Politics
California gas jumps 13 cents overnight. There’s no telling when prices will drop
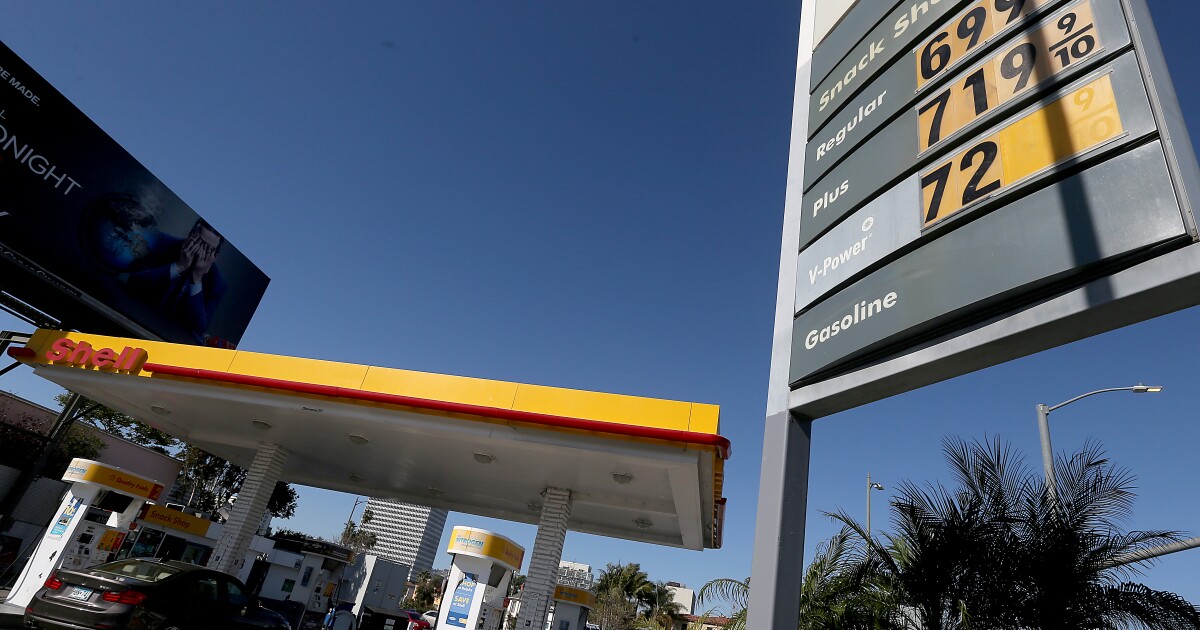

California gasoline costs proceed to skyrocket as Russia’s conflict on Ukraine grinds on — and consultants say there’s no telling when aid may arrive on the pump.
The state’s common value for a gallon of standard gasoline hit $5.57 on Wednesday, rising 13 cents in a single day and cementing it as the costliest within the nation, in response to the American Car Assn.
Golden State gasoline is now $1.32 greater than the nationwide common of $4.25, stated Doug Shupe, a spokesperson for AAA. The worth marks an all-time excessive, although the determine doesn’t account for inflation.
Even inside California’s expensive petroleum panorama, sure areas stand out for his or her eye-popping value tags.
Stations in Mono County at the moment are charging a median of $6.14 for a gallon of standard, making it the costliest place in California to replenish, in response to a tracker maintained by AAA.
Los Angeles and Lengthy Seashore additionally exceed the state common, rising to a wallet-constricting common of $5.65 per gallon on Wednesday. Orange County reached $5.64. The hikes replicate a 13-cent bounce from a day prior, Shupe stated.
Some stations within the Southland replicate wildly larger costs — surging previous $7 a gallon — seemingly untethered from financial actuality.
At this level, oil and gasoline consultants aren’t positive what’s in retailer, however predict costs may enhance additional until there’s a dramatic shift within the conflict in Japanese Europe.
“It’s all depending on [Vladimir] Putin,” stated Severin Borenstein, an power economist at UC Berkeley’s Haas College of Enterprise, referring to the Russian president.
“If he have been to determine tomorrow that this was a foul determination and work out a option to declare victory and withdraw, the worth of oil would go approach down,” Borenstein stated Wednesday. “But when he pushes forward, I believe it’s fairly potential it’ll go up additional. Each of these prospects are exhibiting up out there costs.”
