Business
Inside the race to train more workers in the chip-making capital of the world
Build the technology of the future. Protect the nation from attack. Buy a sports car.
These were some of the rewards of working in the semiconductor industry, 200 high school students learned at a recent daylong recruiting event for one of Taiwan’s top engineering schools.
“Taiwan doesn’t have many natural resources,” Morris Ker, the chair of the newly created microelectronics department at National Yang Ming Chiao Tung University told the students. “You are Taiwan’s high-quality ‘brain mine.’ You must not waste the intelligence given to you.”
The island of 23 million people produces nearly one-fifth of the world’s semiconductors, microchips that power just about everything — home appliances, cars, smartphones and more. Furthermore, Taiwan specializes in the smallest, most advanced processors, accounting for 69% of global production in 2022, according to the Semiconductor Industry Assn. and the Boston Consulting Group.
But a pandemic-induced chip shortage, along with rising geopolitical tensions in Asia, have highlighted the fragility of the current supply chain — and its reliance on an island under the specter of a takeover by China.
Across the U.S., Japan, South Korea, Taiwan and China, the semiconductor industry is already short hundreds of thousands of workers. In 2022, the consulting and financial services giant Deloitte estimated that semiconductor companies would need more than 1 million additional skilled workers by 2030.
Morris Ker, the chair of the microelectronics department at NYCU, gives a presentation on why students should join the semiconductor industry.
(Stephanie Yang / Los Angeles Times)
Seeking to maintain Taiwan’s status as the chip-making capital of the world, the government and several corporations here helped the university — known as NYCU — create the microelectronics department last year to fast-track students into industry jobs. Now the department was recruiting its inaugural class.
