Utah
Lakebed dust is a worry in Utah. In California, it’s already a problem
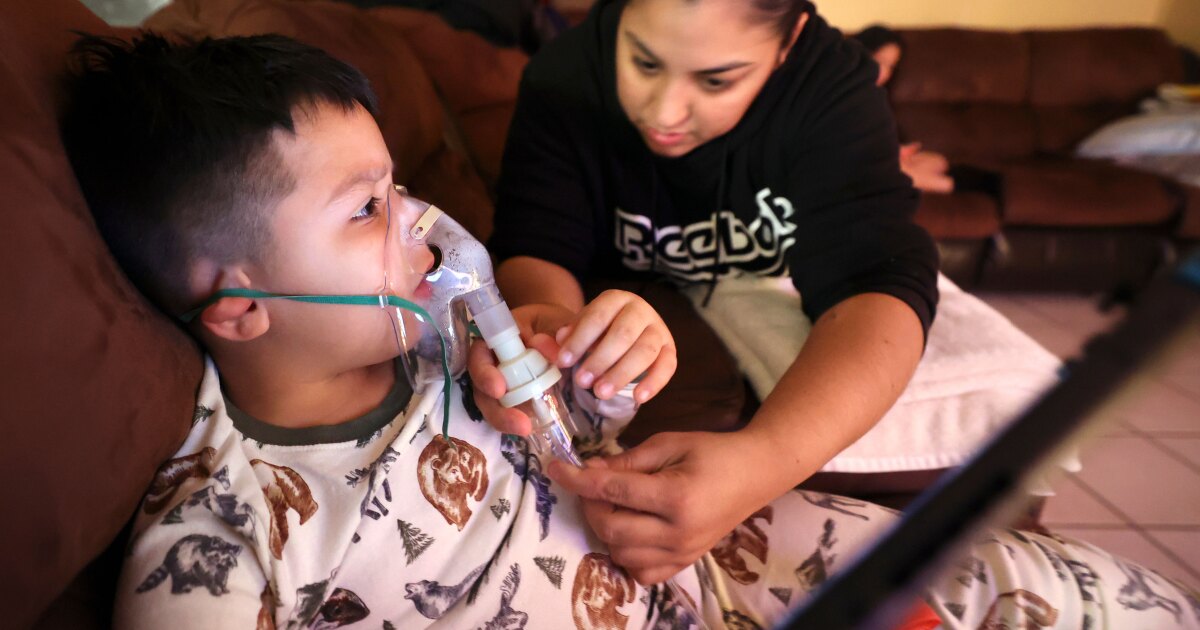
Sitting on the couch next to his mom inside their mobile home in Mecca, California, 5-year-old Ruben Mandujano lets out a gurgled cough while playing on a tablet. The phlegm stuck in his throat is noticeable. But the constant cough is something he’s used to.
His mother, Rosa Mandujano said he came down with some kind of illness about “eight out of the 12 months of the year” when he was younger. Now, after various surgeries, an asthma diagnosis, medications and a nebulizer, Mandujano estimates her son is sick “five months out of the 12.”
The family has grown accustomed to the frequent infections. Both of their children suffer from asthma. A cupboard in their kitchen is dedicated to dozens of over-the-counter and prescription drugs.
Mandujano said her son’s problems get worse when the air quality is awful – another common issue for Coachella and Imperial Valley residents. Mecca, where the Mandujano family lives, is enveloped by agricultural fields and a short distance from the north shore of the declining Salton Sea, a saline lake facing similar turmoil as Utah’s Great Salt Lake.
Dust storms have become the norm being so close to agricultural fields and the Salton Sea, she said. Winds reaching 75 miles per hour whip through predominantly low-income and immigrant communities. The dust gets so bad, Mandujano said, that “you can’t see what’s in front of you.”
Kristin Murphy
/
Deseret News
With the exposed Salton Sea lakebed and the loose dirt and pesticides from the surrounding fields, Mandujano said it’s rare to find a Coachella Valley resident who doesn’t suffer from allergies or asthma. But the impact of the bad air quality and dust storms is worse for some, like Ruben.
“His asthma and his allergies combine, it’s a ticking bomb for him,” Mandujano said. “He says that everything hurts. His ears hurt, his eyes hurt, his nose hurts. He doesn’t even want to get touched.”
When the phlegm won’t leave his throat, Ruben has to use a nebulizer, which circulates well-known asthma medications like Albuterol or Pulmicort through a mask. Mandujano said she hooks her son up to the nebulizer about 121 times a year.
“He hates it because it makes him throw up because it gathers all of the phlegm,” Mandujano said. “He knows he’s going to start throwing up. So he just says, ‘Mommy, I don’t like this,’ and keeps trying to take it off.”
While Rosa Mandujano fights to keep her family healthy, California state leaders, scientists and community advocates are trying to identify solutions to clean up the air, especially as it pertains to the dust accumulated from the Salton Sea. Like Great Salt Lake, there are toxins in the sediment of the exposed lake bed.