California gasoline costs are inclined to pattern among the many highest within the nation as a consequence of taxes and environmental rules that dictate the usage of a particular mix of gasoline. Gov. Gavin Newsom has proposed to pause a deliberate gasoline tax enhance, and expanded on that in his State of the State speech Tuesday when he stated he would introduce a tax rebate proposal for Californians to offset rising gasoline costs.
However the conflict in Ukraine has wreaked havoc on costs throughout the globe, that are primarily pushed by the price of crude oil. President Biden’s determination Tuesday to halt U.S. purchases of Russian oil solely added to the broader nervousness about rising costs.
Crude oil costs have been down on Wednesday, dropping $15 from the day gone by at one level, however consultants warned that additional fluctuations have been potential all through the buying and selling day.
When markets closed Tuesday, oil was buying and selling at about $128 a gallon, a large spike from a month in the past, Borenstein stated.
Borenstein stated the typical value for gasoline may hit $6 or $7 per gallon in California, given the latest massive jumps in crude oil costs.
In keeping with Borenstein, a rise of $1 within the value of a barrel of crude oil interprets to a further 2½ cents per gallon on the pump. Due to this fact, if crude oil costs enhance by $20 a barrel, it’ll lead to a 50-cent enhance for a median gallon of gasoline.
“So it wouldn’t take rather a lot to push it above $6,” he stated.
Patrick De Haan, head of petroleum evaluation at value tracker GasBuddy, stated “it’s potential, perhaps probably” that L.A.’s common value per gallon will inch towards $6.
“I don’t suppose $6 is a assure but, however actually much more stations are going to get there,” he added.
The one certainty expressed by De Haan and Borenstein was that there isn’t a certainty within the instant future.
“Analysts don’t have the crystal ball both,” De Haan stated
Nevertheless, these buying and selling on the futures marketplace for crude oil are betting will probably be more cost effective a few 12 months from now, in response to Borenstein.
Futures markets anticipate the price of supply a month to a 12 months or extra down the road. The value for Could 2023 is $30 a barrel decrease than for this Could, Borenstein stated.

Politics
This Tiny Fish’s Mistaken Identity Halted a Dam’s Construction

For such a tiny fish, the snail darter has haunted Tennessee. It was the endangered species that swam its way to the Supreme Court in a vitriolic battle during the 1970s that temporarily blocked the construction of a dam.
On Friday, a team of researchers argued that the fish was a phantom all along.
“There is, technically, no snail darter,” said Thomas Near, curator of ichthyology at the Yale Peabody Museum.
Dr. Near, also a professor who leads a fish biology lab at Yale, and his colleagues report in the journal Current Biology that the snail darter, Percina tanasi, is neither a distinct species nor a subspecies. Rather, it is an eastern population of Percina uranidea, known also as the stargazing darter, which is not considered endangered.
Dr. Near contends that early researchers “squinted their eyes a bit” when describing the fish, because it represented a way to fight the Tennessee Valley Authority’s plan to build the Tellico Dam on the Little Tennessee River, about 20 miles southwest of Knoxville.
“I feel it was the first and probably the most famous example of what I would call the ‘conservation species concept,’ where people are going to decide a species should be distinct because it will have a downstream conservation implication,” Dr. Near said.
The T.V.A. began building the Tellico Dam in 1967. Environmentalists, lawyers, farmers and the Cherokee, whose archaeological sites faced flooding, were eager to halt the project. In August 1973, they stumbled upon a solution.
David Etnier, a dam opponent and a zoologist at the University of Tennessee, went snorkeling with students in the Little Tennessee River at Coytee Spring, not far from Tellico. There, they found a fish on the river bottom that Dr. Etnier said he had never seen before, and he named it the snail darter.
The fish became a “David” to pit against “Goliath” — because if it were to be protected under the Endangered Species Act, the dam’s construction would be blocked.
“Here’s a little fish that might save your farm,” Dr. Etnier told a local farmer, according to the book “The Snail Darter and the Dam,” by Zygmunt Plater, an emeritus law professor at Boston College.
Elected officials were eager to finish the dam, and grew increasingly frustrated.
