Science
While COVID raged, another deadly threat was on the rise in hospitals
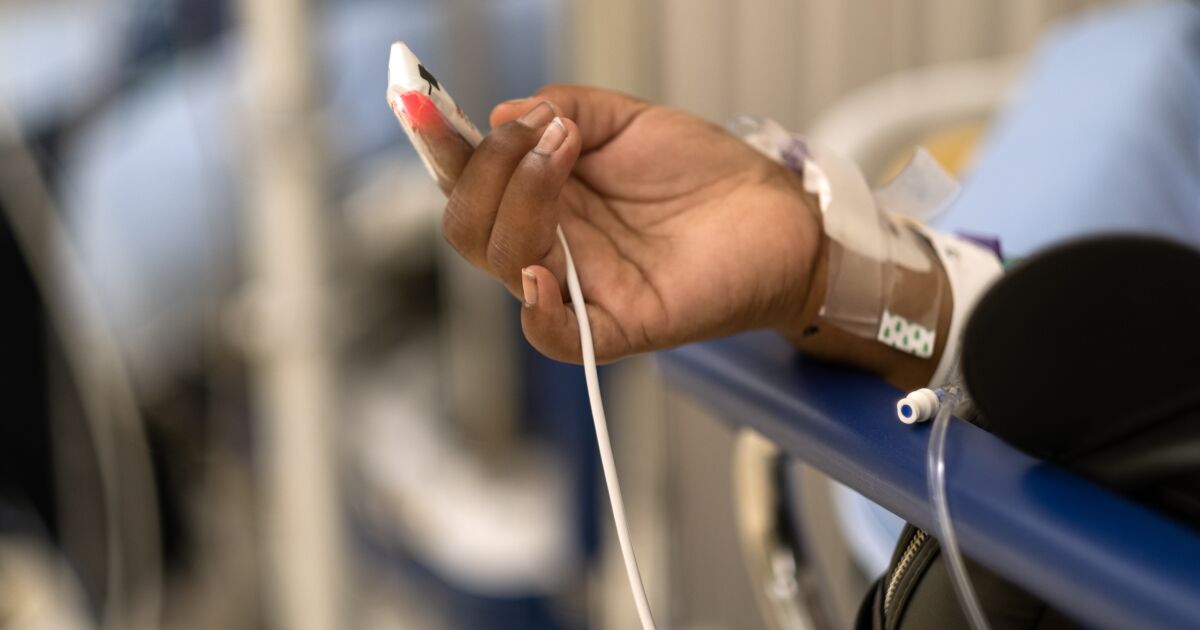
As COVID-19 started to tear via California, hospitals have been deluged with sickened sufferers. Medical workers struggled to handle the onslaught.
Amid the brand new menace of the coronavirus, an outdated one was additionally quietly on the rise: Extra folks have suffered extreme sepsis in California hospitals in recent times — together with a troubling surge in sufferers who bought sepsis contained in the hospital itself, state knowledge present.
Sepsis occurs when the physique tries to battle off an an infection and finally ends up jeopardizing itself. Chemical substances and proteins launched by the physique to fight an an infection can injure wholesome cells in addition to contaminated ones and trigger irritation, leaky blood vessels and blood clots, in line with the Nationwide Institutes of Well being.
It’s a perilous situation that may find yourself damaging tissues and triggering organ failure. Throughout the nation, sepsis kills extra folks yearly than breast most cancers, HIV/AIDS and opioid overdoses mixed, mentioned Dr. Kedar Mate, president and chief govt of the Institute for Healthcare Enchancment.
“Sepsis is a number one explanation for loss of life in hospitals. It’s been true for a very long time — and it’s turn into much more true in the course of the pandemic,” Mate mentioned.
The majority of sepsis instances start exterior of hospitals, however persons are additionally vulnerable to getting sepsis whereas hospitalized for different sicknesses or medical procedures. And that hazard solely grew in the course of the pandemic, in line with state knowledge: In California, the variety of “hospital-acquired” instances of extreme sepsis rose greater than 46% between 2019 and 2021.
Consultants say the pandemic exacerbated a persistent menace for sufferers, faulting each the risks of the coronavirus itself and the stresses that hospitals have confronted in the course of the pandemic. The rise in sepsis in California got here as hospital-acquired infections elevated throughout the nation — an issue that worsened throughout surges in COVID hospitalizations, researchers have discovered.
