World
Are airlines returning to Israel, despite the war on Gaza?

Almost as soon as Israel’s war on Gaza broke out on October 7, many airlines suspended or cancelled their flights to Israel.
Last week, Yossi Fattal, director general of Israel’s Chamber of Inbound Tourism Organisers, complained that Israel had become isolated – “like North Korea” – as dozens of airlines remained reluctant to fly there.
The war has significantly affected Israeli tourism and flights. Yet, things are beginning to change.
Which airlines have resumed flights to Israel?
United Airlines announced on Wednesday last week that it will begin flights to Israel again from March, becoming the first United States carrier to resume flights after suspensions at the start of the war.
United plans initial flights to Tel Aviv from New York and New Jersey in the US on March 2 and 4, with a goal of having daily non-stop service restored from March 6. The carrier said in a news release that it had undertaken a detailed safety analysis before making this decision.
British Airways, which used to operate two flights between the United Kingdom and Israel daily, will resume operations on April 1, operating one flight daily for four days a week.
German airline Lufthansa, Switzerland’s flag carrier Swiss and Austrian flag carrier Austrian Airlines resumed flights to Tel Aviv on January 8. Meanwhile, Spanish airline Air Europa resumed flights to Tel Aviv on February 19. The Greek and French flag carriers, Aegean and Air France, both restarted flights to Tel Aviv in January.
Italy’s ITA Airways will resume flights between Tel Aviv and Rome from March 1, starting with three return trips weekly.
Brussels Airlines, the Belgian carrier, also announced on Wednesday last week that it will resume flights from March 24, with three flights per week from Brussels to Tel Aviv.
The Israel Airports Authority (IAA) also announced that the US-based Delta Air Lines will resume flights to Israel in May. Delta has not officially confirmed this yet, but the last update from the carrier said that flights will be suspended between New York and Israel until April 30.
Still, that’s only a fraction of the flights Israel used to attract before the war.

Which airlines do not plan to resume flights to Israel any time soon?
American Airlines has halted flights until October 28. Emirates, Turkish Airlines and Pegasus Airlines have also suspended flights to Israel until further notice.
TAP Air Portugal has suspended flights to and from Tel Aviv indefinitely, while Finland’s flag carrier, Finnair, announced it had cancelled its flights to Tel Aviv until October 29. Icelandair has cancelled flights to Tel Aviv, without any further update on its website.
Bulgaria Air cancelled all flights to and from Tel Aviv, also without providing details about a timeline to restart operations.
How has the war affected air travel in Israel?
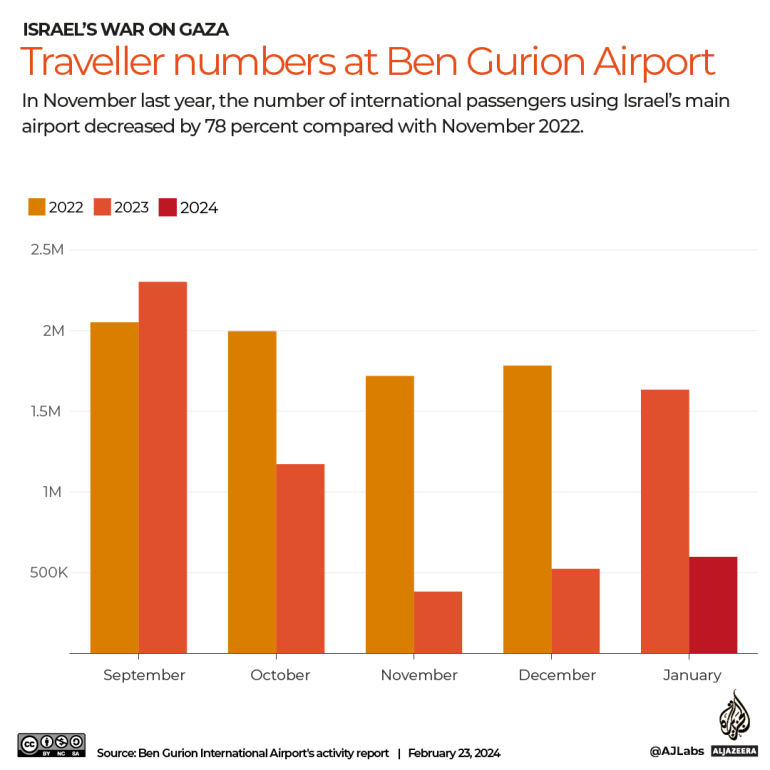
The number of international travellers arriving in Israel by air rose from 19.2 million in 2022 to 21.1 million in 2023, the IAA reported on January 21.
