Health
More COVID deaths reported in US counties with lower internet access: study

NEWNow you can take heed to Fox Information articles!
U.S. communities with restricted web entry had increased COVID-19 mortality charges in the course of the first full 12 months of the pandemic, in response to researchers.
In a examine revealed earlier this month within the journal JAMA Community Open, College of Chicago authors wrote that for locations with extra restricted entry between 2.4 and 6 deaths per 100,000 individuals could possibly be prevented, relying on whether or not they had been rural, suburban or city.
“Adopting an asset-based strategy, we consider this discovering means that extra consciousness is required concerning the important asset of technological entry to dependable data, distant work, education alternatives, useful resource buying and/or social neighborhood. Populations with restricted web entry stay understudied and are sometimes excluded in pandemic analysis,” they famous.
UPTICK IN COVID VIRUS CASES DETECTED IN WASTEWATER SAMPLE SITES: CDC
Analyzing Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention (CDC) mortality information for all U.S. counties in 50 states and the District of Columbia reported from Jan. 22, 2020 to Feb. 28, 2021, the group recognized counties with a excessive focus of a single racial and ethnic inhabitants and a excessive stage of COVID-19 mortality as “concentrated longitudinal-impact counties.”
Different racial and ethnic demographic information was sourced from publicly accessible information units.
The social determinants of well being (SDOH) that could possibly be related to mortality throughout the counties had been examined, with researchers specializing in Black, Hispanic and non-Hispanic White Individuals in rural, suburban or city areas.
A wi-fi router with three antennas and cable related.
(iStock)
4 indexes had been used to measure a number of dimensions of SDOH: a socioeconomic benefit index, restricted mobility index, city core alternative index and combined immigrant cohesion and accessibility index.
Utilizing modeling to look at the associations between the SDOH and county-level COVID-19 mortality charge, they discovered that 531 of three,142 counties had been recognized as concentrated longitudinal-impact counties.
Of these counties 347 had a big inhabitants of Black Individuals, 198 had a big Hispanic inhabitants and 33 had a big non-Hispanic White inhabitants.
As well as, practically 490,000 COVID-19-related deaths had been reported.
PFIZER-BIONTECH SEEK AUTHORIZATION FOR SECOND COVID-19 BOOSTER

“Most concentrated longitudinal-impact counties with a big Black or African American inhabitants in contrast with different counties had been unfold throughout city, suburban and rural areas and skilled quite a few disadvantages, together with increased revenue inequality and extra preventable hospital stays. Most concentrated longitudinal-impact counties with a big Hispanic or Latinx inhabitants in contrast with different counties had been positioned in city areas, and 130 of those counties had a excessive share of people that lacked medical health insurance. Most concentrated longitudinal-impact counties with a big non-Hispanic White inhabitants in contrast with different counties had been in rural areas, included a big group of older adults, and had restricted entry to high quality well being care,” the examine concluded.
In city areas, the combined immigrant cohesion and accessibility index was inversely related to COVID-19 mortality and better COVID-19 mortality charges had been additionally related to preventable hospital stays in rural areas and better socioeconomic standing vulnerability in suburban areas.
For many concentrated longitudinal-impact counties with a big Black or Hispanic populations in contrast with different counties, extreme housing downside charges had been increased than the nationwide median stage and most concentrated longitudinal-impact counties with massive Black and non-Hispanic White populations had increased percentages of households with out entry to the web.
The examine’s outcomes, they stated, underscore how locations and other people intersect throughout the multifaceted energy constructions that produce and reproduce inequity in well being outcomes.
“Clearly, SDOH dimensions matter for well being outcomes, however the outcomes of this examine add nuance to this assumption by demonstrating that SDOH probably form well being in distinctive methods, relying on a neighborhood’s rural and concrete contexts in addition to its racial and ethnic make-up,” the authors wrote. “We discovered that non-Hispanic White populations in rural areas and Hispanic or Latinx populations in city areas had been particularly weak to COVID-19 mortality, whereas Black or African American populations throughout rural and concrete contexts fared poorly (by way of mortality charge) in the course of the first 12 months of the pandemic. For city, rural, and suburban communities, some dimensions of SDOH gave the impression to be extra consequential for COVID-19 mortality charges, pointing to the social levers that may play the most important function in shifting the needle on inhabitants well being in various kinds of communities.”
Limitations to their examine embrace that analyses for different racial and ethnic teams had been excluded, that the cross-sectional examine used an exploratory spatial information evaluation strategy, that the county-level scale could not seize the complete image of affected populations, that there’s the potential confounding issue of vaccines being accessible on the finish of 2020 and that they primarily analyzed SDOH obstacles related to vulnerability to COVID-19 mortality.
To deal with well being inequities and information insurance policies and applications, they known as for additional examine.

