Hawaii
Amid spike in respiratory illnesses, some Hawaii shelves run low on cold medicines
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/L2ZYVNAZK5GBHF4RO7NTWL5MNU.jpg)
HONOLULU (HawaiiNewsNow) – Some Hawaii drug shops are operating low on chilly medicines and youngsters’s painkillers ― a nationwide development as demand will increase together with respiratory viruses.
At a drug retailer in East Honolulu, some cabinets for grownup and youngsters’s chilly medicines have been empty.
Drugmaker Johnson & Johnson says it’s seeing excessive demand and is working to extend manufacturing. In the meantime, Hawaii docs who’re monitoring respiratory viruses are nervous about extra sickness round holidays.
“A variety of of us are calling in for coughs and sniffles and it might not be RVS, COVID or flu once we swab, there’s lots of different respiratory viruses circulating,” stated Dr. Sharyl Shultz, who’s household medication at Kaiser Permanente.
RELATED COVERAGE:
Statistics present a slight improve in Hawaii COVID and flu circumstances whereas RSV peaked in October and November.
Shultz says Hawaii docs are carefully watching what’s occurring on the mainland.
Emergency and hospital beds in Los Angeles County are filling amid a so-called “tridemic” and Hawaii sometimes lags the area by a couple of month.
“We’re nervous that with RSV circulating and with flu and COVID on the rise since Thanksgiving and can largely probably proceed by means of the vacations as we collect, we’ll be dealing with a respiratory trifecta,” Shultz stated.
Sufferers are asking what to do.
“The American Academy of Pediatrics doesn’t advocate over-the-counter chilly medicines usually for youths,” stated Shultz.
Additionally, contact your supplier.
“If there’s extra extreme sickness, important coughing, any hassle respiratory, excessive fever, any indicators of dehydration particularly within the keiki, we advocate that you will have to come back in for additional testing,” she added.
However for gentle sickness, Shultz offers her sufferers and youngsters the identical recommendation: “Relaxation up, drink water and you will have to remain residence from faculty tomorrow.:
Docs say it’s additionally a good suggestion to get vaccinated in opposition to COVID and the flu.
Copyright 2022 Hawaii Information Now. All rights reserved.

Hawaii
Hawaii Imposes the Nation’s First Climate Change Tax for Tourists — And It's Expected to Generate $100 Million Annually
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(736x503:738x505)/hawaii-hotel-3-052925-6d8eecfa70e04c49a926f7f7556d8051.jpg)
Hawaii
Lawmakers demand answers from Navy on dummy bombing plan of remote Hawaiian island
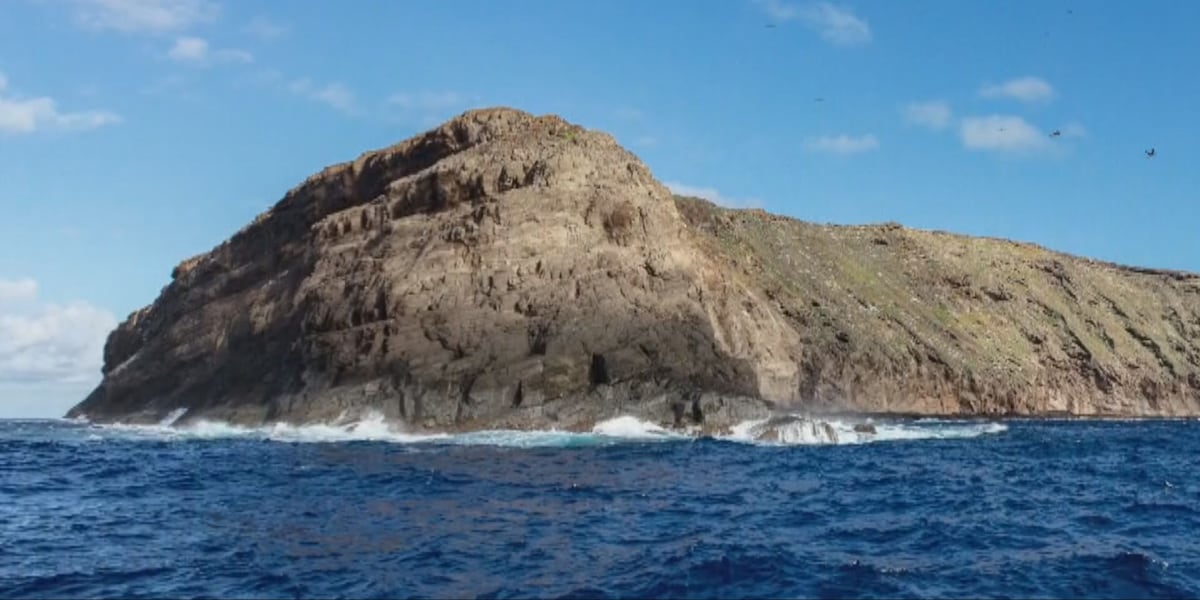

HONOLULU (HawaiiNewsNow) – Hawaiʻi’s congressional delegation is demanding answers from the secretary of the Navy about why the military wants to increase its bombing of a tiny island off Niʻihau.
The bombs are 500-pound dummies and the military’s past exercises there have been shrouded in mystery.
Sens. Brian Schatz and Mazie Hirono, and Reps. Ed Case and Jill Tokuda want the Navy to complete a full environmental impact statement that could shed light on a lot of unanswered questions.
