Business
Column: How a surgeon general's warning and a Supreme Court ruling may place gun control on the front burner

For decades, gun control policy in the U.S. has been virtually untouchable — except through efforts to make America’s gun culture deadlier, raising the toll of innocent victims.
Two recent developments suggest that the ground may finally be shifting toward rationality.
One is an “advisory” from Surgeon General Vivek Murthy identifying firearm violence as a public health crisis — the boldest statement from a government official calling attention to the horrific consequences of the nation’s turn away from common sense gun control.
Originalism tells judges not to consider the practical consequences of their interpretations.
— Former Supreme Court Justice Stephen Breyer explains why America can’t pass workable gun laws
Murthy’s report is in the finest tradition of public health policy, akin to the 1964 report by Surgeon General Luther Terry that placed the links between smoking and cancer, bronchitis and coronary disease into the public record.
As Murthy himself observes, that initiative placed the U.S. on a course of tobacco regulation that reduced the prevalence of smoking from 42% of adults in 1964 to 11.5% in 2022.
The other is a June 21 Supreme Court decision finding that laws barring domestic abusers from possessing guns are constitutional. The ruling is an indication — albeit slight — that a majority on the court has concluded that earlier decisions that found almost any state and local restrictions violated the 2nd Amendment were far too indulgent.
Let’s take the advisory and ruling in order.
Murthy’s advisory is an extraordinary synopsis of the toll of America’s fascination with firearms and its failure to regulate gun ownership.
Firearms passed motor vehicles as the leading cause of death of children and adolescents in the U.S. in 2019.
(U.S. Surgeon General)
He reports that firearms are now the leading cause of death among children and adolescents, having passed motor vehicles in 2019. In 2022, guns killed more than 48,200 Americans through homicides, suicides and accidents, rising by about 16,000 over the previous 10 years.
Murthy’s report notes that guns are used in 55% of all suicide attempts and that their lethality in those cases is unmatched — nearly 90% end in death, higher than any other method.
The report treats mass shootings (defined as those with four or more victims, not counting the shooter) soberly. These account for only about 1% of all firearm deaths, but their impact is far greater due to their “outsized collective trauma on society” and their “strong negative effect on the public’s perception of safety.” One in three adults “say fear prevents them from going to certain places or events.”
Murthy’s report puts the lie to the familiar claim by Republicans and gun rights fanatics that the problem, especially when it comes to mass shooting, is mental health, not firearms.
House Speaker Mike Johnson (R-La.), for instance, told Fox News anchor Sean Hannity in October, after a gunman killed 18 people in Lewiston, Maine: “Mental health, obviously, as in this case, is a big issue, and we have got to seriously address that as a society and as a government.”
Yet Murthy reports that “one’s mental health diagnosis or psychological profile alone is not a strong predictor of perpetrating violence of any type…. Importantly, most people with serious mental illness are not violent against others. In fact, people with serious mental illnesses are more likely to be victims of violence.”
For all their nattering about the need to address mental health, anyway, Republicans have never lifted a finger to promote any programs to do so.
Now to the Supreme Court.
