Health
Promising cancer vaccine in the works utilizing similar mRNA technology that combats COVID: Duke researchers
NEWNow you can take heed to Fox Information articles!
COVID-19 vaccine know-how doesn’t simply combat viruses – it could fight most cancers.
Duke researchers discover potential in a most cancers vaccine based mostly on the identical messenger RNA, or mRNA, know-how utilized by COVID-19 vaccines to fight a sort of breast most cancers that over expresses a protein referred to as HER2, based on a latest Fox 8 report.
“It’s a product which is RNA nucleic acid which encodes a selected protein after which that may be encapsulated in one thing we prefer to name a lipid nanoparticle, which can be a little fats bubble, and that may be injected into your physique and kind of teaches your physique what to go after immunologically,” stated Dr. Zachary Hartman, assistant professor within the departments of surgical procedure, pathology, and immunology at Duke College College of Drugs,
Hartman works within the lab at Duke that’s spearheading the analysis.
EAST COAST COVID-19 CASES ON THE RISE
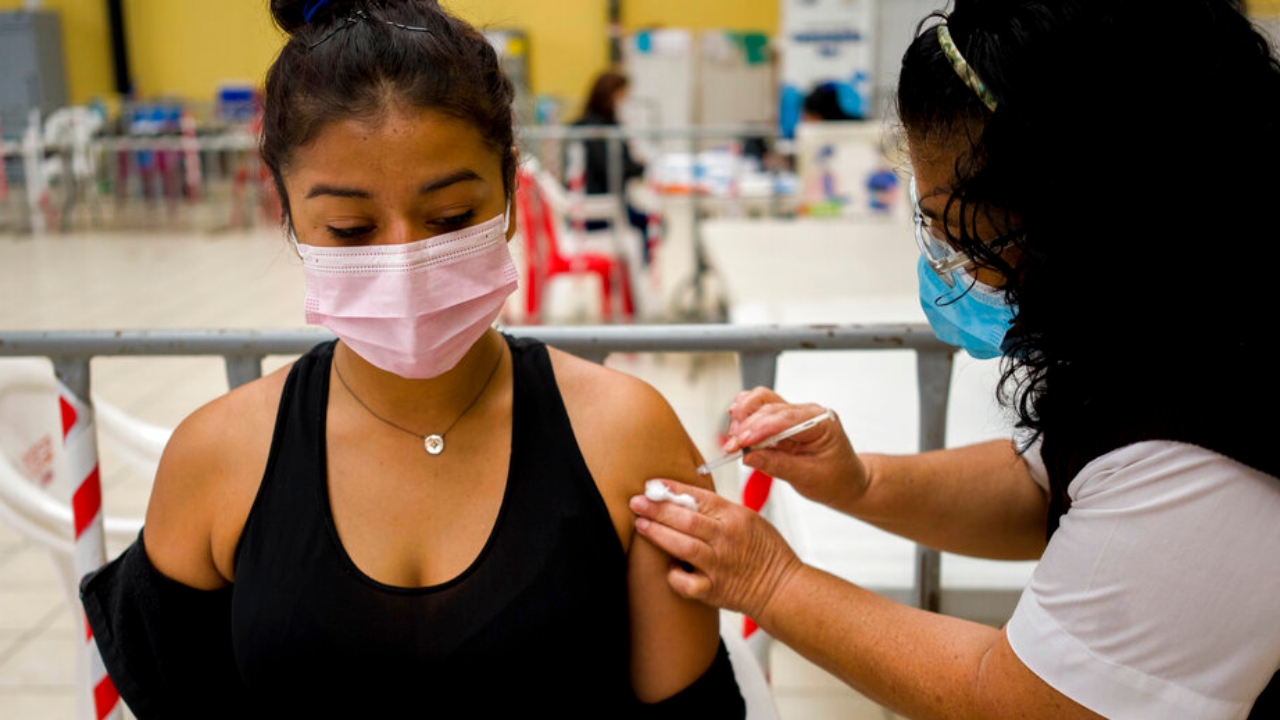
A healthcare employee administers a booster dose of a COVID 19 vaccine at a short lived vaccine middle in Guatemala Metropolis, Tuesday, March 1, 2022.
(AP Photograph/Moises Castillo)
Dr. Herbert Kim Lyerly, who runs the lab, has been at Duke for nearly 40 years, seeing first-hand how most cancers remedy has advanced from chemotherapy, with its myriad unintended effects, to focused immunotherapy, per the report.
“Take into consideration that: in my profession, an entire reversal of fortune for immunotherapy to be one thing to being thought-about an outsider, not prone to ever work, to being probably the most outstanding type of most cancers remedy and the event of recent most cancers therapeutics on this planet, right now,” added Lyerly, George Barth Gellar professor of most cancers analysis and professor of surgical procedure, immunology and pathology at Duke College.
In accordance with Scientific Most cancers Analysis, the HER2 protein, which is related to aggressive tumor development, goes on overdrive in 20% to 30% of breast cancers, so therapies are focused towards this protein, however drug resistance limits its use, stated Lyerly.