Wu Min-han, 20, who sat front row with his mother, didn’t need much convincing.
He had first applied to college to major in mathematics, but dropped out after he lost interest in the subject. Then he read about the new microelectronics program and decided to apply. He’s waiting to hear.
“This department could have a pretty positive impact on my future career prospects,” he said.
Others were torn.
Lian Yu-yan, 18, said that while the new department seems impressive, she’s also interested in majoring in mechanical engineering and photonics. She hopes to find a high-paid tech job after graduating from college, but wants to keep her options open.
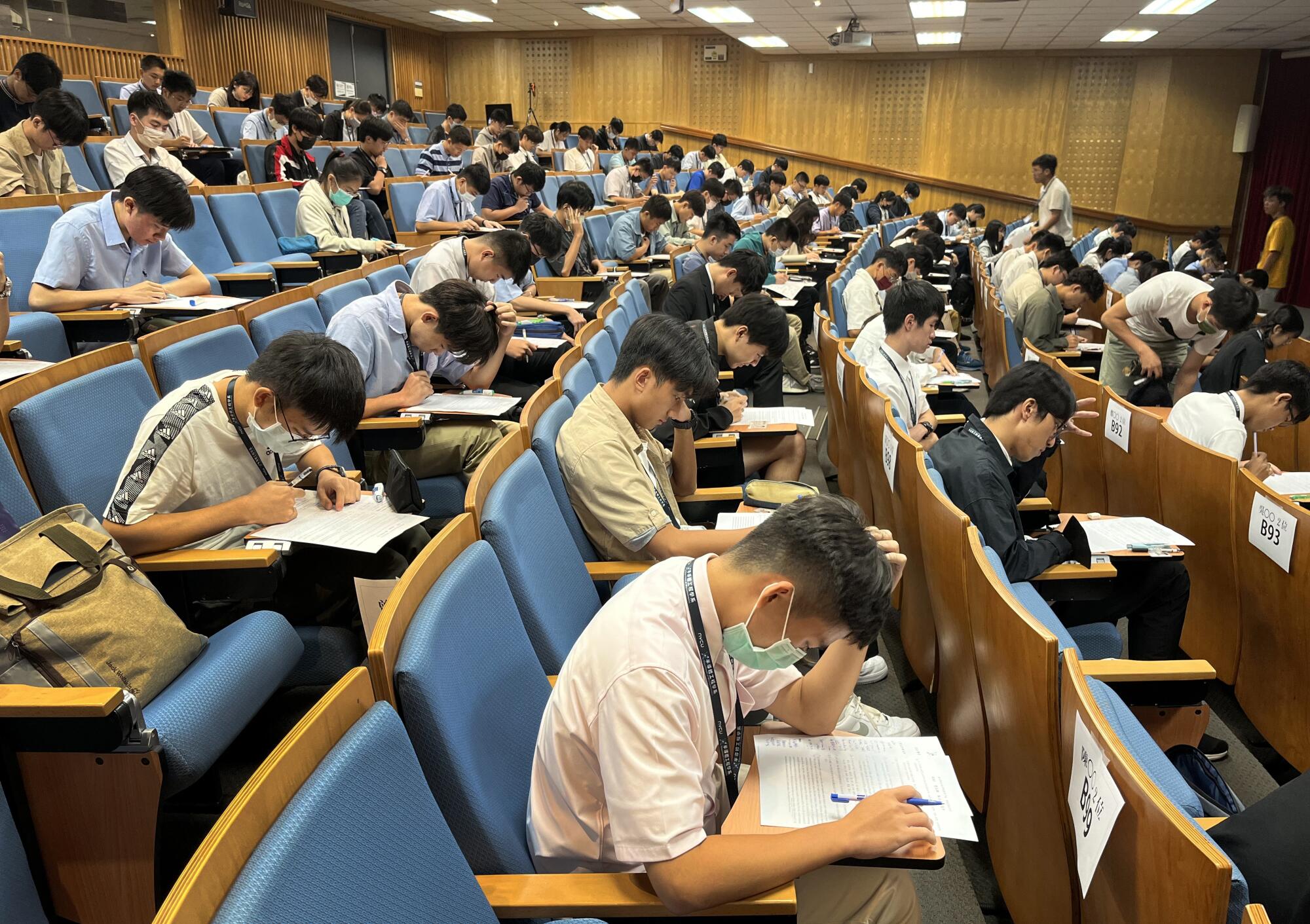

Prospective students for a new microelectronics department at NYCU take an entrance exam.
(Xin-yun Wu / For The Times)
Her father, who accompanied her to the event, has worked in the semiconductor industry and sees high growth potential with the evolution of AI. However, that hasn’t done much to persuade his daughter.
“You can’t control Gen Z,” he said with a laugh and a shrug.
Many prospective students competing for the 65 slots in next semester’s program listed salary and job stability among their top considerations. In Taiwan, there are few industries that can compete with semiconductors on pay and prestige.
As the rise of electric vehicles, artificial intelligence and other advanced technologies demand more semiconductors, many nations are making chip self-sufficiency a top priority.
In the U.S., Europe and Asia, governments have announced more than $316 billion in tax incentives for the semiconductor industry since 2021, according to Semiconductor Industry Assn. and the Boston Consulting Group.
A May report by those organizations projected that private companies will spend an additional $2.3 trillion through 2032 to build more facilities that make semiconductors, also known as fabrication plants, or fabs.