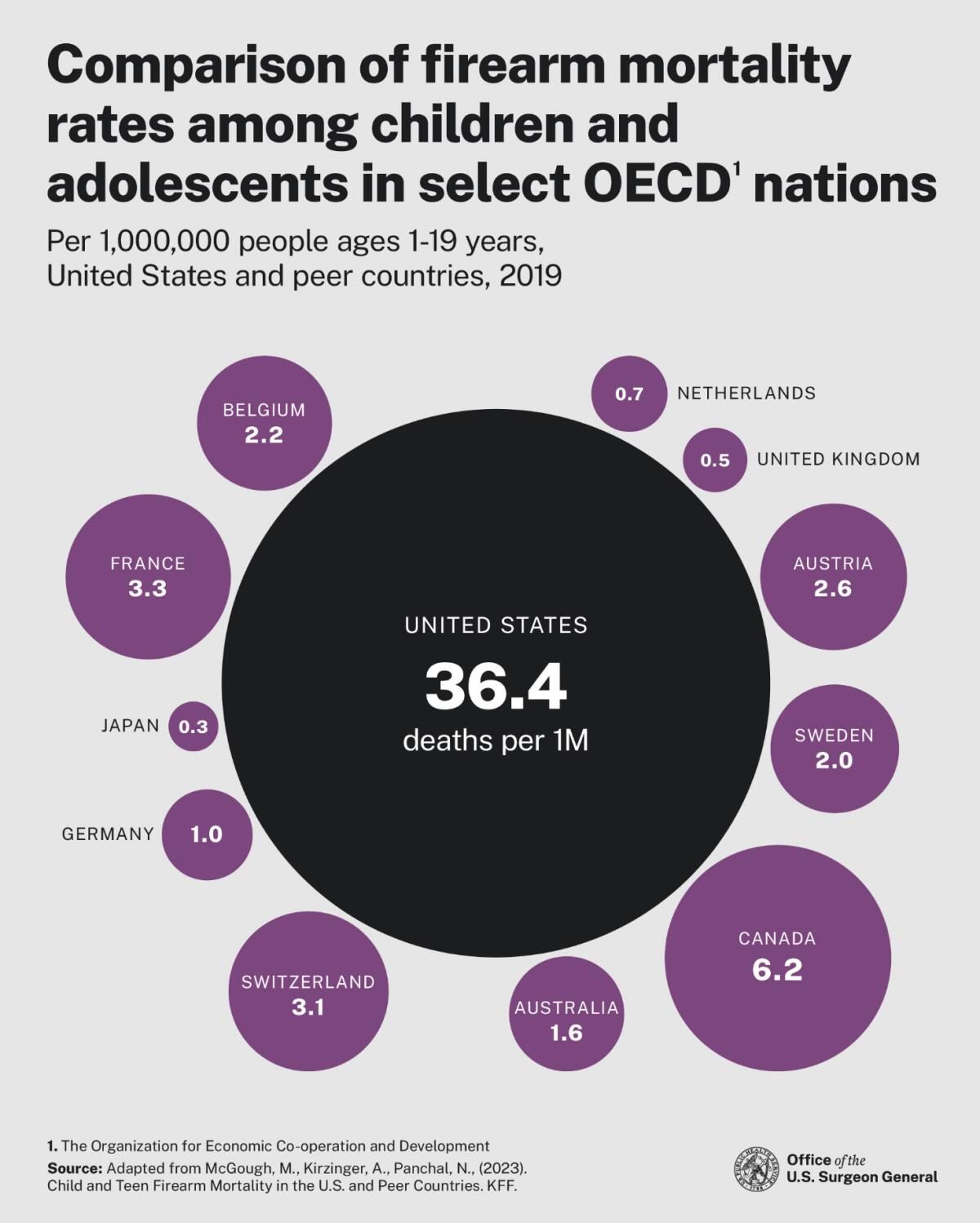
The rate of firearm deaths of childen and adolescents in the U.S. vastly surpassed the rates in other developed countries.
(U.S. Surgeon General)
Rahimi v. United States, which yielded an 8-1 decision on June 21, is the first gun-rights case to come before the court since a 2022 decision known as Bruen, in which Clarence Thomas, writing for a 6-3 majority, essentially found that all modern efforts to regulate firearms are unconstitutional.
Thomas held, in effect, that the only legitimate basis for judging gun laws is historical — weighing the laws against the language of the 2nd Amendment to determine how the amendment was viewed by its drafters in 1789 and how their approach was dictated by the political and social context of that time.
In Bruen, Thomas ridiculed Justice Stephen Breyer’s dissent (with which justices Sonia Sotomayor and Elena Kagan concurred). Breyer had opened his argument with nine pages of statistics about gun ownership and its consequences for health and safety.
“It is hard to see what legitimate purpose can possibly be served” by Breyer’s figures, Thomas sneered. “Why, for example, does the dissent think it is relevant to recount the mass shootings that have occurred in recent years?”
In Rahimi, however, Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. asserted that the consequences of unrestricted gun ownership were highly relevant. To be fair, this was easy. The record made clear that Zackey Rahimi, the gun owner at the center of the case, was one vicious specimen indeed. As Roberts laid out in the opening three pages of his majority opinion, Rahimi had beat up his girlfriend (the mother of his child) and fired in her direction or at a bystander as she fled his grasp.