“This two-inch fish, which surely kept the lowest profile of all God’s creatures until a few years ago, has been the bane of my existence and the nemesis of what I fondly hoped would be my golden years,” Senator Howard H. Baker Jr., of Tennessee said about the snail darter in 1979.
That year, Representative John Duncan Sr., a Tennessee Republican, also described the snail darter as a “worthless, unsightly, minute, inedible minnow.”
After the Supreme Court upheld the protection of the snail darter, President Jimmy Carter signed a bill that exempted the Tellico Dam from the Endangered Species Act. The dam began operating in 1979.
Jeffrey Simmons, an author of the study who formerly worked as a biologist at the T.V.A., discovered what appeared to be snail darters in 2015 on the border of Alabama and Mississippi, far from the Tellico Dam.
“Holy crap, do you know what this is?” Mr. Simmons said to a colleague in the creek that day.
Mr. Simmons knew it shouldn’t be there if it were truly a snail darter.
Ava Ghezelayagh, now at the University of Chicago, and colleagues conducted analysis of the fish’s DNA and compared snail darter physical traits with other fish. That led to confirmation that it was a match with the stargazing darter.
Dr. Plater, who also argued successfully for the fish in the Supreme Court case, took issue with the Yale study. He said the approach favored by Dr. Near and colleagues makes them genetic “lumpers” instead of “splitters,” meaning they reduce species instead of making more. He believes the findings also lean too heavily on genetics.
“Whether he intends it or not, lumping is a great way to cut back on the Endangered Species Act,” Dr. Plater said of Dr. Near.
Dr. Near said being described as a “lumper” was a pejorative in his world, and he added that most of the research he and colleagues had performed had resulted in speciation splits, including a 2022 study.
“The work strengthens the Endangered Species Act, because it shows how science can be revised with additional information and newer perspectives,” he said. “The methods we use in this study are leading to the discovery of scores of new species, many of which are more endangered.”
Decades after the Tellico Dam battle, the fish formerly known as the snail darter is thriving. It left the endangered species list in 2020.
“This is still a success story,” Mr. Simmons said. “Its listing under the Endangered Species Act worked, regardless of what you call this fish.”
While Mr. Duncan died in 1988, his son, former Representative John J. Duncan Jr., known as Jimmy, said his father would have felt vindicated.
“He felt the project should have never been stopped by that little snail darter,” he said.
Politics
