Science
Stanford scientist, after decades of study, concludes: We don’t have free will

Before epilepsy was understood to be a neurological condition, people believed it was caused by the moon, or by phlegm in the brain. They condemned seizures as evidence of witchcraft or demonic possession, and killed or castrated sufferers to prevent them from passing tainted blood to a new generation.
Today we know epilepsy is a disease. By and large, it’s accepted that a person who causes a fatal traffic accident while in the grip of a seizure should not be charged with murder.
That’s good, says Stanford University neurobiologist Robert Sapolsky. That’s progress. But there’s still a long way to go.
After more than 40 years studying humans and other primates, Sapolsky has reached the conclusion that virtually all human behavior is as far beyond our conscious control as the convulsions of a seizure, the division of cells or the beating of our hearts.
This means accepting that a man who shoots into a crowd has no more control over his fate than the victims who happen to be in the wrong place at the wrong time. It means treating drunk drivers who barrel into pedestrians just like drivers who suffer a sudden heart attack and veer out of their lane.
“The world is really screwed up and made much, much more unfair by the fact that we reward people and punish people for things they have no control over,” Sapolsky said. “We’ve got no free will. Stop attributing stuff to us that isn’t there.”
We’ve got no free will. Stop attributing stuff to us that isn’t there.
— Stanford neurobiologist Robert Sapolsky
Sapolsky, a MacArthur “genius” grant winner, is extremely aware that this is an out-there position. Most neuroscientists believe humans have at least some degree of free will. So do most philosophers and the vast majority of the general population. Free will is essential to how we see ourselves, fueling the satisfaction of achievement or the shame of failing to do the right thing.
Saying that people have no free will is a great way to start an argument. This is partly why Sapolsky, who describes himself as “majorly averse to interpersonal conflict,” put off writing his new book “Determined: A Science of Life Without Free Will.”
Sapolsky, 66, has a mild demeanor and a Jerry Garcia beard. For more than three decades, he escaped the politics of academia to study baboons in rural Kenya for a few months every year.
Robert Sapolsky sits with a baboon while doing field research in the 1980s.
(Courtesy of Robert Sapolsky)
“I’m really, really, really trying not to sound like a combative jerk in the book,” he said. “I deal with human complexities by going and living in a tent. So yeah, I’m not up for a lot of brawls about this.”
Analyzing human behavior through the lens of any single discipline leaves room for the possibility that people choose their actions, he says. But after a long cross-disciplinary career, he feels it’s intellectually dishonest to write anything other than what he sees as the unavoidable conclusion: Free will is a myth, and the sooner we accept that, the more just our society will be.
“Determined,” which comes out today, builds on Sapolsky’s 2017 bestseller “Behave: The Biology of Humans at Our Best and Worst,” which won the Los Angeles Times Book Prize and a slew of other accolades.
The book breaks down the neurochemical influences that contribute to human behaviors, analyzing the milliseconds to centuries preceding, say, the pulling of a trigger or the suggestive touch on an arm.

Robert Sapolsky’s latest book is called “Determined: A Science of Life Without Free Will.”
(Josh Edelson/ For The Times)
“Determined” goes a step further. If it’s impossible for any single neuron or any single brain to act without influence from factors beyond its control, Sapolsky argues, there can be no logical room for free will.
Many people with even a passing familiarity with human biology can comfortably agree with this — up to a point.
We know we make worse decisions when hungry, stressed or scared. We know our physical makeup is influenced by the genes inherited from distant ancestors and by our mothers’ health during her pregnancy. Abundant evidence indicates that people who grew up in homes marked by chaos and deprivation will perceive the world differently and make different choices than people raised in safe, stable, resource-rich environments. A lot of important things are beyond our control.
But, like — everything? We have no meaningful command over our choice of careers, romantic partners or weekend plans? If you reach out right now and pick up a pen, was even that insignificant action somehow preordained?
