Business
As Biden Pleads for More Covid Aid, States Are Awash in Federal Dollars

FRANKFORT, Ky. — Gov. Andy Beshear has been toting oversize checks round his state in current weeks, handing them out to metropolis and county officers for desperately wanted water enhancements.
The tiny metropolis of Mortons Hole acquired $109,000 to convey operating water to 6 households who shouldn’t have it. The individuals of Martin County, whose water has been too contaminated to drink since a coal slurry spill twenty years in the past, acquired $411,000. The checks bear Mr. Beshear’s signature, however the cash comes from the federal authorities, a part of an enormous infusion of coronavirus reduction help that’s serving to to gasoline file funds surpluses in Kentucky and plenty of different states.
Therein lies a Washington controversy. The funds, which Congress permitted at a second when the pandemic was nonetheless raging, are allowed for use for much broader functions than combating the virus, together with water tasks like these in Kentucky. Most states will get one other spherical of “fiscal restoration funds” — a part of President Biden’s $1.9 trillion American Rescue Plan — subsequent month.
However in Washington, Mr. Biden is out of cash to pay for probably the most primary technique of defending individuals through the pandemic — drugs, vaccines, testing and reimbursement for care. Republicans have refused to log out on new spending, citing the state restoration funds for instance of cash that may very well be repurposed for pressing nationwide priorities.
“These states are awash in cash — everyone from Kentucky to California,” stated Scott Jennings, a former aide to Senator Mitch McConnell of Kentucky, the Republican chief. “Persons are like: ‘We’ve printed all this cash; we’ve despatched it out. These states have these huge surpluses, and now you want extra?’”
Republicans have been by no means followers of Mr. Biden’s rescue plan, which Democrats muscled by means of Congress with out their help. Regardless of the various methods it’s benefiting his state, Mr. McConnell as soon as referred to as it a “multitrillion-dollar, nontargeted Band-Support” that might dump “one other big mountain of debt on our grandkids.”
On Capitol Hill on Thursday, a day after Mr. Biden made a public attraction to Congress for more cash, Senate Republicans and Democrats have been nearing a deal on a $10 billion emergency help package deal — lower than half of Mr. Biden’s preliminary request. However that they had not resolved essential variations over the dimensions and the way to pay for it. Republicans wish to use unspent cash already permitted by Congress, however the events have been unable to agree on which packages ought to be tapped.
Because the outset of the pandemic, the Trump and Biden administrations have injected $5 trillion into the American financial system, together with the rescue plan. With midterm elections approaching, the gush of federal stimulus spending will draw even higher scrutiny as Republicans accuse Democrats of losing funds and fueling inflation, and demand a exact accounting of how the cash has been spent.
David Adkins, the chief director and chief government of the Council of State Governments, stated such questions have been inevitable now that policymakers may catch their collective breath.
“Now we have to lean into the notion that states are laboratories of democracy,” Mr. Adkins stated. “A few of these issues will fail; a few of this cash won’t be spent effectively. However that’s the nature of attempting to navigate disruptive occasions.”
The rescue plan put aside $195 billion to assist states recuperate from the financial and well being results of the pandemic. When Mr. Biden made his preliminary help request, senior lawmakers in each events negotiated a plan to pay for it partly by taking again $7 billion from states, as a part of a $1.5 trillion spending invoice.
Governors and rank-and-file Democrats balked, saying that to take action would disproportionately damage the 31 states that haven’t but gotten all their rescue funds, and the deal fell aside. Now it seems the state funds will probably be spared, although the fracas has forged a pointy highlight on how the fiscal restoration funds are being spent.
“I used to be by no means for giving this cash to the states, however I used to be at all times of the idea that after you gave it to them, politics wouldn’t assist you to get it again,” Senator Roy Blunt of Missouri, the highest Republican on the subcommittee that controls well being spending, stated in a current interview.
All advised, the White Home says 93 p.c of the American Rescue Plan {dollars} which can be at present accessible have been “legally obligated,” which means they’ve both already been spent or are dedicated to being spent.
Most states have both began spending their fiscal restoration funds, or have plans to take action. A current evaluation by the Heart on Funds and Coverage Priorities discovered that whereas most states are nonetheless growing budgets for the upcoming fiscal 12 months, states have already budgeted 78 p.c of their fiscal restoration fund allocation.
