. The lawmakers assumed that Gov. Austin Peay would simply veto the bill. The president of the University of Tennessee disdained it, but kept mum because he didn’t want the issue to complicate a plan for university funding then before the Legislature.
Peay signed the bill, asserting that it was an innocuous law that wouldn’t interfere with anything being taught in the state’s schools. The law “probably … will never be applied,” he said. Bryan, who approved of the law as a symbolic statement of religious principle, had advised legislators to leave out any penalty for violation, lest it be declared unconstitutional.
The lawmakers, however, made it a misdemeanor punishable by a fine for any teacher in the public schools “to teach any theory that denies the story of the Divine Creation of man as taught in the Bible, and to teach instead that man had descended from a lower order of animal.”
Scopes’ arrest and trial proceeded in similarly desultory manner. Scopes, a school football coach and science teacher filling in for an ailing biology teacher, assigned the students to read a textbook that included evolution. He wasn’t a local and didn’t intend to set down roots in Dayton, but his parents were socialists and agnostics, so when a local group sought to bring a test case, he agreed to be the defendant.
The play and movie of “Inherit the Wind” portray the townspeople as religious fanatics, except for a couple of courageous individuals. In fact, they were models of tolerance. Even Mencken, who came to Dayton expecting to find a squalid backwater, instead discovered “a country town full of charm and even beauty.”
Dayton’s civic boosters paid little attention to the profound issues ostensibly at play in the courthouse; they saw the trial as a sort of economic development project, a tool for attracting new residents and businesses to compete with the big city nearby, Chattanooga. They couldn’t have been happier when Bryan signed on as the chief prosecutor and a local group solicited Darrow for the defense.
“I knew that education was in danger from the source that has always hampered it — religious fanaticism,” Darrow wrote in his autobiography. “My only object was to focus the attention of the country on the programme of Mr. Bryan and the other fundamentalists in America.” He wasn’t blind to how the case was being presented in the press: “As a farce instead of a tragedy.” But he judged the press publicity to be priceless.
The press and and the local establishment had diametrically opposed visions of what the trial was about. The former saw it as a fight to protect from rubes the theory of evolution, specifically that humans descended from lower orders of primate, hence the enduring nickname of the “monkey trial.” For the judge and jury, it was about a defendant’s violation of a law written in plain English.
The trial’s elevated position in American culture derives from two sources: Mencken’s coverage for the Baltimore Sun, and “Inherit the Wind.” Notwithstanding his praise for Dayton’s “charm,” Mencken scorned its residents as “yokels,” “morons” and “ignoramuses,” trapped by their “simian imbecility” into swallowing Bryan’s “theologic bilge.”
The play and movie turned a couple of courtroom exchanges into moments of high drama, notably Darrow’s calling Bryan to the witness stand to testify to the truth of the Bible, and Bryan’s humiliation at his hands.
In truth, that exchange was a late-innings sideshow of no significance to the case. Scopes was plainly guilty of violating the law and his conviction preordained. But it was overturned on a technicality (the judge had fined him $100, more than was authorized by state law), leaving nothing for the pro-evolution camp to bring to an appellate court. The whole thing fizzled away.
The idea that despite Scopes’ conviction, the trial was a defeat for fundamentalism, lived on. Scopes was one of its adherents. “I believe that the Dayton trial marked the beginning of the decline of fundamentalism,” he said in a 1965 interview. “I feel that restrictive legislation on academic freedom is forever a thing of the past, … that the Dayton trial had some part in bringing to birth this new era.”
That was untrue then, or now. When the late biologist and science historian Stephen Jay Gould quoted that interview in a 1981 essay, fundamentalist politics were again on the rise. Gould observed that Jerry Falwell had taken up the mountebank’s mission of William Jennings Bryan.
It was harder then to exclude evolution from the class curriculum entirely, Gould wrote, but its enemies had turned to demanding “‘equal time’ for evolution and for old-time religion masquerading under the self-contradictory title of ‘scientific creationism.’”
