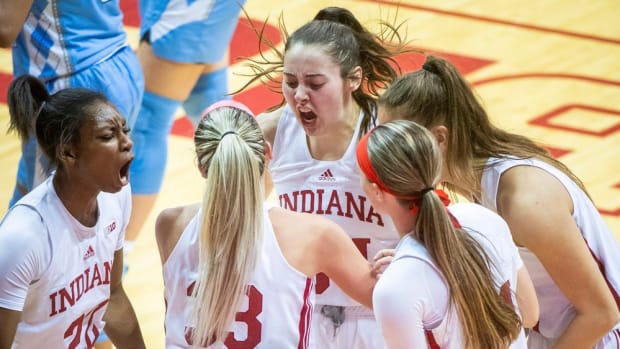Indiana
Mackenzie Holmes Gets Spot on Wooden Award Late Season Top 20
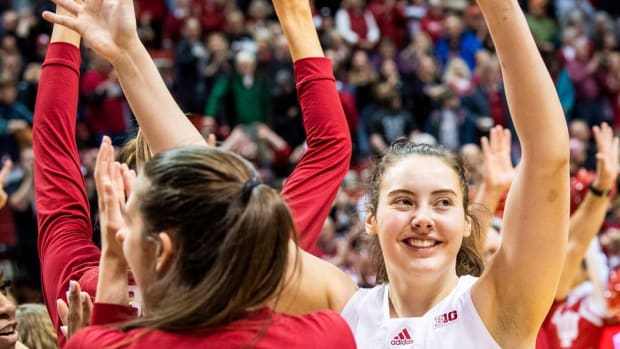