“This setback can and should be momentary,” mentioned Lindsey Lastinger, a well being scientist within the CDC’s Division of Healthcare High quality Promotion.
Physicians describe sepsis as exhausting to identify and straightforward to deal with in its earliest phases, however tougher to deal with by the point it turns into evident. It could possibly present up in a variety of the way, and detecting it’s sophisticated by the truth that its signs — which might embrace confusion, shortness of breath, clammy pores and skin and fever — aren’t distinctive to sepsis.
There’s no “gold customary take a look at to say that you’ve sepsis or not,” mentioned Dr. Santhi Kumar, interim chief of pulmonology, vital care and sleep medication at Keck Medication of USC. “It’s a constellation of signs.”
Christopher Lin, 28, endured excruciating ache and a broiling fever of 102.9 levels Fahrenheit at residence earlier than heading to the Kaiser Permanente Los Angeles Medical Middle. It was October 2020 and the hospital regarded “surreal,” Lin mentioned, with a tent arrange exterior and chairs spaced sparsely within the ready room.
His fever raised considerations about COVID-19, however Lin examined unfavourable. At one level on the emergency division his blood stress abruptly dropped, Lin mentioned, and “it felt like my soul had left my physique.”
Lin, who suffered sepsis in reference to a bacterial an infection, isn’t positive the place he first bought contaminated. Days earlier than he went to the hospital, he had undergone a fast process at pressing care to empty a painful abscess on his chest, and bought the gauze modified by a nurse the next day, he mentioned. Such outpatient procedures aren’t included in state knowledge on “hospital-acquired” sepsis.
Somebody with sepsis might need a excessive temperature or a low one, a coronary heart charge that has sped or slowed, a respiration charge that’s excessive or low.
It could possibly end result from micro organism, fungal infections, viruses and even parasites — “and the problem is that when somebody walks into the emergency division with a fever, we don’t know which of these 4 issues they’ve,” mentioned Dr. Karin Molander, an emergency medication doctor and previous board chair of Sepsis Alliance. Therapy can fluctuate relying on what’s driving the an infection that spurred sepsis, however antibiotics are frequent as a result of many instances are tied to bacterial infections.
The pandemic piled on the dangers: A coronavirus an infection can itself result in sepsis, and the virus additionally ushered extra aged and medically weak folks into hospitals who’re at increased threat for the damaging situation, consultants mentioned. Almost 40% of extreme sepsis sufferers who died in California hospitals in 2021 have been identified with COVID-19, in line with state knowledge. Some COVID-19 sufferers have been hospitalized for weeks at a time, ramping up their threat of different issues that may result in sepsis.
“The longer you’re within the hospital, the extra issues occur to you,” mentioned Dr. Maita Kuvhenguhwa, an attending doctor in infectious illness at MLK Group Healthcare. “You’re immobilized, so you may have a threat of growing stress ulcers” — not simply on the bottom, however doubtlessly on the face below an oxygen gadget — “and the wound can get contaminated.”
“Strains, tubes, being right here a very long time — all put them in danger for an infection,” Kuvhenguhwa mentioned.
Consultants mentioned the pandemic might have additionally pulled away consideration from other forms of an infection management, as workers have been strained and hospital routines have been disrupted. California, which is uncommon nationwide in mandating minimal ratios for nurse staffing, allowed some hospitals to loosen up these necessities amid the pandemic.
Nurses juggling extra sufferers won’t verify and clear sufferers’ mouths as usually to assist stop bacterial infections, Kumar mentioned. Mate mentioned that hospitalized sufferers won’t get their catheters modified as usually amid workers shortages, which might enhance the danger of urinary tract infections.
Hospitals might need introduced in touring nurses to assist plug the gaps, however “in the event that they don’t know the identical programs, it’s going to be tougher for them to observe the identical processes” to discourage infections, mentioned Catherine Cohen, a coverage researcher with the RAND Corp.
Armando Nahum, one of many founding members of Sufferers for Affected person Security U.S., mentioned that pandemic restrictions on hospital guests might have additionally worsened the issue, stopping members of the family from with the ability to spot {that a} relative was appearing unusually and lift considerations.
Molander echoed that time, saying that it’s essential for sufferers to have somebody who is aware of them effectively and would possibly have the ability to alert docs, “My mother has dementia, however she’s usually very talkative.”
