Health
Some breast cancer patients could be at risk of another type of cancer, study reveals
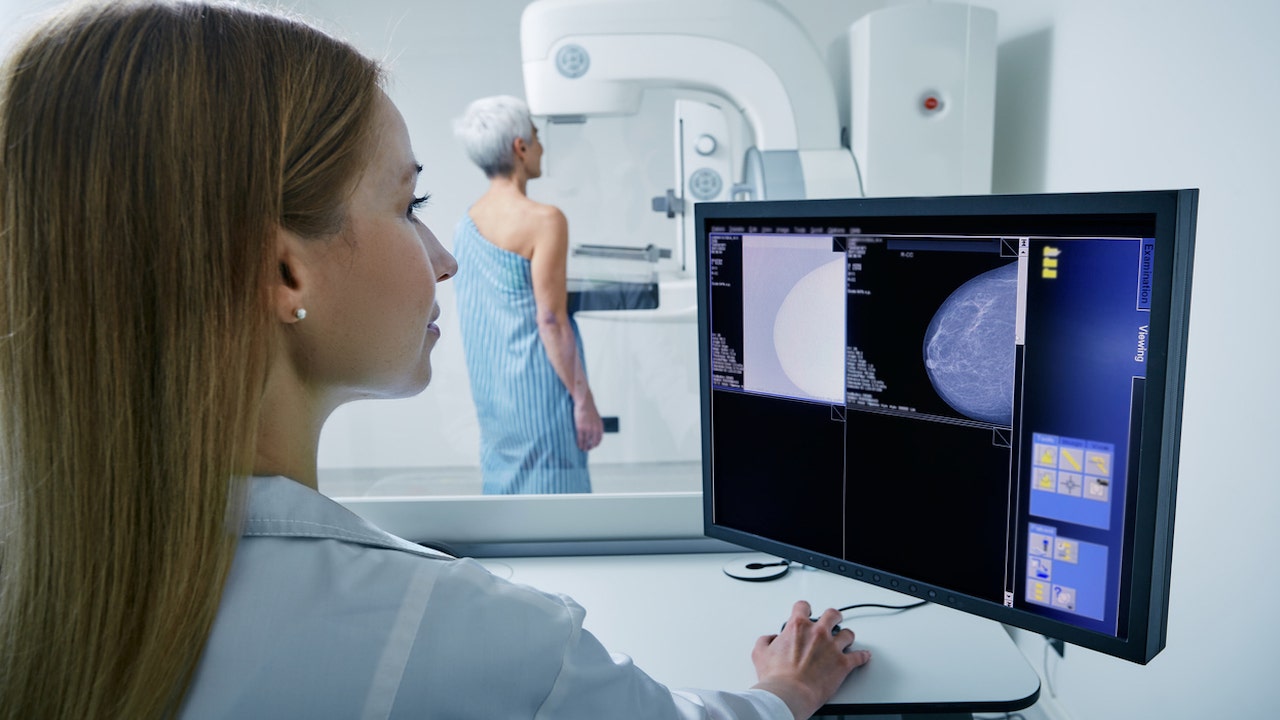
Women with breast cancer who have received chemotherapy are at an increased risk of developing lung cancer, a new study suggests.
Epic Research, a health data group based in Delaware, found that women in this category have a 57% higher lung cancer risk than those who received radiation.
In comparison to patients who received endocrine therapy, those who have undergone chemo have a 171% increase in lung cancer risk, the study found.
BREAST CANCER DRUG COULD HAVE POTENTIALLY SERIOUS SIDE EFFECT, NEW RESEARCH REVEALS
In a statement sent to Fox News Digital, the Epic Research team said the key takeaway from their research is that primary lung cancer is more than twice as prevalent in women who were previously diagnosed with breast cancer — compared to those who did not have it.
“Furthermore, women who had breast cancer and received chemotherapy have the greatest risk of subsequent primary lung cancer,” the researchers wrote.
Women with breast cancer who have received chemotherapy are at an increased risk of developing lung cancer, a new study is suggesting. (iStock)
“This suggests that patients diagnosed with breast cancer are at an increased risk of developing second primary lung cancer, especially if their treatment included chemotherapy.”