So in 2019, the Duke researchers discovered potential in a part 1 medical trial with a vaccine that induced anti-tumor development in seven of the 22 sufferers who had recurrent breast most cancers, with two persevering with to outlive on the time of the revealed analysis, based on an up to date July 9, 2019 press launch.
He advised Fox Information, “We have now been engaged on this [vaccine mRNA] know-how for a few years. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the efficiency of the method.”
Though the present vaccine, which is an artificial mRNA vaccine, is directed towards breast most cancers, it may be used for different cancers that categorical the HER2 protein, together with lung most cancers, abdomen, and esophageal most cancers, Lverly added.
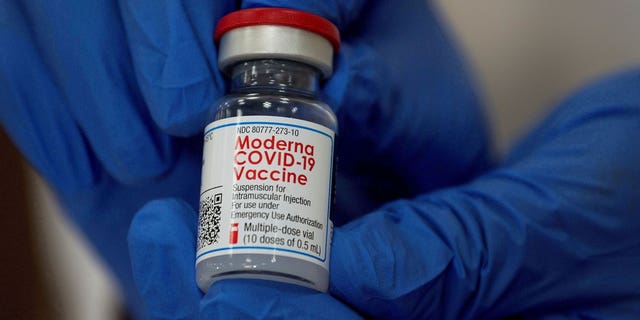
An worker reveals the Moderna COVID-19 vaccine at Northwell Well being’s Lengthy Island Jewish Valley Stream hospital in New York, U.S., December 21, 2020.
(REUTERS/Eduardo Munoz)
“Vaccines stimulate the immune system, particularly killer T cells, that now are energetic and react to hunt and destroy tumor cells. It applications the immune system to not ignore the tumor cells, however to acknowledge them as unhealthy guys to kill them,” Lyerly advised Fox Information.
He assuages some individuals’s concern that mRNA know-how could be dangerous by explaining the context of how mRNA vaccines work in our physique through the pandemic, per the information outlet.
2021 DEADLIEST YEAR IN US HISTORY DUE TO COVID-19, DRUG OVERDOSES
“You’ve got mRNAs – billions of mRNA copies in your physique, proper now. And so, to be involved that the introduction of an mRNA coding of a viral protein goes to be dangerous to you, once more, doesn’t make quite a lot of sense to me, as a result of should you occur to be contaminated with a coronavirus, you’re going to have a thousand occasions extra mRNAs from the virus invading your physique.”
Vaccination is one of the best ways to guard towards COVID-19, he added, who disclosed to Fox Information that he has fairness in AlphaVax, a biopharmaceutical firm that has patents on mRNA vaccines.
An individual receives a COVID vaccine
(Paul Hennessy/SOPA Photos/LightRocket through Getty Photos)
However though the research’s vaccine works to a sure diploma by itself towards breast most cancers, the tumor can recruit “backup methods” to remain alive, based on a 2020 Duke press launch.
So the researchers are actually within the a part of the analysis that exams whether or not a brand new remedy works, referred to as a Part 2 trial, that mixes the vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor referred to as pembrolizumab, which when used alone confirmed restricted profit towards breast most cancers however when mixed with the vaccine, carries a “one-two punch,” the press launch added.
“By working in tandem, the vaccine primes the immune system and the checkpoint inhibitor then rallies the T-cells to motion, leading to pronounced tumor discount and long-term tumor-free survival,” the press launch stated.
“I believe that inside my lifetime we’ll see most cancers as a extra managed illness,” stated Hartman.
“We’re going to show the dial and be capable of deal with increasingly of those sorts of cancers within the coming years and many years to the place it’s not fairly the identical sentence it was 20 or 30 years in the past. I don’t assume we’ll ever be capable of rid the world of most cancers, however I believe we will forestall quite a lot of cancers after which quite a lot of cancers that we’ll be capable of catch early and deal with, we’ll have very efficient therapies.”

Health
In Colorado, plague case confirmed in human, health officials say: ‘Must be treated promptly’

A human case of the plague has been confirmed in Pueblo County, Colorado, according to health officials.
The Pueblo Department of Public Health and Environment (PDPHE) is working with the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment to investigate, according to a press release.
No specific information was provided about the person who contracted the plague.
BUBONIC PLAGUE IN THE US: DO YOU NEED TO WORRY ABOUT CATCHING THE RODENT-BORNE DISEASE?
“We advise all individuals to protect themselves and their pets from plague,” Alicia Solis, program manager of the Office of Communicable Disease and Emergency Preparedness at PDPHE, stated in the release.
What is the plague?
The bubonic plague is caused by Yersinia pestis, a bacterium that was likely first introduced in North America around 1900 from rats on ships coming from South Asia, according to Timothy Brewer, M.D., professor of medicine and epidemiology at UCLA.
The bubonic plague is caused by Yersinia pestis, a bacterium that was likely first introduced in North America around 1900 from rats on ships coming from South Asia. (Smith Collection/Gado/Getty Images)
“Since its introduction 120 years ago, it has become endemic in ground squirrels and rodents in the rural Southwestern U.S.,” he told Fox News Digital.