Sepsis has been a longstanding battle for hospitals: One-third of people that die in U.S. hospitals had sepsis throughout their hospitalization, in line with analysis cited by the CDC. However Mate argued that sepsis deaths could be decreased considerably “with the fitting actions that we all know how you can take.”
In Pennsylvania and New Jersey, Jefferson Well being started rolling out a brand new effort to fight sepsis in fall of 2021 — simply earlier than the preliminary Omicron wave started to hit hospitals.
Its system consists of predictive modeling that makes use of data from digital medical data to alert clinicians that somebody is perhaps affected by sepsis. It additionally arrange a “standardized workflow” for sepsis sufferers in order that essential steps resembling prescribing antibiotics occur as rapidly as potential, hospital officers mentioned.
The objective was to reduce the psychological burden on docs and nurses pulled in lots of instructions, mentioned Dr. Patricia Henwood, its chief medical officer. “Clinicians throughout the nation are strained, and we don’t essentially want higher clinicians — we want higher programs,” she mentioned.
Jefferson Well being credit the brand new system with serving to to cut back deaths from extreme sepsis by 15% in a yr.
In New York state, uproar over the loss of life of 12-year-old Rory Staunton led to new necessities for hospitals to undertake protocols to quickly establish and deal with sepsis and report knowledge to the state. State officers mentioned the trouble saved greater than 16,000 lives between 2015 and 2019, and researchers discovered better reductions in sepsis deaths in New York than in states with out such necessities.
In case your baby will get sick, he mentioned, “you shouldn’t need to surprise if the hospital on the fitting has sepsis protocols and the one on the left doesn’t,” mentioned Ciaran Staunton, who co-founded the group Finish Sepsis after the loss of life of his son. His group welcomed the information when federal businesses have been not too long ago directed to develop “hospital high quality measures” for sepsis.
Such a transfer may face opposition. Robert Imhoff, president and chief govt of the Hospital High quality Institute — an affiliate of the California Hospital Assn. — contended that increasing the sort of necessities in impact in New York was pointless.
“I don’t suppose hospitals have to be mandated to supply secure, high quality care,” Imhoff mentioned.
State knowledge present that extreme sepsis — together with instances originating each inside and outside hospitals — has been on the rise in California during the last decade, however Molander mentioned the long-term enhance could also be tied to adjustments in reporting necessities that led to extra instances being tracked. California has but to launch new knowledge on extreme sepsis acquired in hospitals final yr, and isn’t anticipated to take action till this fall.
For Lin, surviving sepsis left him decided to make it possible for the phrase will get out about sepsis — and never simply in English. Within the hospital, he had struggled to elucidate what was taking place to his mom, who speaks Cantonese. After recovering, Lin labored with native officers to get supplies from Sepsis Alliance translated into Mandarin.
“I can’t think about if it have been my dad and mom within the hospital,” he mentioned, “going via what I used to be going via.”

Science
Judge halts ban on syringe programs as El Dorado County legal battle continues
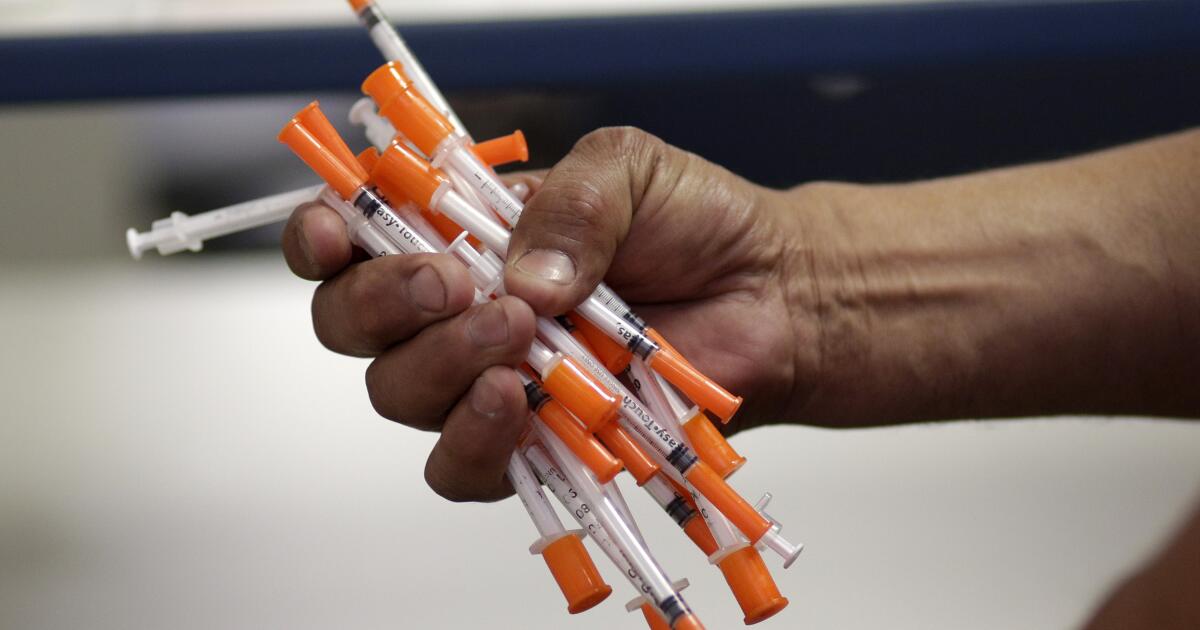
El Dorado County cannot enforce its ban on programs that hand out clean syringes as a legal battle continues between the county and the California Department of Public Health, a Superior Court judge has ruled.
