Science
What are the blue blobs washing up on SoCal beaches? Welcome to Velella velella Valhalla
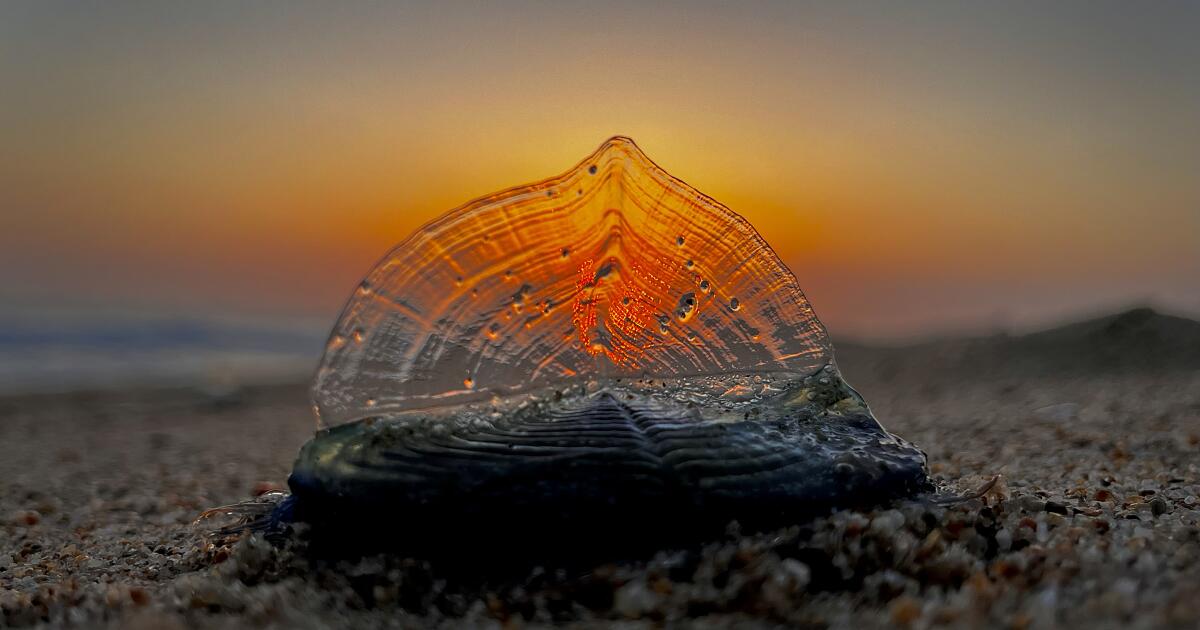