Yes, Sapolsky says, both in the book and to the countless students who have asked the same question during his office hours. What the student experiences as a decision to grab the pen is preceded by a jumble of competing impulses beyond his or her conscious control. Maybe their pique is heightened because they skipped lunch; maybe they’re subconsciously triggered by the professor’s resemblance to an irritating relative.
Then look at the forces that brought them to the professor’s office, feeling empowered to challenge a point. They’re more likely to have had parents who themselves were college educated, more likely to hail from an individualistic culture rather than a collective one. All of those influences subtly nudge behavior in predictable ways.
You may have had the uncanny experience of talking about an upcoming camping trip with a friend, only to find yourself served with ads for tents on social media later. Your phone didn’t record your conversation, even if that’s what it feels like. It’s just that the collective record of your likes, clicks, searches and shares paints such a detailed picture of your preferences and decision-making patterns that algorithms can predict — often with unsettling accuracy — what you are going to do.
Something similar happens when you reach for that pen, Sapolsky says. So many factors beyond your conscious awareness brought you to that pen that it’s hard to say how much you “chose” to pick it up at all.
Sapolsky was raised in an Orthodox Jewish household in Brooklyn, the son of immigrants from the former Soviet Union.
Biology called to him early — by grade school he was writing fan letters to primatologists and lingering in front of the taxidermied gorillas at the American Museum of Natural History — but religion shaped life at home.
That all changed on a single night in his early teens, he says. While grappling with questions of faith and identity, he was struck by an epiphany that kept him awake until dawn and reshaped his future: God is not real, there is no free will, and we primates are pretty much on our own.
“That was kind of a big day,” he said with a chuckle, “and it’s been tumultuous since then.”
Skeptics could seize on this to rebut his arguments: If we aren’t free to choose our actions or beliefs, how does a boy from a deeply religious conservative home become a self-professed liberal atheist?
Change is always possible, he argues, but it comes from external stimuli. Sea slugs can learn to reflexively retreat from an electrical shock. Through the same biochemical pathways, humans are changed by exposure to external events in ways we rarely see coming.
Imagine, he offers, a group of friends that goes to see a biopic about an inspiring activist. One applies the next day to join the Peace Corps. One is struck by the beautiful cinematography and signs up for a filmmaking course. The rest are annoyed they didn’t see a Marvel film.