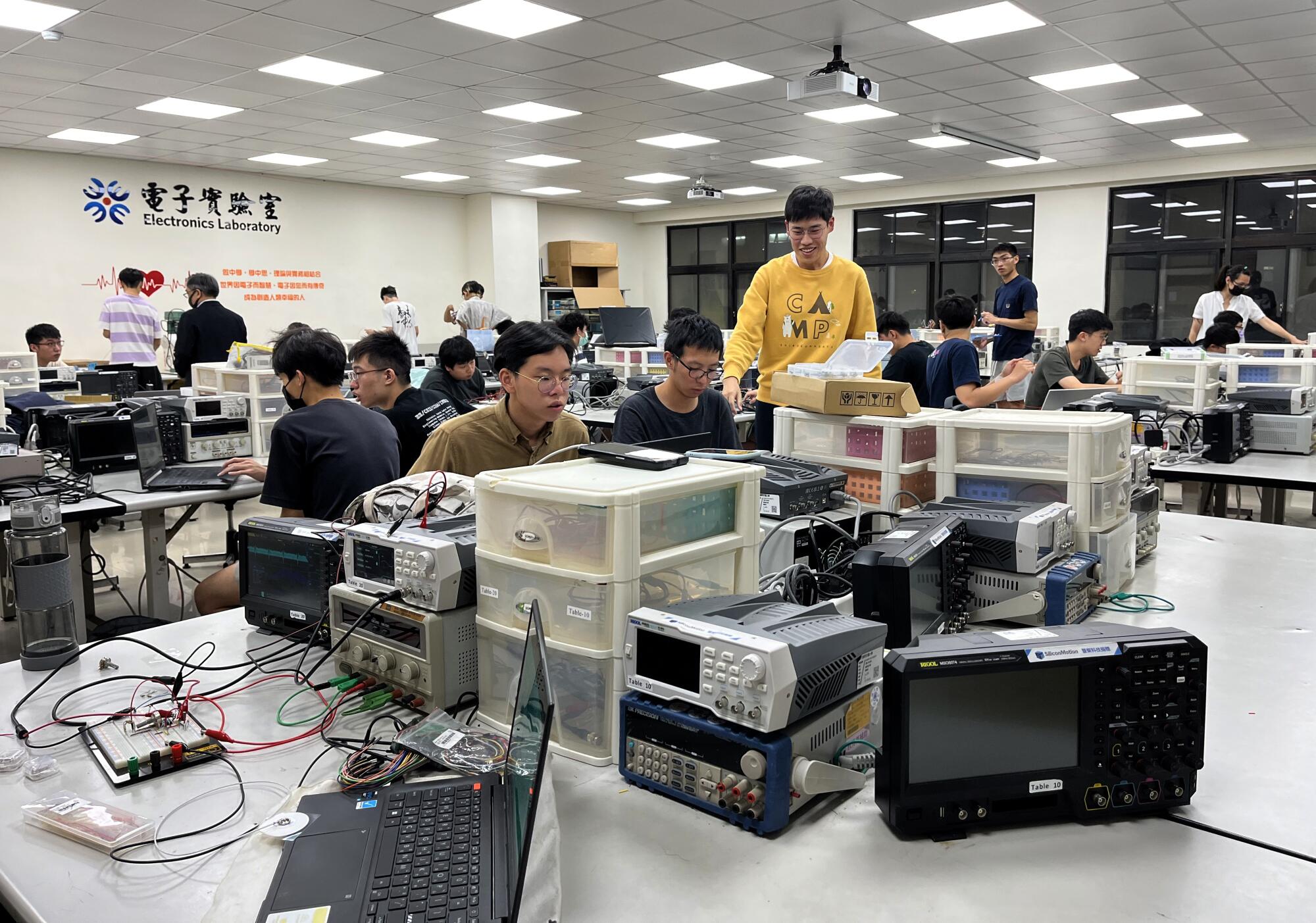

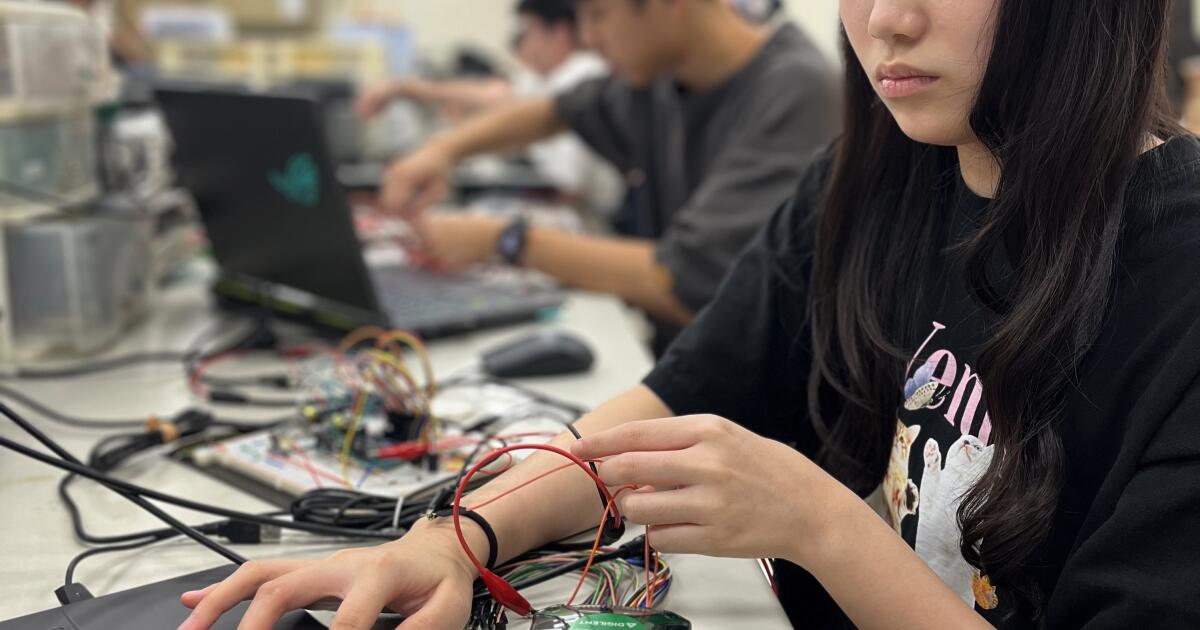
NYCU students work on building ECG heart monitors in Thursday evening lab.
(Stephanie Yang / Los Angeles Times)
Meanwhile, the expansion of chip-making capabilities is exacerbating another shortage: in the people trained to make them.
As the global battle for talent heats up and Taiwan loses manufacturing market share, the island has even more incentive to cultivate its next generation of workers.
Known as Taiwan’s “silicon shield,” the semiconductor industry is considered so critical to the global economy that it could deter Beijing, which lays claim to the island democracy, from launching a military assault. Taiwanese often refer to Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, the world’s largest chipmaker and a major Apple supplier, as the “sacred mountain protecting the nation.”
In his presentation, Ker gave another example of the industry’s indispensability. When Taiwan’s worst earthquake in a quarter-century hit in April, factory workers were evacuated but quickly returned — a sign, Ker said, of the manufacturing hub’s resilience.
But to Su Xin-zheng, a second-year engineering student at NYCU, the natural disaster response was representative of the drudgery required to keep churning out so many of the world’s chips.

Su Xin-zheng, a second-year student, works on his final project in electronics engineering lab.
(Xin-yun Wu / For The Times)
“People are always on call,” said Su, who added that he would prioritize having leisure time over a hefty salary. “We saw that they all went back in to protect the machines.”
Industry veterans evoke brutal hours and sacrifice when they describe how Taiwan built its semiconductor industry from the ground up. With black humor they speak, metaphorically, of ruining their livers by working through the night.
They fear that the younger generation is less inclined to such punishing work.
In particular, the growing emphasis on work-life balance is eroding interest in jobs at the fabrication plants that Taiwan and TSMC are known for.
For the past two years, labor demand in manufacturing has exceeded that of other parts of the chip-making process, such as designing the circuit boards or packaging them after they are made, according to the local recruitment platform 104 Job Bank. Engineering students enrolled at NYCU said such jobs seemed draining, with lower pay than research or design positions.
Ting Cheng-wei, 23, frequents anonymous online forums to learn more about the salaries and job descriptions at different companies. That’s how he knows that manufacturing positions, which require full-body suits to guard against contamination and 12-hour shifts on two-day rotations, don’t appeal to him.