Kentucky, the place Mr. Beshear, a Democrat, is selling file job development and financial growth occasions, ended 2021 with a file $1.1 billion surplus, and one other surplus is anticipated this 12 months. The state has already obtained $1.1 billion in federal funds and expects one other $1 billion in Could. It’s spending the cash on broadband, bolstering tourism and shoring up the unemployment insurance coverage fund in addition to coronavirus testing, along with water enhancements.
“These {dollars} are too essential and too transformational to get caught up in a partisan combat,” Mr. Beshear stated in an interview, including: “These are {dollars} which can be serving to us as we emerge from Covid. We’ve acquired a option to limp out of the pandemic or dash out of the pandemic, and reducing off this help solely hurts the those who want it.”
Congress specified 4 broad functions for the cash: to reply to the pandemic’s well being and financial impacts; to offer bonus pay to important staff; to stop cuts in public companies; and to put money into sewer, water or broadband infrastructure. However states can even use the funds to switch misplaced revenues, which provides them nice flexibility in spending the cash.
Arkansas, as an illustration, has awarded $374,000 to a rape disaster heart; $6.3 million to the Arkansas Coalition In opposition to Sexual Assault; and one other $6.3 million to the Arkansas Alliance of Boys & Women Golf equipment. However the bulk of the cash has gone towards bettering broadband entry and addressing the wants of the well being care system.
“The Omicron variant got here in, circumstances skyrocketed, hospitals crammed up and so we needed to make the most of a big quantity of our ARPA cash for increasing hospital area, house testing and different public well being response,” stated Gov. Asa Hutchinson, a Republican, utilizing the acronym for the rescue plan. “In order that’s clearly the primary accountability, after which we checked out these different wants.”
Different states are utilizing the cash in methods which can be solely tangentially associated to Covid-19, however which can be permissible underneath tips issued by the Treasury Division.
Alabama devoted $400 million of its allocation, or roughly one-fifth, to constructing two new prisons, regardless of a public outcry from advocates for racial justice and civil liberties. Florida devoted $2 billion, almost one-quarter of its $8.8 billion allotment, to freeway development — a call that has drawn criticism from the nonpartisan Florida Coverage Institute.
“The supposed goal of the American Rescue Plan Act {dollars} was to make sure that people and communities may recuperate from the pandemic, and I feel in some ways there have been higher makes use of for this cash,” stated Esteban Leonardo Santis, the group’s tax and income analyst.
Twenty states, together with Kentucky, spent a complete of $15 billion to construct up their depleted unemployment insurance coverage belief funds. Impartial analysts say that’s successfully a tax break for companies, which in any other case might have needed to make up for the misplaced revenues. However Mr. Beshear defended it, saying that Kentucky companies stepped up through the pandemic. A neighborhood Toyota plant made face shields, and bourbon distillers manufactured hand sanitizer, he stated.
The governor’s Twitter feed is rife with images of huge checks and smiling metropolis and county officers; he’s operating for re-election in 2023.
“If there’s one factor a governor is aware of the way to do, it’s drive round their state and hand out big checks and reduce huge ribbons with outsized scissors,” Mr. Jennings stated. “They’re like recreation present hosts on the market.”
Specialists say, and the White Home acknowledges, that the fiscal restoration funds have helped create state funds surpluses. Gene B. Sperling, a senior adviser to the president who’s overseeing the American Rescue Plan, stated the surpluses have been proof that Mr. Biden’s stimulus package deal was working — and this was no time to pare again.
“Guaranteeing that states and localities have a cushion for some fairly critical bumps within the highway is sensible coverage,” Mr. Sperling stated, “and a lesson discovered from what occurred after the Nice Recession.”
However these surpluses are prone to be momentary, and the way states are utilizing them has performed into the controversy over Covid reduction funds. The Heart on Funds and Coverage Priorities says 14 states are utilizing momentary funds surpluses “to name for expensive and everlasting tax cuts focused extra to rich individuals” — a transfer the middle described as a “unhealthy alternative.”
Right here in Frankfort, the state capital, Kentucky lawmakers in a rush to wrap up their 2022 legislative session have been engaged on pushing by means of a hefty earnings tax reduce this week. However a proposal to make use of the state’s funds surplus to offer Kentuckians a tax rebate of as much as $500 appeared unlikely to cross, stated its creator, State Senator Chris McDaniel, the appropriations committee chairman.
Mr. McDaniel, a Republican, spent a lot of this week immersed in funds talks, together with planning the way to use Kentucky’s subsequent tranche of fiscal restoration funds. One other $1 billion is coming, and regardless of some philosophical misgivings, he stated he noticed no purpose to not spend it.