All of the friends were primed to respond as they did when they sat down to watch. Maybe one had heightened adrenaline from a close call with another car on the drive over; maybe another was in a new relationship and awash in oxytocin, the so-called love hormone. They had different levels of dopamine and serotonin in their brains, different cultural backgrounds, different sensitivities to sensory distractions in the theater. None chose how the stimulus of the film would affect them anymore than the sea slug “decided” to wince in response to a jolt.
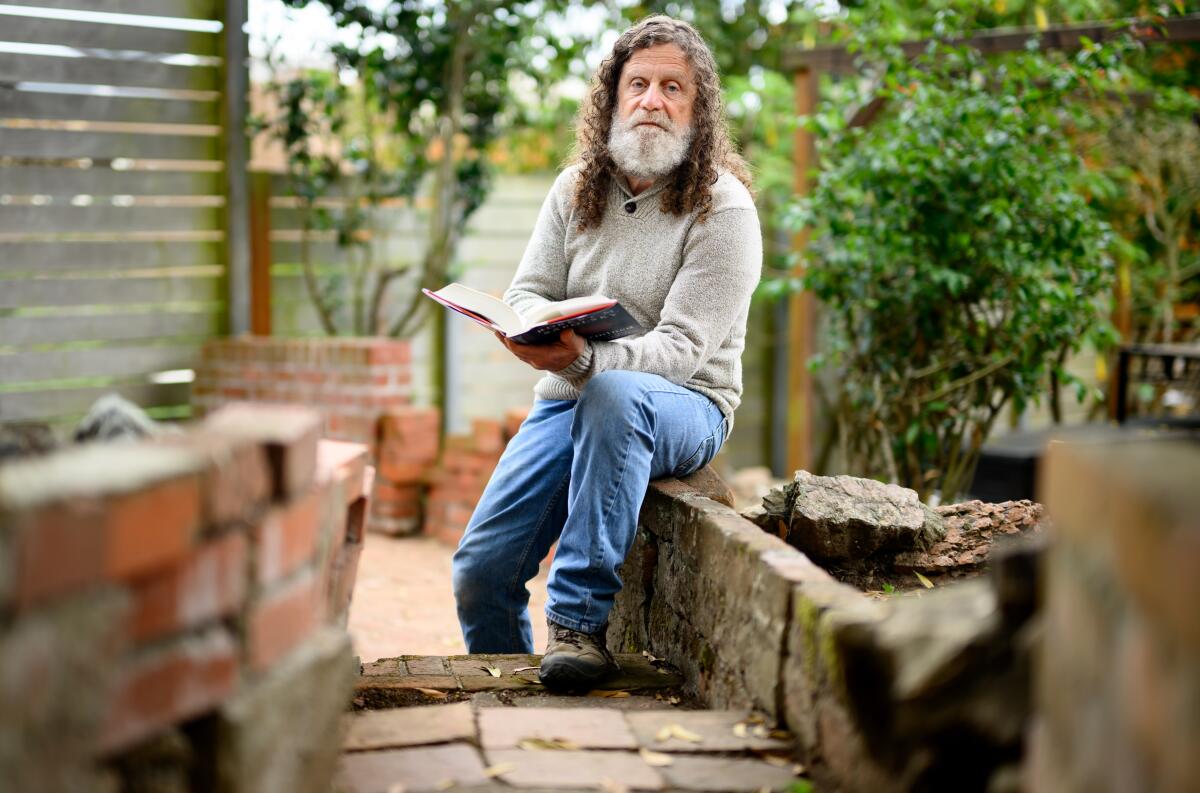

Robert Sapolsky understands that saying that people have no free will is a great way to start an argument. This is partly why he put off writing his new book for years.
(Josh Edelson / For The Times)
For fellow adherents of determinism — the belief that it’s impossible for a person in any situation to have acted differently than they did — Sapolsky’s scientific defense of the cause is welcome.
“Who we are and what we do is ultimately the result of factors beyond our control and because of this we are never morally responsible for our actions in the sense that would make us truly deserving of praise and blame, punishment and reward,” said Gregg Caruso, a philosopher at SUNY Corning who read early drafts of the book. “I am in agreement with Sapolsky that life without belief in free will is not only possible but preferable.”
Caruso is co-director of the Justice Without Retribution Network, which advocates for an approach to criminal activity that prioritizes preventing future harm rather than assigning blame. Focusing on the causes of violent or antisocial behavior instead of fulfilling a desire for punishment, he said, “will allow us to adopt more humane and effective practices and policies.”
Theirs is very much a minority viewpoint.
Sapolsky is “a wonderful explainer of complex phenomena,” said Peter U. Tse, a Dartmouth neuroscientist and author of the 2013 book “The Neural Basis of Free Will.” “However, a person can be both brilliant and utterly wrong.”
Neural activity is highly variable, Tse said, with identical inputs often resulting in non-identical responses in individuals and populations. It’s more accurate to think of those inputs as imposing parameters rather than determining specific outcomes. Even if the range of potential outcomes is limited, there’s simply too much variability at play to think of our behavior as predetermined.
What’s more, he said, it’s harmful to do so.
“Those who push the idea that we are nothing but deterministic biochemical puppets are responsible for enhancing psychological suffering and hopelessness in this world,” Tse said.
Even those who believe biology limits our choices are wary of how openly we should embrace that.
Saul Smilansky, a philosopher at the University of Haifa in Israel and author of the book “Free Will and Illusion,” rejects the idea that we can will ourselves to transcend all genetic and environmental constraints. But if we want to live in a just society, we have to believe that we can.
“Losing all belief in free will and moral responsibility would likely be catastrophic,” he said, and encouraging people to do so is “dangerous, even irresponsible.”