BREAST CANCER BREAKTHROUGH: AI PREDICTS A THIRD OF CASES PRIOR TO DIAGNOSIS IN MAMMOGRAPHY STUDY
The research group studied more than two million women ages 50 to 84 who received a screening mammogram between 2010 and 2023.
Patients with an elevated breast cancer risk due to a previous breast or lung cancer diagnosis, those who had been screened within the past three months and those who started mammogram screenings prior to age 50 were excluded from the study.
“This could potentially limit the generalizability of our findings,” the researchers said.
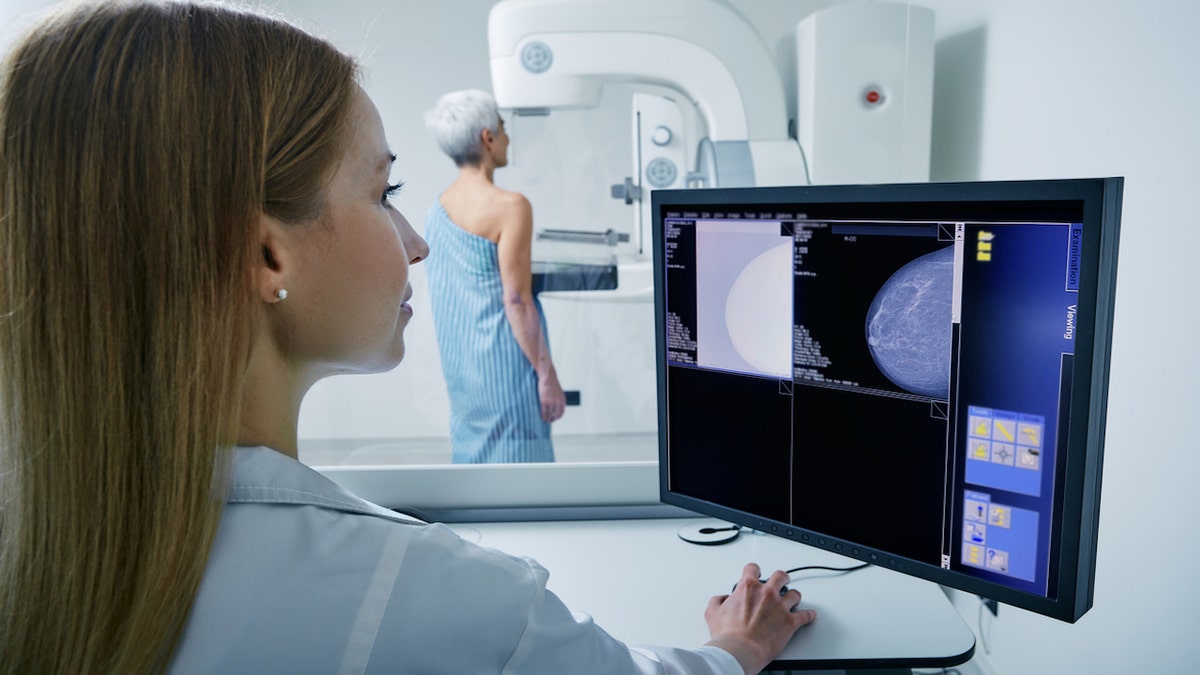
The research group (not pictured) studied more than two million women ages 50 to 84 who received a mammogram screening between 2010 and 2023. (iStock)
The team encouraged patients with a history of breast cancer — especially those who have had chemotherapy — to monitor for the development of primary lung cancer.
“It is important to remember that while our study found a correlation between breast cancer, its treatments and subsequent primary lung cancer, this does not mean that every woman who has had breast cancer will develop lung cancer,” the researchers said.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Fox News medical contributor Dr. Marc Siegel, clinical professor of medicine at NYU Langone Medical Center, told Fox News Digital that one cancer can cause a “higher genetic risk” for others.
“We don’t know the exact etiology, but one cancer puts you in a higher genetic risk pool for other cancers, either because of cancer genes that increase the risk of both, or because of a tendency for mutations that is increased in this pool,” he said.
