Science
More parents are delaying their kids’ vaccines, and it’s alarming pediatricians
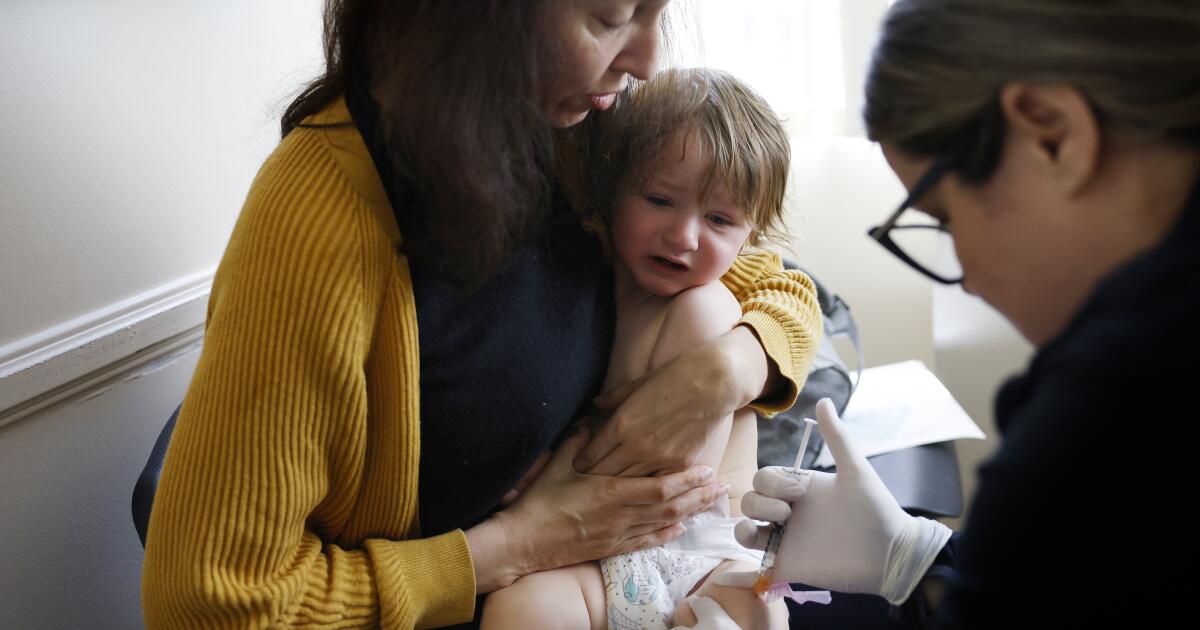
As measles cases pop up across the country this winter — including several in California — one group of children is stirring deep concerns among pediatricians: the babies and toddlers of vaccine-hesitant parents who are delaying their child’s measles-mumps-rubella shots.
Pediatricians across the state say they have seen a sharp increase recently in the number of parents with concerns about routine childhood vaccinations who are demanding their own inoculation schedules for their babies, creating a worrisome pool of very young children who may be at risk of contracting measles, a potentially deadly yet preventable disease.
“Especially early on, when a parent is already feeling really vulnerable and doesn’t want to give something to their beautiful baby who was just born if they don’t need it, it makes them think, ‘Maybe I’ll just delay it and wait and see.’” said Dr. Whitney Casares, a pediatrician and author who has written on vaccination for the American Academy of Pediatrics. “What they don’t realize is if they don’t vaccinate according to the recommended schedule, that can really set their child up for a whole lot of risks.”
It is difficult to know how widespread such delays have become. California keeps careful track of the rate of kindergartners who have been vaccinated against measles, but does not have comprehensive data for children at younger ages.
Dr. Eric Ball has seen the shift firsthand. At his Orange County pediatric practice, Ball said, he has noticed an increase in parents asking about delays since the COVID-19 pandemic, as politicization of and misinformation about that vaccine has seeped into discussions about routine childhood vaccinations, including measles-mumps-rubella, known as MMR.
Dr. Eric Ball examines 9-month-old Noah at Southern Orange County Pediatric Associates in Ladera Ranch on Feb. 28.
(Christina House / Los Angeles Times)
Rather than an outright refusal, however, these vaccine-hesitant parents express a softer kind of reluctance, asking if it’s possible to use an “alternative schedule” of vaccines, rather than sticking to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s recommendations. Sometimes they seek to delay the shots by a few months, and sometimes by several years.