“I consider firmly that it was an excessive amount of cash that got here down,” Mr. McDaniel stated. “However I additionally consider that Kentuckians will bear the tax burden ultimately, identical to everybody else down the road, and I’m not going to drawback future Kentuckians out of a degree of philosophical delight.”
Emily Cochrane contributed reporting from Washington.

Business
Downtown Los Angeles Macy's is among 150 locations to close

The downtown Los Angeles Macy’s department store, situated on 7th Street and a cornerstone of retail in the area, will shut down as the company prepares to close 150 underperforming locations in an effort to revamp and modernize its business.
The iconic retail center announced this week the first 66 closures, including nine in California spanning from Sacramento to San Diego. Stores will also close in Florida, New York and Georgia, among other states. The closures are part of a broader company strategy to bolster sustainability and profitability.
Macy’s is not alone in its plan to slim down and rejuvenate sales. The retailer Kohl’s announced on Friday that it would close 27 poor performing stores by April, including 10 in California and one in the Los Angeles neighborhood of Westchester. Kohl’s will also shut down its San Bernardino e-commerce distribution center in May.
“Kohl’s continues to believe in the health and strength of its profitable store base” and will have more than 1,100 stores remaining after the closures, the company said in a statement.
Macy’s announced its plan last February to end operations at roughly 30% of its stores by 2027, following disappointing quarterly results that included a $71-million loss and nearly 2% decline in sales. The company will invest in its remaining 350 stores, which have the potential to “generate more meaningful value,” according to a release.
“We are closing underproductive Macy’s stores to allow us to focus our resources and prioritize investments in our go-forward stores, where customers are already responding positively to better product offerings and elevated service,” Chief Executive Tony Spring said in a statement. “Closing any store is never easy.”
Macy’s brick-and-mortar locations also faced a setback in January 2024, when the company announced the closures of five stores, including the location at Simi Valley Town Center. At the same time, Macy’s said it would layoff 3.5% of its workforce, equal to about 2,350 jobs.
Farther north, Walgreens announced this week that it would shutter 12 stores across San Francisco due to “increased regulatory and reimbursement pressures,” CBS News reported.
Business
The justices are expected to rule quickly in the case.

When the Supreme Court hears arguments on Friday over whether protecting national security requires TikTok to be sold or closed, the justices will be working in the shadow of three First Amendment precedents, all influenced by the climate of their times and by how much the justices trusted the government.
During the Cold War and in the Vietnam era, the court refused to credit the government’s assertions that national security required limiting what newspapers could publish and what Americans could read. More recently, though, the court deferred to Congress’s judgment that combating terrorism justified making some kinds of speech a crime.
The court will most likely act quickly, as TikTok faces a Jan. 19 deadline under a law enacted in April by bipartisan majorities. The law’s sponsors said the app’s parent company, ByteDance, is controlled by China and could use it to harvest Americans’ private data and to spread covert disinformation.
The court’s decision will determine the fate of a powerful and pervasive cultural phenomenon that uses a sophisticated algorithm to feed a personalized array of short videos to its 170 million users in the United States. For many of them, and particularly younger ones, TikTok has become a leading source of information and entertainment.
As in earlier cases pitting national security against free speech, the core question for the justices is whether the government’s judgments about the threat TikTok is said to pose are sufficient to overcome the nation’s commitment to free speech.
Senator Mitch McConnell, Republican of Kentucky, told the justices that he “is second to none in his appreciation and protection of the First Amendment’s right to free speech.” But he urged them to uphold the law.
“The right to free speech enshrined in the First Amendment does not apply to a corporate agent of the Chinese Communist Party,” Mr. McConnell wrote.
Jameel Jaffer, the executive director of the Knight First Amendment Institute at Columbia University, said that stance reflected a fundamental misunderstanding.
“It is not the government’s role to tell us which ideas are worth listening to,” he said. “It’s not the government’s role to cleanse the marketplace of ideas or information that the government disagrees with.”
The Supreme Court’s last major decision in a clash between national security and free speech was in 2010, in Holder v. Humanitarian Law Project. It concerned a law that made it a crime to provide even benign assistance in the form of speech to groups said to engage in terrorism.
One plaintiff, for instance, said he wanted to help the Kurdistan Workers’ Party find peaceful ways to protect the rights of Kurds in Turkey and to bring their claims to the attention of international bodies.
When the case was argued, Elena Kagan, then the U.S. solicitor general, said courts should defer to the government’s assessments of national security threats.