Although the disease can affect people of all ages, half the cases involve patients between the ages of 12 and 45, as stated on the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) website.
‘ARCTIC ZOMBIE VIRUSES’ COULD BE RELEASED BY CLIMATE CHANGE FROM THAWING PERMAFROST, SOME SCIENTISTS CLAIM
Globally, between 1,000 and 2,000 cases of plague are reported to the World Health Organization each year — although only an average of seven annual cases are in the U.S.
If left untreated, the plague has a fatality rate of 30% to 60%.
With antibiotics, that drops to below 5%.

“Since its introduction 120 years ago, [bubonic plague] has become endemic in ground squirrels and rodents in the rural Southwestern U.S.,” an expert told Fox News Digital. (iStock)
Symptoms and spread
Symptoms of the plague typically include severe headache, fever and chills, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting and swollen lymph nodes, the health department listed.
The plague can spread by droplets from one person infected with Y. pestis to another, according to Erica Susky, a certified infection control practitioner based in Canada.
“The more common risk of exposure in the U.S. is from pets, rodents and fleas,” she told Fox News Digital.

Symptoms of the plague typically include severe headache, fever and chills, muscle aches, nausea, vomiting and swollen lymph nodes. (iStock)
“Pets can sometimes be infected when encountering an infected flea or rodent and may pass it along to their pet owners from a bite or if the pet is ill.”
Another possible source is from hunting, she said — “skinning animals is also a risk, as the bacterium can spread via infected body fluids.”
“Treat pets promptly if they have a flea infestation and seek veterinary treatment if a pet becomes ill.”
Breathing in dust contaminated by dried rodent urine or feces with the bacteria can also spread the infection, according to Brewer.
Preventing the plague
The best means of prevention is to avoid rodents and fleas whenever possible, including dead rodents, Susky said.
“One way to do this is to ensure the home is rodent-proof by eliminating places where rodents may enter and hide,” she told Fox News Digital.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Whenever possible, pets should be kept indoors, Susky recommended.
If pets are outdoors, they should be leashed.
“Treat pets promptly if they have a flea infestation and seek veterinary treatment if a pet becomes ill,” Susky advised.
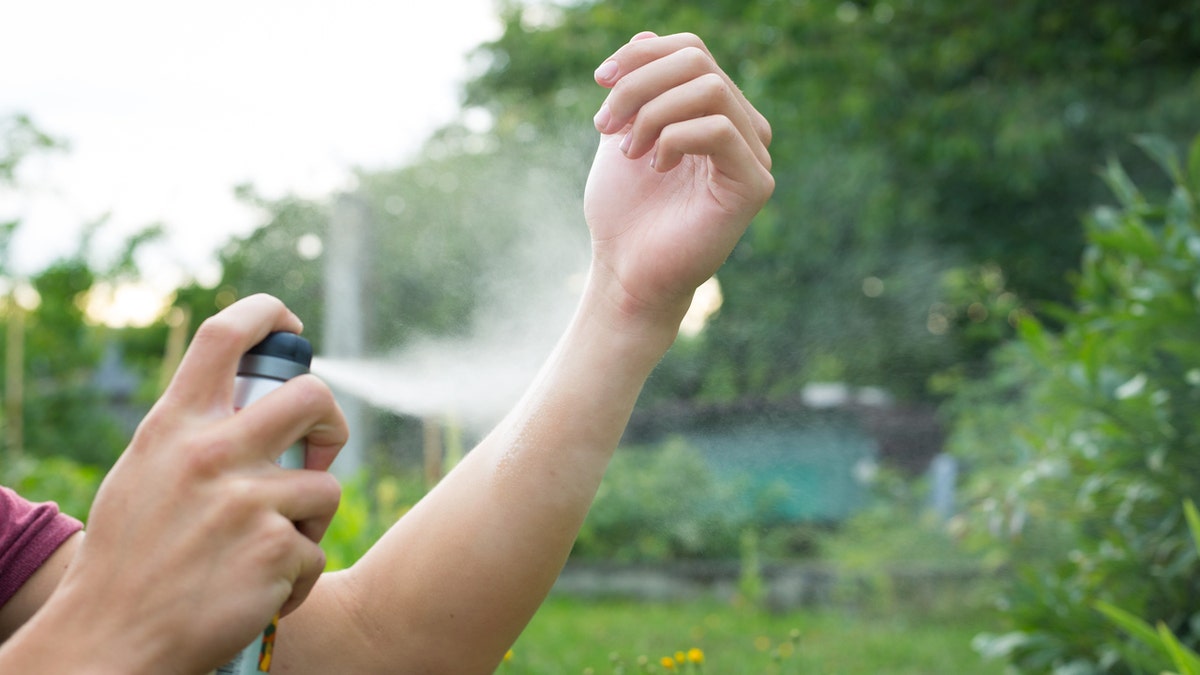

“If spending time outdoors where one may be bitten by fleas and other insects, repellent should be applied to minimize potential bites, which are a portal of entry for the bacterium if one is bitten by an infected flea,” an infectious diseases expert advised. (iStock)
Hunters should wear gloves and wash their hands after skinning animals, and should change and wash their clothes afterward, she added.