A widely cited 2008 study found that people who read passages dismissing the idea of free will were more likely to cheat on a subsequent test. Other studies have found that people who feel less control over their actions care less about making mistakes in their work, and that disbelief in free will leads to more aggression and less helpfulness.
Sapolsky discusses such concerns in his book, ultimately concluding that the effects seen in such experiments are too small and their lack of reproducibility too great to support the idea that civilization will crumble if we think we can’t control our fates.
The more compelling critique, he says, is eloquently articulated in the short story “What’s Expected of Us,” by speculative fiction writer Ted Chiang. The narrator describes a new technology that convinces users their choices are predetermined, a discovery that saps them of their will to live.
“It’s essential that you behave as if your decisions matter,” the narrator warns, “even though you know that they don’t.”
The greatest risk of abandoning free will, Sapolsky concedes, isn’t that we’ll want to do bad things. It’s that, without a sense of personal agency, we won’t want to do anything.
“It may be dangerous to tell people that they don’t have free will,” Sapolsky said. “The vast majority of the time, I really think it’s a hell of a lot more humane.”
Sapolsky knows he won’t persuade most of his readers. It’s hard to convince people who have been harmed that perpetrators deserve less blame because of their history of poverty. It’s even harder to convince the well-off that their accomplishments deserve less praise because of their history of privilege.
“If you have time to be bummed out by that, you’re one of the lucky ones,” he said.
His true hope, he says, is to increase compassion. Maybe if people understand how thoroughly an early history of trauma can rewire a brain, they’ll stop lusting for harsh punishments. Maybe if someone realizes they have a brain condition like depression or ADHD, they’ll stop hating themselves for struggling with tasks that seem easier for others.
Just as previous generations thought seizures were brought on by witchcraft, some of our current beliefs about personal responsibility may eventually be undone by scientific discovery.
We are machines, Sapolsky argues, exceptional in our ability to perceive our own experiences and feel emotions about them. It is pointless to hate a machine for its failures.
There is only one last thread he can’t resolve.
“It is logically indefensible, ludicrous, meaningless to believe that something ‘good’ can happen to a machine,” he writes. “Nonetheless, I am certain that it is good if people feel less pain and more happiness.”

Robert Sapolsky’s fellow adherents of determinism — the belief that it’s impossible for a person in any situation to have acted differently than they did — have welcomed his scientific defense of their cause.
(Josh Edelson / For The Times)

Science
There's a reason you can't stop doomscrolling through L.A.'s fire disaster
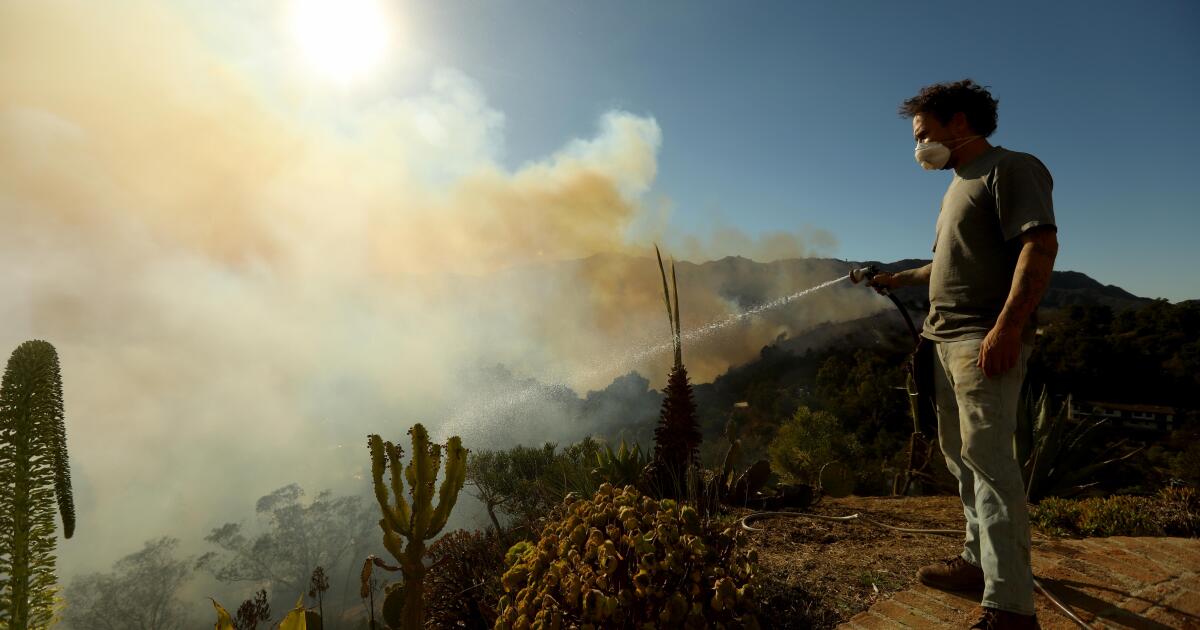

Even for those lucky enough to get out in time, or to live outside the evacuation zones, there has been no escape from the fires in the Los Angeles area this week.