Judge Gary S. Slossberg granted a preliminary injunction to prevent El Dorado County from enforcing an ordinance that makes it unlawful to operate syringe programs in its unincorporated areas.
The judge said he was not weighing in on the heated arguments for or against syringe programs, which provide sterile needles to people who use drugs, but whether the Department of Public Health had a “reasonable probability” of prevailing in its argument that the county ordinance clashes with state law.
Friday’s decision does not end the courtroom dispute over whether the ban passed by the El Dorado County Board of Supervisors was preempted by state law, as public health officials have argued, or opposing claims by county officials that the syringe program was improperly approved by the state. Slossberg said Friday that the preliminary injunction is meant to remain in place pending a later trial.
The Department of Public Health filed suit against El Dorado County and its county seat of Placerville this year contending that their bans on syringe programs defied the state health and safety code.
The state health department first authorized the nonprofit Sierra Harm Reduction Coalition to operate a syringe program in the county four years ago. State officials have long endorsed such programs as a proven way to prevent HIV and hepatitis C from running rampant as people share contaminated syringes.
California law gives the public health agency the power to approve syringe programs anywhere that deadly or disabling infections might spread through used needles, “notwithstanding any other law.”
Local bans on syringe programs have nonetheless sprung up across California as city and county officials argue that handing out free syringes does more harm than good. El Dorado County leaders passed their rule in December, which was followed in February by a similar ordinance in Placerville.
The lawsuit lodged by the California Department of Public Health drew objections from El Dorado County leaders: Earlier this year, Dist. Atty. Vern Pierson called it “madness” and argued that California officials were “seeking to impose the normalization of hardcore drug use.”
In a cross-complaint filed against the Department of Public Health, the county said that the syringe program approved by the state had caused “profound nuisance and public safety impacts,” including a “drastic increase in discarded needles,” and that overdoses had risen since it started.
The county said in a legal filing that since the ban went into effect, “there has been a reduction of syringe waste, decreased incidents of public nuisance, and a resulting reduction of the burdens on law enforcement.”
It also accused the public health department of failing to follow state requirements when it approved the syringe program.
The judge did not weigh in on the cross-complaint lodged by El Dorado County at the Friday hearing. In a court filing, California officials said studies show that syringe programs provide important resources for needle disposal and play a crucial role in preventing overdoses. They credited the Sierra Harm Reduction Coalition with handing out thousands of boxes of Narcan, a brand of naloxone, a medication that reverses the effects of an opioid overdose.
The Department of Public Health argued in a legal filing that stopping the syringe program would be likely to ramp up HIV and hepatitis C infections among people who use drugs, increasing state costs for their care; lead to more deaths from drug overdoses; and reduce access to options for syringe disposal, among other harmful effects.
Because of the bans, “our most vulnerable, stigmatized, and marginalized community members are actively being denied lifesaving interventions,” Sierra Harm Reduction Coalition interim executive director Shilo Jama said in a court filing.
Slossberg said that although he was preventing the El Dorado County ordinance from being enforced, the county might have other mechanisms to address nuisance issues that were not addressed by the decision.
Pierson, the district attorney, said in a statement Friday that “we will propose narrowing the ordinance” in response to comments made by the judge.
The California Department of Public Health said in a statement that it was “pleased with the court’s decision that upholds that state’s role in protecting the public’s health while this case proceeds.”
