Health
As Lyme disease tests miss many acute infections, potential at-home test offers hope for earlier diagnosis

When Americans spend time in the great outdoors this summer, they don’t want to come back home with any uninvited guests.
Lyme disease, the most common tick-borne disease in the United States, can have severe complications if left untreated or unnoticed.
Prompt treatment is essential to prevent the spread of the disease elsewhere in the body.
TICK BITES AND LYME DISEASE: WHAT TO DO IF A TICK BITES YOU OR YOUR PET
Yet the current recommended laboratory test to diagnose Lyme disease misses many early cases.
Now, a Virginia Tech research team is developing a promising at-home test that can diagnose the illness within hours of transmission, according to a recent report.
This undated photo provided by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows a blacklegged tick, also known as a deer tick. Officials said ticks would be more active than usual early in spring 2023, which means Lyme disease and other tick-borne infections could spread earlier and in greater numbers than in a typical year. Ticks can transmit multiple diseases that sicken humans, and deer ticks, which spread Lyme, are a fact of life in the warm months in New England and the Midwest. (CDC via AP/File)
Lyme disease is caused by a bacterium known as Borrelia burgdorferi and rarely, borrelia mayonii, which is transmitted to humans after an infected blacklegged tick bites them, per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
“The only FDA-approved diagnostic for Lyme disease measures antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi, not the presence of the bacterium itself,” Linda Giampa, executive director of the Bay Area Lyme Foundation in San Francisco, California, told Fox News Digital.
“Lyme disease has been commonly misdiagnosed by unreliable tests for far too long.”
“It misses up to 60% of acute cases of Lyme, as it takes several weeks for these antibodies to rise to detectable levels in people,” she added.
TICK BITES ON THE RISE: HOW TO STAY SAFE AS YOU HEAD OUTDOORS
“Lyme disease has been commonly misdiagnosed by unreliable tests for far too long, and there are currently no reputable at-home tests on the market,” she also said.
Symptoms may mimic the flu
Some 35,000 cases of Lyme disease are reported to the CDC every year, but the number of cases is grossly underreported — with insurance records estimating the true annual number around 476,000, according to experts.
The infection was named where it was first discovered: Lyme, Connecticut.

The CDC says people may experience symptoms that could mimic the flu — such as fever, chills, muscle and joint aches — within several days to one month after they’re bitten by a tick. (Elijah Nouvelage/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
Within several days to one month after a tick bite, someone may experience symptoms that could mimic the flu, such as fever, chills, muscle and joint aches, per the CDC.
In 70-80% of cases, a classically non-itchy rash that resembles a “bull’s-eye” develops at the site of the bite, often within a week of the infection, the agency added.
Prompt treatment helps decrease signs and symptoms of the disease and prevents spread to later stages of illness.
In later stages of the disease, such as days to months after the tick bite, untreated Lyme disease can spread to other parts of the body in about 60% of the patients.
Prompt treatment helps decrease signs and symptoms of the disease and prevents spread to later stages of illness.
DEBBIE GIBSON SPILLS HER SECRET TO STAYING FIT AMID STRUGGLES WITH LYME DISEASE
Diagnosis relies on the body’s immune response to the Lyme bacteria because it’s very difficult to culture the bacteria directly in lab.

A tick is shown running over a hand in June 2021. (Bernd Weissbrod/picture alliance via Getty Images)
“This requires both a healthy immune system and time to produce a robust enough response that can be detected (i.e., anti-B. burgdorferi titer),” Dr. Brandon Jutras, associate professor in the department of biochemistry and a member of the Fralin Life Sciences Institute at Virginia Tech in Blacksburg, Virginia, told Fox News Digital via email.
At-home test directly detects bacteria
Last year, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, in partnership with the Steven and Alexandra Cohen Foundation, a nonprofit to advance research of Lyme disease, initiated a competition known as the LymeX Diagnostics Prize.
The Jutras team at Virginia Tech is focusing on a component in the cell wall that’s unique to the bacteria that cause the disease.
The goal was to inspire researchers to develop better diagnostic tests to detect active Lyme disease infections in people more accurately.
There are 10 teams competing in the second round, including the team at Virginia Tech.