“I have patients who have three kids, and they vaccinated the first two kids on schedule. And then since COVID, with their third kid, they are like, ‘I don’t know if this is safe. I want to wait until the kids are older’, or ‘instead of doing two shots today, I want to do one shot,’” said Ball. “It just prolongs the time where you have a child who’s unprotected and potentially can get sick from these diseases.”
He tries his best to explain to parents the importance and safety of vaccines, including MMR. He even brings out his own children’s vaccine records to prove his point, and he is often successful. But not always.
At Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, attending pediatrician Dr. Colleen Kraft said about half of parents are questioning the CDC’s recommended vaccine schedule — a significant increase since the pandemic.
“Even my most reasonable parents ask questions. So it’s definitely in the mainstream,” she said. She also worries about her patients who are behind on vaccines because they missed so many appointments during the pandemic and are only now returning to her office.
Karla Benzl holds her son, 15-month-old Marcus, before he gets vaccinated at Southern Orange County Pediatric Associates in Ladera Ranch on Feb. 28.
(Christina House / Los Angeles Times)
In Marin County, parents’ requests to delay vaccinations have become so frequent that Dr. Nelson Branco said last month his practice decided to tighten vaccine requirements as cases of both measles and pertussis have spread. Babies seen by doctors in the practice will need to have their first set of vaccines completed by 4 months of age. The primary series of vaccines against the most serious and common diseases, including measles, must be completed by 24 months.
If parents don’t agree, they must leave the practice.
“Kids are doing a lot of things that are high risk before they’re 5 and are required to be vaccinated to attend kindergarten, said Branco. “They’re getting on international flights, they’re going to Disneyland where there are lots of kids,” leaving young children vulnerable to measles when they could be protected.
The CDC recommends that the first dose of MMR be given when a baby is 12 to 15 months old. Usually this happens at a child’s 12-month well visit. A second dose is then given at 4 to 6 years of age.
At least 95% of people in a community must be vaccinated to achieve a level of “herd immunity” that protects everyone in a community, including those who cannot get the vaccine because they are too young or are immunocompromised, according to the World Health Organization.
Low vaccination rates have led to measles outbreaks in several states over the last decade, most recently in Florida.
Nationally, the rate of kindergartners fully immunized against the measles dropped from 95% in the 2019-20 school year to 93% in 2022-23, according to the CDC.
But there is overall good news in California. Since the state’s 2015 ban on parents’ personal beliefs as a reason to skip vaccinating children before school, the measles vaccination rate for kindergartners has grown from 92% in the 2013-2014 school year to 96.5% in 2022-2023.
Are you a SoCal mom?
The L.A. Times early childhood team wants to connect with you! Find us in The Mamahood’s mom group on Facebook.
Share your perspective and ask us questions.
But those postponing vaccinations have created a potential vulnerability gap in a child’s first four years.
One in 5 unvaccinated people who get measles in the U.S. will be hospitalized. Since there is no good treatment for measles, doctors can often do little more than offer supportive care. One in 1,000 children with measles will develop brain swelling that can leave a child deaf or with an intellectual disability; 1 to 3 children in 1,000 will die, according to the CDC.
Measles is so contagious that 90% of people close to an infected person will catch it if they are not immune, according to the CDC. The virus can remain contagious in a room or on a surface for up to two hours after the infected person has left.
In the Children’s Hospital Orange County primary care network, which has more than 130 pediatricians, the share of 15-month-olds with an MMR vaccine has been dropping consistently over the past last few years, from 98% in 2019, down to 93.5% in 2023.
For years in the early 2000s, anti-vaccine sentiment was at an all-time high after the publication of a now-debunked and retracted study that falsely tied the MMR vaccine to autism. In December 2014, an unvaccinated 11-year-old was hospitalized with measles following a visit to Disneyland. Over the next few months, measles spread to 125 people across seven states.
The outbreak helped galvanize support for vaccination nationwide. A year after the Disneyland outbreak, California passed its ban on personal exemption.
“The pendulum swung back the other way, and we had a few years where vaccination rates were really high,” said Ball. But the rumors and rhetoric surrounding the COVID vaccines have caused the pendulum to swing in the other direction. “We’re back to dealing with conspiracy theories, things that people heard on the internet, or something that their cousin’s neighbor’s roommate said. It’s really hard.”