The Friday ruling applies only to the ordinance passed by El Dorado County. Attorney Mona Ebrahimi, who represents the city of Placerville, said a hearing involving the city had been postponed.
Science
This one thing may derail your shot at healthy aging, scientists say

Before you settle in to binge the new season of “The Bear” or watch Team USA go for the gold at the Paris Olympics, think twice about the amount of time you spend on the couch in front of the TV. Your future self may thank you.
A new study by Harvard researchers links the popular pastime of sitting and watching television to the likelihood of reaching one’s senior years in a state of good health: the more time spent doing the former, the lower the odds of achieving the latter.
The problem doesn’t seem to be with sitting in general. After controlling for a variety of risk factors such as diet quality and smoking history, the researchers found no relationship between time spent in a chair at work and the chances of aging well. Ditto for sitting in cars or at home doing something besides watching TV, such as reading, eating meals or paying bills.
Yet for every additional two hours spent in front of the boob tube, a person’s chance of meeting the researchers’ definition of healthy aging declined by 12%, according to their study published this week in JAMA Network Open.
That does not bode well for the United States, where 62% of adults between the ages of 20 and 64 say they watch TV for at least two hours a day, as do 84% of senior citizens.
The findings are based on data from more than 45,000 women who participated in the Nurses Heath Study. All of them were at least 50 years old and had no major chronic diseases back in 1992, when they answered a slew of questions about their health and what they did all day.
For instance, the nurses were asked how much time they spent standing or walking around at work or at home. They were asked about various types of exercise, including jogging, swimming laps, playing tennis and doing yoga. They were asked if they mowed their own lawns.
And they were asked how many hours they spent doing all kinds of sitting.
A couple watches a movie on TV at their home in Norwalk while sharing a bowl of popcorn.
(Francine Orr / Los Angeles Times)
You might not be surprised to learn that the most popular type of sitting was sitting while watching television. More than half of the women — 53% — said they watched between six and 20 hours of TV a week. (The median among this group was around 15.4 hours per week.) Another 15% of the women said they watched between 21 and 40 hours of TV each week, and 2% watched even more.
The nurses were tracked for 20 years or until they died, whichever came first. By the end of the study period, 41% of them were still free of 11 major health conditions, including cancer, diabetes, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and multiple sclerosis. In addition, 44% of the nurses were in good mental health, 52% had no memory impairments and 16% had no physical impairments.
Only 8.6% of the women met all four of those criteria, which was what it took to achieve healthy aging.
On the whole, the women who watched more TV tended to be older, were more likely to be smokers or drinkers, consumed more calories and had higher body mass index scores than women who watched less TV. The more devoted TV watchers were also more likely to have high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
Once the researchers accounted for these and a host of other differences, they found that the women who spent an hour or less each week sitting in front of the TV were the most likely to achieve healthy aging. Compared to them, women who watched TV for two to five hours per week were 9% less likely to be healthy agers; those who watched for six to 20 hours per week were 19% less likely; those who watched for 21 to 40 hours per week were 40% less likely; and those who watched for at least 41 hours a week were 45% less likely.
The researchers also found that replacing TV time with pretty much anything else — including sleep, for women who got no more than seven hours of shut eye per night — would increase their odds of healthy aging. The more vigorous the new activity, the bigger the boost.
Although the actual percentage of women who succeeded in healthy aging was low, the study authors estimated that another 61% of the women could have joined that rarefied group if they had done four things:
- Spent at least three hours per day engaged in light physical activity at work.
- Invested at least 30 minutes a day in moderate to vigorous physical activity.
- Kept their weight in the normal range instead of being overweight or obese.
- Limited their TV-watching time to less than three hours a day.
The study didn’t show that excess TV time caused any of the nurses to miss out on healthy aging, only that there was a significant inverse correlation between the two. Still, there’s good reason to suspect that their favorite sedentary behavior bore at least some of the responsibility.
Previous studies have linked prolonged sitting — especially while watching television — to a variety of health problems, including diseases like breast cancer, colorectal cancer, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and early death. (That particular study found that compared to sitting for less than three hours a day, sitting for at least twice that long was associated with a 17% increased risk of premature death for men and a 34% increased risk of premature death for women.)
But the researchers from Harvard’s T.H. Chan School of Public Health have taken things a step further, said Dr. I-Min Lee, an epidemiologist at Brigham & Women’s Hospital in Boston who studies how physical activity can prevent chronic diseases and extend life.