After she got a restraining order against him, he stalked her, threatened a different woman with a gun, was suspected by police of at least five other shootings, fired at motorists in at least two road-rage incidents and fired his gun indiscriminately at least two other times. Police searched his home and found a pistol and a rifle. He was charged under a Texas law that criminalized possessing a gun while under a retraining order due to domestic violence.
Despite all that, the 5th Circuit Court of Appeals overturned Rahimi’s conviction, citing Bruen.
Roberts’ decision in Rahimi is a step toward ratcheting back the Bruen effect, in which almost every gun regulation is suspect. That brings us to the “originalism” principle, which undergirds the court conservatives’ distaste for restrictions on gun rights. As expressed by Thomas in his Bruen opinion, originalism holds that interpreting the constitution must depend on the “public understanding of a legal text in the period after its enactment or ratification.”
As the now-retired Breyer put it in a recent essay, “the originalist, instead of looking to the text and asking what the words mean now, may well ask what they would have meant to an ordinary eighteenth-century person” and applies them to the world of today. (Breyer isn’t a fan of originalism.)
Scholars such as Stanford historian Jack Rakove argue that interpretations of the 2nd Amendment depend more on originalism than any other provisions of the Constitution. Its impact emerged most notably in the Supreme Court’s so-called Heller decision. In that 2008 decision written by Justice Antonin Scalia, a 5-4 majority overturned a Washington, D.C., ordinance largely barring citizens from possessing handguns for self-defense in their own home.
Heller overturned more than the D.C. law — it upended more than 200 years of scholarship about the meaning of the 2nd Amendment’s preamble, which links “the right of the people to keep and bear arms” to the establishment of “a well regulated Militia.”
As Breyer pointed out, historians and linguists had argued (in a friend-of-the-court brief in the Bruen case) that the phrase “bear arms” overwhelmingly referred to “war, soldiering, or other forms of armed action by a group” — not to an individual right. Heller, however, established an individual right to gun ownership for the first time.
Bruen expanded that right to gun ownership outside the home. The ruling deemed unconstitutional a New York law requiring citizens to have a license to carry firearms in public. America’s rising tide of gun violence can fairly be traced to Heller.
Scholars have pointed to numerous problems with originalism. One is that judges are (usually) not historians. They may be utterly at sea when trying to find the apposite historical application to contemporary conditions.
The drafters of the 2nd Amendment, as it happens, were concerned about the public threat of a government’s standing army; historians argue that the amendment was designed to prevent the federal government from interfering with the creation of state militias.
Firearms in the 18th century were “not nearly as threatening or lethal as those available today,” Rakove writes; people in that era were concerned not with threats from “casual strangers, embittered family members, violent youth gangs, freeway snipers, and careless weapons keepers.”
In other words, applying an 18th century mind-set to 21st century conditions is a fool’s errand. “Originalism” only interferes with judges’ responsibility to ponder the real-world impacts of their decision — their option, Rakove says, is to “ransack” the historical record for quotations that can support their preexisting goals.
“Originalism,” says Breyer, “tells judges not to consider the practical consequences of their interpretations.” Its product is the paralysis of federal, state, and local efforts to regulate gun ownership. It’s also responsible for the contraction of individual rights being rolled back almost gleefully by the current Supreme Court majority, notably abortion and other women’s reproductive healthcare rights, as originalists argue that the concept of privacy on which those other rights are based can’t be found in the Constitution.
It’s also proper to note that the public during the time the 2nd Amendment was drafted, enacted and ratified is very different from the public affected by its consequences today. In 1791, among other distinctions, enslaved people were not considered citizens and women could not vote. Who set the terms back then under which today’s Americans must live?
Rahimi won’t solve the mess in gun regulation created by the Heller and Bruen rulings. A multitude of pending cases might strengthen it or undermine it. But at least it’s a step back from the abyss.
Murthy’s advisory gives a similar impression of being a first step on a path that might lead nowhere. He calls for more research on violence prevention strategies and laws preventing children’s access to guns, universal background checks, banning assault weapons and restricting the carrying of loaded firearms in public.
The bottom line, of course, is that America’s gun violence crisis can only be solved by fewer guns. There’s a long road ahead to reaching that goal.

Business
Paramount outlines plans for Warner Bros. cuts

Many in Hollywood fear Warner Bros. Discovery’s sale will trigger steep job losses — at a time when the industry already has been ravaged by dramatic downsizing and the flight of productions from Los Angeles.