There is hardly a vantage point in the city from which flames or plumes of smoke are not visible, nowhere the scent of burning memories can’t reach.
And on our screens — on seemingly every channel and social media feed and text thread and WhatsApp group — an endless carousel of images documents a level of fear, loss and grief that felt unimaginable here as recently as Tuesday morning.
Even in places of physical safety, many in Los Angeles are finding it difficult to look away from the worst of the destruction online.
“To me it’s more comfortable to doomscroll than to sit and wait,” said Clara Sterling, who evacuated from her home Wednesday. “I would rather know exactly where the fire is going and where it’s headed than not know anything at all.”
A writer and comedian, Sterling is — by her own admission — extremely online. But the nature of this week’s fires make it particularly hard to disengage from news coverage and social media, experts said.
For one, there’s a material difference between scrolling through images of a far-off crisis and staying informed about an active disaster unfolding in your neighborhood, said Casey Fiesler, an associate professor specializing in tech ethics at the University of Colorado Boulder.
“It’s weird to even think of it as ‘doomscrolling,’ ” she said. “When you’re in it, you’re also looking for important information that can be really hard to get.”
When you share an identity with the victims of a traumatic event, you’re more likely both to seek out media coverage of the experience and to feel more distressed by the media you see, said Roxane Cohen Silver, distinguished professor of psychological science at UC Irvine.
For Los Angeles residents, this week’s fires are affecting the people we identify with most intimately: family, friends and community members. They have consumed places and landmarks that feature prominently in fond memories and regular routines.
The ubiquitous images have also fueled painful memories for those who have lived through similar disasters — a group whose numbers have increased as wildfires have grown more frequent in California, Silver said.
This she knows personally: She evacuated from the Laguna Beach fires in 1993, and began a long-term study of that fire’s survivors days after returning to her home.
“Throughout California, throughout the West, throughout communities that have had wildfire experience, we are particularly primed and sensitized to that news,” she said. “And the more we immerse ourselves in that news, the more likely we are to experience distress.”
Absorption in these images of fire and ash can cause trauma of its own, said Jyoti Mishra, an associate professor of psychiatry at UC San Diego who studied the long-term psychological health of survivors of the 2018 Camp fire.
The team identified lingering symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder, depression and anxiety both among survivors who personally experienced fire-related trauma such as injury or property loss, and — to a smaller but still significant degree — among those who indirectly experienced the trauma as witnesses.
“If you’re witnessing [trauma] in the media, happening on the streets that you’ve lived on and walked on, and you can really put yourself in that place, then it can definitely be impactful,” said Mishra, who’s also co-director of the UC Climate Change and Mental Health Council. “Psychology and neuroscience research has shown that images and videos that generate a sense of personal meaning can have deep emotional impacts.”
The emotional pull of the videos and images on social media make it hard to look away, even as many find the information there much harder to trust.
Like many others, Sterling spent a lot of time online during the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic. Back then, Sterling said, the social media environment felt decidedly different.