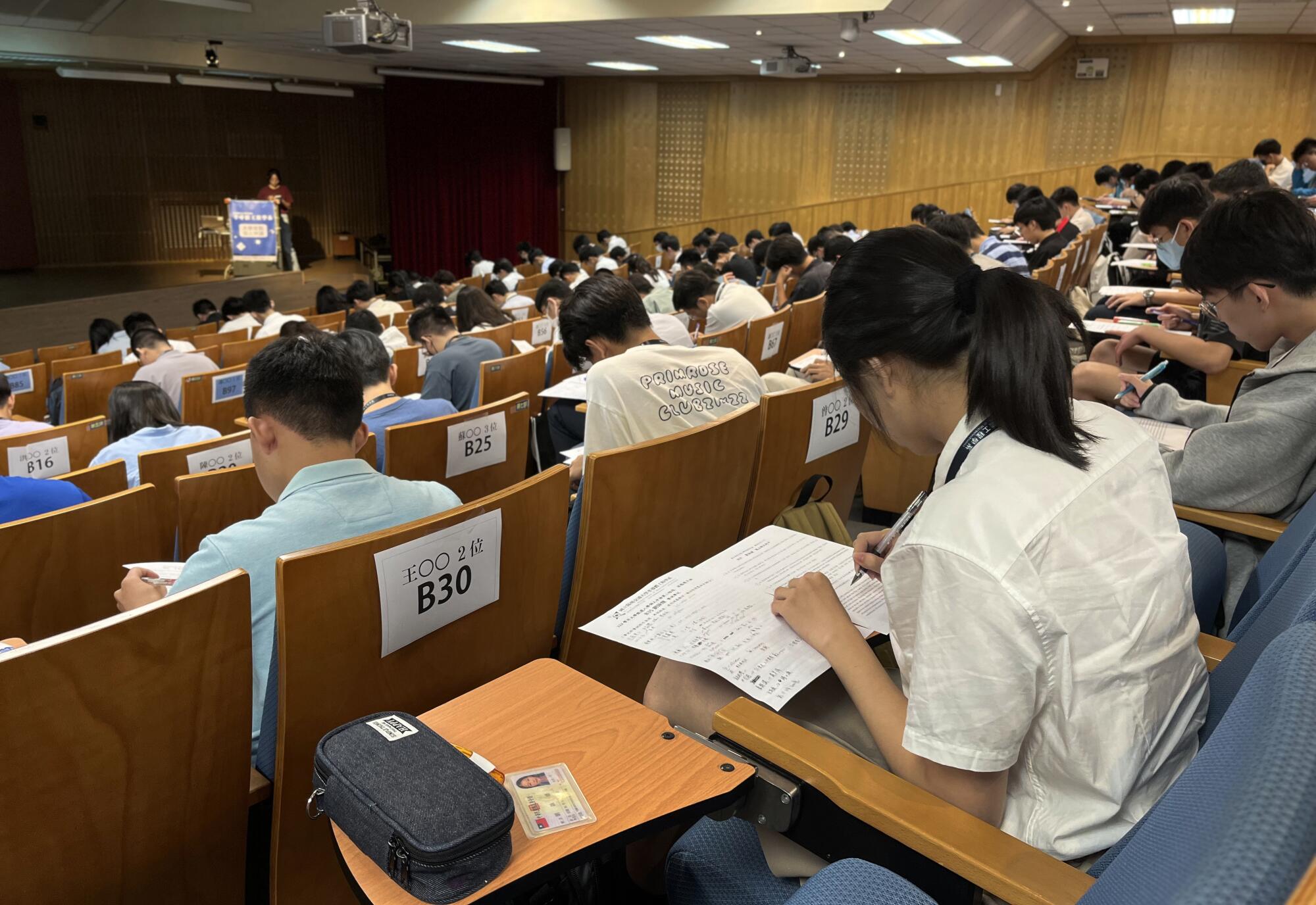

Students attend a recruitment event for a program created to train the next generation of semiconductor workers.
(Xin-yun Wu / For The Times)
“Working in the fab seems like working as a laborer,” said Ting, a master’s student and teaching assistant at the university. “Why would I work at a fab when I can sit in an office with higher pay?”
He speculated that job shortages at semiconductor plants could be solved by simply offering more money.
That would be enough for 19-year-old Wei Yu-han, who was ambivalent about semiconductors after her first year studying mechanical engineering. After visiting a fab on a school trip, she thought the work seemed straightforward and well-paid.