The goal of the competition known as the LymeX Diagnostics Prize is to inspire researchers to develop better diagnostic tests to detect active Lyme disease infections in people more accurately. The group at Virginia Tech is working on an at-home test that could enable “direct detection” of Lyme disease within just hours of transmission. (iStock)
“Among the promising diagnostics supported by the LymeX Diagnostics Prize are at-home tests, which are being developed by a research group at Virginia Tech to enable direct detection of the Lyme disease bacterium within hours of transmission,” Giampa noted.
The Jutras team is focusing on a component in the cell wall that’s unique to the bacteria that cause the disease.
There are hopes the team’s work “will lead to a rapid, specific test that doesn’t rely on a patient response.”
“Virtually all bacteria have layer(s) of peptidoglycan, and many of the components that make up peptidoglycan are highly similar,” Jutras told Fox News Digital.
AI TECH AIMS TO HELP PATIENTS CATCH DISEASE EARLY, EVEN ‘REVERSE THEIR BIOLOGICAL AGE’
“As it turns out, the peptidoglycan from the bacterium that causes Lyme disease is vastly different.”
As the bacteria grow, they shed these unique pieces of their peptidoglycan that are highly abundant — which makes it a “perfect biomarker for diagnostics,” he added.

A close-up of an adult female, an adult male, nymph and larva tick are shown here. Ticks can cause Lyme disease, an acute inflammatory disease characterized by skin changes, joint inflammation and flu-like symptoms. (Getty Images)
“We have created several monoclonal antibodies that are capable of specifically detecting the peptidoglycan pieces,” he said.
Antibodies to the Lyme bacteria can linger for months, he said.
So it’s not always clear from the current recommended testing available if the patient has an active infection — or was infected in the past.
Although it will be likely several years before his test may be ready for use, “our approach would, in theory, work immediately after transmission because as long as the bacterium is replicating, [it is] shedding peptidoglycan,” he said.
It will be likely several years before this test may be ready for use.
“This is a basic feature of this unusual organism,” he added.
“Our test exploits this process,” he said — noting that he hopes it “will lead to a rapid, specific test that doesn’t rely on a patient response.”
LymeX Diagnostic Prize officials note on the competition’s website, “As the geographic range of ticks, mosquitoes, and fleas that can transmit pathogens and cause disease expands within the United States, the need for diagnostic innovation will only become more urgent.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Jutras also said, as noted on that site, that he hopes long term, “we can do exactly what happened with COVID-19 and turn it into an at-home test. You wouldn’t be able to do a blood test; that’s not safe. But where we would optimize this is the urine test.”

Health
Paleo and Atkins Diets: Low-Carb for Different Reasons | Woman's World

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Health
7 important health stories this week you simply can't miss

Every day of the week, Fox News Digital publishes a range of health and wellness pieces to keep you up-to-date on medical research, new medications, mental health trends, success stories and more.
In case you missed them, here are a few of the biggest health stories from the past week.
As always, you can see a full list of recent health pieces at http://www.foxnews/health.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
1. FDA tells COVID vaccine makers to update their fall shots
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration recommended that COVID vaccine manufacturers update their formulas for fall doses, in an attempt to target the KP.2 strain of the JN.1 variant.
Dr. Marc Siegel shared insights on the risks as this variant grows more prominent. Click here to get the story.
“It makes sense to target the KP.2 strain because it is becoming the predominant strain — it is surging in California and will spread across the country,” Siegel told Fox News Digital. (iStock)
2. Expert offers 7 tips to soothe sunburned skin
If not treated properly, sunburn can lead to severe skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer, experts warn.
Angela Rosoff, a San Francisco-based wellness and beauty expert, shared some proven remedies to treat sun-damaged skin. Click here to get the story.