Health
Scientists May Be Able to Make Grapefruits Compatible With Medications They Currently Interfere With

You may be among the millions of people who have seen a surprisingly specific warning like this on the labels of drugs you take:
Avoid eating grapefruit or drinking grapefruit juice while using this medication.
Such warnings are issued for dozens of substances, including docetaxel, a cancer drug; erythromycin, an antibiotic; and some statins, the cholesterol-lowering drugs prescribed to more than a third of American adults over 40.
The problem is a set of molecules, furanocoumarins. High levels of furanocoumarins interfere with human liver enzymes, among other processes. In their presence, medications can build up to unhealthy levels in the body. And grapefruits and some related citrus fruits are full of them.
But there is no such warning for other kinds of citrus, such as mandarins and other oranges. Citrus researchers at the Volcani Center in Israel reported Wednesday in the journal The New Phytologist that, by crossing mandarins and grapefruit, they’ve uncovered genes that produce furanocoumarins in some citrus fruits. It’s a finding that opens the possibility of creating grapefruit that doesn’t require a warning label.
Scientists had worked out the compounds’ structures and pieced together a basic flowchart of how they are made years ago, said Yoram Eyal, a professor at the Volcani Center. But the precise identities of enzymes catalyzing the process — the proteins that snip off a branch here, or add a piece there — remained mysterious. He and his colleagues knew that one way to identify them was to breed citrus high in furanocoumarins with those without. If the offspring of such a cross had varying levels of the substances, it should be possible, by digging into their genetics, to pinpoint the genes for the proteins.
“We were afraid to approach it, because it’s very time-consuming and it takes many years,” he said, noting how involved it can be to grow new trees from seeds and assess their genetics. “But finally, we decided we have to dive in.”
When they examined the offspring of a mandarin and a grapefruit, the researchers saw something remarkable. Fifty percent of the young plants had high levels of furanocourmains, and 50 percent had none. That particular signature meant something very specific, in terms of how the ability to make these substances is inherited.
“We saw there was only one gene that could have controlled it,” said Livnat Goldenberg, a Volcani Center researcher who is the lead author of the new study.