The PDPHE also recommends keeping pet food in rodent-proof containers and not allowing pets to sleep in bed.
“If spending time outdoors where one may be bitten by fleas and other insects, repellent should be applied to minimize potential bites, which are a portal of entry for the bacterium if one is bitten by an infected flea,” Susky said.
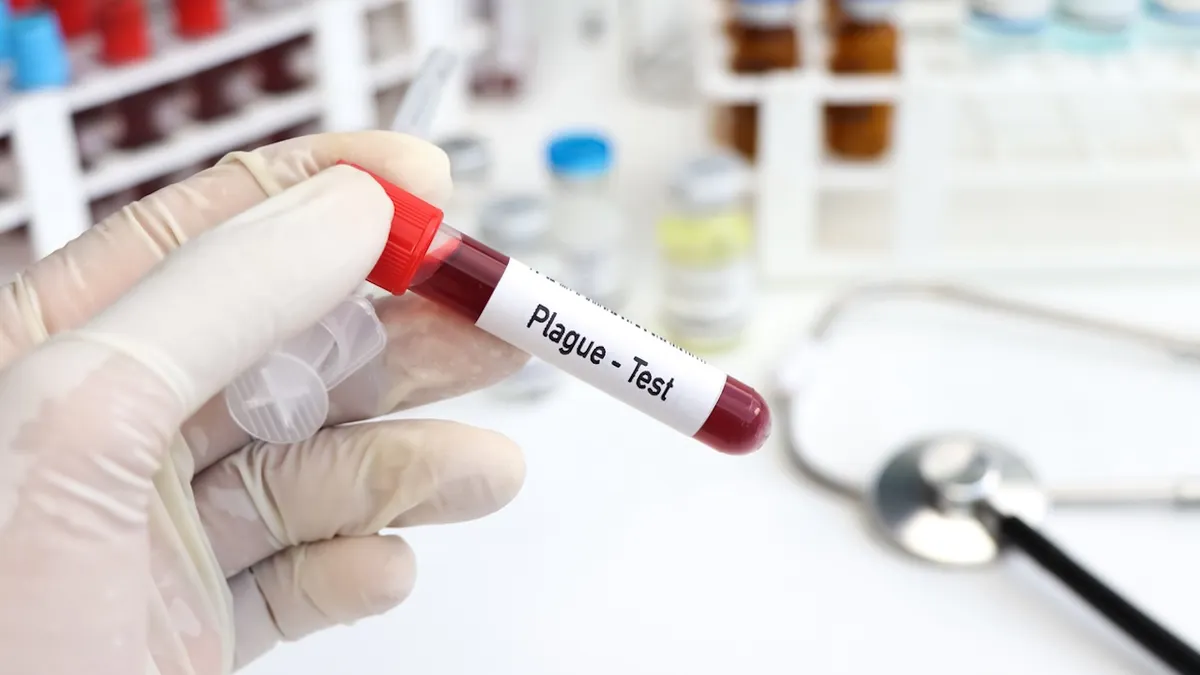
Anyone who develops symptoms of plague should see a health care provider immediately, officials advised. (iStock)
Anyone who develops symptoms of plague should see a health care provider immediately, Solis advised in the PDPHE alert.
“Plague can be treated successfully with antibiotics, but an infected person must be treated promptly to avoid serious complications or death.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health
Fox News Digital reached out to the Pueblo Department of Public Health and Environment and the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment for comment.
Health
Potassium chloride medications recalled due to failure that could cause heart attacks: FDA
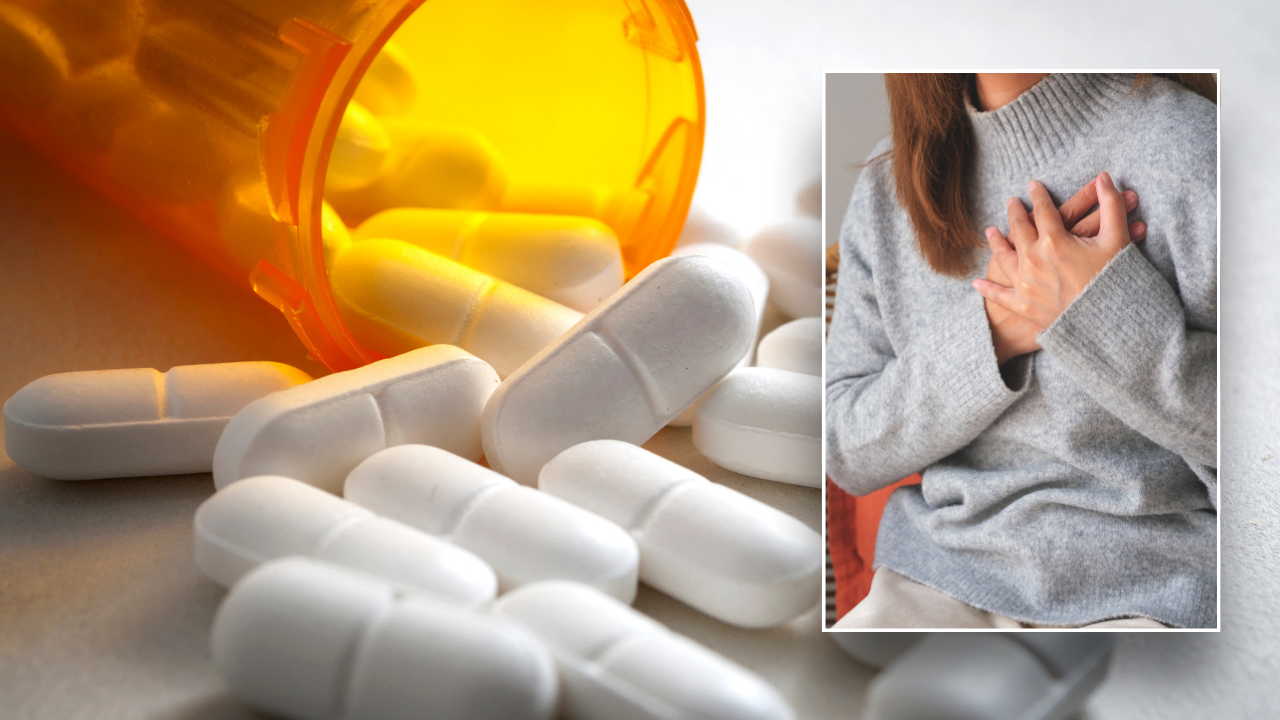

Two brands of potassium chloride capsules are being recalled because they may not dissolve as they should, which could cause a person to have a heart attack, according to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
In a press release published on June 25, the FDA explained that Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc. is recalling 114 batches of a product called Potassium Chloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP (750 mg) 10 mEq K. The reason is because of “failed dissolution” in the pills.
The product is intended for patients who suffer from low potassium levels, or hypokalemia.
According to the FDA, the failed dissolution could elevate consumers’ potassium to the point where a heart attack is possible.
VIRAL HOSTAGE TAPE SLEEPING TREND GAINS STEAM AS DOCTORS WARN OF POTENTIAL DANGERS
The FDA announced the recall of two different medications that, due to a failure to dissolve, have the potential to cause heart attacks. (iStock)