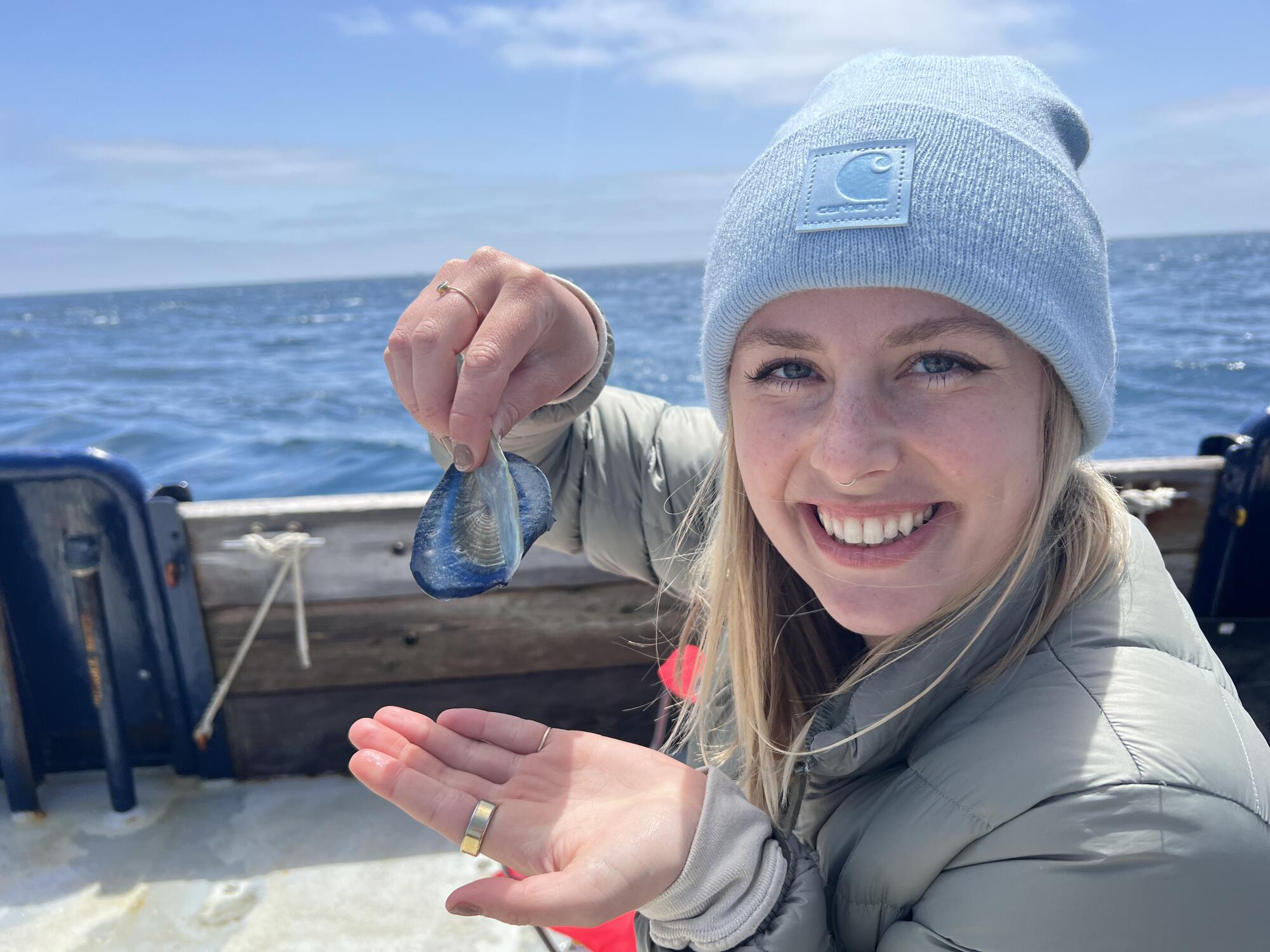
The corpses are washing up by the thousands on Southern California’s beaches: a transparent ringed oval like a giant thumbprint 2 to 3 inches long, with a sail-like fin running diagonally down the length of the body.
Those only recently stranded from the sea still have their rich, cobalt-blue color, a pigment that provides both camouflage and protection from the sun’s UV rays during their life on the open ocean.
Aggressive and impactful reporting on climate change, the environment, health and science.
These intriguing creatures are Velella velella, known also as by-the-wind sailors or, in marine biology circles, “the zooplankton so nice they named it twice,” said Anya Stajner, a biological oceanography PhD student at UC San Diego’s Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
A jellyfish relative that spends the vast majority of its life on the surface of the open sea, velella move at the mercy of the wind, drifting over the ocean with no means of locomotion other than the sails atop their bodies. They tend to wash up on the U.S. West Coast in the spring, when wind conditions beach them onshore.
Springtime velella sightings documented on community science platforms like iNaturalist spiked both this year and last, though scientists say it’s too early to know if this indicates a rise in the animal’s actual numbers.
Velella are an elusive species whose vast habitat and unusual life cycle make them difficult to study. Though they were documented for the first time in 1758, we still don’t know exactly what their range is or how long they live.
These beaching events confront us with a little-understood but essential facet of marine ecology — and may become more common as the oceans warm.
“Zooplankton” — the tiny creatures at the base of the marine food chain — “are sort of this invisible group of animals in the ocean,” Stajner said. “Nobody really knows anything about them. No one really cares about them. But then during these mass Velella velella strandings, all of a sudden there’s this link to this hidden part of the ocean that most of us don’t get to experience.”
What looks like an individual Velella velella is actually a colony of teeny multicellular animals, or zooids, each with their own function, that come together to make a single organism. They’re carnivorous creatures that use stinging tentacles hanging below the surface to catch prey such as copepods, fish eggs, larval fish and smaller plankton.
Unlike their fellow hydrozoa, the Portuguese man o’ war, the toxin in their tentacles isn’t strong enough to injure humans. Nevertheless, “I wouldn’t encourage anyone to touch their mouth or their eyes after they pick one up on the beach,” said Nate Jaros, senior director of fishes and invertebrates at the Aquarium of the Pacific in Long Beach.
Velella that end their lives on California beaches typically have sails that run diagonally from left to right along the length of their bodies, an orientation that catches the onshore winds heading in this direction. As the organism’s carcass dries in the sun and the soft tissues decay, the blue color disappears, leaving the transparent chitinous float behind.
“The wind really just brings them to our doorstep in the right conditions,” Jaros said. “But they’re designed as open ocean animals. They’re not designed to interact with the shoreline, which is usually why they meet their demise when they come into contact with the shore.”
1
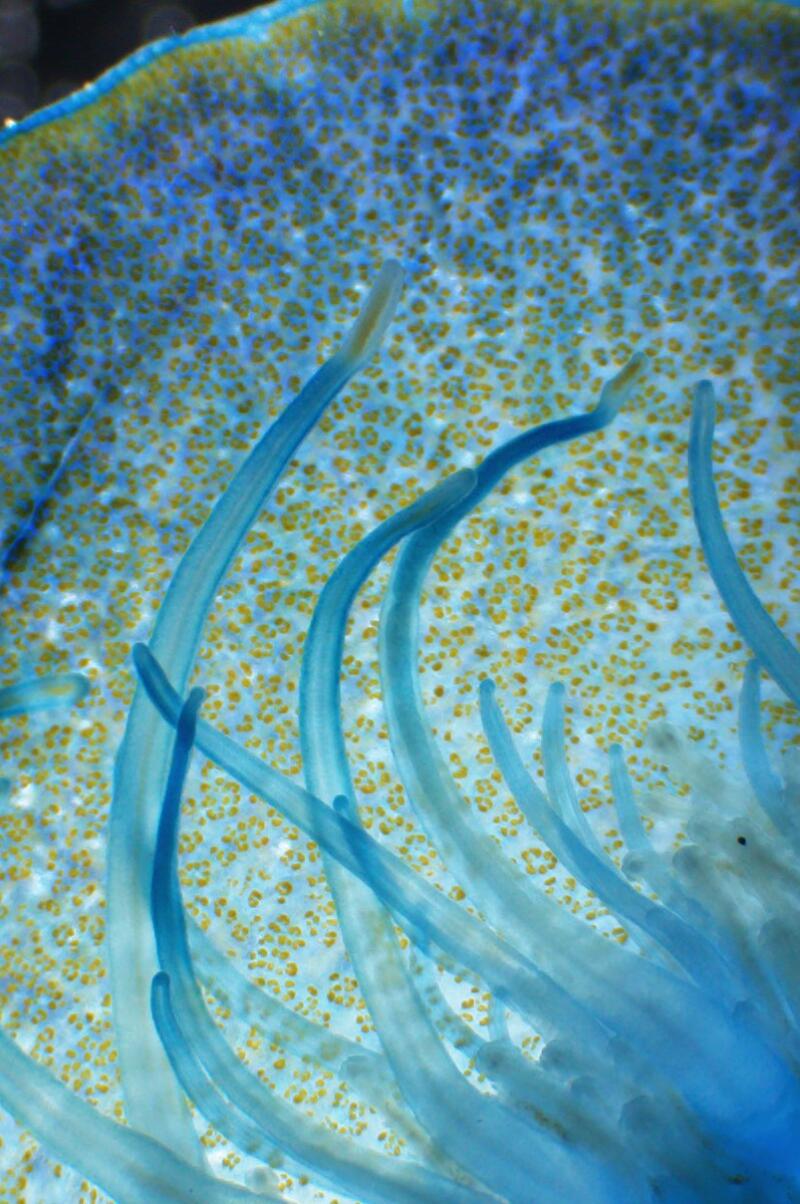