“It could also be because of environmental factors or carcinogens, including diet, or the result of toxicities from the treatment for breast cancer,” Siegel added.
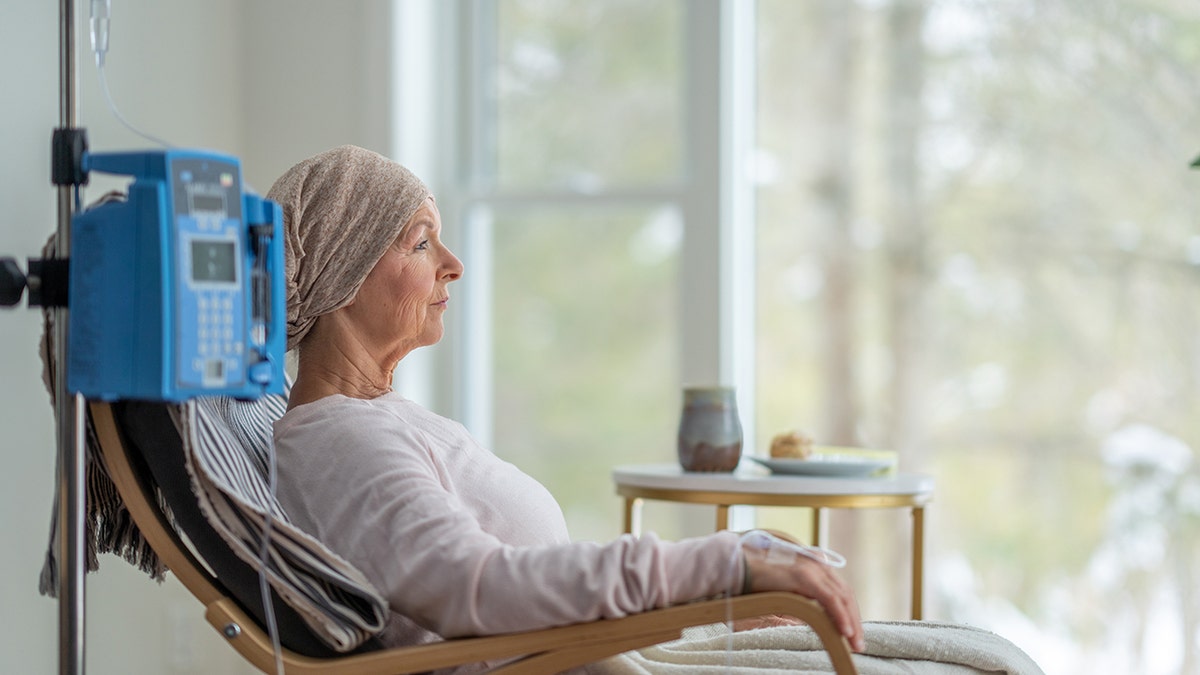

The researchers encouraged patients with a history of breast cancer, especially those who have had chemotherapy, to monitor for the development of primary lung cancer. (iStock)
Jack Manley, M.D., head of new markets and growth at Viz.ai, a San Francisco-based AI-powered disease detection platform, shared with Fox News Digital that Epic Research’s findings and methodology speak to “the power of incorporating multi-modal data in predictive algorithms.”
Said Manley as well, “Companies with capabilities to incorporate both structured and unstructured EHR (electronic health record) data with conventional imaging will have a higher predictive performance than those that don’t.”
He was not involved in the study.
“Currently, a large majority of patients with pulmonary nodules (a possible indicator of early lung cancer) are missed on conventional imaging, while less than half of these detected patients receive subsequent guideline-recommended follow up,” he said.
Artificial intelligence tools are “well-positioned” to address these challenges, Manley noted — but EHR integration is “key to finding those patients at the highest risk.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.

Health
Americans breathe in carcinogenic chemicals found in cars: study

Researchers have found that a source of carcinogenic chemicals is in Americans’ cars – but there may be a way to reduce your risk.
Environmental Science and Technology, a peer-reviewed scientific journal, published a study called “Flame Retardant Exposure in Vehicles Is Influenced by Use in Seat Foam and Temperature” on Tuesday.