Noah, who is 9 months old, gets his measurements taken by medical assistant Shellee Rayl at Southern Orange County Pediatric Associates in Ladera Ranch on Feb. 28.
(Christina House / Los Angeles Times)
A Pew Research poll conducted in March 2023 found that 88% of Americans are confident that the benefits of an MMR vaccine outweigh the risks, a percentage that has remained fairly consistent since before the pandemic.
But support for all school-based vaccine mandates has fallen; 28% now say that parents should be able to decide not to vaccinate their children, even if it causes health risks for others, up from 16% in October 2019. Among Republicans, the share has more than doubled, from 20% in 2019 to 42% in 2023.
Support for the MMR vaccine was lower among parents with young children, the poll found. About 65% of parents with children under age 5 reported that the preventative health benefits of MMR were high — compared to 88% of all adults — and 39% said the risk of side effects was either medium or high; half said they worried about whether all childhood vaccines are necessary.
Tara Larson, a former ER nurse who lives in Santa Monica, said she became concerned about childhood vaccination when she was pregnant last year. She started watching anti-vaccine documentaries, reading vaccine safety inserts, and following several social media accounts “to make us an informed vaxxer. We’re not anti-vax,” she said.
Larson decided that she wanted to delay vaccinating her son until he was 3 months old, to limit him to just three vaccines in his first year that she felt were essential, and to spread them out so that he would only get one shot per month. “By the time he starts playing on the playground and goes to school, he’ll need to start his course of Hep B, but why overload his course of vaccines right now?” she said.
The first pediatrician she saw refused to follow her requested schedule. But, Larson said, “in my gut, I just felt like this is the right thing to be doing for our baby, and I left.” After weeks of searching, she found a holistic provider who charges a $250 monthly fee and agreed with her approach.
She said she hasn’t yet decided whether to give her son, who is now 8 months old, the MMR vaccine when he becomes eligible. “I think some doctors will say to wait until they’re 3, but that was when there wasn’t a resurgence of measles,” she said. “That’s my next thing to dive into.”
Karla Benzl of Mission Viejo comforts her 15-month-old son, Marcus, after he received his vaccinations.
(Christina House / Los Angeles Times)
But there’s no scientific basis and no known benefits to delaying vaccines except in very rare medical circumstances, said Casares, whose pediatric practice is in Oregon.
Casares said the problem is that parents have an “exposure bias.” They often consume an onslaught of information on social media about the risks, but very little about the benefits of vaccines or the enormous risks of the diseases themselves. She said in a country such as the United States, where vaccination rates are fairly high, most people don’t see the ravages that the diseases can cause if rates fall.
This article is part of The Times’ early childhood education initiative, focusing on the learning and development of California children from birth to age 5. For more information about the initiative and its philanthropic funders, go to latimes.com/earlyed.

Science
Commentary: My toothache led to a painful discovery: The dental care system is full of cavities as you age

I had a nagging toothache recently, and it led to an even more painful revelation.
If you X-rayed the state of oral health care in the United States, particularly for people 65 and older, the picture would be full of cavities.
“It’s probably worse than you can even imagine,” said Elizabeth Mertz, a UC San Francisco professor and Healthforce Center researcher who studies barriers to dental care for seniors.
Mertz once referred to the snaggletoothed, gap-filled oral health care system — which isn’t really a system at all — as “a mess.”
But let me get back to my toothache, while I reach for some painkiller. It had been bothering me for a couple of weeks, so I went to see my dentist, hoping for the best and preparing for the worst, having had two extractions in less than two years.
Let’s make it a trifecta.
My dentist said a molar needed to be yanked because of a cellular breakdown called resorption, and a periodontist in his office recommended a bone graft and probably an implant. The whole process would take several months and cost roughly the price of a swell vacation.
I’m lucky to have a great dentist and dental coverage through my employer, but as anyone with a private plan knows, dental insurance can barely be called insurance. It’s fine for cleanings and basic preventive routines. But for more complicated and expensive procedures — which multiply as you age — you can be on the hook for half the cost, if you’re covered at all, with annual payout caps in the $1,500 range.
“The No. 1 reason for delayed dental care,” said Mertz, “is out-of-pocket costs.”