Federal courts will not make criminal referrals to DOJ over separate ethics complaints against Justice Thomas
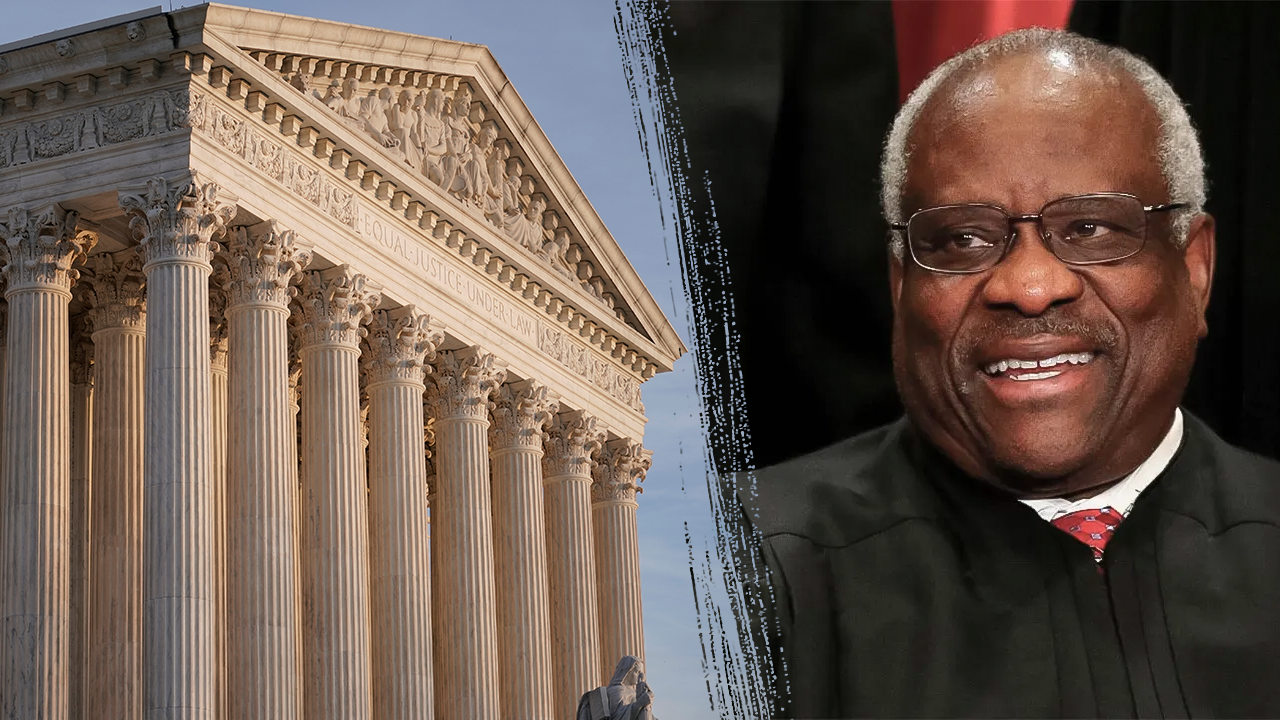
Separate ethics complaints filed by members of Congress and an advocacy group against Justices Clarence Thomas and Ketanji Brown Jackson will not be referred to the Justice Department, federal court officials announced.
The U.S. Judicial Conference said Thomas has agreed to follow updated guidelines on listing free private travel and gifts from friends, following previous reporting on undisclosed hospitality.
For her part, Jackson has amended her financial disclosures following complaints about her husband’s consulting income as a physician.
Democratic Sens. Sheldon Whitehouse (D-RI) and Ron Wyden (D-OR), along with Rep. Hank Johnson (D-GA), had asked for an investigation by the judiciary itself into undisclosed hospitality provided to Thomas by billionaire friend Harland Crow. ProPublica reported on several instances of private travel and lodging over the years.
SUPREME COURT CHEIF JUSTICE ROBERTS ISSUES WARNING ON ‘JUDICIAL INDEPENDENCE’ WEEKS BEFORE TRUMP’S INAUGURATION
Judge Robert Conrad, who heads the judicial conference policymaking body, said in letters to the lawmakers that Thomas had filed amended financial disclosures “that address several issues identified in your letter.”
Additionally, Conrad said that it was not clear whether the judiciary itself could make criminal referrals against a sitting Supreme Court member.
“Because the Judicial Conference does not superintend the Supreme Court and because any effort to grant the Conference such authority would raise serious constitutional questions, one would expect Congress at a minimum to state any such directive clearly. But no such express directive appears in this provision,” Conrad said.
DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE SPENT OVER $100 MILLION ON DEI EDUCATION PROGRAMS OVER LAST FOUR YEARS
The U.S. Supreme Court is seen during sunset. (Aaron Schwartz/SIPA USA)
Conrad noted that Whitehouse and Wyden had separately asked Attorney General Merrick Garland to name a special counsel to investigate then-former President Donald Trump. Garland has not acted yet on that request.
Whitehouse, in a statement, criticized the Judicial Conference’s decision.
“By all appearances, the judicial branch is shirking its statutory duty to hold a Supreme Court justice accountable for ethics violations,” said Whitehouse.
The complaint filed against Jackson came from Citizens for Renewing America, led by Russ Vought, who was nominated by President-elect Trump to lead the Office of Management and Budget.
Questions over ethics, including unreported private travel by some justices, have led the court to adopt its first code of ethics last year.
