World
China accuses US of ‘slander, hype’ after aircraft clash
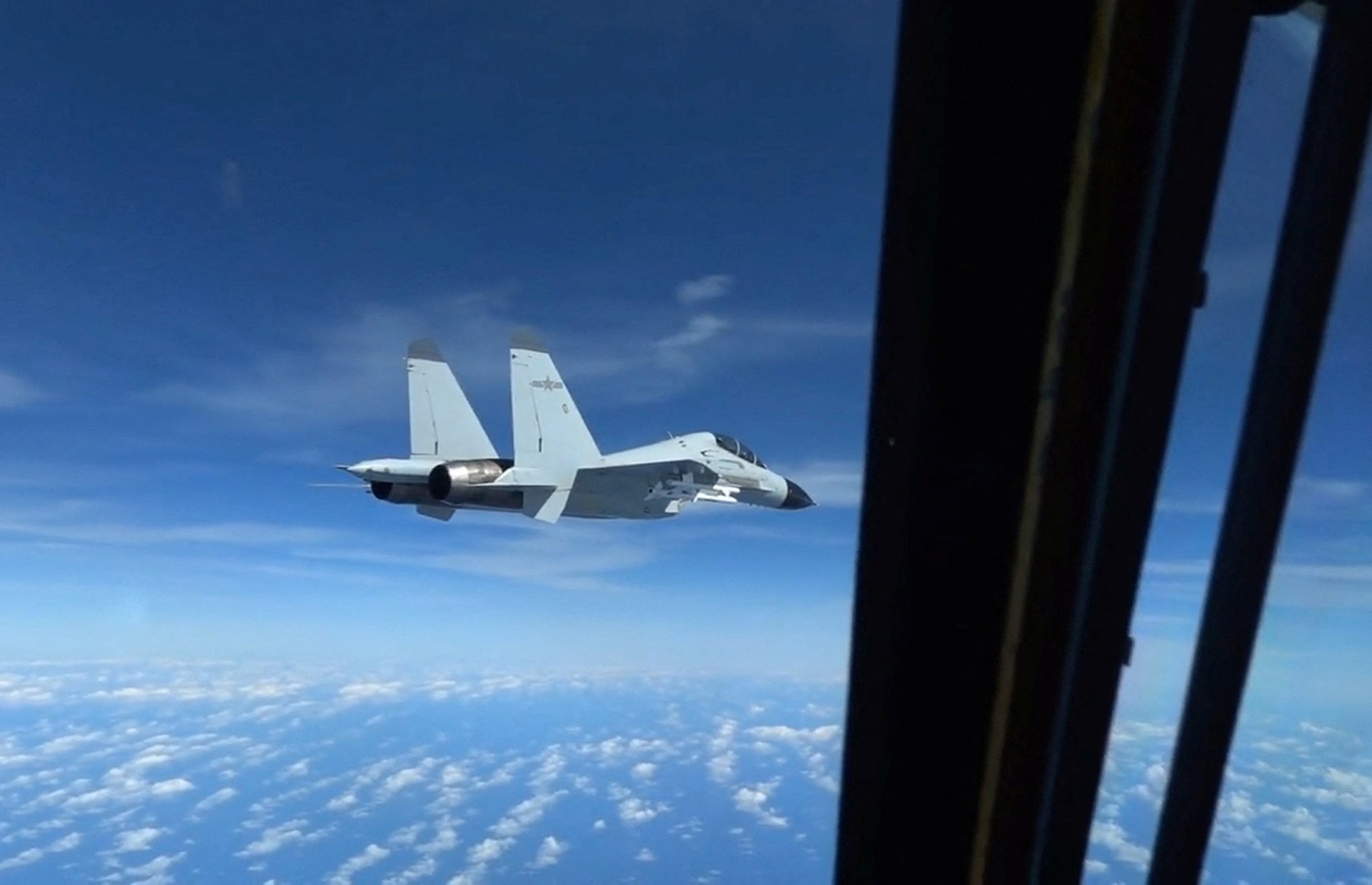

Defence ministry says US distorted info following a confrontation between a Chinese language jet and a US aircraft over the South China Sea.
China’s defence ministry has accused the US of violating worldwide legislation and of “slander and hype” following a confrontation between a Chinese language fighter jet and an American reconnaissance aircraft over the contested waters of the South China Sea.