The researchers soon identified the gene controlling the production of furanocoumarins in leaves and fruit, which produces an enzyme called 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, or 2OGD for short. Mandarins, it turns out, have a mutated form of this gene that keeps the enzyme from functioning properly. This version cropped up in all the mandarin and orange varieties the researchers checked, explaining why they do not cause the same problems as grapefruit in people taking prescription medications. In these plants, furanocoumarin production is paused.
With gene editing technology, it should be possible to alter the gene in grapefruit as well, Dr. Eyal suggests. The team at the Volcani Center is now exploring that project.
Looking at how widespread this mutated version is in mandarins and some other citrus, the scientists speculate that some gene nearby on the genome must play an important role in a highly prized trait. A long-ago citrus breeder, selecting for some unknown quality, must have unwittingly spread this furanocoumarin-busting version of the gene to an ancestor of modern varieties of mandarins and oranges.
All these years later, that person’s work is coming to light, under the gaze of geneticists, who may, someday, put grapefruit back on the menu.
Health
‘Rabbit fever’ cases rising in US as CDC warns of zoonotic bacterial disease
Cases of tularemia, also known as “rabbit fever,” are on the rise in the U.S., according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Caused by the bacteria Francisella tularensis, the disease commonly infects rabbits, hares and rodents. However, it is zoonotic, which means it can spread from animals to humans.
The bacteria is a “tier-1 select agent,” a classification given to agents and toxins that “present the greatest risk of deliberate misuse with significant potential for mass casualties or devastating effects to the economy, critical infrastructure or public confidence, and pose a severe threat to public health and safety,” per the CDC.
SUPERBUGS DUE TO ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE COULD KILL 39 MILLION PEOPLE BY 2050, LARGE STUDY FINDS
Although tularemia is relatively rare, with only 2,462 diagnoses between 2011 and 2022, cases have risen 56% compared to the prior decade (2001 to 2010), as reported in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
Cases of tularemia, also known as “rabbit fever,” are on the rise in the U.S., according to a new report from the CDC. (iStock)
“Increased reporting of probable cases might be associated with an actual increase in human infection, improved tularemia detection or both,” the report states.
Health
Diabetes, heart disease cases skyrocket — and scientists pinpoint one key reason
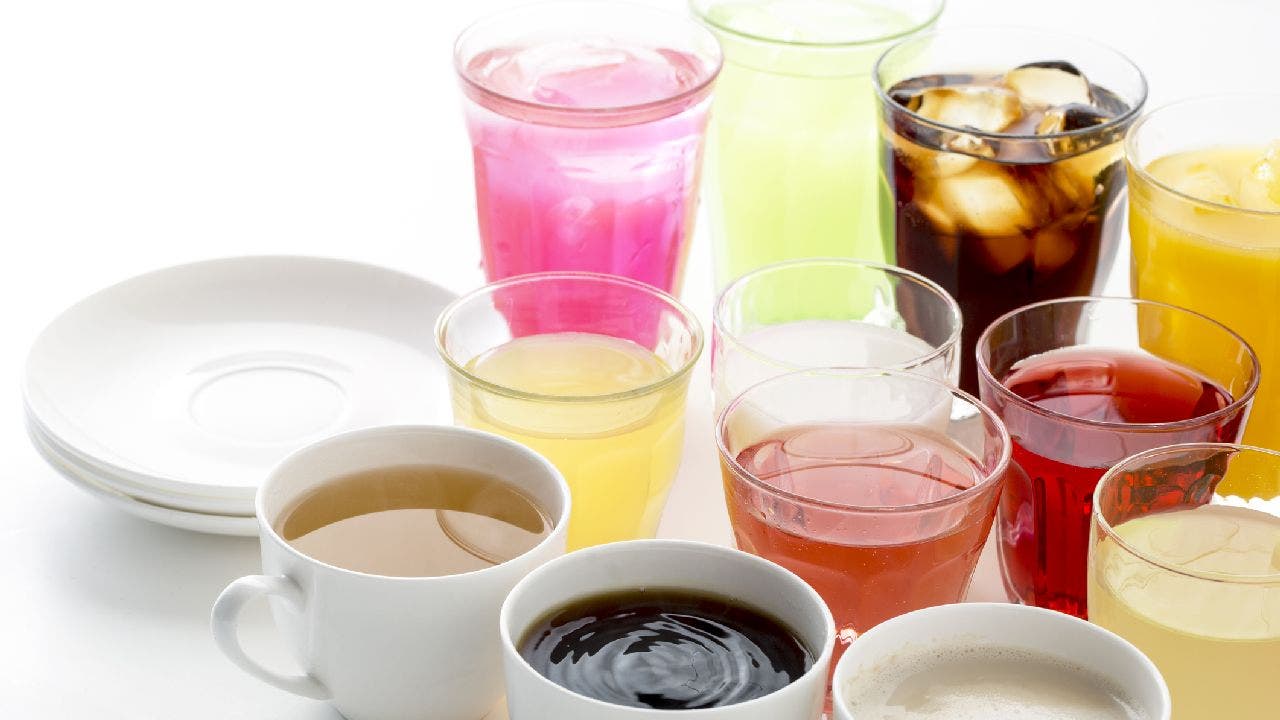