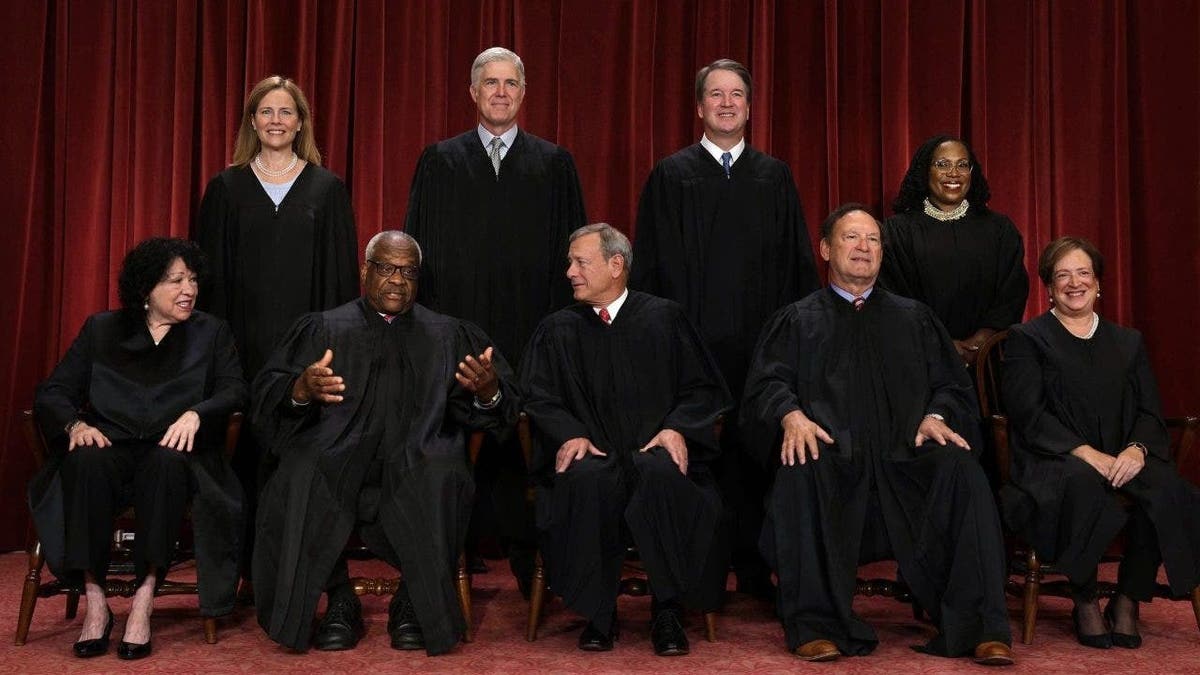

United States Supreme Court (front row L-R) Associate Justice Sonia Sotomayor, Associate Justice Clarence Thomas, Chief Justice of the United States John Roberts, Associate Justice Samuel Alito, and Associate Justice Elena Kagan, (back row L-R) Associate Justice Amy Coney Barrett, Associate Justice Neil Gorsuch, Associate Justice Brett Kavanaugh and Associate Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson pose for their official portrait at the East Conference Room of the Supreme Court building on October 7, 2022 in Washington, DC. The Supreme Court has begun a new term after Associate Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson was officially added to the bench in September. ((Photo by Alex Wong/Getty Images))
However, compliance is left to each of the nine justices, leading to concerns the court is not taking its own ethics enforcement standards seriously.
A two-year investigation by Senate Democrats released last week found additional luxury travel by Justice Thomas in 2021 was not noted on his annual financial disclosure form.
Fix the Court, a group which advocates for greater judicial transparency, urged Congress to act.
“The Conference’s letters further underscore the need for Congress to create a new and transparent mechanism to investigate the justices for ethics violations since the Conference is unwilling to act upon the one method we had presumed existed to do that,” said Executive Director Gabe Roth.
Politics
Newsom aims to limit unhealthy food in California, getting ahead of Trump administration and RFK Jr.

Gov. Gavin Newsom issued an executive order on Friday attempting to limit access to ultra-processed foods, a directive he cast as a continuation of California’s “nation leading” nutrition and health standards.
“The food we eat shouldn’t make us sick with disease or lead to lifelong consequences,” Newsom said in a statement. “California has been a leader for years in creating healthy and delicious school meals, and removing harmful ingredients and chemicals from food. We’re going to work with the industry, consumers and experts to crack down on ultra-processed foods, and create a healthier future for every Californian.”
The order directs state agencies to develop recommendations to limit the health harms of ultra-processed foods and calls for proposals to reduce the purchase of candy, soda and other unhealthy foods made with synthetic dyes or additives by recipients of government food benefits.