American Health Packaging issued a similar recall of 21 batches of the same capsules. The capsules were also made by Glenmark but distributed by BluePoint Laboratories.
“The failed dissolution of potassium chloride extended release capsules may cause high potassium levels, also known as hyperkalemia, which can result in irregular heart beat that can lead to cardiac arrest,” the FDA’s statement read.
“For patients who require chronic use of potassium chloride extended-release oral capsules… there is a reasonable probability of developing hyperkalemia that may lead to a range of severity of adverse events from being asymptomatic to more severe potential life-threatening adverse events of hyperkalemia such as cardiac arrythmias, severe muscle weakness, and death,” the agency added.
MORE AMERICANS SMOKE MARIJUANA DAILY THAN DRINK ALCOHOL, STUDY CLAIMS

The product is intended for patients who suffer from low potassium levels, or hypokalemia. (FDA)
The FDA also noted that there have not been any hyperkalemia cases or “serious adverse events” reported related to the product yet. The statement noted that the capsules are sold in bottles of 100-count and 500-count.
“Glenmark is notifying its wholesale and distributor customers by written letters and is arranging for return of all recalled batches,” the FDA said. “Wholesalers, distributors, and retailers that have the recalled products should discontinue distribution of the recalled product lots immediately and follow the instructions provided in the written recall letter.”
“Wholesalers and distributors should conduct a sub-recall to retail or pharmacy customers.”

Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc. is recalling 114 batches of a product called Potassium Chloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP (750 mg) 10 mEq K. (iStock)
Fox News Digital reached out to Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Inc. for comment, but did not hear back.
Health
Is cord blood banking a worthwhile investment in your child’s future?