The study explains that Americans breathe in chemicals from the flame retardants in their vehicles. The chemicals can cause issues ranging from developmental neurotoxicity to thyroid hormone dysregulation and even cancer.
The types of chemicals found in flame retardants range from polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), which were common in cars until the early 2000s, to alternative brominated flame retardants (BFRs) and organophosphate ester flame retardants (OPEs).
STUDY FINDS EVIDENCE OF MICROPLASTICS IN BRAINS AND OTHER ORGANS
Interior detail of an electric car, taken on August 4, 2015. (Neil Godwin/T3 Magazine/Future via Getty Images)
The federal government requires a level of flame retardants in vehicles. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) mandated the use of flame retardants in the 1970s.
“Flame retardant (FR) chemicals are intentionally used in electronics, furnishings, and building materials to meet flammability standards,” the study explains.
STD RATES SKYROCKET AMONG AMERICANS 55 AND OLDER: CDC
“Most [flame retardants] are used in an additive manner (i.e., not chemically bound), and many are semivolatile, indicating that they can be present in both the gas phase and partially in the condensed phase (e.g., particles and surfaces), depending on environmental conditions.”

A motorcycle officer weaves through traffic on a Los Angeles freeway during the evening rush hour on April 12, 2023 in Los Angeles, California. (FREDERIC J. BROWN/AFP via Getty Images)
Americans who drive professionally or face long commutes may be at a higher risk of harm from the chemicals.
“These findings highlight that commuters are likely to be exposed to [flame retardants], especially those with longer commutes or those who drive vehicles full time as part of their employment,” the paper read.
“In addition, children, who breathe a greater amount of air per kg body weight compared to adults, would also be at risk of greater exposures for equivalent commuting times.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
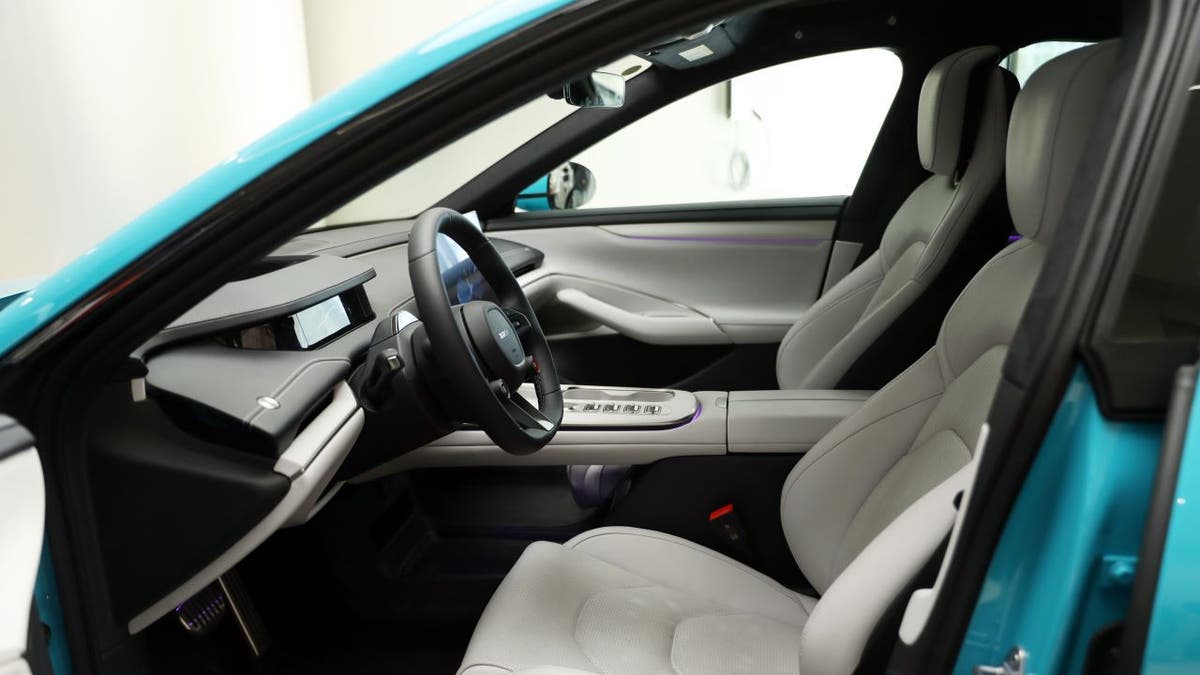

An interior view of a vehicle on April 2, 2024 in Beijing, China (VCG/VCG via Getty Images)
Drivers and passengers in warmer states may face a greater risk of breathing in the flame retardant chemicals. But rolling down car windows, turning off the AC and parking in covered garages may help reduce exposure to the dangerous chemicals, researchers say.