The move comes weeks before President-elect Donald Trump is sworn into office for his second term, with iconoclastic former environmental lawyer Robert F. Kennedy Jr. as his nominee for secretary of Health and Human Services. Kennedy still needs to be confirmed by the Senate, but he has been a vocal critic of ultra-processed foods and promised to radically overhaul the country’s food system. Food dyes, pasteurized milk and seed oils are among the common items he has criticized, sometimes making health claims that are not backed up by science.
Though Newsom didn’t mention Kennedy, the Democratic governor of California is planting a preemptive flag around the issue and signaling his refusal to concede the terrain to the incoming Trump administration. His executive order included a long list of steps the state has taken to improve nutrition.
Processed foods are foods altered from their natural form, like frozen vegetables, whereas ultra — or highly —processed foods are foods that have been significantly altered from their natural state, like packaged chips or soft drinks. Ultra-processed foods make up the vast majority of the U.S. food supply, research shows.
The Golden State has indeed been a national leader in banning food additives, with Newsom signing a 2023 bill that made California the first state in the nation to prohibit four additives found in popular cereal, soda, candy and drinks.
The California Food Safety Act was colloquially referred to as the “Skittles ban” before its passage because an earlier version of the bill also targeted titanium dioxide, which is used to color Skittles and several other popular candies. But the final law was amended to remove reference to the substance, solely banning brominated vegetable oil, potassium bromate, propylparaben and red dye No. 3.
Last year, Newsom signed a separate bill into law that bars snack foods containing a number of synthetic food dyes from California public schools. That law will prevent popular snack foods like Flamin’ Hot Cheetos from being stocked in school vending machines or cafeterias when it goes into effect on Dec. 31, 2027.
Laws to protect students from sugary drinks go back decades: In 2009 California banned all K-12 schools from offering soda.
The governor’s order cites the link between “ultra-processed foods” and cancer, obesity, diabetes and other health problems. The order says the U.S. allows more than 10,000 chemicals in food, color additives, or ingredients, compared to 300 that are allowed in the European Union.
Newsom is requiring the California Department of Public Health to provide recommendations by April 1 to limit the harms associated with ultra-processed foods and food ingredients that pose a health risk, which may include warning labels. He tasked the Californa Department of Social Services to issue recommendations to reduce the purchase by California food-stamp users of soda, candy, other ultra-processed foods, or foods made with synthetic food dye or additives on the same timeline.
Among several health directives, his order also requires state agencies to identify areas to increase standards for healthy school meals and to investigate the negative health consequences of food dyes.
Ultra-processed foods will likely be at the forefront of the national discourse in the coming weeks as Kennedy prepares for his Senate confirmation hearing.
Kennedy, a prominent anti-vaccine activist, has promoted a number of false health claims and fringe conspiracy theories. But his positions against food additives have also brought support from unlikely bedfellows who have criticized other parts of his “Make America Healthy Again” agenda.
“Yes, there are some things that he supports that we would agree with, but they feel more like the stopped clock that’s right twice a day,” Dr. Peter Lurie, president and executive director of the Center for Science in the Public Interest, said in an earlier interview with The Times — citing food additives as one example.
Lurie characterized Kennedy’s potential appointment more broadly as a dangerous choice because of his inability “to discern the difference between good and bad science.”
The Food and Drug Administration — the agency perhaps most publicly in Kennedy’s crosshairs — could be significantly impacted by his leadership if he is confirmed by the Senate.
The agency, which falls under the the Department of Health and Human Services, has a massive purview, regulating about 77% of the U.S. food supply and overseeing the safety of nearly $4 trillion worth of food, tobacco and medical products, according to federal data.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoOn a quest for global domination, Chinese EV makers are upending Thailand's auto industry
-

 Health6 days ago
Health6 days agoNew Year life lessons from country star: 'Never forget where you came from'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24982514/Quest_3_dock.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24982514/Quest_3_dock.jpg) Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoMeta’s ‘software update issue’ has been breaking Quest headsets for weeks
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPassenger plane crashes in Kazakhstan: Emergencies ministry
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoIt's official: Biden signs new law, designates bald eagle as 'national bird'
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'Politics is bad for business.' Why Disney's Bob Iger is trying to avoid hot buttons
-

 Culture3 days ago
Culture3 days agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado