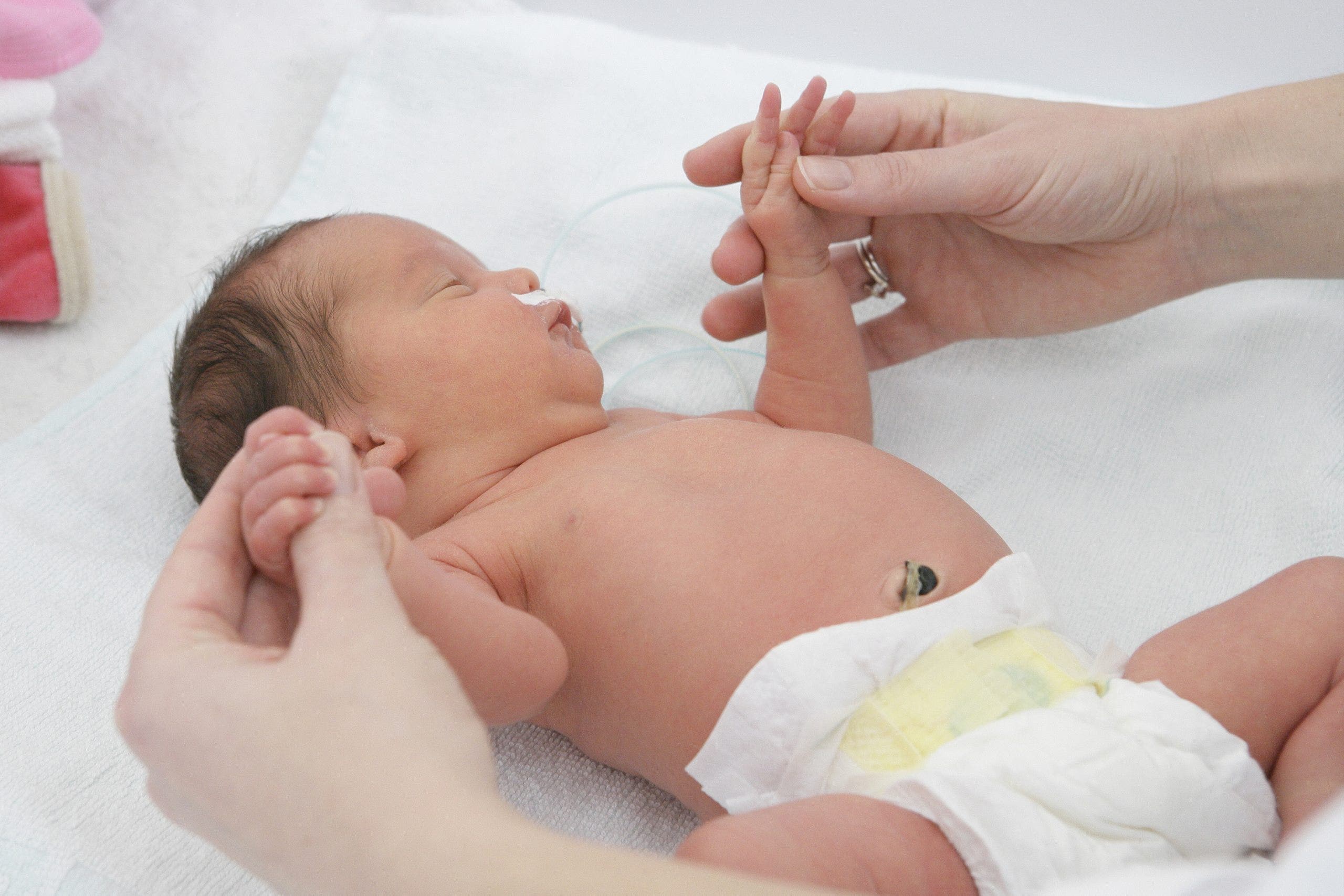
The umbilical cord — the lifeline between mother and baby — was historically discarded as medical waste after birth.
Today, an increasing number of parents are choosing to preserve the cord blood for its potential to safeguard their child’s future health.
The birth of a baby comes with an overwhelming number of decisions, one of which is whether to bank the newborn’s cord blood cells.
MEET THE AMERICAN WHO HELPED SAVE MILLIONS OF NEWBORN BABIES, DR. VIRGINIA APGAR, PHYSICIAN AND MUSICIAN
Whether cord blood banking is worth it for a family hinges on various factors, including the present health of their child, the existence of twins in the family and many other individual considerations.
What is cord blood banking?
Cord blood banking involves the collection and storage of stem cells derived from the blood of a newborn’s umbilical cord immediately after birth.
The reason is its potential life-saving abilities, as the hematopoietic stem cells found in cord blood have the unique ability to differentiate into various types of blood cells.
There are two main types of banks for cord blood: public and private. (BSIP/UIG)
Preserving the cord blood cells provides an option for future therapeutic use in treating a range of diseases for the child or siblings.
These stem cells are less likely to face rejection during transplant due to their immature nature. This widens the blood cells’ applicability in medical procedures for the donor or family members.
Cord blood banking process
Cord blood banking can be done from either a vaginal or surgical birth, and regardless of whether the labor was induced or occurred naturally.
Once the parents decide to store the blood, the doctor will clamp the umbilical cord in two places and cut the cord, separating the mother from the child.
Once the blood has been collected and sealed, it will be sent to a cord blood bank for storage.
The doctor will inject a needle into the cord and collect, in general, between 60 and 300 milliliters (mL) of cord blood. The collected volume can vary, however, and not all collections will be sufficient for future therapeutic use for the child or siblings.
Once the blood has been collected and sealed, it will be sent to a cord blood bank for storage.

In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates cord blood banking and donation. (Education Images/Universal Images Group )
Collecting fluid in this process is relatively easy and does not cause pain to the mother or baby, according to webmd.com.
The collection process generally takes around five minutes to complete.
The blood can be stored at several different sites, based on the family’s decisions and circumstances.
- Public cord banks. These are free to use, but donations made are available to anyone.
- Private cord banks. These blood banks will store the blood for use only by the donor and family members of the donor. This can be an expensive option as there is a processing fee and an annual storage fee.
- Direct-donation banks. These are a mixture of public and private banks. They store cord blood for public use but also accept donations to reserve the stem cells for the child.