The assertion late on Saturday got here days after the US army claimed {that a} Chinese language J-11 fighter jet had come inside 6 metres (20 ft) of a US RC-135 plane on December 21, forcing the latter to take evasive manoeuvres to keep away from a collision.
However Tian Julin, a spokesperson for China’s defence ministry, stated the US Indo-Pacific Command had distorted info in regards to the incident and that it was the US plane that had engaged in “harmful maneuvers” towards the Chinese language jet.
Tian stated the US plane was conducting intentional close-in reconnaissance on China’s southern shoreline when the Folks’s Liberation Military despatched fighter jets to trace and monitor the aircraft.
Regardless of a number of warnings from the Chinese language facet, the US plane abruptly altered its flight stance in a “harmful method motion, which critically compromised the flight security of the Chinese language army plane,” he stated.
The defence ministry additionally launched a video of the incident, which it stated confirmed the US plane manoeuvring in the direction of the Chinese language jet.
“America intentionally misleads public opinion … in an try and confuse the worldwide viewers,” Tian stated.
“We solemnly request the US facet to restrain the actions of frontline naval and air forces, strictly abide by associated worldwide legal guidelines and agreements, and stop accidents within the sea and the air.”
China claims virtually the whole South China Sea as its sovereign territory, however components of it are contested by Vietnam, the Philippines, Malaysia, Taiwan and Brunei.
Trillions of {dollars} in commerce move yearly by way of the waterway, which additionally accommodates wealthy fishing grounds and fuel fields.
US army planes and ships routinely perform surveillance operations and journey by way of the area, strikes that China says should not good for peace.
Relations between the US and China have been tense, with friction rising between the world’s two largest economies over a spread of points, together with Beijing’s human rights file and its claims over the self-ruled island of Taiwan.

World
Hoping to pave pathway to peace, Norway to recognise Palestinian statehood

Norway, alongside Ireland and Spain, recently announced its decision to formally recognise Palestinian statehood based on the pre-1967 borders, starting from Tuesday.
Predictably, as the Palestinian Authority and Hamas welcomed this development, the Israeli government lashed out by quickly withdrawing its ambassadors from Oslo, Dublin and Madrid and summoning the Norwegian, Irish and Spanish representatives in Tel Aviv.
Prime Minister Jonas Gahr Store explained that Norway’s decision was “in support of moderate forces that are on a retreating front in a protracted and cruel conflict”.
He said the move is an investment in the “only solution” that can bring lasting peace in the Middle East – “two states living side by side in peace and security”.
Analysts were not surprised by Norway’s move, which comes 30 years after it hosted the Oslo Accords, the early 1990s peace agreements that ultimately failed.
“The Norwegian population has over a long time been moving towards a more pro-Palestinian view. The political establishment has been more hesitant, not least because of its close ties to the US,” Bjorn Olav Utvik, a professor of Middle East studies at the University of Oslo, told Al Jazeera. “Since the outbreak of the current conflict, popular opinion has swung even further towards the Palestinian cause.”
He cast the recognition as “an important symbolic move” and one that is easier to make than, for instance, “cutting off all investments linked to Israel by the Norwegian sovereign wealth fund”.
With European countries deeply divided by the Israeli war on Gaza, Norway has moved closer to those who vocally support Palestinian rights to self-determination and basic dignity.
“We can’t wait any longer,” Espen Barth Eide, Norway’s foreign minister, recently told Al Jazeera. “The only viable long-term settlement which can bring peace to the Palestinian people and the Israeli people is a two-state solution. These two states, of course, must have logical territories. A lot will have to change.”
Looking back, Oslo’s position on the Israel-Palestine conflict has been steady.
Norwegian officials have maintained high levels of support for the United Nations Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees (UNRWA) and have been quick to demand a ceasefire after the latest conflict erupted.
Previously, Norway has condemned the Israeli occupation before the International Court of Justice. It does not export weapons to Israel and has sanctioned some “extremist” settlers.
“Norway believes that Israeli settlement activity on occupied land is illegal under international law and hinders the peace process and is in firm belief of a two-state solution as the only durable solution,” said Hasini Ransala Liyanage, a doctoral research fellow at the University of Oslo’s political science department.
She described Norway as a “prominent mediator of multiple conflicts in the world” that has “always focused on peaceful solutions”.
Norwegian mediation is characterised by a willingness to provide long-term assistance, impartial facilitation of peace talks and close corporation with parties in conflict, she added.