“The ability of Congress and of the executive branch to regulate the relationships between Americans and foreign governments or foreign organizations has long been acknowledged by this court,” she said. (She joined the court six months later.)
The court ruled for the government by a 6-to-3 vote, accepting its expertise even after ruling that the law was subject to strict scrutiny, the most demanding form of judicial review.
“The government, when seeking to prevent imminent harms in the context of international affairs and national security, is not required to conclusively link all the pieces in the puzzle before we grant weight to its empirical conclusions,” Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. wrote for the majority.
In its Supreme Court briefs defending the law banning TikTok, the Biden administration repeatedly cited the 2010 decision.
“Congress and the executive branch determined that ByteDance’s ownership and control of TikTok pose an unacceptable threat to national security because that relationship could permit a foreign adversary government to collect intelligence on and manipulate the content received by TikTok’s American users,” Elizabeth B. Prelogar, the U.S. solicitor general, wrote, “even if those harms had not yet materialized.”
Many federal laws, she added, limit foreign ownership of companies in sensitive fields, including broadcasting, banking, nuclear facilities, undersea cables, air carriers, dams and reservoirs.
While the court led by Chief Justice Roberts was willing to defer to the government, earlier courts were more skeptical. In 1965, during the Cold War, the court struck down a law requiring people who wanted to receive foreign mail that the government said was “communist political propaganda” to say so in writing.
That decision, Lamont v. Postmaster General, had several distinctive features. It was unanimous. It was the first time the court had ever held a federal law unconstitutional under the First Amendment’s free expression clauses.
It was the first Supreme Court opinion to feature the phrase “the marketplace of ideas.” And it was the first Supreme Court decision to recognize a constitutional right to receive information.
That last idea figures in the TikTok case. “When controversies have arisen,” a brief for users of the app said, “the court has protected Americans’ right to hear foreign-influenced ideas, allowing Congress at most to require labeling of the ideas’ origin.”
Indeed, a supporting brief from the Knight First Amendment Institute said, the law banning TikTok is far more aggressive than the one limiting access to communist propaganda. “While the law in Lamont burdened Americans’ access to specific speech from abroad,” the brief said, “the act prohibits it entirely.”
Zephyr Teachout, a law professor at Fordham, said that was the wrong analysis. “Imposing foreign ownership restrictions on communications platforms is several steps removed from free speech concerns,” she wrote in a brief supporting the government, “because the regulations are wholly concerned with the firms’ ownership, not the firms’ conduct, technology or content.”
Six years after the case on mailed propaganda, the Supreme Court again rejected the invocation of national security to justify limiting speech, ruling that the Nixon administration could not stop The New York Times and The Washington Post from publishing the Pentagon Papers, a secret history of the Vietnam War. The court did so in the face of government warnings that publishing would imperil intelligence agents and peace talks.
“The word ‘security’ is a broad, vague generality whose contours should not be invoked to abrogate the fundamental law embodied in the First Amendment,” Justice Hugo Black wrote in a concurring opinion.
The American Civil Liberties Union told the justices that the law banning TikTok “is even more sweeping” than the prior restraint sought by the government in the Pentagon Papers case.
“The government has not merely forbidden particular communications or speakers on TikTok based on their content; it has banned an entire platform,” the brief said. “It is as though, in Pentagon Papers, the lower court had shut down The New York Times entirely.”
Mr. Jaffer of the Knight Institute said the key precedents point in differing directions.
“People say, well, the court routinely defers to the government in national security cases, and there is obviously some truth to that,” he said. “But in the sphere of First Amendment rights, the record is a lot more complicated.”