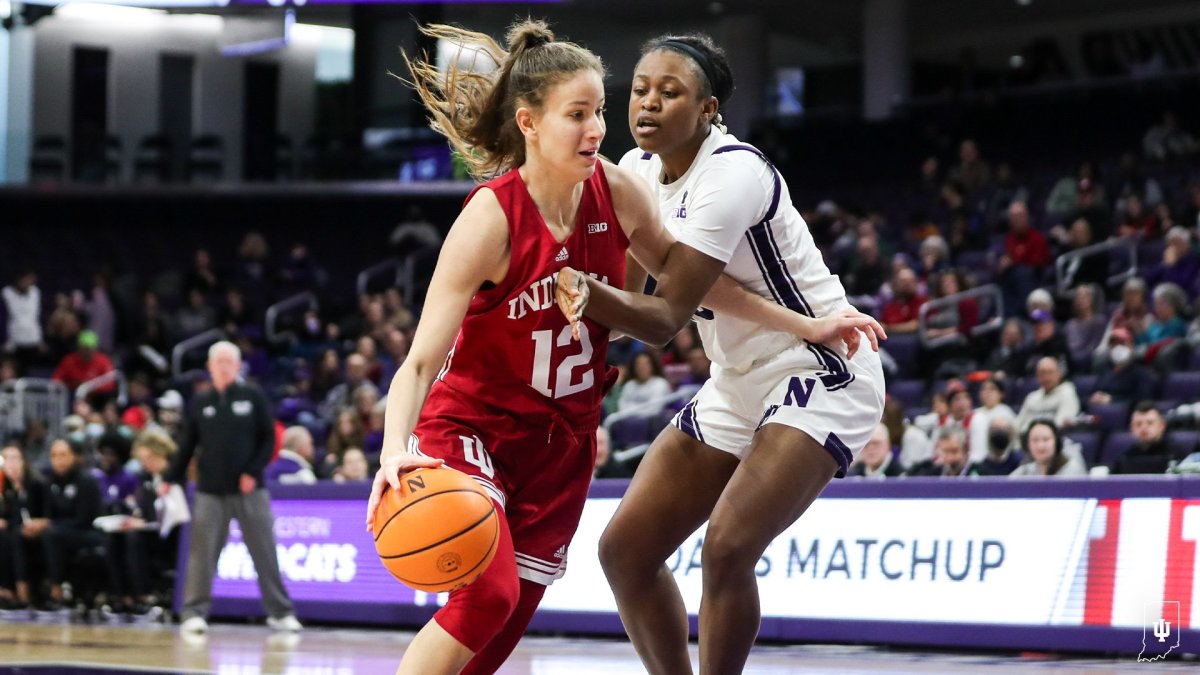
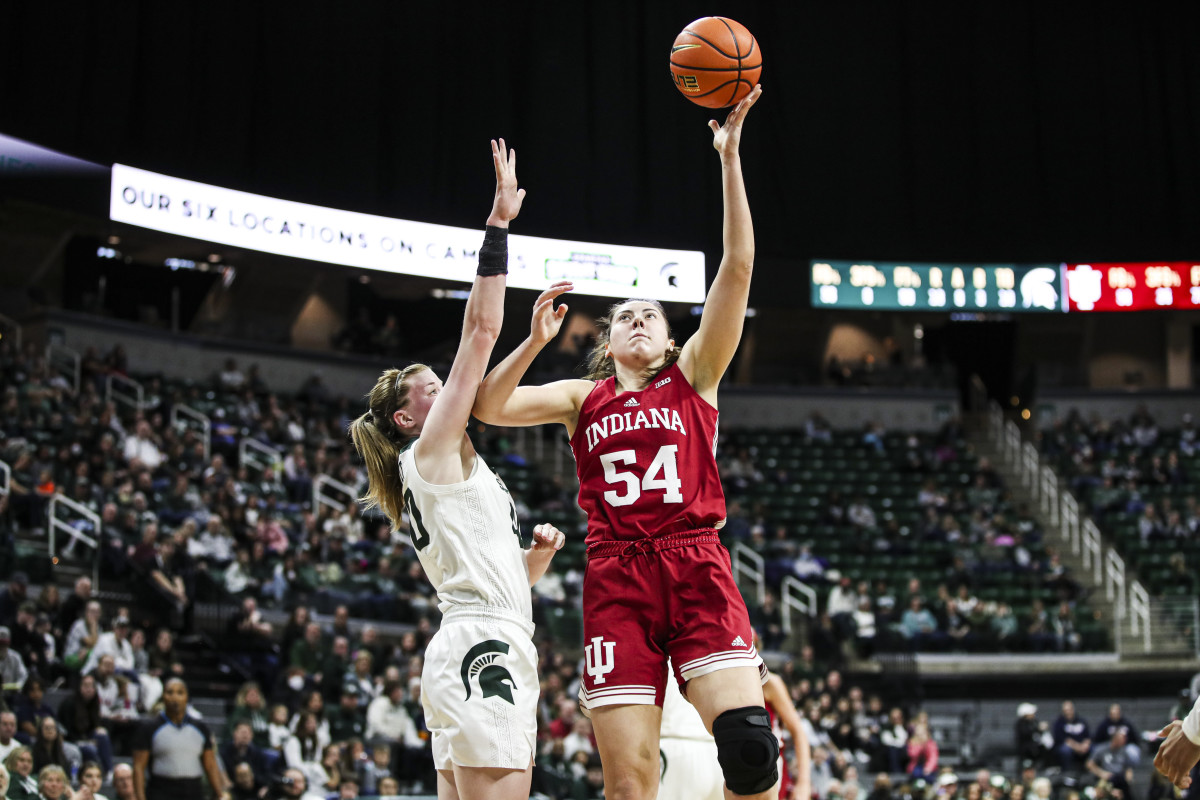
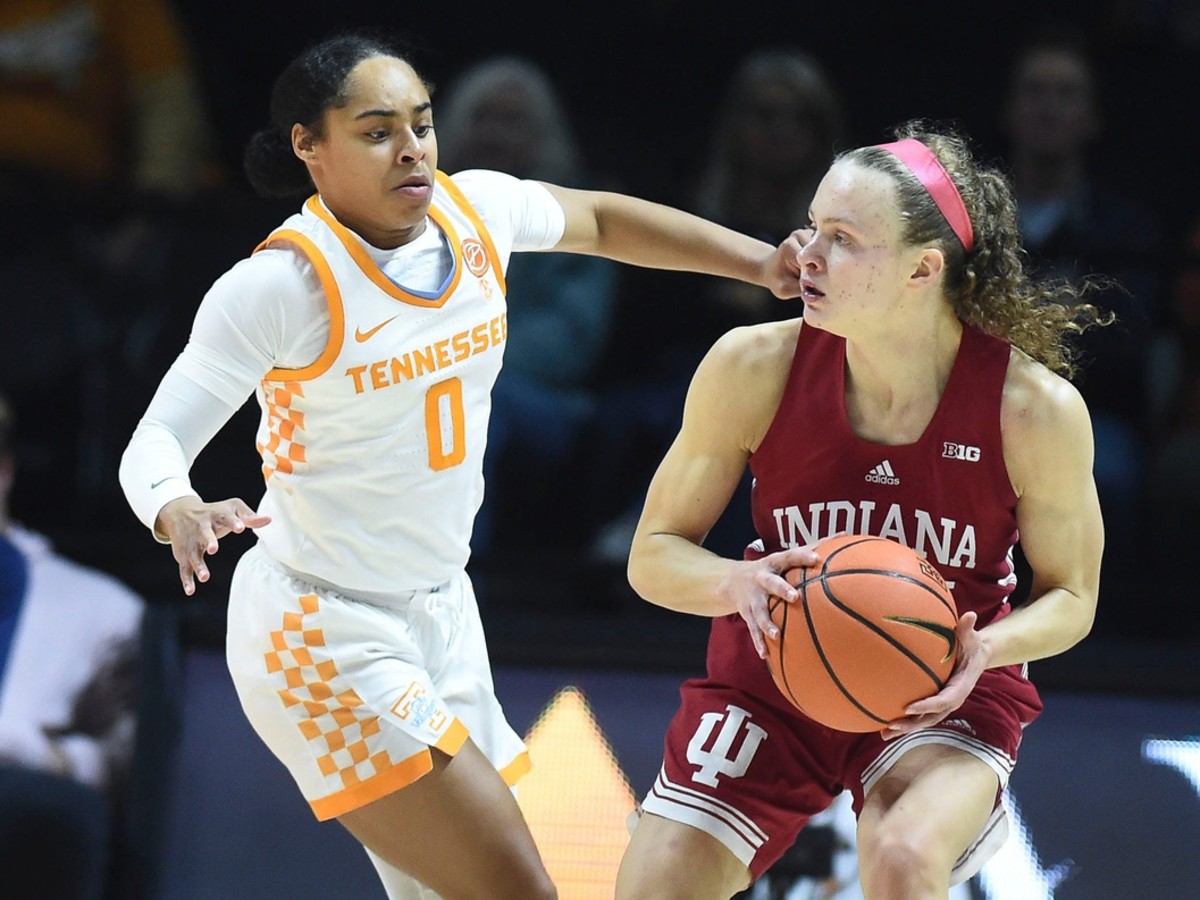
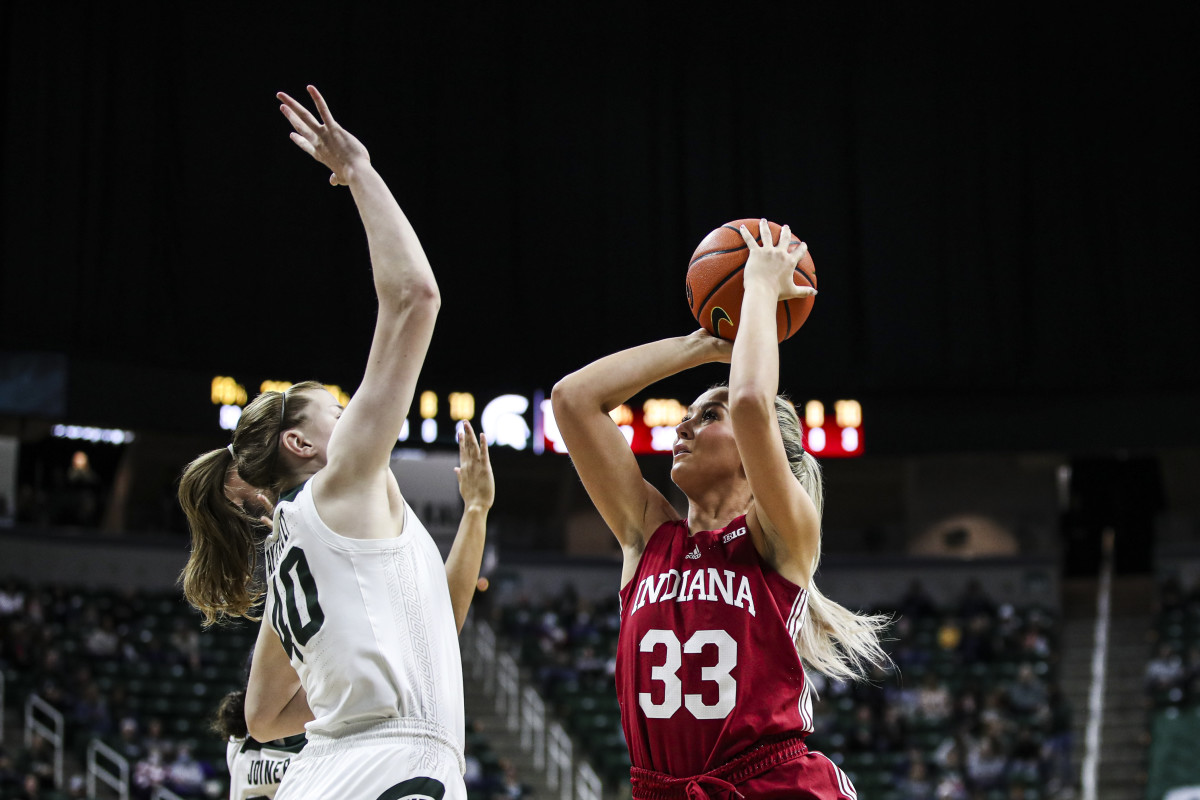