Millions of new cases of diabetes and heart disease every year are caused by sugary drinks, according to newly published research.
Tufts University in Boston led the study, which found that about 2.2 million new diagnoses of type 2 diabetes and 1.2 million new cases of cardiovascular disease were attributed to sugar-sweetened sodas and juices each year, according to a press release.
The findings were published in the journal Nature Medicine this week.
HEART ATTACK RISK COULD RISE WITH ARTIFICIAL SWEETENER CONSUMPTION, STUDY FINDS
The highest rates were found in Colombia, where 48% of new diabetes cases were linked to sugary drinks, and in Mexico, where nearly a third of cases were attributed to them.
Meanwhile, in Latin America, more than 24% of new diabetes cases were linked to sugary beverages, and 21% in sub-Saharan Africa, the study found.
About 2.2 million new cases of type 2 diabetes and 1.2 million new cases of cardiovascular disease occur each year worldwide due to consuming sugar-sweetened soda and juices, according to the findings of a new study. (iStock)
In South Africa, 27.6% of new diabetes cases and 14.6% of cardiovascular disease cases were attributed to sugary drinks.
Sugary drinks are rapidly digested, causing a spike in blood sugar levels with little nutritional value.
Sugary drinks cause blood sugar to spike because they are “rapidly digested,” the research team said.
When consumed on a long-term basis, these types of beverages, in addition to increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes and heart disease, can also lead to weight gain and insulin resistance, the researchers added.

Men are more likely than women to suffer the consequences of sugary drink consumption, as are younger adults compared to their older counterparts, a new study asserts. (iStock)
Professor Dariush Mozaffarian, the study’s senior author, said in a university press release, “Sugar-sweetened beverages are heavily marketed and sold in low- and middle-income nations.”
He added, “Not only are these communities consuming harmful products, but they are also often less well-equipped to deal with the long-term health consequences.”
FRIENDS, FAMILY MAY PROTECT AGAINST HEART ATTACK, STROKE AND TYPE 2 DIABETES, STUDY SUGGESTS
Certain groups are more likely to experience negative health effects from sugary drinks, including men and younger adults, the researchers noted, as news agency SWNS also noted.
New Jersey-based registered dietitian Erin Palinski-Wade, who was not involved in the research, said the findings were to be expected, as diets rich in added sugars are more likely to increase the risk of chronic health conditions, including type 2 diabetes.

When consumed on a long-term basis, these types of beverages can also lead to weight gain and insulin resistance, experts say. (iStock)
“Sugar-sweetened beverages are a major cause of added sugar in the diet and easy to overconsume, as they provide little fullness,” she told Fox News Digital.
“The high calorie content and lack of satisfaction due to little protein, fat or fiber in these drinks can lead to excess calorie consumption, which can lead to weight gain — especially gains in visceral fat (belly fat), which has been found to increase the risk of type 2 diabetes,” she went on.
“Sugar-sweetened beverages are easy to overconsume, as they provide little fullness.”
Palinski-Wade pointed out that there were some limitations to the new research.
“This was an observational study, not a causation study, and shows only an association between diets containing sugar-sweetened beverages and diabetes,” she noted.
“It does not prove that those drinks alone trigger an onset of type 2 diabetes.”
What needs to change?
To remedy the issue, the study authors called for a “multi-pronged approach,” including public health campaigns, regulations on advertising and taxes on sugar-sweetened beverages, the release stated.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“We need urgent, evidence-based interventions to curb consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages globally, before even more lives are shortened by their effects on diabetes and heart disease,” first author Laura Lara-Castor, now at the University of Washington, said in the release.

Approximately 65% of adults in the U.S. consume sugar-sweetened beverages daily. (iStock)
Mexico implemented a sugary drinks tax in 2014, which has shown to be effective in reducing consumption, the researchers stated.
“Much more needs to be done, especially in countries in Latin America and Africa, where consumption is high and the health consequences severe,” wrote Mozaffarian.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“As a species, we need to address sugar-sweetened beverage consumption.”
Many different factors are involved in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, Palinski-Wade noted.
“As a species, we need to address sugar-sweetened beverage consumption.”
“However, reducing your intake of sugar-sweetened beverages can go a long way toward improving overall blood sugar regulation and future health.”
The new research was supported by the Gates Foundation, the American Heart Association and Mexico’s National Council for Science and Technology.
Fox News Digital reached out to the researchers for further comment.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?
-

 Health5 days ago
Health5 days agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIvory Coast says French troops to leave country after decades

