Business
How the devastating Los Angeles fires could deepen California's home insurance crisis
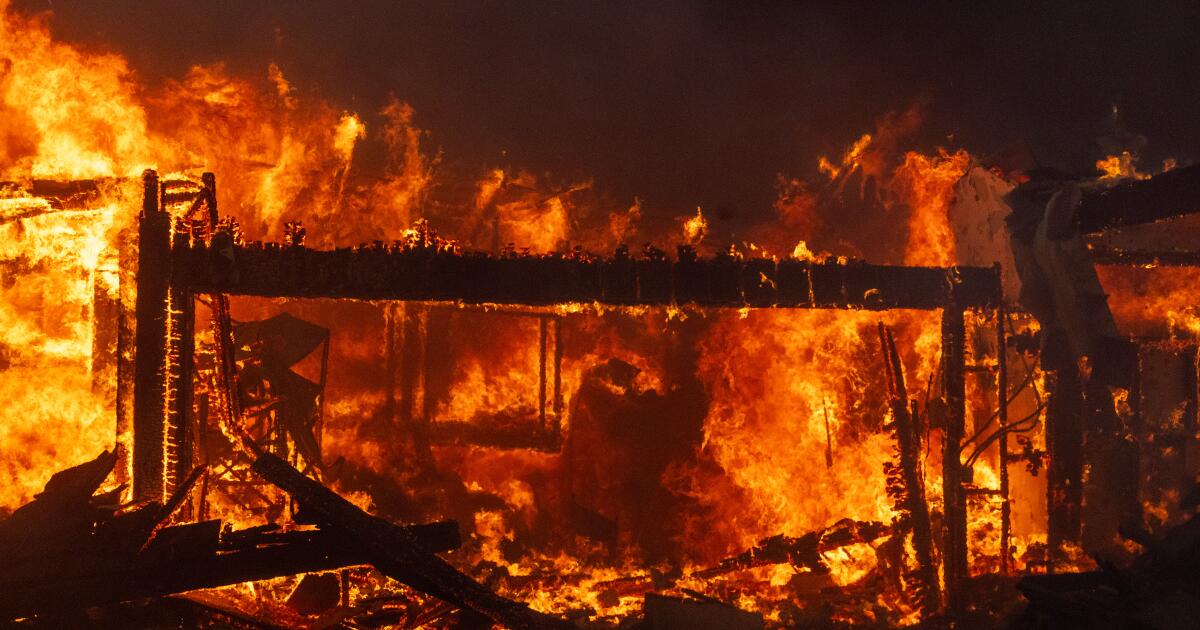

When raging wildfires tore through Pacific Palisades and other local communities this week, they not only left a path of destruction reminiscent of a World War II bombing campaign, but threatened to deepen a crisis that has already left hundreds of thousands of Californians struggling to find and keep affordable homeowners insurance.
The multiple fires from Los Angeles to the San Gabriel Valley that have burned thousands of structures since Tuesday — leading to losses that by one early estimate are well into the tens of billions of dollars — hit Southern California as insurers have been dropping customers statewide citing the increasing number and severity of wildfire-related losses.
The Palisades fire alone, which consumed more than 5,000 homes and structures, is being called the most destructive fire ever to hit the city, while the fires across the county are likely to be one of the most expensive natural disasters in U.S. history.
“It’s just an unmitigated disaster,” said Amy Bach, executive director of United Policyholders, a consumer advocacy group. “Wildfires in January? This just proves insurers’ point that the risk is so significantly increased due to climate change.”
State Farm, the state’s largest home insurer, announced in March it would not renew 72,000 property insurance policies, while Chubb and its subsidiaries stopped writing new high-value homes with higher wildfire risk — just to name two insurers that pulled back from the California market.
It’s not clear how many homeowners in Pacific Palisades and elsewhere might not have had coverage, but at least some homeowners reported that insurers had not renewed their policies before the disaster struck. Actor James Woods, who lost his home in the Palisades fire, tweeted Tuesday that “one of the major insurances companies canceled all the policies in our neighborhood about four months ago.”
State Farm last year told the Department of Insurance it would not renew 1,626 policies in Pacific Palisades when they expired, starting last July.
A spokesperson for State Farm declined to comment on the decision but said: “Our number one priority right now is the safety of our customers, agents and employees impacted by the fires and assisting our customers in the midst of this tragedy.”
The situation has left many homeowners in neighborhoods at high wildfire risk with little choice but to seek relief from the California FAIR Plan, an insurer of last resort that sells policies with lesser coverage. The policies cover losses up to $3 million to a dwelling and its contents caused by certain hazards, such as fire, but do not include personal liability and other protection that are typically offered by private insurers.
The FAIR Plan has seen its policies grow from a little over 200,000 in September 2020 to more than 450,000 as of last September. That has roughly tripled its loss exposure to $458 billion over the same period. Pacific Palisades has one of the state’s highest concentrations of FAIR Plan policy holders, with the insurer estimating its exposure in the neighborhood at $5.89 billion.
JP Morgan analysts estimate that total L.A. County losses could be close to $50 billion, while the losses insurers will have to pay could top $20 billion. Another estimate puts the losses even higher.
Such losses could cause insurers to exit the market completely, which Tokio Marine America Insurance Co. and Trans Pacific Insurance Co. said in April they would do in not renewing 12,556 homeowners.