“This study expands what we know because it looked at ‘healthy aging,’” said Lee, who was not involved in the study. “‘Health’ is not just the absence of disease; it includes dimensions of physical and mental health, function and well-being.”
All of the study subjects were women, but the biological mechanisms are likely to apply to men as well, Lee said. Even so, it would be good to actually test this relationship in men, as well as in people from a wider range of racial and ethnic backgrounds, she said. (The group of women in the original Nurses Health Study was overwhelmingly white.)
The youngest of the Baby Boomers are now turning 60, and the proportion of the U.S. population that’s at least 65 is projected to increase from roughly 17% today to nearly 21% in 2050, according to the U.S. Census Bureau.
“Population aging is an important public health issue,” the study authors wrote, and strategies to promote healthy aging “are urgently needed.”
Science
Column: The abortion pill is safe. Is your uterus?

Huge sigh of relief.
In a ruling that I happily admit surprised me, the Supreme Court on Thursday affirmed the obvious: Women should have the right to safe medication abortions.
But ladies, our uteri are not safe yet.
For now, in a unanimous decision, the justices have tossed a case that would have prevented the drug mifepristone from being used by women seeking to end pregnancies.
So mify, as the drug is commonly called, is safe. But this is far from the end of the MAGA war on women.
Let’s be clear on this: The ruling wasn’t actually about the drug. It was about the folks who brought the suit, a bunch of doctors who really didn’t have much of a reason to keep millions of women from accessing care other than they didn’t like the care those women wanted.
That’s not actually a reason to sue, even by Samuel Alito and Clarence Thomas standards.
So this ruling is about “standing” and the fact that these docs didn’t have it. Already, antiabortion activists are lining up other cases with defendants whose legal footing is much more solid.
And the Supreme Court is hardly the only front in this war for women’s rights. Here’s three other ways the far-right wants to control female bodies:
First, “fetal personhood” has bubbled up as a scary push by the religious right.
Alito hinted at this concept in the Dobbs ruling, which knocked out Roe vs. Wade, when he referred to an embryo as an “unborn human being.”
In Alabama, we saw this take greater life recently when state Supreme Court judges ruled that embryos created during in vitro fertilization should be considered protected human life (though the state Legislature for now has protected the procedure).
And this week, the Southern Baptist Conference, which speaks for more than 10 million Protestant Americans, announced it would now opposes IVF on those embryos-are-life grounds.
If courts do recognize the idea of fetal personhood, it would pave the way for abortion to be considered not just illegal, but murder. It would also give a state the right to police pregnant women in any way it deems necessary to protect the “unborn child.”
We are already seeing some states attempting to prosecute women for abortions under strict new abortion laws and dozens of states (such as Kansas) either have outright legal language broadly giving fetuses rights or language that edges right up to it. We are closer to this than you think.
The second front on the war on women is contraception.
Though it seems insane and inane to most of us to forbid women from taking the pill or an emergency medication in the immediate aftermath of intercourse to prevent pregnancy, some folks do want to ban it as a form of abortion.
There is a logic to it. If all abortion is illegal, then anything affecting the embryo after conception is off limits.
Finally, there’s former President Trump.
I’ve written before about the Comstock Act, an obscure and angry old law that many speculated the Supreme Court justices might dredge up in this mifepristone case.
That law (which is on the books, but not enforced) theoretically makes it illegal to mail anything that could be used in an abortion — so not just the medication. Hard-liners could argue that anything shipped to an abortion clinic to help it operate could be verboten, even latex gloves.
MAGA types are already floating the frightening notion that if Trump were elected, he could simply bypass courts and Congress and order his Department of Justice to enforce the Comstock Act — ending abortion access without technically ending abortion access.
This week, Trump send a recorded message to the Danbury Institute, an ultraconservative organization that has advocated for abortion to be prosecuted as homicide and called it “child sacrifice.”
He didn’t mention abortion, but there’s this:
“These are gonna be your years, because you’re gonna make a comeback like just about no other group,” he said. “I know what’s happening, I know where you’re coming from and where you’re going, and I’ll be with you side by side.”
So while Thursday’s ruling is a welcome win in the fight to keep women equal, it’s a victorious battle.