In November 2023, however, the number of aircraft arriving at Ben Gurion International Airport was 68 percent lower than the same month the year before.
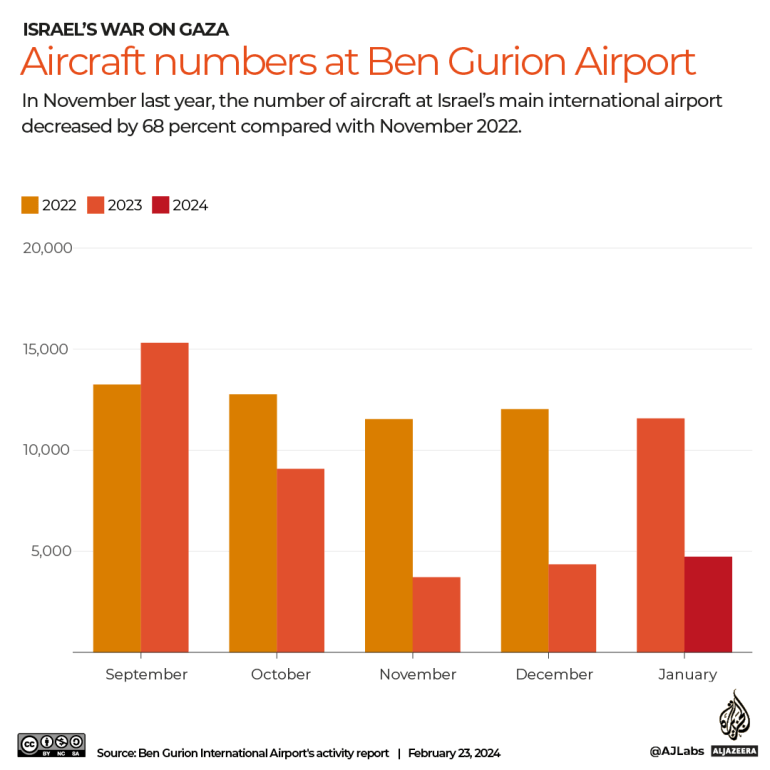
Fattal said that while 250 airlines had been operating in and out of Israel before October 7, the number dipped to just seven last December. It has since crawled back up to 45.
In the three-month period from October 7, 900,000 tourists had been expected to visit Israel. However, the Israeli daily Calcalist reported that only 190,000 people had actually visited.
Prior to October 7, more than 300,000 people visited Israel every month. In November 2023, that figure reportedly dropped to 39,000.
The number of travellers using Ben Gurion airport in November 2023 was 78 percent lower than in November 2022.
The tourism industry in Israel accounted for 2.6 percent of gross domestic product (GDP) before the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019, before falling to 1.1 percent in 2021. Both foreign and domestic tourism in Israel have flatlined since the start of the war.
Which airlines have continued to fly to Israel throughout the war?
In December, when only seven carriers were flying to Israel, around 80 percent of passengers were carried by Israel’s national carrier, El Al, followed by smaller Israeli carrier Israir at 10 percent and FlyDubai at 3.2 percent.
With almost all airlines suspending and cancelling flights after October 7, El Al saw a 32.5 percent rise in passenger numbers to 5.5 million for 2023 at Ben Gurion airport, which has continued to operate throughout the war.

World
Ukraine's divisive mobilization law comes into force as a new Russian push strains front-line troops
KYIV, Ukraine (AP) — A divisive mobilization law in Ukraine came into force on Saturday, as Kyiv struggles to boost troop numbers after Russia launched a new offensive that some fear could close in on Ukraine’s second-largest city.
The legislation, which was watered down from its original draft, will make it easier to identify every conscript in the country. It also provides incentives to soldiers, such as cash bonuses or money toward buying a house or car, that some analysts say Ukraine cannot afford.
Lawmakers dragged their feet for months and only passed the law in mid-April, a week after Ukraine lowered the age for men who can be drafted from 27 to 25. The measures reflect the growing strain that more than two years of war with Russia has had on Ukraine’s forces, who are trying to hold the front lines in fighting that has sapped the country’s ranks and stores of weapons and ammunition.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy also signed two other laws Friday, allowing prisoners to join the army and increasing fines for draft dodgers fivefold. Russia enlisted its prisoners early on in the war, and personnel shortages compelled Ukraine to adopt the new measures.
Russian troops, meanwhile, are pushing ahead with a ground offensive that opened a new front in northeastern Ukraine’s Kharkiv region and put further pressure on Kyiv’s overstretched military. After weeks of probing, Moscow launched the new push knowing that Ukraine suffered personnel shortages, and that its forces have been spread thin in the northeast.