The losses also could prompt insurers to further raise premiums, even though some insurers already have been granted big rate hikes, such as a 34% increase Allstate received last year.
Denise Rappmund, senior analyst at Moody’s Ratings, said, “These events will continue to have widespread, negative impacts for the state’s broader insurance market — increased recovery costs will likely drive up premiums and may reduce property insurance availability.”
Should insurers further withdraw from the market, that would put additional pressure on the FAIR Plan, which is is backed by the state’s licensed insurers, such as State Farm, who have to pay claims if they exceed the FAIR Plans reserves, reinsurance and catastrophe bonding. The insurers also can assess their own policyholders surcharges in the billions of dollars to bail out the plan under regulations put in place last year by Insurance Commissioner Ricardo Lara as part of his Sustainable Insurance Strategy to help the crippled market.
It’s unclear whether the plan will be able to absorb the losses like it did after the 2018 Camp fire that destroyed the town of Paradise in North California. That conflagration was the single costliest natural disaster in the world that year with $12.5 billion in covered losses and $16.5 billion in total losses, according to the reinsurance firm, Munich RE.
“This further complicates an already complicated and hardened market,” Lara said of the fires, in an interview with The Times.
Nonetheless, Lara’s reforms seek to ensure the FAIR Plan remains solvent and to make it more attractive for insurers to write policies in fire risky neighborhoods now being absorbed by the program. He said the regulations should encourage insurers to write more homeowners policies, and if not, they can be adjusted. “I feel very confident,” he said.
For the first time, California insurers can use so-called “catastrophe models” in setting their rates. Instead of largely relying on past claims data, the computer programs attempt to better refine an insurer’s risk by taking into account a multitude of variables that affect a property’s likelihood to suffer a loss.
The other major policy change allows insurers to charge California homeowners for the cost of reinsurance they buy from other insurers to limit their losses during huge catastrophes, such as wildfires and floods. This cost shift to policyholders is common elsewhere but a big change for California, where it will raise premiums.
In return for those concessions, insurers will have to write insurance in high-risk wildfire neighborhoods equivalent to 85% of their market share, meaning an insurer with a 10% statewide market share would have to cover 8.5% of the homes in such neighborhoods — a target they have at least two years to reach. Lara’s plan has been blasted by the Los Angeles group, Consumer Watchdog, which says the regulations lack teeth in actually requiring insurers to meet the coverage goals.
“The Sustainable Insurance Strategy is not a magic wand. It’s a set of incentives,” Bach said. “At the end of the day, insurers are always still going to analyze, ‘Are we going to make money here or not?’”
How much this week’s fires will disrupt the already troubled insurance market depends, of course, on how big a disaster they are — but all indications are that insurers will have to absorb billions of dollars of claims given the number of homes destroyed, especially in the wealthy enclave of Pacific Palisades, where the average home is valued at about $3.5 million by Zillow.
Insurance industry experts say a clearer picture on the estimated losses will only come after adjusters have time to review submitted claims.
“I think it’s going to be 45 days before we know what the true damage is,” said Max Gilman, president of California personal lines at the brokerage HUB International.
Whatever the final cost, Gilman noted that the fires came after a couple of relatively light fire seasons — though in November the Mountain fire in Ventura County scorched more than some 20,640 acres and destroyed more than 130 homes amid parched conditions. That made it at the time the third most destructive fire in Southern California in a decade.
“I think what’s currently transpiring is going to be of grave concern for the future,” he said. “I feel like we we took three steps forward to take five steps back.”
Denne Ritter, a vice president with the American Property Casualty Insurance Assn. trade group, said it is too early to assess the impact of the fires on Lara’s reforms, especially given how they are just being put in place. Only one catastrophe model has been submitted for review to regulators, while the reinsurance regulation released last month still awaits final approval by the Office of Administrative Law.
“What the insurance industry wants is a healthy market in California where we can compete for business, as we have historically. And the number one priority right now is helping our customers get the resources they need to rebuild their lives and restore their property,” she said.
However, she noted that Mercury Insurance — which recently announced it started writing insurance again in Paradise — and Farmers Insurance, which said last month it is increasing the number of new home policies it will write, have “certainly made moves indicating a more bullish approach on the market.”
Allstate also has said it will resume writing new policies once Lara’s reforms are in place and it can get rates that fully cover its costs.
But all those pronouncements came before this week’s catastrophic fires.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIvory Coast says French troops to leave country after decades