“Increasing ventilation by opening vehicle windows and avoiding recirculating interior cabin air may also reduce exposures,” the study said. “However, the greatest reduction in exposure from vehicle air would come from significantly reducing the amount of FRs added to personal vehicles.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
Ask a doc: 'Is it dangerous to crack my neck or back?'

Cracking your back or neck might provide quick relief and a satisfying popping noise — but is it a safe practice?
“When you stretch or manipulate your spine, such as by twisting or bending, the pressure within the joint changes,” Dr. William Kemo, a neurosurgeon at the Virginia Spine Institute, told Fox News Digital.
“This can cause a sudden release of gas bubbles, leading to a cracking sound.”
BE WELL: KEEP YOUR BONES STRONG TO PREVENT OSTEOPOROSIS
People often crack their back or neck out of habit, or to temporarily relieve tension or stiffness, Kemo noted.
“Typically, they do this to loosen up their back or neck when it is feeling tight or stiff. The ‘cracking’ is the popping of a tight or stiff facet joint.”
People often crack their back or neck out of habit to temporarily relieve tension or stiffness, a doctor noted. (iStock)
While the act of cracking can release endorphins (feel-good chemicals) for temporary relief, it doesn’t address the source of the tension, according to Tori Hartline, a chiropractor at Sunlife Chiropractic in Frisco, Texas.
ASK A DOC: ‘HOW CAN I IMPROVE MY POSTURE?’
Popping or cracking can even lead to injury, she warned.
“Chiropractors are trained to look for restricted areas in the spine and perform specific adjustments to decrease tension and improve range of motion,” Hartline said.

Cracking your back or neck can cause a myriad of health issues, experts are warning. (iStock)
“When an individual tries to pop their own back or neck, the segments that release gas are hypermobile segments versus the area of restriction. The joints above and below the area of restriction will move too much to compensate.”
She added, “Therefore, these cracks do not address the problem and can instead lead to further injury.”
The impacts of cracking your back or neck can include joint hypermobility, sprains or strains due to taking the joint too far past its proper range of motion — and even a fracture if too much pressure is applied, Hartline noted.
FOR ACUTE LOWER BACK PAIN, THESE ARE THE BEST MEDICATIONS, NEW STUDY FINDS
Kemo agreed, warning that cracking your back can cause unnecessary wear and tear on your spine.
“It may lead to strain on the muscles and ligaments surrounding the spine, potentially causing injury or exacerbating existing issues,” he added.