“I probably just brainwashed myself into liking it,” she said. “I can give up my freedom for money.”
At the end of the introductory seminar, all students in attendance took a short entrance exam as part of their applications. Still, enrollment in the new department is restricted by another squeeze on human resources — Ker added that the school is desperately looking to hire more semiconductor teachers as well.
Special correspondent Xin-yun Wu in Taipei contributed to this report.

Business
How our AI bots are ignoring their programming and giving hackers superpowers

Welcome to the age of AI hacking, in which the right prompts make amateurs into master hackers.
A group of cybercriminals recently used off-the-shelf artificial intelligence chatbots to steal data on nearly 200 million taxpayers. The bots provided the code and ready-to-execute plans to bypass firewalls.
Although they were explicitly programmed to refuse to help hackers, the bots were duped into abetting the cybercrime.
According to a recent report from Israeli cybersecurity firm Gambit Security, hackers last month used Claude, the chatbot from Anthropic, to steal 150 gigabytes of data from Mexican government agencies.
Claude initially refused to cooperate with the hacking attempts and even denied requests to cover the hackers’ digital tracks, the experts who discovered the breach said. The group pummelled the bot with more than 1,000 prompts to bypass the safeguards and convince Claude they were allowed to test the system for vulnerabilities.
AI companies have been trying to create unbreakable chains on their AI models to restrain them from helping do things such as generating child sexual content or aiding in sourcing and creating weapons. They hire entire teams to try to break their own chatbots before someone else does.
But in this case, hackers continuously prompted Claude in creative ways and were able to “jailbreak” the chatbot to assist them. When they encountered problems with Claude, the hackers used OpenAI’s ChatGPT for data analysis and to learn which credentials were required to move through the system undetected.
The group used AI to find and exploit vulnerabilities, bypass defences, create backdoors and analyze data along the way to gain control of the systems before they stole 195 million identities from nine Mexican government systems, including tax records, vehicle registration as well as birth and property details.
AI “doesn’t sleep,” Curtis Simpson, chief executive of Gambit Security, said in a blog post. “It collapses the cost of sophistication to near zero.”
“No amount of prevention investment would have made this attack impossible,” he said.
Anthropic did not respond to a request for comment. It told Bloomberg that it had banned the accounts involved and disrupted their activity after an investigation.
OpenAI said it is aware of the attack campaign carried out using Anthropic’s models against the Mexican government agencies.
“We also identified other attempts by the adversary to use our models for activities that violate our usage policies; our models refused to comply with these attempts,” an OpenAI spokesperson said in a statement. “We have banned the accounts used by this adversary and value the outreach from Gambit Security.”
Instances of generative AI-assisted hacking are on the rise, and the threat of cyberattacks from bots acting on their own is no longer science fiction. With AI doing their bidding, novices can cause damage in moments, while experienced hackers can launch many more sophisticated attacks with much less effort.
Earlier this year, Amazon discovered that a low-skilled hacker used commercially available AI to breach 600 firewalls. Another took control of thousands of DJI robot vacuums with help from Claude, and was able to access live video feed, audio and floor plans of strangers.
“The kinds of things we’re seeing today are only the early signs of the kinds of things that AIs will be able to do in a few years,” said Nikola Jurkovic, an expert working on reducing risks from advanced AI. “So we need to urgently prepare.”
Late last year, Anthropic warned that society has reached an “inflection point” in AI use in cybersecurity after disrupting what the company said was a Chinese state-sponsored espionage campaign that used Claude to infiltrate 30 global targets, including financial institutions and government agencies.
Generative AI also has been used to extort companies, create realistic online profiles by North Korean operatives to secure jobs in U.S. Fortune 500 companies, run romance scams and operate a network of Russian propaganda accounts.
Over the last few years, AI models have gone from being able to manage tasks lasting only a few seconds to today’s AI agents working autonomously for many hours. AI’s capability to complete long tasks is doubling every seven months.