Oslo’s recognition of a Palestinian state also underlines its support for the Arab Peace Initiative, which calls for recognition of Israel’s right to exist and normalisation of ties in exchange for its withdrawal from lands captured since 1967 and a Palestinian state with East Jerusalem as its capital.
“To me, it seems the announcement is designed to create attention for this initiative and contribute to diplomatic momentum to increase European support for the Arab peace plan,” Sverke Runde Saxegaard, a doctoral researcher at the University of Oslo, told Al Jazeera.
“The government has been emphasising throughout the day that this is not in any way a sign of support for Hamas but a sign of support for forces and actors that seek a nonviolent solution to the conflict within both Israel and Palestine. To provide a glimmer of hope in a dark time, so to speak,” he added.
Israel’s latest and deadliest war on Gaza has killed almost 36,000 people, most of them women and children. Its campaign began after Hamas, the group that governs the Gaza Strip, launched an unprecedented incursion into southern Israel during which 1,139 people were killed and dozens captured.
‘Strong diplomatic move’
Oslo’s recognition of a Palestinian state may also bode well for Norway’s image and reputation in the Global South.
Liyanage said Oslo’s “strong diplomatic move” signals support for people in the Middle East and Muslim world as well as citizens of Global South nations who suffer from violence and protracted conflicts.
Norway will “stand as a state that acts against war crimes [and] violations of international humanitarian law and a state that recognises another state’s legitimate right to defend its citizens and borders”.
Norwegian politicians have also acknowledged the risks of applying international law inconsistently and the message that sends to non-Western audiences.
“Doing and saying popular things rarely hurt a country’s standing. And although I do not see this as the primary motivation here, the minister of foreign affairs has long been vocal about how Norway and the West cannot afford to be seen as hypocritical,” Saxegaard said. “If the West wants the world to be outraged about Russia in Ukraine, it needs to be outraged about Israel in Gaza.”
Noting how Arab governments welcomed Norway’s recent move, Hugh Lovatt, a senior policy fellow at the European Council on Foreign Relations, said the move “goes some small way to counter Global South perceptions of European double standards and blind support for Israel”.
‘Final demise of the Oslo peace process’
It seems as though Oslo has realised that the time has come to approach the Israel-Palestine issue in new ways and abandon failed approaches from previous decades.
Jorgen Jensehaugen, a senior researcher at the Peace Research Institute Oslo, said the prime minister has implied that he believes that since there is no peace process, waiting for one to start as the war rages on “is no longer a viable alternative”.
Lovatt added: “This move by Norway in my opinion also symbolises the final demise of the Oslo peace process and the urgent need to elaborate a new post-Oslo peacemaking strategy which should involve concrete steps to challenge Israeli occupation and support Palestinian rights.
“The hope is that a strong endorsement of Palestinian self-determination can demonstrate to the Palestinian public that diplomacy can deliver results and provide a credible alternative to armed violence.”
World
Video: In Interview, Zelensky Challenges West Over Hesitations to Support Ukraine

In a wide-ranging interview with The New York Times, President Volodymyr Zelensky of Ukraine urged the United States and Europe to do more to defend his nation, dismissing fears of nuclear escalation and proposing that NATO planes shoot down Russian missiles in Ukrainian airspace.
World
International Criminal Court: 20 years, billions spent, limited success as US considers sanctions
As the U.S. weighs sanctions against the International Criminal Court (ICC) over potential arrest warrants for Israeli officials, some experts have questioned the value of the court, given its track record since its founding.
“[The ICC] has been around for over two decades, [but] it has less than 10 successful prosecutions,” Orde Kittrie, a senior fellow at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies and law professor at Arizona State University’s Sandra Day O’Connor College of Law, told Fox News Digital. “It’s spent over $2 billion. It’s been really ineffective.”
As of July 2022, 31 cases have appeared before the ICC, which resulted in 10 convictions and four acquittals. The court has issued 37 arrest warrants, with 21 people ultimately detained while 12 people remain at large, according to the European Union’s External Action Service.
The ICC’s total annual budget for 2023 totaled around $183,500,000, which is an increase of around $34,500,000 or around 20% increase from 2022’s budget.
VISA BANS FOR ICC OFFICIALS URGED BY BIPARTISAN SENATORS AFTER ISRAEL ARREST WARRANT REQUESTS
Member states each bear a portion of the overall budget based on the size of their economies, with the most significant funds coming from large European economies, Japan, South Korea, Australia and Brazil, according to the Journal of Human Rights.