The crescent-shaped island called Kaʻula, 23 miles southwest of Niʻihau, is so remote it’s mostly known by fishermen and cultural practitioners.
The Navy wants to increase inert bombings there with 500-pound ordnance that doesn’t explode from 12 per year to 31 on the island’s southern end.
“We just want answers. If they’re going to bomb a Hawaiian island, even if it’s several miles off the coast of Niʻihau, anything in the Hawaiian Island chain is the business of the people of Hawaiʻi,” said Schatz.
Schatz told Hawaii News Now he doesn’t know when the inert bombing happened in the past.
“Those are some of the answers that we’re trying to pursue,” he said.
“I think one of the lessons from the Red Hill experience is to not just accept that if they say national security, we stop asking questions. We have a lot of questions and we are not satisfied that this is necessary for national security,” he added.
Practitioners and conservations say they welcome the Hawaiʻi congressional delegation’s demand for an environmental impact statement.
Mike Nakachi of Moana ʻOhana and his son have traveled by boat off shore of Kaʻula island. They haven’t seen any damage, but say there are stories of bombings within the past 30 years.
“I have heard stories from other fishermen in the past that were on the island or fishing close to the island and engaged in just diving operations, holoholo operations, when all of a sudden, I guess a bomb hit the island,” said Nakachi.
The island is a year-round nursery for nesting seabirds.
“They’re babies. They can’t fly away and remember, this is an island the size of Ala Moana Beach Park, so dropping 500-pound inert bombs is going to be felt no matter where you are on this island,” said Hob Osterlund, Kauai Albatross Network.
In its draft environmental assessment, the Navy said the training was vital to military readiness, no cultural resources were identified, and impacts to wildlife would be less than significant
Osterlund of the Kauaʻi Albatross Network says one unanswered question is if the state handed over the land to the Navy or any other entity.
Hawaiʻi’s attorney general told HNN it and the Department of Land and Natural Resources is looking into the matter.
HNN contacted the secretary of the Navy for comment.
Copyright 2025 Hawaii News Now. All rights reserved.
Hawaii
3 Hawaii Locals Share What They Want Travelers to Know About Their Culture
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TAL-episode-2-oahu-hawaii-TLLCEP20525-42c307f537944959b7ecc453c1741727.jpg)
In this week’s podcast episode of Lost Cultures: Living Legacies, we journey to Hawaii to explore the deep roots and living traditions of Kānaka Maoli, the Native Hawaiian people.
You may think you know Hawaii. But there’s more to these stunning islands than white-sand beaches and breezy palm trees.
Beyond the surf breaks and world-class sunsets, Hawaii has a complex story. Navigators were born here. There’s an unmatched reverence for the land. It’s a place once—and still—filled with warriors, working hard to fight for their cultural preservation. And as our guests share, Hawaiian culture isn’t just alive on the islands—it touches the far corners of the world, too.
In this week’s episode of Lost Cultures: Living Legacies, we’re exploring Hawaii through the voices of cultural practitioners, historians, and teachers, including Evan Mokuahi Hayes, a Hawaiian historian who returned to the islands in search of healing. He found it, unexpectedly, in a taro patch.
“Hawaii has this beautiful way of, even when you have nothing to give, it will meet you there,” he shares on the episode. “It has a way of healing broken parts of you, essentially, and filling those empty spaces.”
That connection to ʻāina—to land and Earth—runs deep for many. As Dr. J. Uluwehi Hopkins, a professor of Hawaiian history, explains on the episode, “We have cosmogonic genealogies … that say we grew right out of the land here, that the land itself is our ancestors.” The result is a worldview built on stewardship, not ownership.
That view was almost shattered in the late 1700s, when Western contact reshaped the islands’ political and spiritual landscapes.
“Our Hawaiian chiefs wanted to form a government that other nations would respect and therefore interact with in an equal way,” Hopkins explains. “And the Hawaiian people actually didn’t want land ownership, but the government enacted it because they realized that if we established land in a way that had an owner, if another foreign power came and took us over, they had to respect the landowners.”
This episode also explores the arrival of American missionaries in the 19th century, the rise of the sugar industry, and the illegal overthrow of Queen Lili‘uokalani. “She crafted this really wonderful, brilliant response in which she says, ‘I will yield my authority until the U.S. president realizes the illegality of his own minister,’” Hopkins shares.
Through it all, Hawaiian culture has endured, especially in hula. “Hula is exactly what people see,” says Hokulani Holt, a kumu hula, or teacher of the art of hula. “It is the visual representation of the words that you are hearing. You cannot have hula without words.” Holt adds, hula is not merely a performance; it is history in movement.
To get to know Hawai‘i on a new level, listen to this week’s episode of Lost Cultures: Living Legacies. It’s available now on Apple Podcasts, Spotify, Amazon Music, Player FM, or wherever you get your podcasts.
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Columbia University President Is Booed at Commencement Ceremony
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoAre Character AI’s chatbots protected speech? One court isn’t sure
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoRead the Full ‘Make America Healthy Again’ Report
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoHow Manga Megastar Junji Ito Makes Terrifying Series Like ‘Uzumaki’
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Trump Repeats False Claims to South African President
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoNow you can watch the Internet Archive preserve documents in real time
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoDiscord might use AI to help you catch up on conversations
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoTrump Has Cut Science Funding to Its Lowest Level in Decades