Kristin Murphy
/
Deseret News
Scattered near the roughly 27,000 acres of exposed Salton Sea playa are lines of hay bales.
Charlie Diamond, a researcher with the Salton Sea Task Force at the University of California Riverside, said it’s a “dust suppression project” aimed to “break up the flow of air right at the ground level.” The goal, Diamond said, is for the hay bales to “suppress the dust production or emission.”
During high wind events, Diamond said toxins and other sediments like gypsum and salt get “blown around in the surrounding communities, [and] causes a lot of problems with respiratory health, especially in young folks.”
Usually, Diamond said, the hay bales are planted with native vegetation, which the shoreline severely lacks. That acts as another dust suppressant. But “these projects are really contingent on some external source of freshwater,” Diamond added, and that’s the crux of the issue – in the arid climate, there isn’t enough fresh water making its way to the Salton Sea to begin with.
With an exorbitant amount of dried lakebed, it’s unlikely hay bales will prevent all the dust from pummeling community members.
“That’s not a solution, it’s a band-aid,” Diamond said.
Local officials are working on other remedies. The Imperial Irrigation District, which oversees the hay bale projects, is also planting and germinating natural vegetation near the shoreline. Environmental specialist Ross Wilson said the district is using groundwater to hydrate the plants.

Kristin Murphy
/
Deseret News
Wilson said there isn’t a way to “necessarily make less dust,” the hope is the natural vegetation “catches the dust” like the hay bales and results in better air quality.
The agency also uses a Portable In-Situ Wind ERosion Lab, also known as a PI-SWERL, to figure out what exactly is in the dust. The device, which resembles an industrial floor polisher, replicates wind speeds and collects air quality measurements. Wilson added it also tracks which areas produce the most emissions.
“No one has the money to just mitigate the entire sea. So if we can dial down which areas actually are emissive and which areas are the problem, then we can really nail down our resources to those specific areas,” he said.
If more water isn’t funneled into the Salton Sea, the Imperial Irrigation District predicts upward of 70,000 acres of bare lakebed within the next 10 years.
Utah’s Great Salt Lake is up against the same fate as the Salton Sea when it comes to dust.

Kristin Murphy
/
Deseret News
Great Salt Lake Commissioner Brian Steed noted in the state’s first Great Salt Lake Strategic Plan that the lake’s low water levels are increasing dust emissions. He added the accumulation from the estimated 800 square miles of the exposed lake bed poses a public health risk and is causing snow to melt approximately 17 days sooner than normal.
Steed told KUER’s RadioWest that he believes dust from Great Salt Lake is “going to be the hardest one [problem] to solve.”
“When you have an exposed lake bed that weathers over time, which has happened over years, you see additional dust days and problems with PM 2.5 and PM 10,” he said. “And we know that we’ve had a problem [with air quality] along the Wasatch Front especially.”
The Utah Office of Legislative Auditor General highlighted in the Great Salt Lake Strategic Plan that it would cost a minimum of $1.5 billion to keep the lake’s dust at bay, along with $15 million each year for ongoing maintenance.
Steed recognizes the price tag associated with dust mitigation. In an ideal world, “the lowest cost alternative” is lifting Great Salt Lake’s water levels so the crust “keeps that dust in place.”

Kristin Murphy
/
Deseret News
Utah is just beginning to grapple with its looming dust problem, but for Rosa Mandujano in California, the dust is enough to make her contemplate if it’s worth staying in her hometown. Her two kids love to be outdoors, but the air quality often triggers adverse reactions, especially for Ruben, forcing them to remain inside.
“I’ve talked to my husband and said if we get a good job opportunity and we would have to move out of the state, I mean, let’s go,” Mandujano said. “I know it’s scary because my family’s here. All his family’s here, but I’ve seen friends done it. It’s nothing out of the world. You have to start somewhere.”
KSLTV5’s Alex Cabrero contributed to this report
Copyright 2024 KUER 90.1

Utah
Utah man dies of injuries sustained in avalanche in Big Cottonwood Canyon

SALT LAKE CITY (KUTV) — A man died after he was caught in an avalanche in Big Cottonwood Canyon over the weekend.
A spokesperson for the Salt Lake County Sheriff’s Office confirmed on Thursday that Kevin Williams, 57, had died.
He, along with one other person, was hospitalized in critical condition after Saturday’s avalanche in the backcountry.
MORE | Big Cottonwood Canyon Avalanche
In an interview with 2News earlier this week, one of Williams’ close friends, Nate Burbidge, described him as a loving family man.
“Kevin’s an amazing guy. He’s always serving, looking for ways that he can connect with others,” Burbidge said.
A GoFundMe was set up to help support Williams’ family.
BE THE FIRST TO COMMENT
_____
Utah
911 recordings detail hours leading up to discovery of Utah girl, mother dead in Las Vegas