Cord blood is collected immediately after birth in a painless process that does not harm the mother or the baby. (BSIP/Universal Images Group)
When discussing the options, cord blood banking often refers to private banking, while cord blood donation generally refers to public banking.
Private cord banking may not be worth the financial expense for the family, according to the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the American Academy of Pediatrics. The reason is that the price is steep for the chance that the child will need to use the blood at some point in time.
PARENTS WELCOME 14-POUND BABY, THE LARGEST ON RECORD SINCE 2010: ‘EVERYBODY WAS MAKING BETS’
These organizations suggest that routine storage of cord blood for stem cells as a sort of insurance is unproven, and therefore they caution parents when considering it.
Donating to a public storage bank could benefit the community, however, according to these organizations.
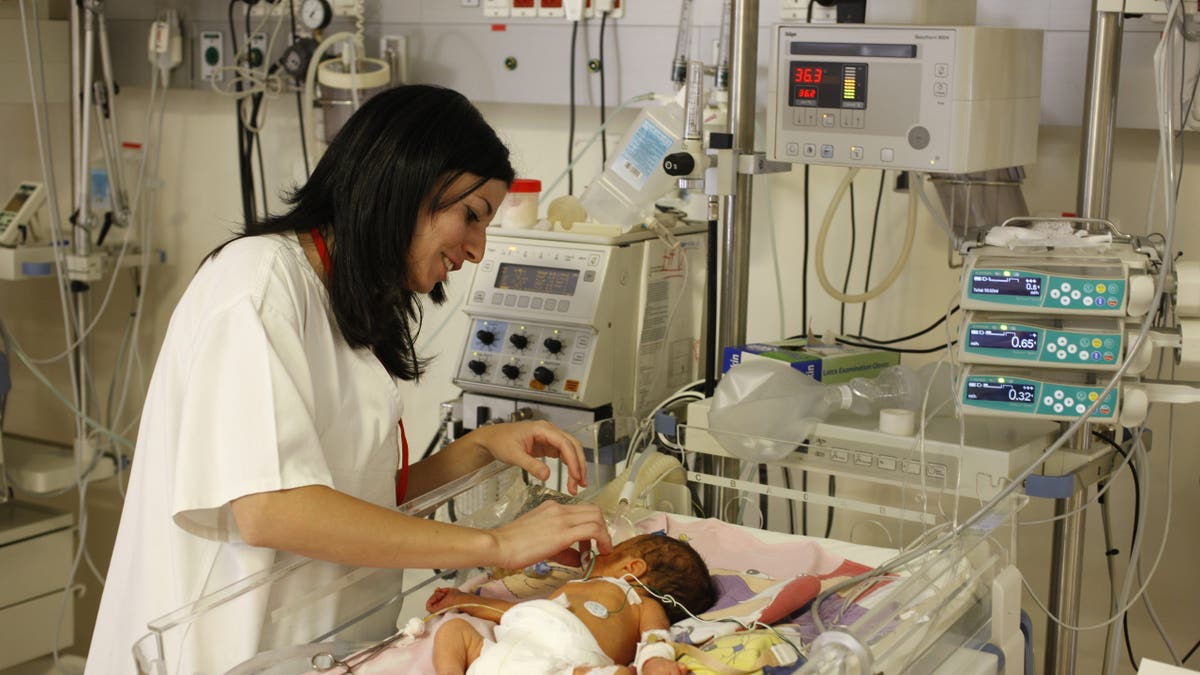

There is usually no cost to donate cord blood to a public bank, but private banking can be pricey, involving initial collection fees and annual storage fees. (BSIP/UIG)
What are the uses of cord blood banking?
Cord blood banking can be beneficial because the stem cells are hematopoietic stem cells, meaning they are immature but can become mature cells of different types within the body.
Not only do they require less matching, they also cause fewer infections.
BABY SLEEP DANGERS REVEALED IN NEW STUDY AS NEARLY 70% OF INFANT DEATHS WERE DUE TO CO-SLEEPING
The stem cells within the umbilical cord can provide life-saving assistance for several conditions later in life.