David Ellison‘s Paramount Skydance is seeking to allay some of those concerns by detailing its plans to save $6 billion, including job cuts, should Paramount succeed in its bid to buy the larger Warner Bros. Discovery.
Leaders of the combined company would search for savings by focusing on “duplicative operations across all aspects of the business — specifically back office, finance, corporate, legal, technology, infrastructure and real estate,” Paramount said in documents filed with the Securities & Exchange Commission.
Paramount is locked in an uphill battle to buy the storied studio behind Batman, Harry Potter, Scooby-Doo and “The Big Bang Theory.” The firm’s proposed $108.4-billion deal would include swallowing HBO, HBO Max, CNN, TBS, Food Network and other Warner cable channels.
Warner’s board prefers Netflix’s proposed $82.7-billion deal, and has repeatedly rebuffed the Ellison family’s proposals. That prompted Paramount to turn hostile last month and make its case directly to Warner investors on its website and in regulatory filings.
Shareholders may ultimately decide the winner.
Paramount previously disclosed that it would target $6 billion in synergies. And it has stressed the proposed merger would make Hollywood stronger — not weaker. The firm, however, recently acknowledged that it would shave about 10% from program spending should it succeed in combining Paramount and Warner Bros.
Paramount said the cuts would come from areas other than film and television studio operations.
A film enthusiast and longtime producer, David Ellison has long expressed a desire to grow the combined Paramount Pictures and Warner Bros. slate to more than 30 movies a year. His goal is to keep Paramount Pictures and Warner Bros. stand-alone studios.
This year, Warner Bros. plans to release 17 films. Paramount has said it wants to nearly double its output to 15 movies, which would bring the two-studio total to 32.
“We are very focused on maintaining the creative engines of the combined company,” Paramount said in its marketing materials for investors, which were submitted to the SEC on Monday.
“Our priority is to build a vibrant, healthy business and industry — one that supports Hollywood and creative, benefits consumers, encourages competition, and strengthens the overall job market,” Paramount said.
If the deal goes through, Paramount said that it would become Hollywood’s biggest spender — shelling out about $30 billion a year on programming.
In comparison, Walt Disney Co. has said it plans to spend $24 billion in the current fiscal year.
Paramount also added a dig at Warner management, saying: “We expect to make smarter decisions about licensing across linear networks and streaming.”
Some analysts have wondered whether Paramount would sell one of its most valuable assets — the historic Melrose Avenue movie lot — to raise money to pay down debt that a Warner acquisition would bring.
Paramount is the only major studio to be physically located in Hollywood and its studio lot is one of the company’s crown jewels. That’s where “Sunset Boulevard,” several “Star Trek” movies and parts of “Chinatown” were filmed.
A Paramount spokesperson declined to comment.
Sources close to the company said Paramount would scrutinize the numerous real estate leases in an effort to bring together far-flung teams into a more centralized space.
For example, CBS has much of its administrative offices on Gower in Hollywood, blocks away from the Paramount lot. And HBO maintains its operations in Culver City — miles from Warner’s Burbank lot.
Paramount pushed its deadline to Feb. 20 for Warner investors to tender their shares at $30 a piece.
The tender offer was set to expire last week, but Paramount extended the window after failing to solicit sufficient interest among Warner shareholders.
Some analysts believe Paramount may have to raise its bid to closer to $34 a share to turn heads. Paramount last raised its bid Dec. 4 — hours before the auction closed and Netflix was declared the winner.
Paramount also has filed proxy materials to ask Warner shareholders to reject the Netflix deal at an upcoming stockholder meeting.
Earlier this month, Netflix amended its bid, converting its $27.75-a-share offer to all-cash to defuse some of Paramount’s arguments that it had a stronger bid.
Should Paramount win Warner Bros., it would need to line up $94.65 billion in debt and equity.
Billionaire Larry Ellison has pledged to backstop $40.4 billion for the equity required. Paramount’s proposed financing relies on $24 billion from royal families in Saudi Arabia, Qatar and Abu Dhabi.
The deal would saddle Paramount with more than $60 billion of debt — which Warner board members have argued may be untenable.
