Vermont
Vermont State University hires new diversity officer
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/F57RJBEQQVMPNL7RE3C5ZJL73Q.jpg)
BURLINGTON, Vt. (WCAX) – The brand new Vermont State College is taking a brand new strategy to inclusivity with the return to campus this fall.
The varsity has created a brand new place — chief range officer — to supervise the College’s Castleton, Johnson, Lyndon, and Randolph Heart campuses.
Darren Perron spoke with Jae Basiliere, who can be filling that new position.
Copyright 2022 WCAX. All rights reserved.

Vermont
U.S. Chamber, Oil Industry Sue Vermont Over Law Requiring Companies To Pay For Climate Change Damage

MONTPELIER, Vt. (AP) — The U.S. Chamber of Commerce and a top oil and gas industry trade group are suing Vermont over its new law requiring that fossil fuel companies pay a share of the damage caused over several decades by climate change.
The federal lawsuit filed Monday asks a state court to prevent Vermont from enforcing the law, which was passed last year. Vermont became the first state in the country to enact the law after it suffered catastrophic summer flooding and damage from other extreme weather. The state is working to estimate the cost of climate change dating back to Jan. 1, 1995.
The lawsuit argues the U.S. Constitution precludes the act and that the state law is preempted by the federal Clean Air Act. It also argues that the law violates domestic and foreign commerce clauses by discriminating “against the important interest of other states by targeting large energy companies located outside of Vermont.”
The Chamber and the other plaintiff in the lawsuit, the American Petroleum Institute, argue that the federal government is already addressing climate change. And because greenhouse gases come from billions of individual sources, they argue it is impossible to measure “accurately and fairly” the impact of emissions from a particular entity in a particular location over decades.
“Vermont wants to impose massive retroactive penalties going back 30 years for lawful, out-of-state conduct that was regulated by Congress under the Clean Air Act,” said Tara Morrissey, senior vice president and deputy chief counsel of the Chamber’s litigation center. “That is unlawful and violates the structure of the U.S. Constitution — one state can’t try to regulate a global issue best left to the federal government. Vermont’s penalties will ultimately raise costs for consumers in Vermont and across the country.”
A spokesman for the state’s Agency of Natural Resources said it had not been formally served with this lawsuit.
Anthony Iarrapino, a Vermont-based lobbyist with the Conservation Law Foundation, said the lawsuit was the fossil fuel industry’s way of “trying to avoid accountability for the damage their products have caused in Vermont and beyond.”
“More states are following Vermont’s lead holding Big Oil accountable for the disaster recovery and cleanup costs from severe storms fueled by climate change, ensuring that families and businesses no longer have to foot the entire bill time and time again,” Iarrapino added.
Under the law, the Vermont state treasurer, in consultation with the Agency of Natural Resources, is to issue a report by Jan. 15, 2026, on the total cost to Vermonters and the state from the emission of greenhouse gases from Jan. 1, 1995, to Dec. 31, 2024. The assessment would look at the effects on public health, natural resources, agriculture, economic development, housing and other areas. The state would use federal data to determine the amount of covered greenhouse gas emissions attributed to a fossil fuel company.
It’s a polluter-pays model affecting companies engaged in the trade or business of extracting fossil fuel or refining crude oil attributable to more than 1 billion metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions during the time period. The funds could be used by the state for such things as improving stormwater drainage systems; upgrading roads, bridges and railroads; relocating, elevating or retrofitting sewage treatment plants; and making energy efficient weatherization upgrades to public and private buildings. It’s modeled after the federal Superfund pollution cleanup program.
We Need Your Support
Support HuffPost
Already contributed? Log in to hide these messages.
The approach taken by Vermont has drawn interest from other states, including New York, where Gov. Kathy Hochul signed into law a similar bill in December.
The New York law requires companies responsible for substantial greenhouse gas emissions to pay into a state fund for infrastructure projects meant to repair or avoid future damage from climate change. The biggest emitters of greenhouse gases between 2000 and 2018 would be subjected to the fines.
Vermont
Police: Vt. woman wanted after not returning car loaned to her

BERLIN, Vt. (WCAX) – Berlin Police say a Vermont woman is accused of stealing car that was loaned to her.
Officers say Suzette Santiago, 45 of Berlin was loaned a 2005 gold Subaru Outback on New Year’s Eve, and was expected to return it on New Year’s Day. But police say, that never happened.
Berlin Police say the vehicle was last seen by law enforcement cameras in Wareham, Massachusetts Friday morning. Police say Santiago has ties to Massachusetts.
The car has Vermont plates with registration KSS 140.
If you know where Santiago or the car are located, Berlin Police want to hear from you.
Copyright 2025 WCAX. All rights reserved.
Vermont
US Chamber of Commerce, oil group sue Vermont over law requiring companies to pay for climate change damage