So I wondered if cost-wise, it would be better to dump my medical and dental coverage and switch to a Medicare plan that costs extra — Medicare Advantage — but includes dental care options. Almost in unison, my two dentists advised against that because Medicare supplemental plans can be so limited.
Sorting it all out can be confusing and time-consuming, and nobody warns you in advance that aging itself is a job, the benefits are lousy, and the specialty care you’ll need most — dental, vision, hearing and long-term care — are not covered in the basic package. It’s as if Medicare was designed by pranksters, and we’re paying the price now as the percentage of the 65-and-up population explodes.
So what are people supposed to do as they get older and their teeth get looser?
A retired friend told me that she and her husband don’t have dental insurance because it costs too much and covers too little, and it turns out they’re not alone. By some estimates, half of U.S. residents 65 and older have no dental insurance.
That’s actually not a bad option, said Mertz, given the cost of insurance premiums and co-pays, along with the caps. And even if you’ve got insurance, a lot of dentists don’t accept it because the reimbursements have stagnated as their costs have spiked.
But without insurance, a lot of people simply don’t go to the dentist until they have to, and that can be dangerous.
“Dental problems are very clearly associated with diabetes,” as well as heart problems and other health issues, said Paul Glassman, associate dean of the California Northstate University dentistry school.
There is one other option, and Mertz referred to it as dental tourism, saying that Mexico and Costa Rica are popular destinations for U.S. residents.
“You can get a week’s vacation and dental work and still come out ahead of what you’d be paying in the U.S.,” she said.
Tijuana dentist Dr. Oscar Ceballos told me that roughly 80% of his patients are from north of the border, and come from as far away as Florida, Wisconsin and Alaska. He has patients in their 80s and 90s who have been returning for years because in the U.S. their insurance was expensive, the coverage was limited and out-of-pocket expenses were unaffordable.
“For example, a dental implant in California is around $3,000-$5,000,” Ceballos said. At his office, depending on the specifics, the same service “is like $1,500 to $2,500.” The cost is lower because personnel, office rent and other overhead costs are cheaper than in the U.S., Ceballos said.
As we spoke by phone, Ceballos peeked into his waiting room and said three patients were from the U.S. He handed his cellphone to one of them, San Diegan John Lane, who said he’s been going south of the border for nine years.
“The primary reason is the quality of the care,” said Lane, who told me he refers to himself as 39, “with almost 40 years of additional” time on the clock.