Russian President Vladimir Putin said on Friday during a visit to China that the Russian push aims to create “a buffer zone” rather than capturing Kharkiv, the local capital and Ukraine’s second-largest city.
Still, Moscow’s forces have pummeled Kharkiv with strikes in recent weeks, hitting civilian and energy infrastructure and prompting angry accusations from Zelenskyy that the Russian leadership sought to reduce the city to rubble. On Friday, Mayor Ihor Terekhov said that Russian guided bombs killed at least three residents and injured 28 others that day.
Moscow denies deliberately targeting civilians, but thousands have died or suffered injuries in the more than 27 months of fighting.
The U.S. last week announced a new $400 million package of military aid for Ukraine, and President Joe Biden has promised that he would rush badly needed weaponry to the country to help it stave off Russian advances. Still, only small batches of U.S. military aid have started to trickle into the front line, according to Ukrainian military commanders, who said it will take at least two months before supplies meet Kyiv’s needs to hold the line.
Thousands of Ukrainians have fled the country to avoid the draft since Russia’s all-out invasion in February 2022, some risking their lives as they tried to swim across a river separating Ukraine from neighboring Romania and Hungary.
Late on Friday, Ukraine’s border service said that at least 30 people have died trying to cross the Tisza River since the full scale-invasion.
Romanian border guards days earlier retrieved the near-naked, disfigured body of a man that appeared to have been floating in the Tisza for days, and is the 30th known casualty, the Ukrainian agency said in an online statement. It said the man has not yet been identified.
___
Follow AP’s coverage at https://apnews.com/hub/russia-ukraine
World
An unusual autumn freeze grips parts of South America, giving Chile its coldest May in 74 years

Chileans are bundling up for their coldest autumn in more than 70 years mere days after sunning in T-shirts — a dramatic change of wardrobe brought on this week by a sudden cold front gripping portions of South America unaccustomed to bitter wind chills this time of year.
CHILE SHUTS DOWN A POPULAR GLACIER, SPARKING DEBATE OVER CLIMATE CHANGE AND ADVENTURE SPORTS
Temperatures broke records along the coast of Chile and in Santiago, the capital, dipping near freezing and making this month the coldest May that the country has seen since 1950, the Chilean meteorological agency reported.
An unusual succession of polar air masses has moved over southern swaths of the continent, meteorological experts say, pushing the mercury below zero Celsius (32 Fahrenheit) in some places. It’s the latest example of extreme weather in the region — a heat wave now baking Mexico, for instance — which scientists link to climate change.
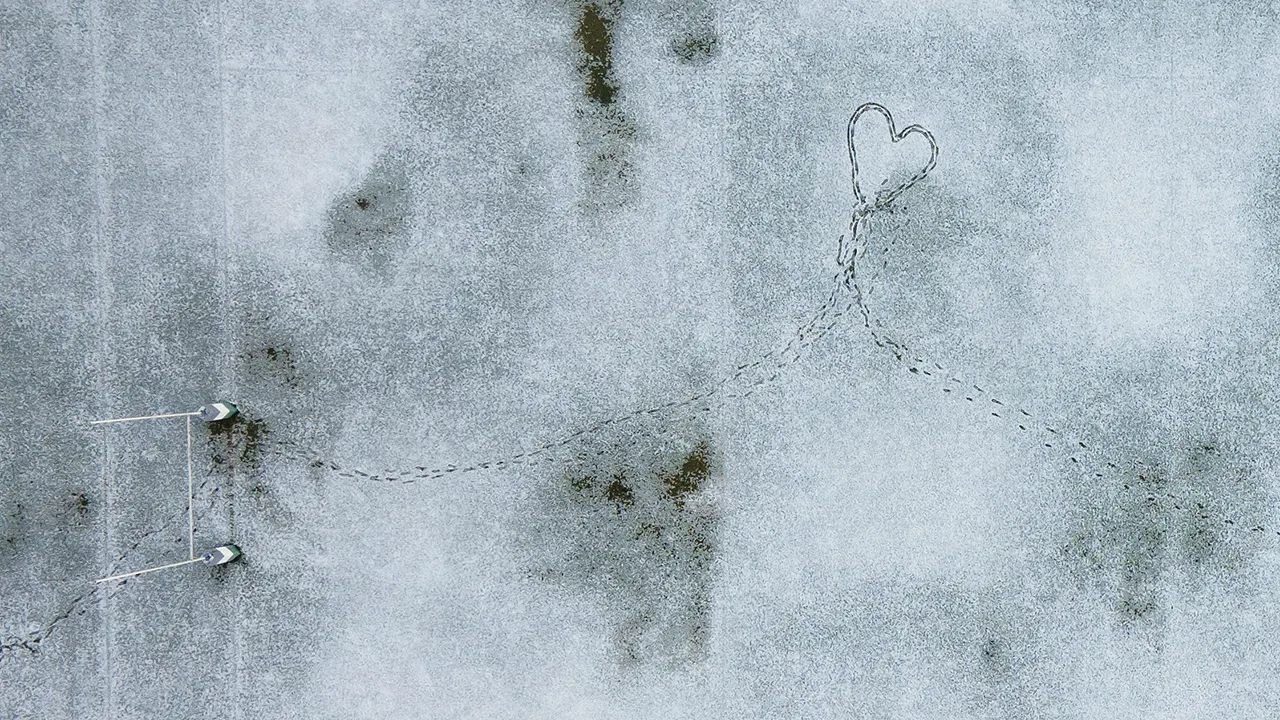
Footprints create the shape of a heart in a snow-covered rugby field in Santiago, Chile, Wednesday, May 8, 2024. (AP Photo/Matias Basualdo)
“The past few days have been one of the longest (cold fronts) ever recorded and one of the earliest ever recorded” before the onset of winter in the Southern Hemisphere, said Raul Cordero, a climatologist at Santiago University. “Typically the incursions of cold air from the Antarctic that drive temperatures below zero occur from June onwards, not so much in May.”
The cold front sweeping in from Antartica has collided with warm air pushing in from the northwestern Amazon, helping fuel heavy rainstorms battering Brazil, according to that country’s National Meteorological system.