“This time around I think I feel less informed about what’s going on because there’s been such a big push toward not fact-checking and getting rid of verified accounts,” she said.
The rise of AI-generated images and photos has added another troubling kink, as Sterling highlighted in a video posted to TikTok early Thursday.
“The Hollywood sign was not on fire last night. Any video or photos that you saw of the Hollywood sign on fire were fake. They were AI generated,” she said, posting from a hotel in San Diego after evacuating.
Hunter Ditch, a producer and voice actor in Lake Balboa, raised similar concerns about the lack of accurate information. Some social media content she’s encountered seemed “very polarizing” or political, and some exaggerated the scope of the disaster or featured complete fabrications, such as that flaming Hollywood sign.
The spread of false information has added another layer of stress, she said. This week, she started turning to other types of app — like the disaster mapping app, Watch Duty — to track the spreading fires and changing evacuation zones.
But that made her wonder: “If I have to check a whole other app for accurate information, then what am I even doing on social media at all?”
Science
Pink Fire Retardant, a Dramatic Wildfire Weapon, Poses Its Own Dangers

From above the raging flames, these planes can unleash immense tankfuls of bright pink fire retardant in just 20 seconds. They have long been considered vital in the battle against wildfires.
But emerging research has shown that the millions of gallons of retardant sprayed on the landscape to tame wildfires each year come with a toxic burden, because they contain heavy metals and other chemicals that are harmful to human health and the environment.
The toxicity presents a stark dilemma. These tankers and their cargo are a powerful tool for taming deadly blazes. Yet as wildfires intensify and become more frequent in an era of climate change, firefighters are using them more often, and in the process releasing more harmful chemicals into the environment.
Some environmental groups have questioned the retardants’ effectiveness and potential for harm. The efficiency of fire retardant has been hard to measure, because it’s one of a barrage of firefighting tactics deployed in a major fire. After the flames are doused, it’s difficult to assign credit.
The frequency and severity of wildfires has grown in recent years, particularly in the western United States. Scientists have also found that fires across the region have become faster moving in recent decades.
There are also the longer-term health effects of exposure to wildfire smoke, which can penetrate the lungs and heart, causing disease. A recent global survey of the health effects of air pollution caused by wildfires found that in the United States, exposure to wildfire smoke had increased by 77 percent since 2002. Globally, wildfire smoke has been estimated to be responsible for up to 675,000 premature deaths per year.
Fire retardants add to those health and environmental burdens because they present “a really, really thorny trade-off,” said Daniel McCurry, an assistant professor of civil and environmental engineering at the University of Southern California, who led the recent research on their heavy-metal content.
The United States Forest Service said on Thursday that nine large retardant-spraying planes, as well as 20 water-dropping helicopters, were being deployed to fight the Southern California fires, which have displaced tens of thousands of people. Several “water scooper” amphibious planes, capable of skimming the surface of the sea or other body of water to fill their tanks, are also being used.
Two large DC-10 aircraft, dubbed “Very Large Airtankers” and capable of delivering up to 9,400 gallons of retardant, were also set to join the fleet imminently, said Stanton Florea, a spokesman for the National Interagency Fire Center in Boise, Idaho, which coordinates national wildland firefighting efforts across the West.
Sprayed ahead of the fire, the retardants coat vegetation and prevent oxygen from allowing it to burn, Mr. Florea said. (Red dye is added so firefighters can see the retardant against the landscape.) And the retardant, typically made of salts like ammonium polyphosphate, “lasts longer. It doesn’t evaporate, like dropping water,” he said.
The new research from Dr. McCurry and his colleagues found, however, that at least four different types of heavy metals in a common type of retardant used by firefighters exceeded California’s requirements for hazardous waste.
Federal data shows that more than 440 million gallons of retardant were applied to federal, state, and private land between 2009 and 2021. Using that figure, the researchers estimated that between 2009 and 2021, more than 400 tons of heavy metals were released into the environment from fire suppression, a third of that in Southern California.