Ceballos is “conscientious and he has facilities that are as clean and sterile and as medically up to date as anything you’d find in the U.S.,” said Lane, who had driven his wife down from San Diego for a new crown.
“The cost is 50% less than what it would be in the U.S.,” said Lane, and sometimes the savings is even greater than that.
Come this summer, Lane may be seeing even more Californians in Ceballos’ waiting room.
“Proposed funding cuts to the Medi-Cal Dental program would have devastating impacts on our state’s most vulnerable residents,” said dentist Robert Hanlon, president of the California Dental Assn.
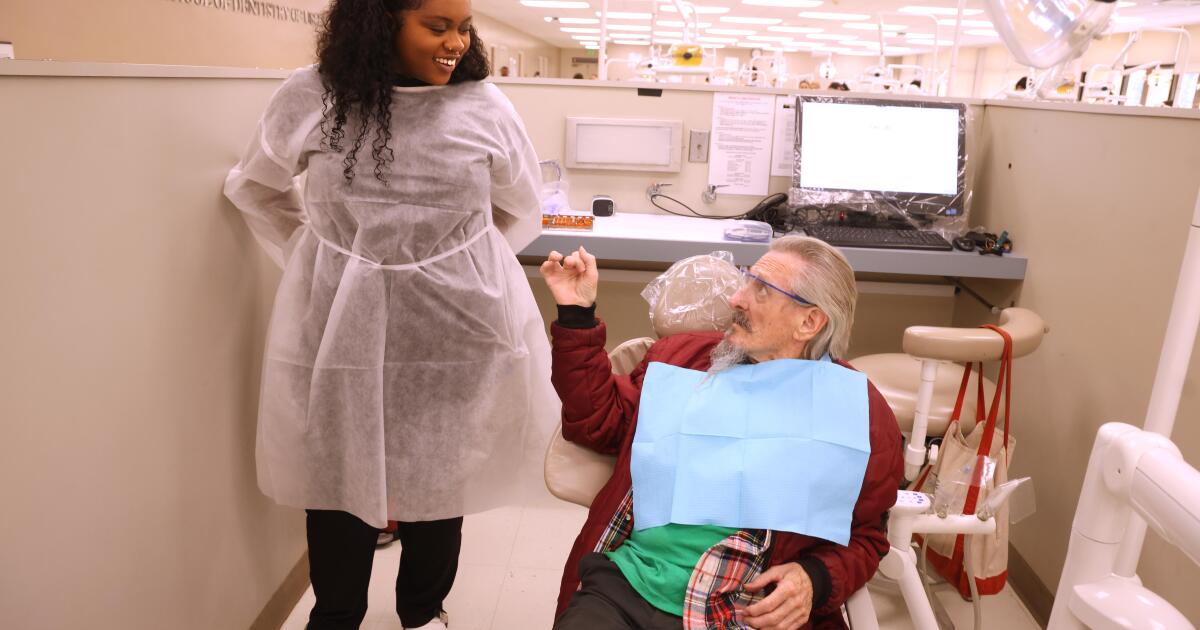
Dental student Somkene Okwuego smiles after completing her work on patient Jimmy Stewart, 83, who receives affordable dental work at the Ostrow School of Dentistry of USC on the USC campus in Los Angeles on February 26, 2026.
(Genaro Molina / Los Angeles Times)
Under Proposition 56’s tobacco tax in 2016, supplemental reimbursements to dentists have been in place, but those increases could be wiped out under a budget-cutting proposal. Only about 40% of the state’s dentists accept Medi-Cal payments as it is, and Hanlon told me a CDA survey indicates that half would stop accepting Medi-Cal patients and many others will accept fewer patients.
“It’s appalling that when the cost of providing healthcare is at an all-time high, the state is considering cutting program funding back to 1990s levels,” Hanlon said. “These cuts … will force patients to forgo or delay basic dental care, driving completely preventable emergencies into already overcrowded emergency departments.”
Somkene Okwuego, who as a child in South L.A. was occasionally a patient at USC’s Herman Ostrow School of Dentistry clinic, will graduate from the school in just a few months.
I first wrote about Okwuego three years ago, after she got an undergrad degree in gerontology, and she told me a few days ago that many of her dental patients are elderly and have Medi-Cal or no insurance at all. She has also worked at a Skid Row dental clinic, and plans after graduation to work at a clinic where dental care is free or discounted.
Okwuego said “fixing the smiles” of her patients is a privilege and boosts their self-image, which can help “when they’re trying to get jobs.” When I dropped by to see her Thursday, she was with 83-year-old patient Jimmy Stewart.
Stewart, an Army veteran, told me he had trouble getting dental care at the VA and had gone years without seeing a dentist before a friend recommended the Ostrow clinic. He said he’s had extractions and top-quality restorative care at USC, with the work covered by his Medi-Cal insurance.
I told Stewart there could be some Medi-Cal cuts in the works this summer.
“I’d be screwed,” he said.
Him and a lot of other people.