Japan ranked as the largest contributor in 2022 with around $26,850,000, while Germany and France rank thereafter with around $19,000,000 and $14,400,000, respectively.
President Biden speaks during a Jewish American Heritage Month reception in the Rose Garden of the White House on May 20, 2024. (Samuel Corum/Sipa/Bloomberg via Getty Images)
Appropriations for the court are divided into nine categories: the Judiciary, Office of the Prosecutor, the Registry, Secretariat of the Assembly of States Parties, Premises, Secretariat of the Trust Fund for Victims, Permanent Premises Project – Host State Loan, Independent Oversight Mechanism and Office of Internal Audit. The court also notes that “assets that the Court holds are normally not held to generate commercial returns and are therefore non-cash generating assets,” meaning it must build its budget from contributions alone.
Even with that sizable budget, and the significant increase year over year, the court relies heavily on the cooperation of members to enable its operations. Outgoing Registrar Peter Lewis in 2023 said the court faced an unprecedented workload – even before taking on the investigation into alleged crimes in the Gaza Strip – and that state parties’ cooperation remained crucial to any success.
US ALLIES FRANCE, BELGIUM DEFEND ICC PROSECUTOR’S REQUEST FOR ISRAELI ARREST WARRANTS
US sanctions
This makes any sanctions against the organization a potentially crippling measure: Then-President Trump in 2020 authorized an asset freeze and family entry ban against ICC officials after the court opened investigations into alleged U.S. war crimes conducted in Afghanistan.
“The ICC Prosecutor … thinks the Biden administration is more interested in a cozy relationship with the ICC than with protecting Israelis and Americans from its power grab,” Anne Bayefsky, director of the Touro Institute on Human Rights and the Holocaust as well as president of Human Rights Voices, told Fox News Digital.

International Criminal Court prosecutor Karim Khan (Dimitar Dilkoff/AFP via Getty Images)
“If President Biden does not immediately invoke the American Service Members Protection Act, terminate all cooperation and support of the ICC, and use his authority to sanction ICC officials for their outrageous prosecution – actually persecution – of the democratic representatives of the Jewish state … justice will have been dealt a disastrous blow,” Bayefsky said.
The Biden administration increased its cooperation with the ICC, offering assistance and intelligence to the court to bolster its investigation into alleged Russian war crimes during the invasion of Ukraine, though Kittrie noted that the ICC case against Putin “hasn’t made a difference” and possibly merely added “some sense” of legitimacy for the ICC prosecutor.
PROGRESSIVE SENATOR BACKS POTENTIAL ICC ARREST WARRANT FOR NETANYAHU: ‘UNPRECEDENTED WAR’
Bayefsky and others have urged the Biden administration to invoke the American Servicemembers Protection Act and sanction the ICC in response to any arrest warrants for Israeli officials.
During a speech in the Rose Garden on Wednesday at a press conference with Kenyan President William Ruto, Biden reiterated that the U.S. “made our position clear on the ICC … we don’t recognize the jurisdiction of the ICC, the way it’s being exercised, and it’s that simple. We don’t think there’s an equivalence between what Israel did and Hamas did.”

This view shows the International Criminal Court building in The Hague in the Netherlands on April 30, 2024. (Selman Aksunger/Anadolu via Getty Images)
The Rome Statute counts 124 signatories, including most of Africa, Europe and South America, but it does not include some notable holdouts: the United States, China, Russia, Ukraine, Israel, Saudi Arabia, Iran, North Korea and Turkey, among others.
The Biden administration reversed the sanctions but reinforced the position that the U.S. continued to “disagree strongly with the ICC’s actions relating to the Afghanistan and Palestinian situations.”
The Center for Constitutional Rights argued that the sanctions delayed critical investigations at the ICC, “directly and indirectly negatively” impacting the work at the ICC, though perhaps not as drastically as the U.S. would have hoped.