Chile’s government issued frosty weather alerts for most of the country and ramped up assistance for homeless people struggling to endure the frigid temperatures on the streets. Snow cloaked the peaks of the Andes and fell in parts of Santiago, leading to power outages in many areas this week.
“Winter came early,” said Mercedes Aguayo, a street vendor hawking gloves and hats in Santiago.
She said she was glad for a boost in business after Chile’s record winter heat wave last year, which experts pinned on climate change as well as the cyclical El Niño weather pattern.
“We had stored these goods (hats and gloves) for four years because winters were always more sporadic, one day hot, one day cold,” Aguayo said.
This week’s cold snap also took parts of Argentina and Paraguay by surprise.
Energy demand soared across many parts of Argentina. Distributors cut supplies to dozens of gas stations and industries in several provinces to avoid outages in households, , the country’s main hydrocarbon company, CECHA, said Thursday.
World
Brussels, my love? Transparency over MEPs' side jobs

In this edition, we look at what lawmakers’ extracurricular activities mean for their core role.
This week, we are joined by Sophia Russack, senior researcher from the Centre for European Policy Studies, Petros Fassoulas, secretary general of European Movement International and Anna Nalyvayko, senior project officer from the Wilfried Martens Center.
Panelists debate the ethical questions raised by MEPs who have side jobs. Those extra roles are legal, but the political earthquake caused by the Qatarargate scandal led to tighter rules and more transparency.
Is this enough to bridge the gulf between citizens and politicians, in today’s fractured political landscape?
“We see that they have improved rules when it comes to reporting requirements, to laying open your financial situation before and after the offers, and so on. But to be honest, none of these things will prevent another Qatargate,” said Sophia Russack, a think tanker who is an expert in EU institutional architecture, decision-making processes and institutional reform.
Despite these concerns, Petros Fassoulas said MEPs shouldn’t abandon contact with the real world altogether.
“It’s important for them to have the opportunity to bring expertise from outside and engage also with the world outside of the chamber,” Fassoulas said. “An MEP or any parliamentarian should be in contact with the people that they regulate, the businesses that they have an impact on.”
Guests also discussed the reasons for the crisis of public confidence in politicians, and gave some ideas for solutions.
Watch “Brussels, my love?” in the player above.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPentagon chief confirms US pause on weapons shipment to Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRFK Jr said a worm ate part of his brain and died in his head
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoOhio AG defends letter warning 'woke' masked anti-Israel protesters they face prison time: 'We have a society'
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoNine Things We Learned From TikTok’s Lawsuit Against The US Government
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoBiden’s decision to pull Israel weapons shipment kept quiet until after Holocaust remembrance address: report
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Police Use Pepper Spray on Protesters on G.W.U.’s Campus
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoA look at Chinese investment within Hungary
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoThe Major Supreme Court Cases of 2024


