Both the federal government and the retardant’s manufacturer, Perimeter Solutions, have disputed that analysis, saying the researchers had evaluated a different version of the retardant. Dan Green, a spokesman for Perimeter, said retardants used for aerial firefighting had passed “extensive testing to confirm they meet strict standards for aquatic and mammalian safety.”
Still, the findings help explain why concentrations of heavy metals tend to surge in rivers and streams after wildfires, sometimes by hundreds of times. And as scrutiny of fire suppressants has grown, the Forestry Service has set buffer zones surrounding lakes and rivers, though its own data shows retardant still inadvertently drifts into those waters.
In 2022, the environmental nonprofit Forest Service Employees for Environmental Ethics sued the government in federal court in Montana, demanding that the Forest Service obtain a permit under the Clean Water Act to cover accidental spraying into waterways.
The judge ruled that the agency did indeed need to obtain a permit. But it allowed retardant use to continue to protect lives and property.
Science
2024 Brought the World to a Dangerous Warming Threshold. Now What?

Source: Copernicus/ECMWF
Note: Temperature anomalies relative to 1850-1900 averages.
At the stroke of midnight on Dec. 31, Earth finished up its hottest year in recorded history, scientists said on Friday. The previous hottest year was 2023. And the next one will be upon us before long: By continuing to burn huge amounts of coal, oil and gas, humankind has all but guaranteed it.
The planet’s record-high average temperature last year reflected the weekslong, 104-degree-Fahrenheit spring heat waves that shuttered schools in Bangladesh and India. It reflected the effects of the bathtub-warm ocean waters that supercharged hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico and cyclones in the Philippines. And it reflected the roasting summer and fall conditions that primed Los Angeles this week for the most destructive wildfires in its history.
“We are facing a very new climate and new challenges, challenges that our society is not prepared for,” said Carlo Buontempo, director of the Copernicus Climate Change Service, the European Union monitoring agency.
But even within this progression of warmer years and ever-intensifying risks to homes, communities and the environment, 2024 stood out in another unwelcome way. According to Copernicus, it was the first year in which global temperatures averaged more than 1.5 degrees Celsius, or 2.7 degrees Fahrenheit, above those the planet experienced at the start of the industrial age.
For the past decade, the world has sought to avoid crossing this dangerous threshold. Nations enshrined the goal in the 2015 Paris agreement to fight climate change. “Keep 1.5 alive” was the mantra at United Nations summits.
Yet here we are. Global temperatures will fluctuate somewhat, as they always do, which is why scientists often look at warming averaged over longer periods, not just a single year.
But even by that standard, staying below 1.5 degrees looks increasingly unattainable, according to researchers who have run the numbers. Globally, despite hundreds of billions of dollars invested in clean-energy technologies, carbon dioxide emissions hit a record in 2024 and show no signs of dropping.
One recent study published in the journal Nature concluded that the absolute best humanity can now hope for is around 1.6 degrees of warming. To achieve it, nations would need to start slashing emissions at a pace that would strain political, social and economic feasibility.
But what if we’d started earlier?
By spewing heat-trapping gases into the atmosphere, humankind has lifted global temperatures to record highs.
If nations had started reducing emissions in 2005, they could have made gradual cuts to limit warming to 1.5 degrees.
Starting in 2015, when the Paris agreement was adopted, would have required steeper cuts.
Starting today would require cuts so drastic as to appear essentially impossible.
“It was guaranteed we’d get to this point where the gap between reality and the trajectory we needed for 1.5 degrees was so big it was ridiculous,” said David Victor, a professor of public policy at the University of California, San Diego.
The question now is what, if anything, should replace 1.5 as a lodestar for nations’ climate aspirations.
“These top-level goals are at best a compass,” Dr. Victor said. “They’re a reminder that if we don’t do more, we’re in for significant climate impacts.”
The 1.5-degree threshold was never the difference between safety and ruin, between hope and despair. It was a number negotiated by governments trying to answer a big question: What’s the highest global temperature increase — and the associated level of dangers, whether heat waves or wildfires or melting glaciers — that our societies should strive to avoid?