steve.lopez@latimes.com
Science
Diablo Canyon clears last California permit hurdle to keep running
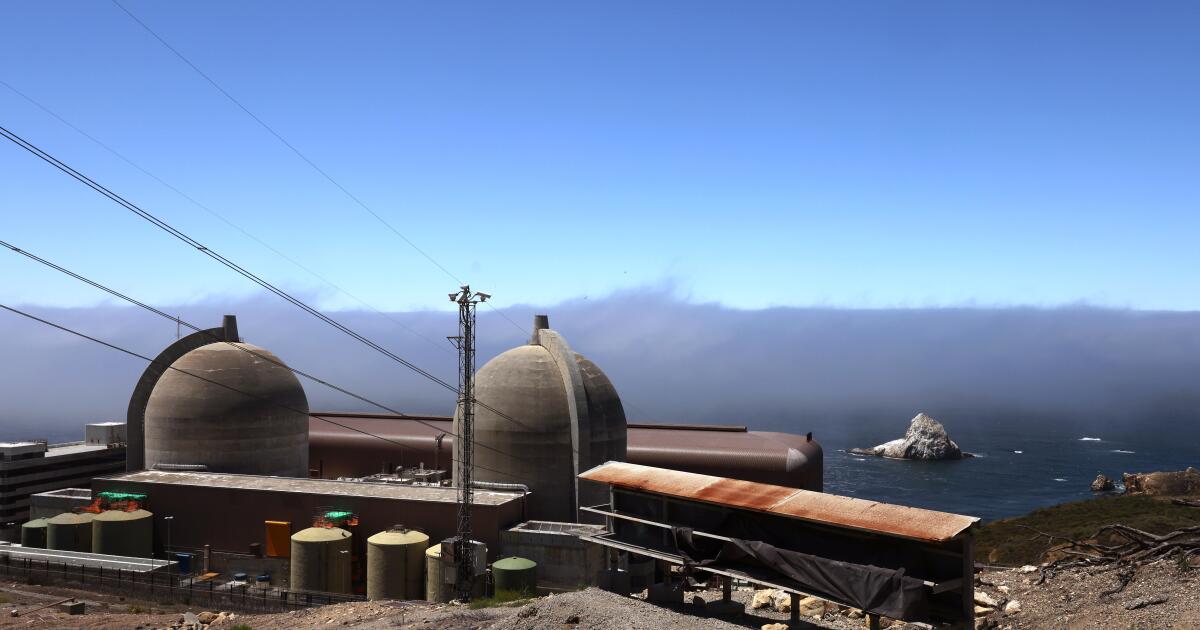

Central Coast Water authorities approved waste discharge permits for Diablo Canyon nuclear plant Thursday, making it nearly certain it will remain running through 2030, and potentially through 2045.
The Pacific Gas & Electric-owned plant was originally supposed to shut down in 2025, but lawmakers extended that deadline by five years in 2022, fearing power shortages if a plant that provides about 9 percent the state’s electricity were to shut off.
In December, Diablo Canyon received a key permit from the California Coastal Commission through an agreement that involved PG&E giving up about 12,000 acres of nearby land for conservation in exchange for the loss of marine life caused by the plant’s operations.
Today’s 6-0 vote by the Central Coast Regional Water Board approved PG&E’s plans to limit discharges of pollutants into the water and continue to run its “once-through cooling system.” The cooling technology flushes ocean water through the plant to absorb heat and discharges it, killing what the Coastal Commission estimated to be two billion fish each year.
The board also granted the plant a certification under the Clean Water Act, the last state regulatory hurdle the facility needed to clear before the federal Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is allowed to renew its permit through 2045.
The new regional water board permit made several changes since the last one was issued in 1990. One was a first-time limit on the chemical tributyltin-10, a toxic, internationally-banned compound added to paint to prevent organisms from growing on ship hulls.
Additional changes stemmed from a 2025 Supreme Court ruling that said if pollutant permits like this one impose specific water quality requirements, they must also specify how to meet them.
The plant’s biggest water quality impact is the heated water it discharges into the ocean, and that part of the permit remains unchanged. Radioactive waste from the plant is regulated not by the state but by the NRC.
California state law only allows the plant to remain open to 2030, but some lawmakers and regulators have already expressed interest in another extension given growing electricity demand and the plant’s role in providing carbon-free power to the grid.
Some board members raised concerns about granting a certification that would allow the NRC to reauthorize the plant’s permits through 2045.
“There’s every reason to think the California entities responsible for making the decision about continuing operation, namely the California [Independent System Operator] and the Energy Commission, all of them are sort of leaning toward continuing to operate this facility,” said boardmember Dominic Roques. “I’d like us to be consistent with state law at least, and imply that we are consistent with ending operation at five years.”
Other board members noted that regulators could revisit the permits in five years or sooner if state and federal laws changes, and the board ultimately approved the permit.
Science
Deadly bird flu found in California elephant seals for the first time

The H5N1 bird flu virus that devastated South American elephant seal populations has been confirmed in seals at California’s Año Nuevo State Park, researchers from UC Davis and UC Santa Cruz announced Wednesday.
The virus has ravaged wild, commercial and domestic animals across the globe and was found last week in seven weaned pups. The confirmation came from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Veterinary Services Laboratory in Ames, Iowa.