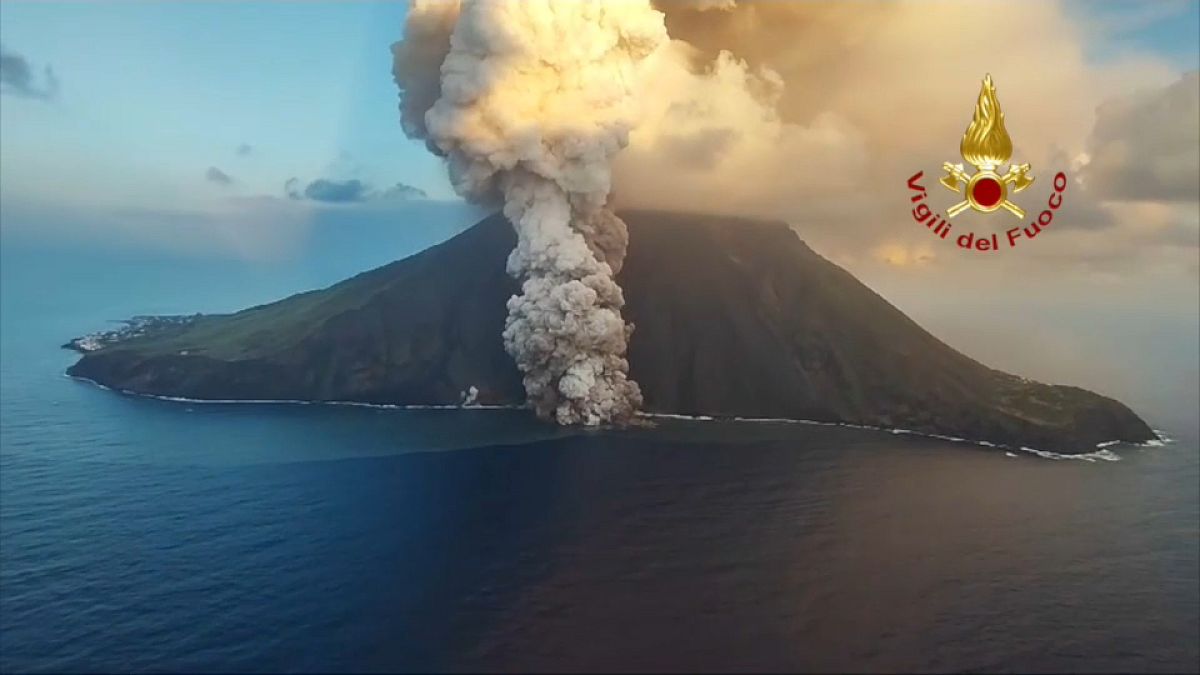
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. — Indiana ladies’s basketball senior ahead Mackenzie Holmes has earned a spot on the John R. Picket Award Late Season High 20 offered by Wendy’s, the Los Angeles Athletic Membership introduced Monday night.