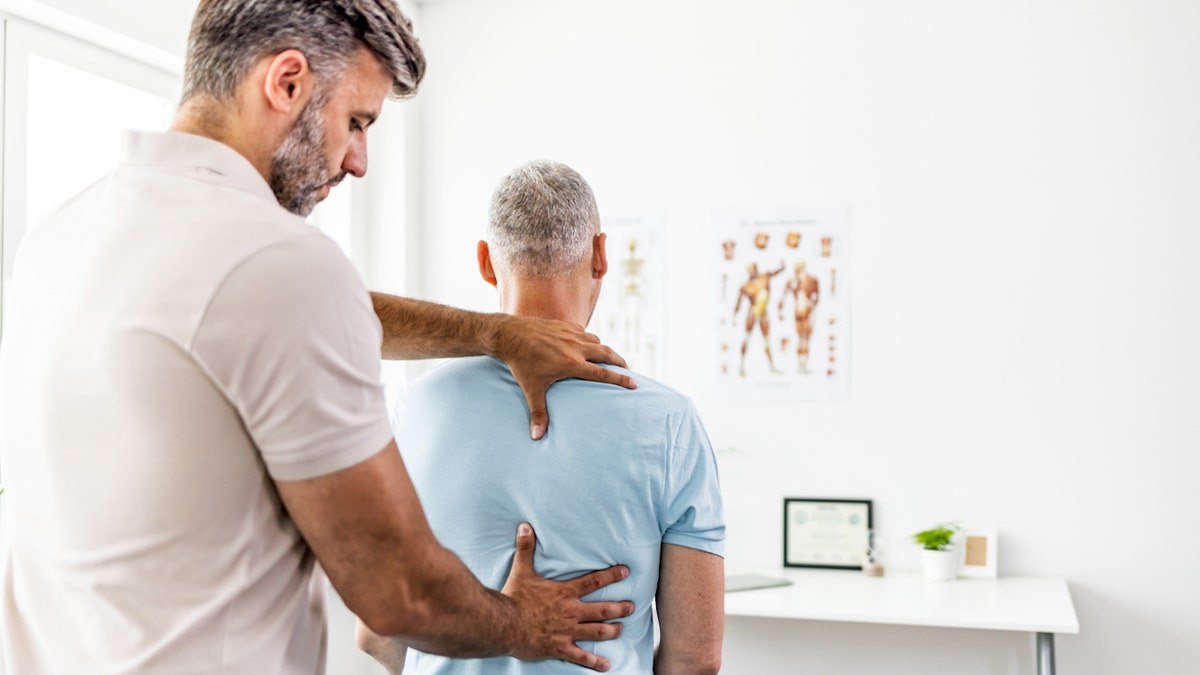
One expert suggested seeing a licensed chiropractor to identify areas of restriction and prescribe therapeutic exercise and stretches. (iStock)
It’s especially dangerous to crack the neck, which could impede blood flow and, in very rare cases, could increase stroke risk, according to Dr. Todd Sinett, a chiropractor at Tru Whole Care in New York.
Alternatives to cracking
There are plenty of safe alternatives that will provide longer-term relief without exacerbating potential issues with the spine, Kemo said.
“Commit to a daily stretching routine, and engage in core muscle exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the spine,” he recommended.
WHAT IS SCOLIOSIS? CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS OF THE SPINAL CONDITION, TREATMENT PLANS AND MORE
Regular physical activity can also be helpful.
“A body in motion stays in motion, and helps avoid stiffness and alleviates tension,” Kemo said.
The doctor also suggested optimizing your ergonomics at home, at work and in the car.

Committing to a daily stretching routine and engaging in core muscle exercises can help strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, one doctor said. (iStock)
“Examine your daily routines to see if there may be repetitive situations that leave you feeling stiff or experiencing tension/tightness,” Kemo suggested.
This might include hunching in your chair or seat in the car, holding your device and looking down for prolonged periods, or sleeping in a certain position.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Hartline also suggested seeing a licensed chiropractor, who can identify the areas of restriction and prescribe therapeutic exercise and stretches to give you the best results.
“If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort or pain, it’s best to consult with a medical specialist for proper evaluation and treatment.”
Overall, both experts agree that it’s important to listen to your body and avoid forceful manipulation of the spine.
“If you’re experiencing persistent discomfort or pain, it’s best to consult with a medical specialist for proper evaluation and treatment,” Kemo said.
“Remember, what works for one person may not be suitable for another — so personalized guidance is key.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
Seniors and breast cancer: Why aren’t older women told to get mammograms?

A major public health agency last week expanded its breast cancer screening guidelines to include younger women — but some people are concerned that one key age group has been excluded.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) announced on April 30 that women between ages 40 and 74 should get mammograms every other year.
This is a significant change from previous guidelines, which said women should begin biennial mammograms at age 50, but could opt to begin as young as 40.
BREAST CANCER MAMMOGRAM SCREENINGS SHOULD START AT AGE 40 INSTEAD OF 50, SAYS HEALTH TASK FORCE
Some experts object to the fact that the agency doesn’t include official screening recommendations for women older than 74.