“The extraordinary amount of debt financing as well as other terms of the PSKY offer heighten the risk of failure to close,” Warner board members said in a filing earlier this month.
Paramount would also have to absorb Warner’s debt load, which currently tops $30 billion.
Netflix is seeking to buy the Warner Bros. television and movie studios, HBO and HBO Max. It is not interested in Warner’s cable channels, including CNN. Warner wants to spin off its basic cable channels to facilitate the Netflix deal.
Analysts say both deals could face regulatory hurdles.
Business
Southwest’s open seating ends with final flight

After nearly 60 years of its unique and popular open-seating policy, Southwest Airlines flew its last flight with unassigned seats Monday night.
Customers on flights going forward will choose where they sit and whether they want to pay more for a preferred location or extra leg room. The change represents a significant shift for Southwest’s brand, which has been known as a no-frills, easygoing option compared to competing airlines.
While many loyal customers lament the loss of open seating, Southwest has been under pressure from investors to boost profitability. Last year, the airline also stopped offering free checked bags and began charging $35 for one bag and $80 for two.
Under the defunct open-seating policy, customers could choose their seats on a first-come, first-served basis. On social media, customers said the policy made boarding faster and fairer. The airline is now offering four new fare bundles that include tiered perks such as priority boarding, preferred seats, and premium drinks.
“We continue to make substantial progress as we execute the most significant transformation in Southwest Airlines’ history,” said chief executive Bob Jordan in a statement with the company’s third-quarter revenue report. “We quickly implemented many new product attributes and enhancements [and] we remain committed to meeting the evolving needs of our current and future customers.”
Eighty percent of Southwest customers and 86% of potential customers prefer an assigned seat, the airline said in 2024.
Experts said the change is a smart move as the airline tries to stabilize its finances.
In the third quarter of 2025, the company reported passenger revenues of $6.3 billion, a 1% increase from the year prior. Southwest’s shares have remained mostly stable this year and were trading at around $41.50 on Tuesday.
“You’re going to hear nostalgia about this, but I think it’s very logical and probably something the company should have done years ago,” said Duane Pfennigwerth, a global airlines analyst at Evercore, when the company announced the seating change in 2024.
Budget airlines are offering more premium options in an attempt to increase revenue, including Spirit, which introduced new fare bundles in 2024 with priority check-in and their take on a first-class experience.
With the end of open seating and its “bags fly free” policy, customers said Southwest has lost much of its appeal and flexibility. The airline used to stand out in an industry often associated with rigidity and high prices, customers said.
“Open seating and the easier boarding process is why I fly Southwest,” wrote one Reddit user. “I may start flying another airline in protest. After all, there will be nothing differentiating Southwest anymore.”
Business
Contributor: The weird bipartisan alliance to cap credit card rates is onto something

Behind the credit card, ubiquitous in American economic life now for decades, stand a very few gigantic financial institutions that exert nearly unlimited power over how much consumers and businesses pay for the use of a small piece of plastic. American consumers and small businesses alike are spitting fire these days about the cost of credit cards, while the companies profiting from them are making money hand over fist.
We are now having a national conversation about what the federal government can do to lower the cost of credit cards. Sens. Bernie Sanders (I-Vt.) and Josh Hawley (R-Mo.), truly strange political bedfellows, have proposed a 10% cap. Now President Trump has too. But we risk spinning our wheels if we do not face facts about the underlying structure of this market.
We should dispense with the notion that the credit card business in the United States is a free market with robust competition. Instead, we have an oligopoly of dominant banks that issue them: JPMorgan Chase, Bank of America, American Express, Citigroup and Capital One, which together account for about 70% of all transactions. And we have a duopoly of networks: Visa and Mastercard, who process more than 80% of those transactions.
The results are higher prices for consumers who use the cards and businesses that accept them. Possibly the most telling statistic tracks the difference between borrowing benchmarks, such as the prime rate, and what you pay on your credit card. That markup has been rising steadily over the last 10 years and now stands at 16.4%. A Federal Reserve study found the problem in every card category, from your super-duper-triple-platinum card to subprime cardholders. Make no mistake, your bank is cranking up credit card rates faster than any overall increase.