More than one out of every three adults experienced a sunburn last year, according to a survey by the American Academy of Dermatology. (iStock)
3. Tiger mosquitoes blamed for spread of dengue fever
As dengue fever continues to spread throughout Europe, experts are naming an invasive mosquito species as the culprit.
CANCER NEARLY TOOK HIS LEG, BUT NEW JERSEY FATHER OF 6 WALKS AGAIN: ‘I SHOULDN’T BE HERE’
Infectious diseases experts weighed in on the level of risk and share prevention tips. Click here to get the story.
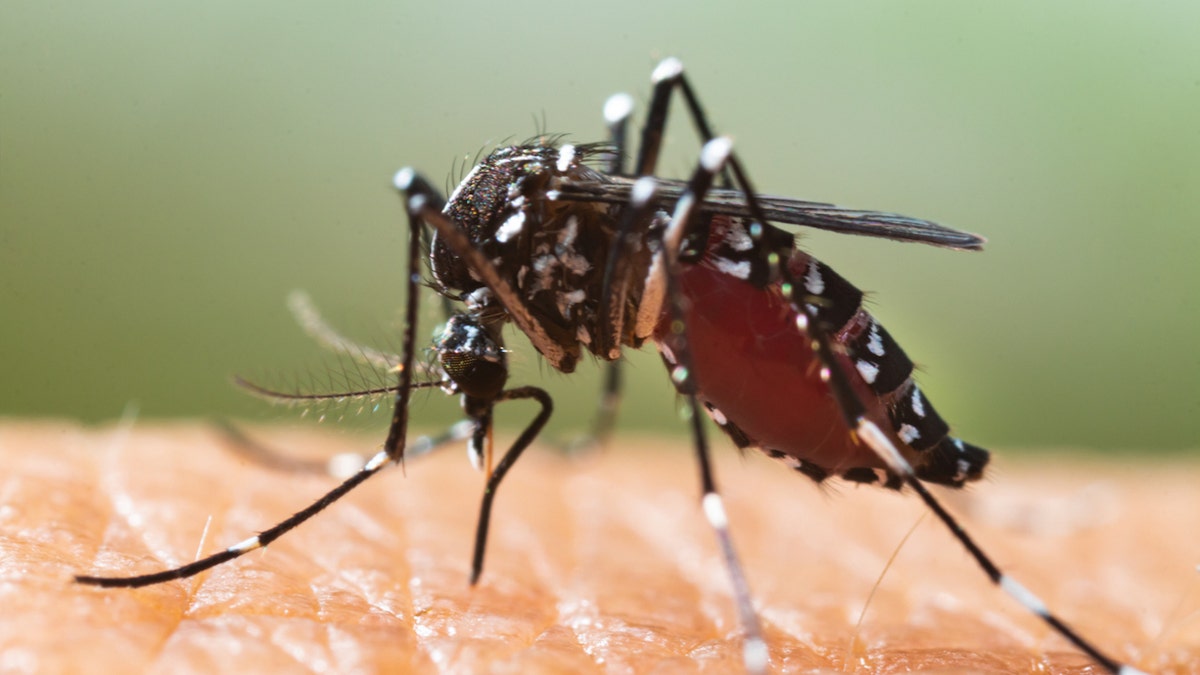

Tiger mosquitoes — the species Aedes albopictus — have spread into 13 EU countries, according to an alert from the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. (iStock)
4. Certain exercises could reverse Alzheimer’s, expert says
In her new book, “Reversing Alzheimer’s,” Dr. Heather Sandison, a renowned expert in dementia care, offered specific recommendations for the types of exercise that can benefit patients living with the disease.
“Exercise benefits several of the root causes of neurological disease,” she wrote. Click here to get the story.

Sunburn remedies, new COVID vaccines, anti-Alzheimer’s exercises and more important stories are covered here. (iStock)
5. Experts bust sunscreen myths
Some claims on social media about sun safety have led to a major misconception that sunscreen could cause skin cancer.
Dermatologists debunk these potentially dangerous myths. Click here to get the story.

Thirty-two percent of Americans believe that a tan makes people look better and healthier, according to the Orlando Health Cancer Institute study. (iStock)
6. New Alzheimer’s drug gets thumbs-up from FDA advisory committee
Donanemab, designed to treat mild cognitive impairment and other symptoms of early Alzheimer’s disease, was endorsed by a U.S. Food and Drug Administration advisory panel.
Here’s what that could mean for patients. Click here to get the story.

Eli Lilly officials presented clinical trial results showing that the drug, donanemab, slowed cognitive and functional decline for people with mild cognitive impairment due to early stages of Alzheimer’s. (iStock)
7. FDA panel rejects MDMA-assisted therapies for PTSD
Many veterans’ hopes were dashed when an FDA advisory committee voted against the overall benefits of MDMA when used to treat PTSD.
Advocates and doctors discussed what this means for the future of psychedelic treatments. Click here to get the story.

“When I heard the verdict, all I could think about was the hopes of those veterans being dashed … and not having a solution for them,” one advocate said. (iStock)
Health
Better Than Ozempic? Doctors Say These Medications Are Better for Weight Loss Than the Popular Semaglutide

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIsrael used a U.S.-made bomb in a deadly U.N. school strike in Gaza
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 833
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoGeorge Clooney called White House to complain about Biden’s criticism of ICC and defend wife’s work: report
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNewson, Dem leaders try to negotiate Prop 47 reform off California ballots, as GOP wants to let voters decide
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago‘Bloody policies’: Bodies of 11 refugees and migrants recovered off Libya
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoEmbattled Biden border order loaded with loopholes 'to drive a truck through': critics
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoDozens killed near Sudan’s capital as UN warns of soaring displacement
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoGun group vows to 'defend' Trump's concealed carry license after conviction