“We just don’t actually know what is the upper limit of AI’s capability, because no one’s made benchmarks that are difficult enough so the AI can’t do them,” said Jurkovic, who works at METR, a nonprofit that measures AI system capabilities to cause catastrophic harm to society.
So far, the most common use of AI for hacking has been social engineering. Large language models are used to write convincing emails to dupe people out of their money, causing an eight-fold increase in complaints from older Americans as they lost $4.9 billion in online fraud in 2025.
“The messages used to elicit a click from the target can now be generated on a per-user basis more efficiently and with fewer tell-tale signs of phishing,” such as grammatical and spelling errors, said Cliff Neuman, an associate professor of computer science at USC.
AI companies have been responding using AI to detect attacks, audit code and patch vulnerabilities.
“Ultimately, the big imbalance stems from the need of the good-actors to be secure all the time, and of the bad-actors to be right only once,” Neuman said.
The stakes around AI are rising as it infiltrates every aspect of the economy. Many are concerned that there is insufficient understanding of how to ensure it cannot be misused by bad actors or nudged to go rogue.
Even those at the top of the industry have warned users about the potential misuse of AI.
Dario Amodei, the CEO of Anthropic, has long advocated that the AI systems being built are unpredictable and difficult to control. These AIs have shown behaviors as varied as deception and blackmail, to scheming and cheating by hacking software.
Still, major AI companies — OpenAI, Anthropic, xAI, and Google — signed contracts with the U.S. government to use their AIs in military operations.
This last week, the Pentagon directed federal agencies to phase out Claude after the company refused to back down on its demand that it wouldn’t allow its AI to be used for mass domestic surveillance and fully autonomous weapons.
“The AI systems of today are nowhere near reliable enough to make fully autonomous weapons,” Amodei told CBS News.
Business
iPic movie theater chain files for bankruptcy

The iPic dine-in movie theater chain has filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection and intends to pursue a sale of its assets, citing the difficult post-pandemic theatrical market.
The Boca Raton, Fla.-based company has 13 locations across the U.S., including in Pasadena and Westwood, according to a Feb. 25 filing in U.S. Bankruptcy Court in the Southern District of Florida, West Palm Beach division.
As part of the bankruptcy process, the Pasadena and Westwood theaters will be permanently closed, according to WARN Act notices filed with the state of California’s Employment Development Department.
The company came to its conclusion after “exploring a range of possible alternatives,” iPic Chief Executive Patrick Quinn said in a statement.
“We are committed to continuing our business operations with minimal impact throughout the process and will endeavor to serve our customers with the high standard of care they have come to expect from us,” he said.
The company will keep its current management to maintain day-to-day operations while it goes through the bankruptcy process, iPic said in the statement. The last day of employment for workers in its Pasadena and Westwood locations is April 28, according to a state WARN Act notice. The chain has 1,300 full- and part-time employees, with 193 workers in California.
The theatrical business, including the exhibition industry, still has not recovered from the pandemic’s effect on consumer behavior. Last year, overall box office revenue in the U.S. and Canada totaled about $8.8 billion, up just 1.6% compared with 2024. Even more troubling is that industry revenue in 2025 was down 22.1% compared with pre-pandemic 2019’s totals.
IPic noted those trends in its bankruptcy filing, describing the changes in consumer behavior as “lasting” and blaming the rise of streaming for “fundamentally” altering the movie theater business.
“These industry shifts have directly reduced box office revenues and related ancillary revenues, including food and beverage sales,” the company stated in its bankruptcy filing.
IPic also attributed its decision to rising rents and labor costs.
The company estimated it owed about $141,000 in taxes and about $2.7 million in total unsecured claims. The company’s assets were valued at about $155.3 million, the majority of which coming from theater equipment and furniture. Its liabilities totaled $113.9 million.
The chain had previously filed for bankruptcy protection in 2019.
Business
Startup Varda Space Industries snags former Mattel plant in El Segundo

In an expansion of its business of processing pharmaceuticals in Earth’s orbit, Varda Space Industries is renting a large El Segundo plant where toy manufacturer Mattel used to design Hot Wheels and Barbie dolls.