The Gorham, Maine native is the group’s main scorer averaging 22 factors per recreation, which ranks seventh within the nation. Holmes additionally averages eight boards per recreation as a robust drive within the put up.
This season, Holmes has scored in double figures all 21 video games with 12 video games reaching 20 or extra factors and a pair with 30 or extra. Within the Hoosiers’ sole lack of the season to Michigan State, Holmes scored a career-high 32 factors.
Her monstrous numbers continued as she turned the second participant in 20 years alongside Maya Moore to attain three straight 20-point video games versus AP High 25 ranked opponents in Illinois, Michigan and Ohio State.
Scroll to Proceed
Due to these performances, she’s now No. 10 on the Hoosiers’ all-time main scorers record with 1,668 profession factors.
The Picket Award Late Season High 20 record is chosen by nationwide faculty basketball specialists based mostly on the gamers’ performances to this point this season. The gamers on the record are thought-about to be the highest candidates for the John R. Picket Ladies’s Participant of the 12 months award offered by Wendy’s in April after the NCAA Event.
There will even be a Picket Award All-American Staff introduced the week of the Elite Eight spherical of the match.
Up subsequent, Holmes and the Hoosiers will begin their highway recreation stretch at Minnesota on Wednesday adopted up by a visit to West Lafayette to face rival Purdue Sunday.
- HOLMES AND GARZON SWEEP BIG TEN WEEKLY HONORS For the second time this season, Indiana ladies’s basketball ahead Mackenzie Holmes and guard Yarden Garzon have swept the Massive Ten weekly honors whereas Holmes additionally earned ESPN Participant of the Week. CLICK HERE
- GRACE BERGER’S INJURY RECOVERY PROCESS Indiana ladies’s basketball guard Grace Berger had her longest profession break this season after struggling a proper knee harm that took her out for six weeks. She’s now performed in seven video games because the incident and has been placing up large numbers identical to her previous self would. CLICK HERE
- INDIANA MOVES UP TWO SPOTS IN AP POLL Within the Week 13 Related Press High 25 Ballot, the Hoosiers transfer up two spots after beating then-ranked No. 2 Ohio State and Rutgers. The complete ballot plus college data are contained in the story. CLICK HERE

Indiana
Crews search for missing boaters near Hammond, Indiana

CHICAGO (CBS) — Crews were searching Lake Michigan on Friday evening for missing boaters near Hammond, Indiana.
Police marine unit officers boarded a small powerboat that had been damaged near the mouth of the Indiana Harbor near the Inland Steel plant.
Crews later started towing the boat back to shore as a U.S. Coast Guard fast rescue boat and other marine unit boats were searching the water for an unknown number of people.
Further details were not immediately available.
Indiana
EF-0 tornado sweeps through Harrison County, Indiana

LOUISVILLE, Ky. (WAVE) – The National Weather Service confirmed two separate tornadoes touched down in WAVE Country on Independence Day. One was an EF-1 tornado in Louisville’s Parkland neighborhood, the other an EF-0 in Harrison County, Indiana.
On Friday, residents in the area were in clean up mode after the storms rolled through. The tornado travelled on a path stretching for around a mile. Bringing winds estimated at 80 miles an hours. The storm topped trees onto driveways, a car and even a home.
One resident cleaning up on Friday was Leo Book, who’s lived in his home for over 30 years. He said this was the second worst storm in terms of damage he’s seen.
“I’ve seen them [trees] go back and forth a lot real bad, but these, some of these trees were going around and around,” Book said. “It’s the first time I had seen that.”
Some people in Harrison County were without power for about six to eight hours, according to the Harrison County Emergency Management. Now all power has been restored.
No injuries were reported from Thursday’s storms.
Copyright 2024 WAVE. All rights reserved.