For the evangelical right, Gould noted, “creationism is a mere stalking horse … in a political program that would ban abortion, erase the political and social gains of women … and reinstitute all the jingoism and distrust of learning that prepares a nation for demagoguery.”
And here we are again. Measures banning the teaching of evolution outright have not lately been passed or introduced at the state level. But those that advocate teaching the “strengths and weaknesses” of scientific hypotheses are common — language that seems innocuous, but that educators know opens the door to undermining pupils’ understanding of science.
In some red states, legislators have tried to bootstrap regulations aimed at narrowing scientific teaching onto laws suppressing discussions of race and gender in the classrooms and stripping books touching those topics from school libraries and public libraries.
The most ringing rejection of creationism as a public school topic was sounded in 2005 by a federal judge in Pennsylvania, who ruled that “intelligent design” — creationism by another name — “cannot uncouple itself from its creationist, and thus religious, antecedents” and therefore is unconstitutional as a topic in public schools. Yet only last year, a bill to allow “intelligent design” to be taught in the state’s public schools was overwhelmingly passed by the state Senate. (It died in a House committee.)
Oklahoma’s reactionary state superintendent of education, Ryan Walters, recently mandated that the Bible should be taught in all K-12 schools, and that a physical copy be present in every classroom, along with the Ten Commandments, the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution. “These documents are mandatory for the holistic education of students in Oklahoma,” he ordered.
It’s clear that these sorts of policies are broadly unpopular across much of the nation: In last year’s state and local elections, ibook-banners and other candidates preaching a distorted vision of “parents’ rights” to undermine educational standards were soundly defeated.
That doesn’t seem to matter to the culture warriors who have expanded their attacks on race and gender teaching to science itself. They’re playing a long game. They conceal their intentions with vague language in laws that force teachers to question whether something they say in class will bring prosecutors to the schoolhouse door.
Gould detected the subtext of these campaigns. So did Mencken, who had Bryan’s number. Crushed by his losses in three presidential campaigns in 1896, 1900 and 1908, Mencken wrote, Bryan had launched a new campaign of cheap religiosity.
“This old buzzard,” Mencken wrote, “having failed to raise the mob against its rulers, now prepares to raise it against its teachers.” Bryan understood instinctively that the way to turn American society from a democracy to a theocracy was to start by destroying its schools. His heirs, right up to the present day, know it too.
Business
NASA identifies Starliner problems but sets no date for astronauts' return to Earth
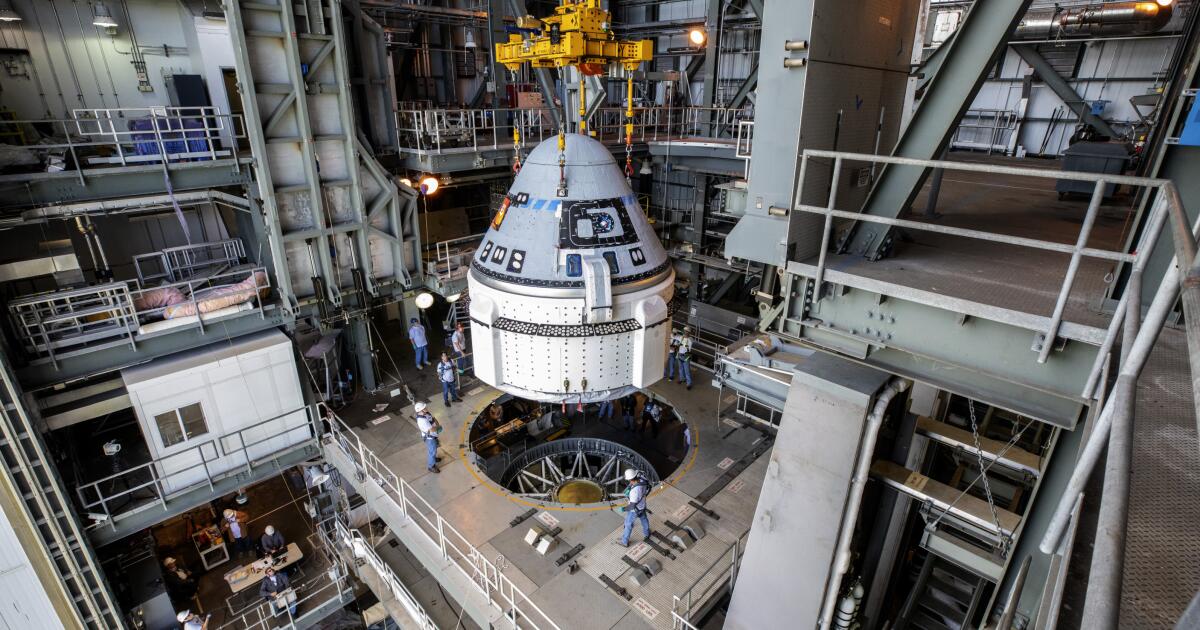

After weeks of testing, NASA and Boeing officials said Thursday they have identified problems with the Starliner’s propulsion system that have kept two astronauts at the International Space Station for seven weeks — but they didn’t set a date to return them to Earth.