The plant in El Segundo’s aerospace corridor will be an extension of Varda Space Industries’ headquarters in a much smaller building on nearby Aviation Boulevard.
Varda will occupy a 205,443-square-foot industrial and office campus at 2031 E. Mariposa Ave., which will give it additional capacity to manufacture spacecraft at scale, the company said.
Originally built in the 1940s as an aircraft facility, the complex has a history as part of aerospace and defense industries that have long shaped the South Bay and is near a host of major defense and space contractors. It is also close to Los Angeles Air Force Base, headquarters to the Space Systems Command.
Workers test AstroForge’s Odin asteroid probe, which was lost in space after launch this year.
(Varda Space Industries)
Varda is one of a new generation of aerospace startups that have flourished in Southern California and the South Bay over the last several years, particularly in El Segundo, often with ties to SpaceX.
Elon Musk’s company, founded in 2002 in El Segundo, has revolutionized the industry with reusable rockets that have radically lowered the cost of lifting payloads into space. Though it has moved its headquarters to Texas, SpaceX retains large-scale operations in Hawthorne.
Varda co-founder and Chief Executive Will Bruey is a former SpaceX avionics engineer, and the company’s spacecraft are launched on SpaceX’s workhorse Falcon 9 rockets from Vandenberg Space Force Base in Santa Barbara County.
Varda makes automated labs that look like cylindrical desktop speakers, which it sends into orbit in capsules and satellite platforms it also builds. There, in microgravity, the miniature labs grow molecular crystals that are purer than those produced in Earth’s gravity for use in pharmaceuticals.
It has contracts with drug companies and also the military, which tests technology at hypersonic speeds as the capsules return to Earth.
Its fifth capsule was launched in November and returned to Earth in late January; its next mission is set in the coming weeks. Varda has more than 10 missions scheduled on Falcon 9s through 2028.
For the last several decades, the Mariposa Avenue property served as the research and development center for Mattel Toys. El Segundo has also long been a center for the toy industry as companies like to set up shop in the shadow of Mattel.
The Mattel facility “has always been an exceptional property with a legacy tied to aerospace innovation, and leasing to Varda Space Industries feels like a natural continuation of that story,” said Michael Woods, a partner at GPI Cos., which owns the property.
“We are proud to support a company that is genuinely pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, and are excited to watch Varda grow and thrive here in El Segundo,” Woods said.
As one of the country’s most active hubs of aerospace and defense innovation, El Segundo has seen its industrial property vacancy fall to 3.4% on demand from space companies, government contractors and technology startups, real estate brokerage CBRE said.
Successful startups often have to leave the neighborhood when they want to expand, real estate broker Bob Haley of CBRE said. The 9-acre Mattel facility was big enough to keep Varda in the city.
Last year, Varda subleased about 55,000 square feet of lab space from alternative protein company Beyond Meat at 888 Douglas St. in El Segundo, which it started moving into in June.
Varda will get the keys to its new building in December and spend four to eight months building production and assembly facilities as it ramps up operations. By the end of next year, it expects to have constructed 10 more spacecraft.
In the future, Varda could consolidate offices there, given its size. Currently, though, the plan is to retain all properties, creating a campus of three buildings within a mile of one another that are served by the company’s transportation services, Chief Operating Officer Jonathan Barr said.
“We already have Varda-branded shuttles running up and down Aviation Boulevard,” he said.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Wisconsin4 days ago
Wisconsin4 days agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Massachusetts1 week ago
Massachusetts1 week agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Maryland5 days ago
Maryland5 days agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Massachusetts3 days ago
Massachusetts3 days agoMassachusetts man awaits word from family in Iran after attacks
-

 Florida5 days ago
Florida5 days agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Denver, CO1 week ago
Denver, CO1 week ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Oregon6 days ago
Oregon6 days ago2026 OSAA Oregon Wrestling State Championship Results And Brackets – FloWrestling


