“This is exceptionally rapid detection of an outbreak in free-ranging marine mammals,” said Professor Christine Johnson, director of the Institute for Pandemic Insights at UC Davis’ Weill School of Veterinary Medicine. “We have most likely identified the very first cases here because of coordinated teams that have been on high alert with active surveillance for this disease for some time.”
Since last week, when researchers began noticing neurological and respoiratory signs of the disease in some animals, 30 seals have died, said Roxanne Beltran, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz. Twenty-nine were weaned pups and the other was an adult male. The team has so far confirmed the virus in only seven of the dead pups.
Infected animals often have tremors convulsions, seizures and muscle weakness, Johnson said.
Beltran said teams from UC Santa Cruz, UC Davis and California State Parks monitor the animals 260 days of the year, “including every day from December 15 to March 1” when the animals typically come ashore to breed, give birth and nurse.
The concerning behavior and deaths were first noticed Feb. 19.
“This is one of the most well-studied elephant seal colonies on the planet,” she said. “We know the seals so well that it’s very obvious to us when something is abnormal. And so my team was out that morning and we observed abnormal behaviors in seals and increased mortality that we had not seen the day before in those exact same locations. So we were very confident that we caught the beginning of this outbreak.”
In late 2022, the virus decimated southern elephant seal populations in South America and several sub-Antarctic Islands. At some colonies in Argentina, 97% of pups died, while on South Georgia Island, researchers reported a 47% decline in breeding females between 2022 and 2024. Researchers believe tens of thousands of animals died.
More than 30,000 sea lions in Peru and Chile died between 2022 and 2024. In Argentina, roughly 1,300 sea lions and fur seals perished.
At the time, researchers were not sure why northern Pacific populations were not infected, but suspected previous or milder strains of the virus conferred some immunity.
The virus is better known in the U.S. for sweeping through the nation’s dairy herds, where it infected dozens of dairy workers, millions of cows and thousands of wild, feral and domestic mammals. It’s also been found in wild birds and killed millions of commercial chickens, geese and ducks.
Two Americans have died from the virus since 2024, and 71 have been infected. The vast majority were dairy or commercial poultry workers. One death was that of a Louisiana man who had underlying conditions and was believed to have been exposed via backyard poultry or wild birds.
Scientists at UC Santa Cruz and UC Davis increased their surveillance of the elephant seals in Año Nuevo in recent years. The catastrophic effect of the disease prompted worry that it would spread to California elephant seals, said Beltran, whose lab leads UC Santa Cruz’s northern elephant seal research program at Año Nuevo.
Johnson, the UC Davis researcher, said the team has been working with stranding networks across the Pacific region for several years — sampling the tissue of birds, elephant seals and other marine mammals. They have not seen the virus in other California marine mammals. Two previous outbreaks of bird flu in U.S. marine mammals occurred in Maine in 2022 and Washington in 2023, affecting gray and harbor seals.
The virus in the animals has not yet been fully sequenced, so it’s unclear how the animals were exposed.
“We think the transmission is actually from dead and dying sea birds” living among the sea lions, Johnson said. “But we’ll certainly be investigating if there’s any mammal-to-mammal transmission.”
Genetic sequencing from southern elephant seal populations in Argentina suggested that version of the virus had acquired mutations that allowed it to pass between mammals.
The H5N1 virus was first detected in geese in China in 1996. Since then it has spread across the globe, reaching North America in 2021. The only continent where it has not been detected is Oceania.
Año Nuevo State Park, just north of Santa Cruz, is home to a colony of some 5,000 elephant seals during the winter breeding season. About 1,350 seals were on the beach when the outbreak began. Other large California colonies are located at Piedras Blancas and Point Reyes National Sea Shore. Most of those animals — roughly 900 — are weaned pups.
It’s “important to keep this in context. So far, avian influenza has affected only a small proportion of the weaned at this time, and there are still thousands of apparently healthy animals in the population,” Beltran said in a press conference.
Public access to the park has been closed and guided elephant seal tours canceled.
Health and wildlife officials urge beachgoers to keep a safe distance from wildlife and keep dogs leashed because the virus is contagious.
-

 World3 days ago
World3 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts4 days ago
Massachusetts4 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Denver, CO4 days ago
Denver, CO4 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Louisiana6 days ago
Louisiana6 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoOpenAI didn’t contact police despite employees flagging mass shooter’s concerning chatbot interactions: REPORT
