Indiana
What is pentobarbital? More questions than answers surround Indiana's new execution drug. • Indiana Capital Chronicle

After state officials announced last week that Indiana will resume executions for the first time in over a decade, secrecy largely shrouds the new drug, pentobarbital, acquired for the impending lethal injections.
The one-drug method is a departure from the state’s protocol used since 1995, involving a series of three chemicals.
Although no state-level executions in Indiana have used pentobarbital before, 13 federal executions carried out at the Federal Correctional Complex in Terre Haute have been carried out with the drug. Fourteen states have used pentobarbital in executions, too.
But state and federal officials alike have remained closed-lipped about where pentobarbital is sourced from and how much it costs. Also still unknown is the amount Indiana has acquired and when the current doses expire.
Robin Maher, executive director of the Death Penalty Information Center (DPIC), a nonprofit based in Washington, D.C. that tracks state and federal executions, said it’s also critical for the public to know who will be administering the drug — and how — as well as what training those individuals will receive.
“These are the hard questions that have to be asked,” Maher told the Indiana Capital Chronicle. “This is an official government function, and in a democracy, we value honesty and transparency in our government officials and the acts they do on our behalf. This is absolutely one of those official acts, and voters in Indiana deserve to know what their government is doing in their name.”
What is pentobarbital?
The Hoosier state has carried out 20 executions since 1981. The first three — in 1981, 1985 and 1994 — were by electrocution. The rest have been by lethal injection — which is now the only method permitted by state law.
The Indiana Code doesn’t specify what drugs are to be used for executions, saying only that the drugs must be injected intravenously in a quantity and for an amount of time sufficient to kill the inmate.
Previously, when a prisoner was executed by lethal injection in Indiana, they were strapped to a gurney, and an IV line was inserted to inject a lethal combination of three substances: a barbiturate to render the person unconscious; pancuronium bromide to paralyze voluntary and reflex muscles; and potassium chloride to stop the heart.
But after Indiana’s last execution in 2009, the state was effectively forced to pause. Increased scrutiny of lethal injection drugs led pharmaceutical companies to refuse to sell their products for use in executions. Indiana Gov. Eric Holcomb said that made acquiring the necessary drugs “harder to get.”
It wasn’t until last week that the governor, along with Indiana Attorney General Todd Rokita, announced that the state’s Department of Correction has obtained the pentobarbital to carry out the death penalty.
The state is so far seeking an execution date for Joseph Corcoran, a man convicted in the killings of four people in Fort Wayne in 1997. There are currently eight men on Indiana’s death row, including Corcoran. No one has been added to the state’s death row since 2014.
In the one-drug executions, a prisoner is injected with an overdose of pentobarbital. The new drug, which Maher described as a sedative, has commonly been used to euthanize pets.
“It’s a barbiturate that explodes the activity of the brain and the nervous system and breathing,” she said. “When you’re given an overdose of that, it will ultimately suppress breath and kill you.”
Pentobarbital was first introduced in 2010, according to the DPIC.
So far, 14 states have used the drug in executions: Alabama, Arizona, Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Idaho, Mississippi, Missouri, Ohio, Oklahoma, South Carolina, South Dakota, Texas and Virginia. Five additional states — Kentucky, Louisiana, Montana, North Carolina and Tennessee — additionally plan to use pentobarbital. Colorado includes pentobarbital as a backup drug in its lethal-injection procedure.
The same drug was also used for the 13 federal executions during the last six months of Donald Trump’s presidency.
In 2019, former U.S. Attorney General Bill Barr approved the use of pentobarbital in executions, though President Joe Biden’s Justice Department announced a moratorium on federal executions in 2021.
A first-time method in Indiana
Whether Indiana uses pentobarbital or other drugs for executions, Maher said there are still concerns about what could go wrong.
She noted that lethal injections have the highest rate of botched executions, which occur when there is a breakdown in — or departure from — the “protocol” for a particular method of execution.
The DPIC describes at least two botched executions that have occurred in Indiana.
In October 1985, it took 17 minutes to execute William Vandiver. Still breathing after the first application of 2,300 volts, four more bursts of electricity were fired into him before he was pronounced dead, according to media reports from that time. The Indiana Department of Corrections admitted the execution “did not go according to plan.”