If you are a small business owner, the situation is equally grim. Credit cards are a major source of credit for small businesses, at an increasingly dear cost. Also, businesses suffer from the fees Visa and Mastercard charge merchants on customer payments; those have climbed steadily as well because the two dominant processors use a variety of techniques to keep their grip on that market. Those fees nearly doubled in five years, to $111 billion in 2024. Largely passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices, these charges often rank as the second- or third-highest merchant cost, after real estate and labor.
There is nothing divinely ordained here. In other industrialized countries, the simple task of moving money — the basic function of Visa and Mastercard — is much, much less expensive. Consumer credit is likewise less expensive elsewhere in the world because of greater competition, tougher regulation and long-standing norms.
Now some American politicians want caps on card interest rates, a tool that absolutely has its place in consumer protection. A handful of states already have strict limits on interest rates, a proud legacy of an ethos of protecting the most vulnerable people against the biblical sin of usury. Texas imposes a 10% cap for lending to people in that state. Congress in 2006 chose to protect military service members via a 36% limit on interest they can be charged. In 2009, it banned an array of sneaky fees designed to extract more money from card users. Federal credit unions cannot charge more than 18% interest, including on credit cards. Brian Shearer from Vanderbilt University’s Policy Accelerator for Political Economy and Regulation has made a persuasive case for capping credit card rates for the rest of us too.
At the very least, there is every reason to ignore the stale serenade of the bank lobby that any regulation will only hurt the people we are trying to help. Credit still flows to soldiers and sailors. Credit unions still issue cards. States with usury caps still have functioning financial systems. And the 2009 law Congress passed convinced even skeptical economists that the result was a better market for consumers.
If consumers receive such commonsense protections, what’s at stake? Profit margins for banks and card networks, and there is no compelling public policy reason to protect those. Major banks have profit margins that exceed 30%, a level that is modest only compared with Visa and Mastercard, which average a margin of 45%. Meanwhile, consumers face $1. 3 trillion in debt. And retailers squeeze by with a margin around 3%; grocers make do with half that.
The market won’t fix what’s wrong with credit card fees, because the handful of businesses that control it are feasting at everyone else’s expense. We must liberate the market from the grip of the major banks and card processors and restore vibrant competition. Harnessing market forces to get better outcomes for consumers, in addition to smart regulation, is as American as apple pie.
Fortunately, Trump has endorsed — via social media — bipartisan legislation, the Credit Card Competition Act, that would crack open the Visa-Mastercard duopoly by allowing merchants to route transactions over competing networks. Here’s hoping he follows through by getting enough congressional Republicans on board.
That change would leave us with the megabanks still controlling the credit card market. One approach would be consumer-friendly regulation of other means of credit, such as buy-now-pay-later tools or innovative payment applications, by including protections that credit cards enjoy. Ideally, Congress would cap the size of banks, something it declined to do after the 2008 financial crisis, to the enduring frustration of reformers who sought structural change. Trump entered the presidency in 2017 calling for a new Glass-Steagall, the Depression-era law that broke up big banks, but he never pursued it.
Fast forward nine years, and we find rising negative sentiment among American voters, groaning under the weight of credit card debt and a cascade of junk fees from other industries. Populist ire at corporate power is rising. The race between the two major parties to ride that feeling to victory in the November midterm elections and beyond has begun. A movement to limit the power of big banks could be but a tweet away.
Carter Dougherty is the senior fellow for anti–monopoly and finance at Demand Progress, an advocacy group and think tank.
-

 Illinois6 days ago
Illinois6 days agoIllinois school closings tomorrow: How to check if your school is closed due to extreme cold
-

 Pittsburg, PA1 week ago
Pittsburg, PA1 week agoSean McDermott Should Be Steelers Next Head Coach
-

 Pennsylvania2 days ago
Pennsylvania2 days agoRare ‘avalanche’ blocks Pennsylvania road during major snowstorm
-

 Lifestyle1 week ago
Lifestyle1 week agoNick Fuentes & Andrew Tate Party to Kanye’s Banned ‘Heil Hitler’
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoMiami star throws punch at Indiana player after national championship loss
-

 Cleveland, OH1 week ago
Cleveland, OH1 week agoNortheast Ohio cities dealing with rock salt shortage during peak of winter season
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoRing claims it’s not giving ICE access to its cameras
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoContributor: New food pyramid is a recipe for health disasters
