The war continues.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIsrael used a U.S.-made bomb in a deadly U.N. school strike in Gaza
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 833
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoGeorge Clooney called White House to complain about Biden’s criticism of ICC and defend wife’s work: report
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNewson, Dem leaders try to negotiate Prop 47 reform off California ballots, as GOP wants to let voters decide
-
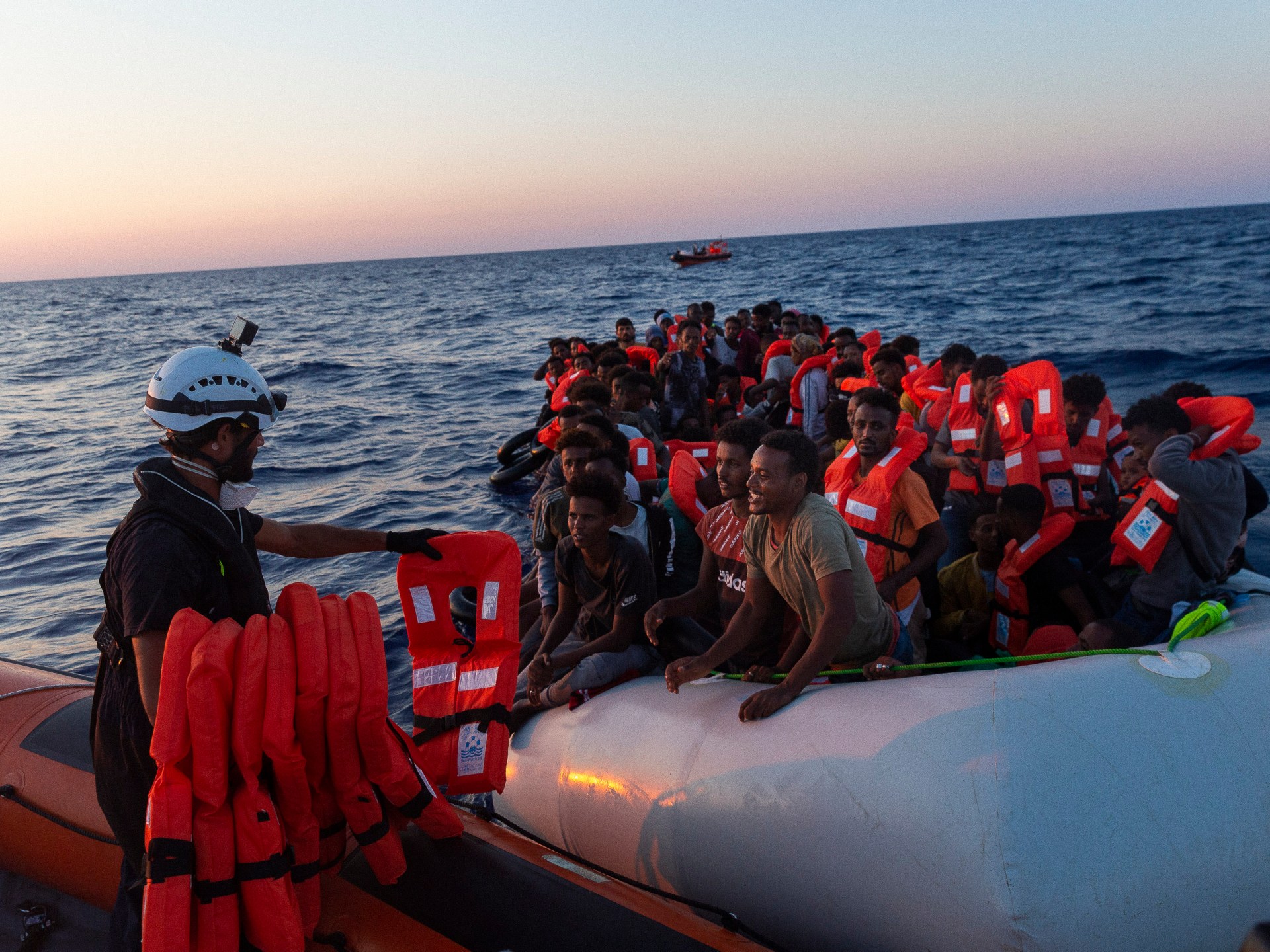

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago‘Bloody policies’: Bodies of 11 refugees and migrants recovered off Libya
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoEmbattled Biden border order loaded with loopholes 'to drive a truck through': critics
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoDozens killed near Sudan’s capital as UN warns of soaring displacement
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoVideo: U.S. Official Responds to Israeli Strike on a U.N. School in Gaza