Check out what’s clicking on FoxBusiness.com.
The U.S. Chamber of Commerce and a top oil and gas industry trade group have filed a lawsuit against Vermont over its new law requiring that fossil fuel companies pay for damage the state attributes to climate change.
The federal lawsuit, which was filed Monday, urges a state court to block the state from enforcing the law, which was passed by lawmakers last year, according to The Associated Press. The state said it is working to estimate the cost of climate change dating back to 1995.
Vermont became the first state in the country to enact a law of its kind after it suffered catastrophic summer flooding and damage from other extreme weather, the outlet noted.
The Chamber and the American Petroleum Institute argue in the lawsuit that the U.S. Constitution precludes the act and that the state law is preempted by the federal Clean Air Act, The Associated Press reported. The lawsuit also says that the law violates domestic and foreign commerce clauses by discriminating against the “important interest of other states by targeting large energy companies located outside of Vermont.”
APPLE TO PAY $95 MILLION IN SIRI SPYING LAWSUIT
Flooding in downtown Montpelier, Vermont on Tuesday, July 11, 2023. (Getty Images)
The plaintiffs say that the federal government is already addressing climate change, according to the report. The plaintiffs add that since greenhouse gases come from billions of individual sources, it is impossible to measure “accurately and fairly” the impact of emissions from a particular entity in a particular location over multiple decades.
“Vermont wants to impose massive retroactive penalties going back 30 years for lawful, out-of-state conduct that was regulated by Congress under the Clean Air Act,” Tara Morrissey, senior vice president and deputy chief counsel of the Chamber’s litigation center, said, according to the report. “That is unlawful and violates the structure of the U.S. Constitution — one state can’t try to regulate a global issue best left to the federal government. Vermont’s penalties will ultimately raise costs for consumers in Vermont and across the country.”

A man watches as heavy rain sends mud and debris down the Ottauquechee River in Vermont. (Getty Images)
The law requires the Vermont state treasurer, in consultation with the Agency of Natural Resources, to issue a report by Jan. 15, 2026, on the total cost to the state and its residents from the emission of greenhouse gases from Jan. 1, 1995, to Dec. 31, 2024. The review would examine the effects of greenhouse gasses on various areas, including public health, natural resources, agriculture, economic development and housing.
The state would use federal data to determine whether the amount of covered greenhouse gas emissions can be traced to a fossil fuel company.
The share of funds collected from the companies could be used by the state for things like improving stormwater drainage systems, upgrading roads and bridges, elevating or retrofitting sewage treatment plants and making energy-efficient weatherization upgrades to public and private buildings.
SUPREME COURT TO TAKE UP CHALLENGE TO TIKTOK BAN
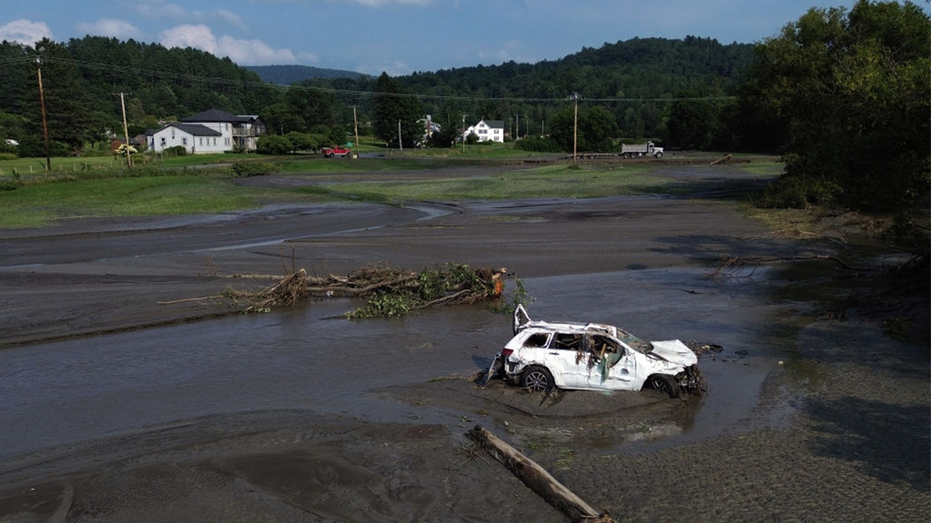

Aftermath of flash flooding on Red Village Road in Vermont. (Getty Images)
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
The law in Vermont captured interest from other states, including New York, where a similar bill was signed into law last month.
The New York law requires companies responsible for substantial greenhouse gas emissions to pay into a state fund for infrastructure projects to repair or prevent future damage from climate change, and the biggest emitters of greenhouse gases between 2000 and 2018 would face fines.
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoNew Year life lessons from country star: 'Never forget where you came from'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24982514/Quest_3_dock.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24982514/Quest_3_dock.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta’s ‘software update issue’ has been breaking Quest headsets for weeks
-

 Business4 days ago
Business4 days agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'Politics is bad for business.' Why Disney's Bob Iger is trying to avoid hot buttons
-

 Culture4 days ago
Culture4 days agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports4 days ago
Sports4 days agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics3 days ago
Politics3 days agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics2 days ago
Politics2 days agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country