2
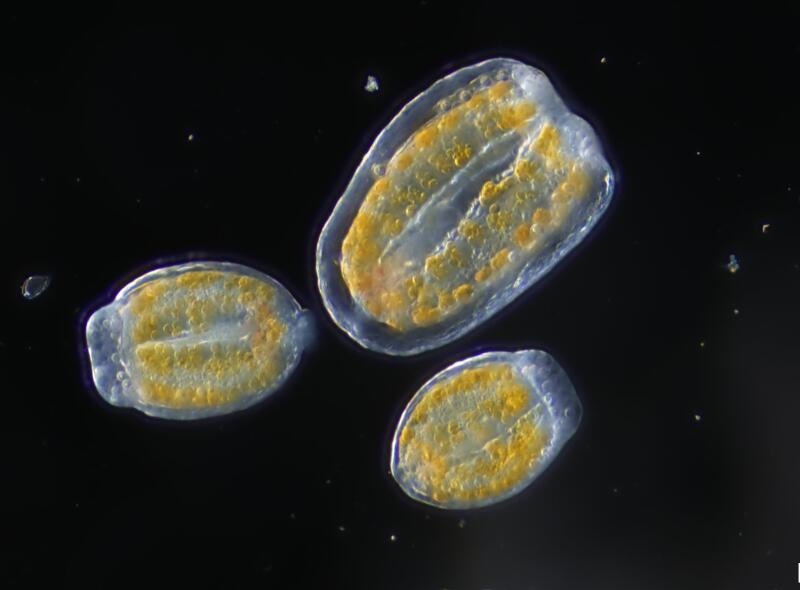
3
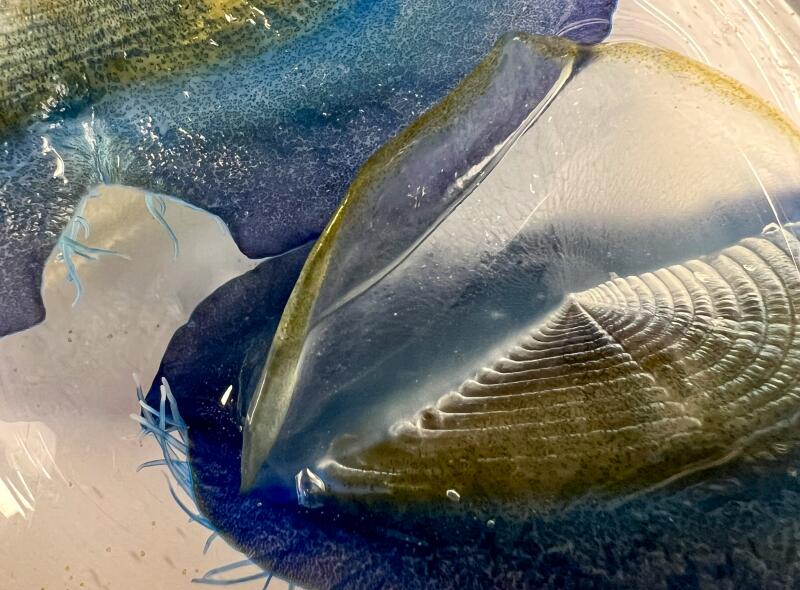

1. Anya Stajner put Velella velella under a microscope. 2. Magnified, you can see more than blue in the organism. “That green and brown coloration comes from their algae symbionts,” Stajner said. 3. Notice the tentacles too. (Anya Stajner)
Velella show up en masse when two key factors coincide, Stajner said: an upwelling of food-rich, colder water from deeper in the ocean, followed by shoreward winds and currents that direct the colonies to beaches.
A 2021 paper from researchers at the University of Washington found a third variable that appears to correlate with more velella sightings: unusually high sea surface temperatures.
After looking at data over a 20-year period, the researchers found that warmer-than-average winter sea surface temperatures followed by onshore winds tended to correlate with higher numbers of velella strandings the following spring, from Washington to Northern California.
“The spring transition toward slightly more onshore winds happens every year, but the warmer winter conditions are episodic,” said co-author Julia K. Parrish, a University of Washington biologist who runs the Coastal Observation and Seabird Survey Team community science project.
Given that sea surface temperatures have been consistently above the historical average every day since March 2023, the current velella bloom is consistent with those findings.
Previous research has found that gelatinous zooplankton like velella and their fellow jellyfish thrive in warmer waters, portending an era some scientists have referred to as the “rise of slime.”
Other winners of a slimy new epoch would be ocean sunfish, a giant bony fish whose individuals can clock in at more than 2,000 pounds and consume jellyfish — and velella — in mass quantities. Ocean sunfish sightings tend to rise when velella observations do, Jaros said.
“The ocean sunfish will actually kind of put their heads out of the water as they eat these. It resembles Pac-Man eating pellets,” he said. (KTLA-TV published a picture of just that this week.)
Though velella blooms are ephemeral, we don’t yet know how long any individual colony lives. The blue seafaring colonies are themselves asexual, though they bud off tiny transparent medusas that are thought to go to the deep sea and reproduce sexually there, Stajner said. The fertilized egg then evolves into a float that returns to the surface and forms another colony.

Anya Stajner, a PhD student at Scripps, collected by-the-wind sailors but was unable to keep them alive in a lab. “Rearing gelatinous organisms is pretty difficult,” she said.
“I was able to actually collect some of those medusae last year during the bloom, but rearing gelatinous organisms is pretty difficult,” Stajner said. The organisms died in the lab.
Stajner left May 1 on an eight-day expedition to sample velella at multiple points along the Santa Lucia Bank and Escarpment in the Channel Islands, with the goal of getting “a better idea of their role in the local ecosystem and trying to understand what these big blooms mean,” she said.

Science
Trump administration declares ‘war on sugar’ in overhaul of food guidelines

The Trump administration announced a major overhaul of American nutrition guidelines Wednesday, replacing the old, carbohydrate-heavy food pyramid with one that prioritizes protein, healthy fats and whole grains.
“Our government declares war on added sugar,” Health and Human Services Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. said in a White House press conference announcing the changes. “We are ending the war on saturated fats.”
“If a foreign adversary sought to destroy the health of our children, to cripple our economy, to weaken our national security, there would be no better strategy than to addict us to ultra-processed foods,” Kennedy said.
Improving U.S. eating habits and the availability of nutritious foods is an issue with broad bipartisan support, and has been a long-standing goal of Kennedy’s Make America Healthy Again movement.
During the press conference, he acknowledged both the American Medical Association and the American Assn. of Pediatrics for partnering on the new guidelines — two organizations that earlier this week condemned the administration’s decision to slash the number of diseases that U.S. children are vaccinated against.
“The American Medical Association applauds the administration’s new Dietary Guidelines for spotlighting the highly processed foods, sugar-sweetened beverages, and excess sodium that fuel heart disease, diabetes, obesity, and other chronic illnesses,” AMA president Bobby Mukkamala said in a statement.
Science
Contributor: With high deductibles, even the insured are functionally uninsured

I recently saw a patient complaining of shortness of breath and a persistent cough. Worried he was developing pneumonia, I ordered a chest X-ray — a standard diagnostic tool. He refused. He hadn’t met his $3,000 deductible yet, and so his insurance would have required him to pay much or all of the cost for that scan. He assured me he would call if he got worse.
For him, the X-ray wasn’t a medical necessity, but it would have been a financial shock he couldn’t absorb. He chose to gamble on a cough, and five days later, he lost — ending up in the ICU with bilateral pneumonia. He survived, but the cost of his “savings” was a nearly fatal hospital stay and a bill that will quite likely bankrupt him. He is lucky he won’t be one of the 55,000 Americans to die from pneumonia each year.
As a physician associate in primary care, I serve as a frontline witness to this failure of the American approach to insurance. Medical professionals are taught that the barrier to health is biology: bacteria, viruses, genetics. But increasingly, the barrier is a policy framework that pressures insured Americans to gamble with their lives. High-deductible health plans seem affordable because their monthly premiums are lower than other plans’, but they create perverse incentives by discouraging patients from seeking and accepting diagnostics and treatments — sometimes turning minor, treatable issues into expensive, life-threatening emergencies. My patient’s gamble with his lungs is a microcosm of the much larger gamble we are taking with the American public.
The economic theory underpinning these high deductibles is known as “skin in the game.” The idea is that if patients are responsible for the first few thousand dollars of their care, they will become savvy consumers, shopping around for the best value and driving down healthcare costs.
But this logic collapses in the exam room. Healthcare is not a consumer good like a television or a used car. My patient was not in a position to “shop around” for a cheaper X-ray, nor was he qualified to determine if his cough was benign or deadly. The “skin in the game” theory assumes a level of medical literacy and market transparency that simply doesn’t exist in a moment of crisis. You can compare the specs of two SUVs; you cannot “shop around” for a life-saving diagnostic while gasping for air.
A 2025 poll from the Kaiser Family Foundation points to this reality, finding that up to 38% of insured American adults say they skipped or postponed necessary healthcare or medications in the past 12 months because of cost. In the same poll, 42% of those who skipped care admitted their health problem worsened as a result.
This self-inflicted public health crisis is set to deteriorate further. The Congressional Budget Office estimates roughly 15 million people will lose health coverage and become uninsured by 2034 because of Medicaid and Affordable Care Act marketplace cuts. That is without mentioning the millions more who will see their monthly premiums more than double if premium tax credits are allowed to expire. If that happens, not only will millions become uninsured but also millions more will downgrade to “bronze” plans with huge deductibles just to keep their premiums affordable. We are about to flood the system with “insured but functionally uninsured” patients.
I see the human cost of this “functional uninsurance” every week. These are patients who technically have coverage but are terrified to use it because their deductibles are so large they may exceed the individuals’ available cash or credit — or even their net worth. This creates a dangerous paradox: Americans are paying hundreds of dollars a month for a card in their wallet they cannot afford to use. They skip the annual physical, ignore the suspicious mole and ration their insulin — all while technically insured. By the time they arrive at my clinic, their disease has often progressed to a catastrophic event, from what could have been a cheap fix.
Federal spending on healthcare should not be considered charity; it is an investment in our collective future. We cannot expect our children to reach their full potential or our workforce to remain productive if basic healthcare needs are treated as a luxury. Inaction by Congress and the current administration to solve this crisis is legislative malpractice.
In medicine, we are trained to treat the underlying disease, not just the symptoms. The skipped visits and ignored prescriptions are merely symptoms; the disease is a policy framework that views healthcare as a commodity rather than a fundamental necessity. If we allow these cuts to proceed, we are ensuring that the American workforce becomes sicker, our hospitals more overwhelmed and our economy less resilient. We are walking willingly into a public health crisis that is entirely preventable.
Joseph Pollino is a primary care physician associate in Nevada.
Insights
L.A. Times Insights delivers AI-generated analysis on Voices content to offer all points of view. Insights does not appear on any news articles.
Viewpoint
Perspectives
The following AI-generated content is powered by Perplexity. The Los Angeles Times editorial staff does not create or edit the content.
Ideas expressed in the piece
-
High-deductible health plans create a barrier to necessary medical care, with patients avoiding diagnostics and treatments due to out-of-pocket cost concerns[1]. Research shows that 38% of insured American adults skipped or postponed necessary healthcare or medications in the past 12 months because of cost, with 42% reporting their health worsened as a result[1].
-
The economic theory of “skin in the game”—which assumes patients will shop around for better healthcare values if they have financial responsibility—fails in medical practice because patients lack the medical literacy to make informed decisions in moments of crisis and cannot realistically compare pricing for emergency or diagnostic services[1].
-
Rising deductibles are pushing enrollees toward bronze plans with deductibles averaging $7,476 in 2026, up from the average silver plan deductible of $5,304[1][4]. In California’s Covered California program, bronze plan enrollment has surged to more than one-third of new enrollees in 2026, compared to typically one in five[1].
-
Expiring federal premium tax credits will more than double out-of-pocket premiums for ACA marketplace enrollees in 2026, creating an expected 75% increase in average out-of-pocket premium payments[5]. This will force millions to either drop coverage or downgrade to bronze plans with massive deductibles, creating a population of “insured but functionally uninsured” people[1].
-
High-deductible plans pose particular dangers for patients with chronic conditions, with studies showing adults with diabetes involuntarily switched to high-deductible plans face 11% higher risk of hospitalization for heart attacks, 15% higher risk for strokes, and more than double the likelihood of blindness or end-stage kidney disease[4].
Different views on the topic
-
Expanding access to health savings accounts paired with bronze and catastrophic plans offers tax advantages that allow higher-income individuals to set aside tax-deductible contributions for qualified medical expenses, potentially offsetting higher out-of-pocket costs through strategic planning[3].
-
Employers and insurers emphasize that offering multiple plan options with varying deductibles and premiums enables employees to select plans matching their individual needs and healthcare usage patterns, allowing those who rarely use healthcare to save money through lower premiums[2]. Large employers increasingly offer three or more medical plan choices, with the expectation that employees choosing the right plan can unlock savings[2].
-
The expansion of catastrophic plans with streamlined enrollment processes and automatic display on HealthCare.gov is intended to make affordable coverage more accessible for certain income groups, particularly those above 400% of federal poverty level who lose subsidies[3].
-
Rising healthcare costs, including specialty drugs and new high-cost cell and gene therapies, are significant drivers requiring premium increases regardless of plan design[5]. Some insurers are managing affordability by discontinuing costly coverage—such as GLP-1 weight-loss medications—to reduce premium rate increases for broader plan members[5].
Science
Trump administration slashes number of diseases U.S. children will be regularly vaccinated against
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services announced sweeping changes to the pediatric vaccine schedule on Monday, sharply cutting the number of diseases U.S. children will be regularly immunized against.
Under the new guidelines, the U.S. still recommends that all children be vaccinated against measles, mumps, rubella, polio, pertussis, tetanus, diphtheria, Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib), pneumococcal disease, human papillomavirus (HPV) and varicella, better known as chickenpox.
Vaccines for all other diseases will now fall into one of two categories: recommended only for specific high-risk groups, or available through “shared clinical decision-making” — the administration’s preferred term for “optional.”
These include immunizations for hepatitis A and B, rotavirus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), bacterial meningitis, influenza and COVID-19. All these shots were previously recommended for all children.
Insurance companies will still be required to fully cover all childhood vaccines on the CDC schedule, including those now designated as optional, according to the Department of Health and Human Services.
Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr., a longtime vaccine critic, said in a statement that the new schedule “protects children, respects families, and rebuilds trust in public health.”
But pediatricians and public health officials widely condemned the shift, saying that it would lead to more uncertainty for patients and a resurgence of diseases that had been under control.
“The decision to weaken the childhood immunization schedule is misguided and dangerous,” said Dr. René Bravo, a pediatrician and president of the California Medical Assn. “Today’s decision undermines decades of evidence-based public health policy and sends a deeply confusing message to families at a time when vaccine confidence is already under strain.”
The American Academy of Pediatrics condemned the changes as “dangerous and unnecessary,” and said that it will continue to publish its own schedule of recommended immunizations. In September, California, Oregon, Washington and Hawaii announced that those four states would follow an independent immunization schedule based on recommendations from the AAP and other medical groups.
The federal changes have been anticipated since December, when President Trump signed a presidential memorandum directing the health department to update the pediatric vaccine schedule “to align with such scientific evidence and best practices from peer, developed countries.”
The new U.S. vaccination guidelines are much closer to those of Denmark, which routinely vaccinates its children against only 10 diseases.
As doctors and public health experts have pointed out, Denmark also has a robust system of government-funded universal healthcare, a smaller and more homogenous population, and a different disease burden.
“The vaccines that are recommended in any particular country reflect the diseases that are prevalent in that country,” said Dr. Kelly Gebo, dean of the Milken Institute School of Public Health at George Washington University. “Just because one country has a vaccine schedule that is perfectly reasonable for that country, it may not be at all reasonable” elsewhere.
Almost every pregnant woman in Denmark is screened for hepatitis B, for example. In the U.S., less than 85% of pregnant women are screened for the disease.
Instead, the U.S. has relied on universal vaccination to protect children whose mothers don’t receive adequate care during pregnancy. Hepatitis B has been nearly eliminated in the U.S. since the vaccine was introduced in 1991. Last month, a panel of Kennedy appointees voted to drop the CDC’s decades-old recommendation that all newborns be vaccinated against the disease at birth.
“Viruses and bacteria that were under control are being set free on our most vulnerable,” said Dr. James Alwine, a virologist and member of the nonprofit advocacy group Defend Public Health. “It may take one or two years for the tragic consequences to become clear, but this is like asking farmers in North Dakota to grow pineapples. It won’t work and can’t end well.”
-

 Detroit, MI6 days ago
Detroit, MI6 days ago2 hospitalized after shooting on Lodge Freeway in Detroit
-

 Technology3 days ago
Technology3 days agoPower bank feature creep is out of control
-

 Dallas, TX5 days ago
Dallas, TX5 days agoDefensive coordinator candidates who could improve Cowboys’ brutal secondary in 2026
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoViral New Year reset routine is helping people adopt healthier habits
-

 Iowa3 days ago
Iowa3 days agoPat McAfee praises Audi Crooks, plays hype song for Iowa State star
-

 Nebraska3 days ago
Nebraska3 days agoOregon State LB transfer Dexter Foster commits to Nebraska
-

 Nebraska3 days ago
Nebraska3 days agoNebraska-based pizza chain Godfather’s Pizza is set to open a new location in Queen Creek
-

 Missouri3 days ago
Missouri3 days agoDamon Wilson II, Missouri DE in legal dispute with Georgia, to re-enter transfer portal: Source



