“The USPSTF concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening mammography in women 75 years or older,” the agency stated in the guidance.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) announced on April 30 that women between the ages of 40 and 74 should get mammograms every other year. (iStock)
Dr. Denise Pate, medical director with Medical Offices of Manhattan and contributor to LabFinder, voiced her disagreement with the lack of mammogram recommendations for older women.
“I think it is an antiquated view that sells short the potential of women older than 75,” she told Fox News Digital.
SOME BREAST CANCER PATIENTS COULD BE AT RISK OF ANOTHER TYPE OF CANCER, STUDY REVEALS
“The recommendations consider that the older population may be over-diagnosed, potentially with slow-growing breast cancers — but this does not take into account the increase in life expectancy for American women.”
A woman who is 75 right now has a life expectancy of 87, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Lack of research
One of the main reasons that women over 74 were excluded is that the age group was not included in clinical trials.
“When the major randomized controlled trials were performed in the 1970s and 1980s to show how effective mammograms are, they didn’t include enough women in those age groups to confirm their necessity,” Dr. Jacqueline Holt, medical director of women’s imaging for national radiology provider RadNet in Wilmington, Delaware, told Fox News Digital.
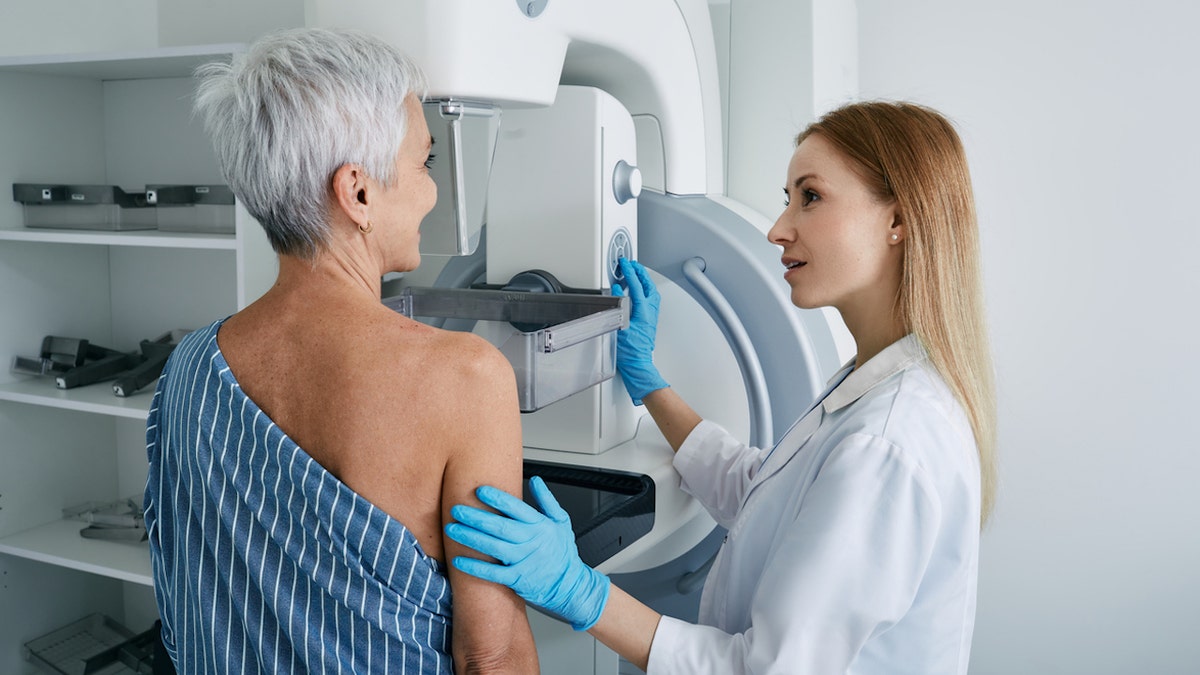
One of the main reasons that women over age 74 were excluded is that the age group was not included in clinical trials. (iStock)
“Cancer risk doesn’t drop off at 74 — the risk increases,” she said.
“It’s misinformation that cancers grow slower in this age group and that women will die of something else first.”
Risks vs. benefits
The primary risk noted for screening older women is the potential for false positives.