The result, as codified in the Paris agreement, was that nations would aspire to hold warming to “well below” 2 degrees Celsius while “pursuing efforts” to limit it to 1.5 degrees.
Even at the time, some experts called the latter goal unrealistic, because it required such deep and rapid emissions cuts. Still, the United States, the European Union and other governments adopted it as a guidepost for climate policy.
Christoph Bertram, an associate research professor at the University of Maryland’s Center for Global Sustainability, said the urgency of the 1.5 target spurred companies of all kinds — automakers, cement manufacturers, electric utilities — to start thinking hard about what it would mean to zero out their emissions by midcentury. “I do think that has led to some serious action,” Dr. Bertram said.
But the high aspiration of the 1.5 target also exposed deep fault lines among nations.
China and India never backed the goal, since it required them to curb their use of coal, gas and oil at a pace they said would hamstring their development. Rich countries that were struggling to cut their own emissions began choking off funding in the developing world for fossil-fuel projects that were economically beneficial. Some low-income countries felt it was deeply unfair to ask them to sacrifice for the climate given that it was wealthy nations — and not them — that had produced most of the greenhouse gases now warming the world.
“The 1.5-degree target has created a lot of tension between rich and poor countries,” said Vijaya Ramachandran, director for energy and development at the Breakthrough Institute, an environmental research organization.
Costa Samaras, an environmental-engineering professor at Carnegie Mellon University, compared the warming goals to health officials’ guidelines on, say, cholesterol. “We don’t set health targets on what’s realistic or what’s possible,” Dr. Samaras said. “We say, ‘This is what’s good for you. This is how you’re going to not get sick.’”
“If we were going to say, ‘Well, 1.5 is likely out of the question, let’s put it to 1.75,’ it gives people a false sense of assurance that 1.5 was not that important,” said Dr. Samaras, who helped shape U.S. climate policy from 2021 to 2024 in the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy. “It’s hugely important.”
Scientists convened by the United Nations have concluded that restricting warming to 1.5 degrees instead of 2 would spare tens of millions of people from being exposed to life-threatening heat waves, water shortages and coastal flooding. It might mean the difference between a world that has coral reefs and Arctic sea ice in the summer, and one that doesn’t.
Each tiny increment of additional warming, whether it’s 1.6 degrees versus 1.5, or 1.7 versus 1.6, increases the risks. “Even if the world overshoots 1.5 degrees, and the chances of this happening are increasing every day, we must keep striving” to bring emissions to zero as soon as possible, said Inger Anderson, the executive director of the United Nations Environment Program.
Officially, the sun has not yet set on the 1.5 target. The Paris agreement remains in force, even as President-elect Donald J. Trump vows to withdraw the United States from it for a second time. At U.N. climate negotiations, talk of 1.5 has become more muted compared with years past. But it has hardly gone away.
“With appropriate measures, 1.5 Celsius is still achievable,” Cedric Schuster, the minister of natural resources and environment for the Pacific island nation of Samoa, said at last year’s summit in Azerbaijan. Countries should “rise to the occasion with new, highly ambitious” policies, he said.
To Dr. Victor of U.C. San Diego, it is strange but all too predictable that governments keep speaking this way about what appears to be an unachievable aim. “No major political leader who wants to be taken seriously on climate wants to stick their neck out and say, ‘1.5 degrees isn’t feasible. Let’s talk about more realistic goals,’” he said.
Still, the world will eventually need to have that discussion, Dr. Victor said. And it’s unclear how it will go.
“It could be constructive, where we start asking, ‘How much warming are we really in for? And how do we deal with that?’” he said. “Or it could look very toxic, with a bunch of political finger pointing.”
Methodology
The second chart shows pathways for reducing carbon emissions that would have a 66 percent chance of limiting global warming this century to 1.5 degrees Celsius above the preindustrial average.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIvory Coast says French troops to leave country after decades