ISRAEL SLAMS GERMAN GOVERNMENT’S VOW TO ARREST PRIME MINISTER NETANYAHU OVER ICC WARRANT
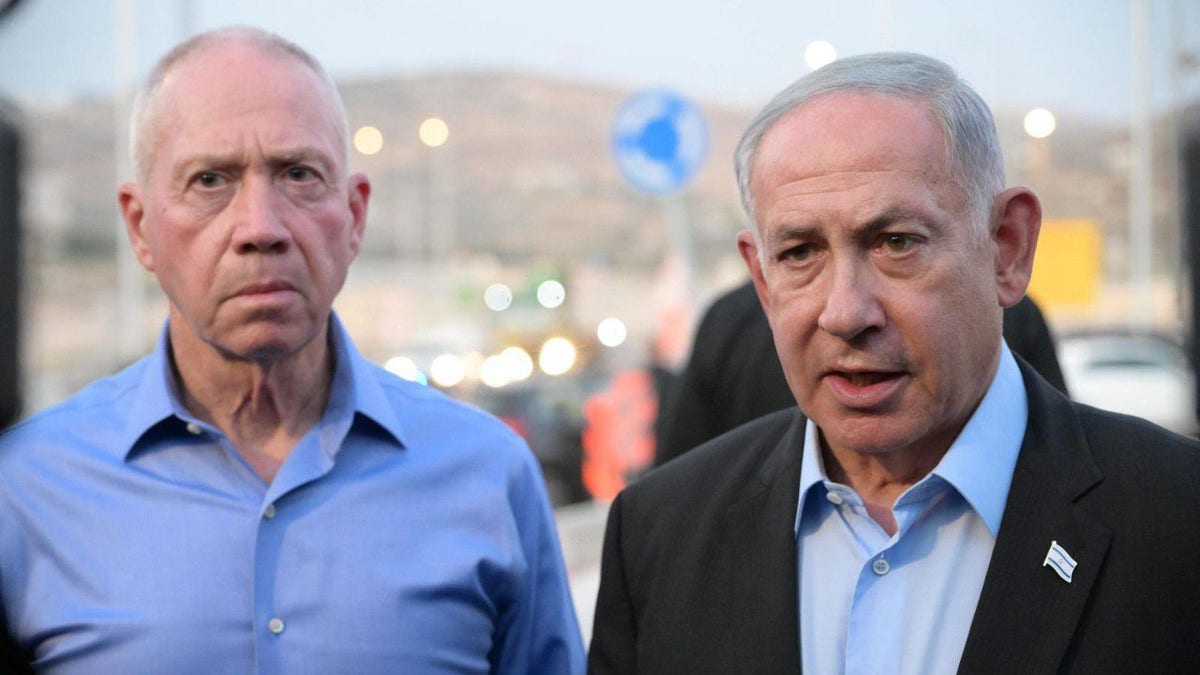

Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, right, and Israeli Defense Minister Yoav Gallant are pictured in the West Bank in August 2023. (Amos Ben-Gershom (GPO)/Handout/Anadolu Agency via Getty Images)
Instead, the group argued that the sanctions created a difficult working relationship for the ICC and any potential collaborators, such as civil society organizations, investigators, lawyers and victims who would worry about facing similar sanctions for helping the ICC.
The ICC, which commenced operations in 2002, bases its authority on the signatories of the Rome Statute, which outlines four core international crimes that the court will prosecute: genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and crimes of aggression, all of which are “not subject to any statute of limitations” but limited to only crimes that occurred after the statute came into force.
President Clinton signed the statute in 2000, but he demanded that the eventual ICC should address “fundamental concerns” before he or any other U.S. president considered putting the statute before the U.S. Senate for ratification. The Bush administration took it a step further, withdrawing the U.S. signature and instead adopting the American Servicemembers Protection Act.
Also known as the “Hague Invasion Act,” the law allows the president to use “all means necessary and appropriate to bring about the release” of U.S. or allied citizens detained or imprisoned by the ICC.
The bill also prevents the U.S. from providing support for the ICC, per Sec. 2004: The U.S. is prohibited from responding to requests for cooperation, of providing support to the court (including from law enforcement), of helping with extradition and using appropriated funds to assist the court, among others.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoSouthern border migrant encounters decrease slightly but gotaways still surge under Biden
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDem newcomer aims for history with primary win over wealthy controversial congressman
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSlovakia PM Robert Fico in ‘very serious’ condition after being shot
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCanadian Nobel-winning author Alice Munro dies aged 92
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoVulnerable Dem incumbents move to the center in key swing states as Biden panders to far-left base
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week ago‘Monstrous crime’: World reacts to attack on Slovakia’s prime minister
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSmall but mighty Nimble becomes first mixed-breed dog to win Westminster agility title
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoHow a migrant aid group got caught up in a right-wing social media thread : Consider This from NPR