“The potential harms of breast cancer screening in older women include false positive results and overdiagnosis,” said one study published in the Journal of the American Board of Family Medicine.
“Cancer risk doesn’t drop off at 74 — the risk increases.”
Among women 75 years and older, 200 out of 1,000 who are screened over a 10-year period will experience a “false alarm,” the researchers noted, “which can cause pain, anxiety and distress.”
Pate acknowledged that this risk does exist.
“Of course, with continued screening, there is the continued risk of finding breast cancer in an earlier stage or finding a suspicious image that prompts recommendations for biopsy, proving to be a false positive — and this can cause a lot of anxiety,” she said.

The risks of not screening are “leaving these women in the dark about their status,” a doctor said. (iStock)
The risks of not screening, however, are “leaving these women in the dark about their status,” the doctor said.
“As I always explain to my patients, knowledge is power,” Pate told Fox News Digital.
“I would rather choose anxiety about a biopsy that may or may not prove breast cancer versus anxiety of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy for a cancer that is found too late due to lack of screening.”
AN OVERVIEW OF BREAST CANCER, SYMPTOMS TO LOOK OUT FOR, WHEN TO START THINKING ABOUT ROUTINE SCREENINGS
Holt agrees the benefits outweigh the risks.
“The primary risk that the USTF focuses on is anxiety due to false positives or callbacks that don’t lead to a diagnosis of cancer,” she told Fox News Digital.
“The death rate has decreased by at least 40% since 1995, thanks to mammographic screenings finding the cancer earlier and better treatment.”

“The death rate has decreased by at least 40% since 1995, thanks to mammographic screenings finding the cancer earlier and better treatment,” a doctor said. (iStock)
Women do have the option to continue screening beyond the age of 74 if they choose, the doctors noted — and this should be covered by their insurance plan.
“There is no cut-off for age,” Holt noted. “Medicare will still cover the cost of a mammogram.”
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), the American Cancer Society (ACS) and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) all recommend mammograms starting at age 40.
“Age alone should not be the basis to continue or discontinue screening.”
“Each of these three groups bases its stop age on a woman’s life expectancy and not simply on their age,” Pate noted.
The ACS has stated that women should continue receiving mammograms as long as they are in overall good health and expect to live for another 10 years or more.
More than one-quarter of cases of breast cancer are diagnosed in women 75 years and older, according to ACOG.
MISSING MAMMOGRAMS: OVER 20% OF WOMEN DON’T FOLLOW BREAST CANCER SCREENING GUIDELINES, STUDY SAYS
“Age alone should not be the basis to continue or discontinue screening,” according to a statement from ACOG.
“Beyond age 75 years, the decision to discontinue screening mammography should be based on a shared decision-making process informed by the woman’s health status and longevity.”

More than one-quarter of cases of breast cancer are diagnosed in women 75 years and older, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (iStock)
Dr. Wanda Nicholson, chair of the USPSTF, sent a statement to Fox News Digital about the decision to omit women over age 74 in the recommendations.
“Women deserve to know what the science says about how they can best stay healthy as they age,” she said.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“We looked carefully at all the available evidence about whether women who are 75 and older should be screened for breast cancer, but unfortunately, the available research was limited.”

“Women deserve to know what the science says about how they can best stay healthy as they age,” a doctor said. (iStock)
“None of the studies of breast cancer screening included women in this age group, so we are urgently calling for more evidence on this important population.”
She added, “In the meantime, we encourage women who are 75 and older to talk with a trusted health care professional about what preventive care is right for them, given their specific health circumstances.”
Fox News Digital reached out to the ACOG and the ACS requesting additional comment.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussian forces gained partial control of Donetsk's Ocheretyne town
-
Movie Reviews1 week ago
Challengers Movie Review
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDems disagree on whether party has antisemitism problem
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoHouse Republicans brace for spring legislative sprint with one less GOP vote
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoAt least four dead in US after dozens of tornadoes rip through Oklahoma
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoAnti-Trump DA's no-show at debate leaves challenger facing off against empty podium
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoStefanik hits special counsel Jack Smith with ethics complaint, accuses him of election meddling
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAs student protesters get arrested, they risk being banned from campus too