Stem cells from the umbilical cord can treat a variety of conditions, including:
- Cancer
- Anemia
- Immune system disorders
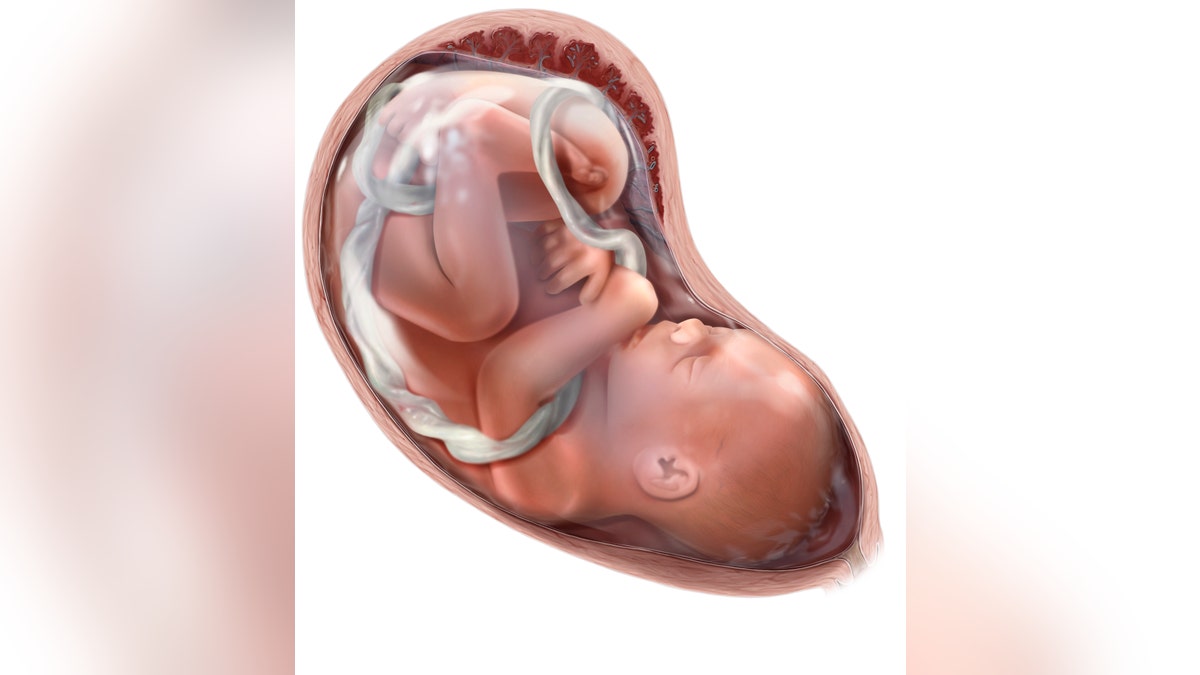
Once the cord blood is collected and stored, it can remain viable for a long time. Research suggests that cord blood can be stored for at least 10 years but often much longer. (QAI Publishing/Universal Images Group )
A benefit of using cord blood stem cells is that they rarely result in infectious diseases.
They are also highly effective as they are half as likely to be rejected compared to other stem cells because they are immunogenic due to their immature nature.
What are the cons of cord blood banking?
There is only about an 8% usage rate of blood that has been stored through this process, according to a study cited by the National Library of Medicine.
Part of the reason for the low rate is that the blood is not always useful for a disease that develops later on in life.
HEALTH BENEFITS OF CONSUMING VINEGAR, PLUS TIPS FROM A DIETITIAN
Many factors go into whether cord blood can be used, such as from a set of twins when one twin is healthy and the other is born with a genetic disorder.
The blood drawn from the ill child can not be used later on for the healthy child, but the reverse could be true if the blood is a good match.

Patients are more likely to find a genetic match among donors of their own ethnic background. (BSIP/Universal Images Group)
There are many circumstances that the American Academy of Pediatrics lays out as not ideal conditions for cord blood banking.
Identical twins are not often the best match for each other because a slight genetic difference in the blood cells is recommended.
Additionally, public blood banks can only accept donations from umbilical cords from a mother carrying a single child. This is due to the possibility that the blood units could get mixed up during the collection with twins.
Another downside of using cord blood cells is that it takes longer for them to create the therapeutic effect desired because they are hematopoietic stem cells.
How much does cord blood banking cost?
Typically, there are two separate fees involved when preserving a child’s cord blood cells, according to the American Pregnancy Association. The initial fee covers the enrollment and collection.
Then, there is an annual storage fee.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Those who go this route can expect to pay in the range of $1,350 and $2,350 for the initial collection, testing and registering, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics. Annual storage fees often range from $100 to $175, but the costs of individual storage banks will vary.
Currently, research into cord blood stem cells is ongoing. Scientists are investigating the potential for treating conditions such as cerebral palsy and Type 1 diabetes. (iStock)
If the parents donate the blood cells from the umbilical cord, there is no cost.
The future of cord blood banking
The future trajectory of cord blood banking remains uncertain. Nonetheless, preserving cord blood cells today may have significant health benefits, offering new avenues for disease treatment as the field advances.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews/health
Considering the first successful umbilical cord blood stem cell transplant was performed as recently as 1988, as documented by the National Library of Medicine, the science around this practice is relatively young.
With ongoing research, the scope and efficacy of cord blood use are bound to expand.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoToplines: June 2024 Times/Siena Poll of Registered Voters Nationwide
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoPopular Republican and Trump running mate contender makes first Senate endorsement in 2024 races
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIowa floodwaters breach levees as even more rain dumps onto parts of the Midwest
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoMike Kennedy advances past crowded GOP primary to secure nomination for open Utah House seat
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoThe many faces of Donald Trump from past presidential debates
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNew Jersey gamer flew to Florida and beat fellow player with hammer, say police
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoVideo: How Blast Waves Can Injure the Brain
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25505687/VERNE_Exterior1.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25505687/VERNE_Exterior1.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoRimac is shifting from electric supercars to robotaxis





/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/24065000/HT015_S_Haddad_ios_iphone_14_04.jpg)