Tommie Smith, who died by lethal Injection in July 1996, also had a prolonged execution, according to the DPIC. Because of unusually small veins, it took more than an hour after the execution team began sticking needles into his body for Smith to be pronounced dead. After multiple attempts, the lethal drugs were finally injected into Smith 49 minutes after the process began. It took another 20 minutes before he was pronounced dead.
Holcomb defends Indiana’s move to carry out execution, saying ‘justice will be served’
Maher said many of the documented botched executions in recent years have occurred because the drugs being used had expired, were contaminated, or they were administered “incorrectly.”
“There are a number of ways that the executions can go wrong, and it doesn’t only have to do with the kind of drug that is used,” she said, noting, for example, that if pentobarbital isn’t stored at a proper temperature, the drug can expire and should not be used.
When asked where DOC acquired the drug — pentobarbital, which can be used to carry out executions – and how much the state paid, Holcomb said he “can’t go into those details, by law.”
Lawmakers made information about the source of the drugs confidential on the last day of the 2017 legislative session.
Indiana Capital Chronicle has filed an official records request seeking the cost of the drugs.
“States have been hiding this information behind secrecy statutes in an effort to avoid answering difficult questions about their execution protocols. These are elected officials. They are using government funding, and they are saying they are conducting an official function,” Maher said. “And all of that means they should be honest and transparent about what they’re doing and why. The fact that they have shrouded everything in secrecy in an attempt to avoid answering these questions is not something that we should simply be accepting.”
Recent reporting by The Intercept and Last Week Tonight with John Oliver identified Connecticut-based Absolute Standards as the source of the pentobarbital used in 13 federal executions in 2020 and 2021. Reporting did not confirm if the company also supplied to specific states, including Indiana.
Absolute Standards produces materials for calibrating research equipment, but in 2018, it applied to the Drug Enforcement Administration to be registered as a bulk producer of pentobarbital. The company has since indicated this week that it will no longer produce the drug.
Maher further pointed to Idaho, which reportedly spent $100,000 earlier this year to purchase three doses of pentobarbital, the drug used in lethal injections. It’s not clear if that’s the same quantity purchased or price paid by Indiana, however.
Need to get in touch?
Have a news tip?
“What officials have said … is that they do not want to have people who are involved in the execution process — for manufacturers of a drug — to be harassed by advocates. But there are almost no real life examples of that happening unless we characterize criticism as harassment, which I don’t think we should in a democracy,” Maher said. “People who are critical of decisions the state is making, in terms of where they are finding their drugs and how they are choosing to administer them, that’s part of being a public official. Responding to those questions from your constituents — that’s part of being a public official. That comes with the territory, and there is no justifiable reason for them to avoid answering those questions.”
The Indiana Public Defender’s Office, which is providing Corcoran with legal counsel, did not reply to the Capital Chonicle’s requests for comment about pentobarbital or the impending execution.
Larry Komp, a federal defender for Corcoran, said the legal team is still seeking clarity on the state’s lethal injection protocol.
Groups are starting to come out against Indiana’s move, including the Libertarian Party of Indiana.
“A government whose primary function is to protect life should not be in the business of ending it, especially given the United States Constitution protects the accused from cruel and unusual punishment. There is no more cruel punishment than putting someone to death,” the party said in a statement. “The state, simply put, should not be killing its citizens. The Libertarian Party of Indiana calls upon Governor Holcomb and the State of Indiana to halt all planned executions and, furthermore, upon the General Assembly to ban the use of the death penalty in Indiana.”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoToplines: June 2024 Times/Siena Poll of Registered Voters Nationwide
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPopular Republican and Trump running mate contender makes first Senate endorsement in 2024 races
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIowa floodwaters breach levees as even more rain dumps onto parts of the Midwest
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoThe many faces of Donald Trump from past presidential debates
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoMike Kennedy advances past crowded GOP primary to secure nomination for open Utah House seat
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNew Jersey gamer flew to Florida and beat fellow player with hammer, say police
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoVideo: How Blast Waves Can Injure the Brain
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25505687/VERNE_Exterior1.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25505687/VERNE_Exterior1.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRimac is shifting from electric supercars to robotaxis