CONTENT WARNING: This report discusses suicide and includes descriptions of audio from 911 calls that some viewers may find disturbing.
LAS VEGAS — Exclusively obtained 911 recordings detail the hours leading up to the discovery of an 11-year-old Utah girl and her mother dead inside a Las Vegas hotel room in an apparent murder-suicide.
Addi Smith and her mother, Tawnia McGeehan, lived in West Jordan and had traveled to Nevada for the JAMZ cheerleading competition.
The calls show a growing sense of urgency from family members and coaches, and several hours passing before relatives learned what happened.
MORE | Murder-Suicide
Below is a timeline of the key moments, according to dispatch records. All times are Pacific Time.
10:33 a.m. — Call 1
After Addi and her mother failed to appear at the cheerleading competition, Addi’s father and stepmother called dispatch for a welfare check.
Addi and her mother were staying at the Rio hotel. The father told dispatch that hotel security had already attempted contact.
“Security went up and knocked on the door. There’s no answer or response it doesn’t look like they checked out or anything…”
11:18 a.m. and 11:27 a.m. — Calls 2 and 3
As concern grew, Addi’s coach contacted the police two times within minutes.
“We think the child possibly is in imminent danger…”
11:26 a.m. — Call 4
Addi’s stepmother placed another call to dispatch, expressing escalating concern.
“We are extremely concerned we believe that something might have seriously happened.”
She said that Tawnia’s car was still at the hotel.
Police indicated officers were on the way.
2:26 p.m. — Call 5
Nearly three hours after the initial welfare check request, fire personnel were en route to the scene. It appeared they had been in contact with hotel security.
Fire told police that they were responding to a possible suicide.
“They found a note on the door.”
2:35 p.m. — Call 6
Emergency medical personnel at the scene told police they had located two victims.
“It’s going to be gunshot wound to the head for both patients with notes”
A dispatcher responded:
“Oh my goodness that’s not okay.”
2:36 p.m. — Call 7
Moments later, fire personnel relayed their assessment to law enforcement:
“It’s going to be a murder suicide, a juvenile and a mother.”
2:39 p.m. — Call 8
Unaware of what had been discovered, Addi’s father called dispatch again.
“I’m trying to file a missing persons report for my daughter.”
He repeats the details he knows for the second time.
3:13 p.m. — Call 9
Father and stepmother call again seeking information and continue to press for answers.
“We just need some information. There was a room check done around 3:00 we really don’t know where to start with all of this Can we have them call us back immediately?”
Dispatch responded:
“As soon as there’s a free officer, we’ll have them reach out to you.”
4:05 p.m. — Call 10
More than an hour later, Addi’s father was put in contact with the police on the scene. He pleaded for immediate action.
“I need someone there I need someone there looking in that room”
The officer confirmed that they had officers currently in the room.
Addi’s father asks again what they found, if Addi and her mother are there, and if their things were missing.
The officer, who was not on scene, said he had received limited information.
5:23 p.m. — Call 11
Nearly seven hours after the first welfare check request, Addi’s grandmother contacted police, describing conflicting information circulating within the family.
“Some people are telling us that they were able to get in, and they were not in the hotel room, and other people saying they were not able to get in the hotel room, and we need to know”
She repeated the details of the case. Dispatch said officers will call her back once they have more information.
Around 8:00 p.m. — Press Conference
Later that evening, Las Vegas Metropolitan Police held a news conference confirming that Addi and her mother, Tawnia McGeehan, were found dead inside the hotel room.
The investigation remains ongoing.
______
Utah
Ban on AI glasses in Utah classrooms inches closer to passing

SALT LAKE CITY (KUTV) — AI glasses could allow you to get answers, snap photos, access audio and take phone calls—and now a proposal moving through the legislature would ban the glasses from Utah school classrooms.
“I think it’s a great idea,” said Kizzy Guyton Murphy, a mother who accompanied her child’s class on a field trip to the state Capitol on Wednesday. “You can’t see inside what the student is looking at, and it’s just grounds for cheating.”
Mom Tristan Davies Seamons also sees trouble with AI glasses.
“I don’t think they should have any more technology in schools than they currently have,” she said.
Her twin daughters, fourth graders Finley and Grayson, don’t have cell phones yet.
“Not until we’re like 14,” said Grayson, adding they do have Chromebooks in school.
2News sent questions to the Utah State Board of Education:
- Does it have reports of students using AI glasses?
- Does it see cheating and privacy as major concerns?
- Does it support a ban from classrooms?
Matt Winters, USBE AI specialist, said the board has not received reports from school districts of students with AI glasses.
“Local Education Agencies (school districts) have local control over these decisions based on current law and code,” said Winters. “The Board has not taken a position on AI glasses.
MORE | Utah State Legislature:
Some districts across the country have reportedly put restrictions on the glasses in schools.
“I think it should be up to the teachers,” said Briauna Later, another mother who is all for preventing cheating, but senses a ban could leave administrators with tired eyes.
“It’s one more thing for the administration to have to keep track of,” said Later.
The proposal, HB 42, passed the House and cleared a Senate committee on Wednesday.
BE THE FIRST TO COMMENT
___
-

 World2 days ago
World2 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts2 days ago
Massachusetts2 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Louisiana5 days ago
Louisiana5 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Oklahoma1 week ago
Oklahoma1 week agoWildfires rage in Oklahoma as thousands urged to evacuate a small city
-

 Denver, CO2 days ago
Denver, CO2 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making



