Ground testing conducted on thrusters that maneuver Boeing’s capsule in space found that Teflon used to control the flow of rocket propellant eroded under high heat conditions, while different seals that control helium gas showed bulging, they said.
The testing was conducted after the thrusters malfunctioned when Starliner docked with the space station on June 6 and a helium leak that was detected before launch worsened on the trip to the station. The helium pressurizes the propulsion system.
However, officials said the problems should not prevent astronauts Suni Williams and Butch Wilmore from returning to Earth aboard the Starliner capsule, which lifted off on its maiden human test flight June 5 for what was supposed to be an eight-day mission.
“I am very confident we have a good vehicle to bring the crew back with,” Mark Nappi, program manager of Boeing’s Commercial Crew Program, said at a news conference.
NASA and Boeing officials have said previously that the Starliner could transport the astronauts to Earth if there were an emergency aboard the space station, but they opted to conduct the ground tests to ensure a safe, planned return.
Decisions on whether and when to use Starliner or another vehicle will be made by NASA leaders after they are presented next week with all the information collected from the testing, which will include a “hot fire” test of the engines of the Starliner docked at the space station, Nappi said.
Rigorous ground testing conducted at NASA’s White Sands Test Facility on a thruster identical to the ones on the Starliner found that, despite the issues with Teflon degradation, the thruster was able to perform the maneuvers that would be needed to return Starliner to Earth, said Steve Stich, program manager for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.
Official also have said that the Starliner still has about 10 times more helium than is needed to bring the capsule back to Earth.
The problems that have cropped up have been an embarrassment for Boeing, which along with SpaceX was given a multibillion-dollar contract in 2014 to service the station with crew and cargo flights after the end of the space shuttle program. Since then, Elon Musk’s Hawthorne-based company has sent more than a half-dozen crews up, while Boeing is still in its testing phase — with the current flight delayed for weeks by the helium leak and other issues that arose even before the thrusters malfunctioned.
Should NASA make a decision not to bring the crew home on the Starliner — which could still return to Earth remotely — the astronauts could be retrieved by SpaceX’s Crew Dragon capsule, though SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9 rocket is currently grounded after a failure this month.
The Russian Soyuz spacecraft also services the station and carries American astronauts.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoOne dead after car crashes into restaurant in Paris
-

 Midwest1 week ago
Midwest1 week agoMichigan rep posts video response to Stephen Colbert's joke about his RNC speech: 'Touché'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Young Republicans on Why Their Party Isn’t Reaching Gen Z (And What They Can Do About It)
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIn Milwaukee, Black Voters Struggle to Find a Home With Either Party
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics: The Call is Coming from Inside the House
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: J.D. Vance Accepts Vice-Presidential Nomination
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: A new generation drives into the storm in rousing ‘Twisters’
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrump to take RNC stage for first speech since assassination attempt