California
California’s Math Misadventure Is About to Go National
When I decided to read every word of California’s 1,000-page proposal to transform math education in public schools, I learned that even speculative and unproved ideas can end up as official instructional policy. In 2021, the state released a draft of the California Mathematics Framework, whose authors were promising to open up new pathways into science and tech careers for students who might otherwise be left behind. At the time, news reports highlighted features of the CMF that struck me as dubious. That draft explicitly promoted the San Francisco Unified School District’s policy of banishing Algebra I from middle school—a policy grounded in the belief that teaching the subject only in high school would give all students the same opportunities for future success. The document also made a broad presumption that tweaking the content and timing of the math curriculum, rather than more effective teaching of the existing one, was the best way to fix achievement gaps among demographic groups. Unfortunately, the sheer size of the sprawling document discouraged serious public scrutiny.
I am a professional mathematician, a graduate of the public schools of a middle-class community in New York, and the son of a high-school math teacher. I have been the director of undergraduate studies in math at Stanford University for a decade. When California released a revised draft of the math framework last year, I decided someone should read the whole thing, so I dove in. Sometimes, as I pored over the CMF, I could scarcely believe what I was reading. The document cited research that hadn’t been peer-reviewed; justified sweeping generalizations by referencing small, tightly focused studies or even unrelated research; and described some papers as reaching nearly the opposite conclusions from what they actually say.
The document tried hard to convince readers that it was based on a serious reading of neuroscience research. The first chapter, for example, cited two articles to claim that “the highest achieving people have more interconnected brains,” implying that this has something to do with learning math. But neither paper says anything about math education.
The CMF is meant only to guide local districts, but in practice it influences the choices they make about what and how to teach. Even so, the version ultimately adopted by the State Board of Education is likely to distort math instruction for years to come. Armed with trendy buzzwords and false promises of greater equity, California is promoting an approach to math instruction that’s likely to reduce opportunities for disadvantaged students—in the state and wherever else educators follow the state’s lead.
In my position at Stanford, I’ve heard from people around the country about the math preparation necessary to attain a variety of degrees and succeed in a range of careers. A solid grounding in math from high school—which traditionally has included two years of algebra, a year of geometry, and then, for more advanced students, other coursework leading up to calculus—is a prerequisite for a four-year college degree in data science, computer science, economics, and other quantitative fields. Such a degree is, in turn, the price of entry for jobs not only in the sciences and Silicon Valley but also in a number of seemingly distant fields. A data scientist at a company that makes decisions about how and when to store, freeze, and transport food once told me that he and his crew “could not do our jobs” without fluency in areas of college-level math that require previous mastery of the basics.
Without overtly saying so, California is building off-ramps from that kind of math. The CMF pitches relatively new courses, branded as “data science,” both as an alternative to a second year of algebra and as an entry point into fast-growing career fields. But the course name is something of a misnomer.
In private industry and higher ed, data science describes a powerful synthesis of computer science, mathematics, and statistics that seeks to extract insights from large data sets. It has applications in industries as varied as health care, retail, and, yes, food-supply logistics. The ability to do actual data science rests on math skills that have been taught for eons. Data literacy would be a better name for the most widely taught high-school data-science classes, which were developed by UCLA’s statistics department and my own university’s Graduate School of Education. To be sure, schools should be teaching citizens enough about statistics and data to follow the news and make educated financial and health decisions. Many parts of the math curriculum can be illustrated with engaging contemporary data-oriented applications. But much as a music-appreciation course won’t teach you how to play a piano, data literacy is not data science.
Advocates of the new courses have suggested that they produce better outcomes for groups, such as girls and students of color, that are traditionally underrepresented in mathematics. But proponents should own up to the downstream effects: In practice, steering sophomores and juniors away from Algebra II forecloses the possibility of careers in certain fast-growing quantitative fields—which would seem to do the opposite of promoting equity. Many schools in Europe and Asia separate students into different career paths early on in their education, but a key goal of the American system has been to help students keep their options open. In other contexts, the CMF is notably skeptical of efforts to group students in math class according to ability, out of a fear that disadvantaged students will be placed in low-expectation tracks that they can never escape. But for some reason, shunting them away from advanced math is portrayed as progress. The STEM fields won’t increase their diversity through math classes that contain very little math.
Ultimately, I ended up submitting 170 pages of documentation about extensive flaws in the CMF draft that I read. I was hardly the only one finding fault. A multiracial national coalition of more than 1,700 quantitative experts from higher education and industry strongly objected to the early drafts. Faculty in the University of California and California State University systems wrote letters warning state officials against prematurely steering students away from algebra-intensive academic and career options. UC administrators had begun to allow data-literacy courses to fulfill Algebra II admissions requirements, but a faculty working group representing all campuses in the system voted unanimously this summer to reverse that policy.
Before the State Board of Education in California approved the third version of the CMF in July, officials did try to address some of its flaws. Although school officials in San Francisco had largely ignored parents who questioned the district’s policy against offering Algebra I in middle school, critics refused to give up, and for good reason. A recent working paper from three Stanford researchers indicates that the San Francisco Unified School District’s decade-long experiment was a bust. The percentage of Black and Latino students taking advanced math courses did not increase. Some students who would otherwise have studied calculus as high-school seniors were unable to do so. The kids who succeeded in reaching calculus typically did so through extracurricular measures, such as summer classes. Later CMF drafts quietly removed the mention of the SFUSD policy while still generally endorsing the ideas behind it.
Meanwhile, the ideas that animate the CMF—particularly its endorsement of data-literacy classes as a substitute for math and its suggestion that large swaths of the traditional high-school math curriculum are obsolete—are popping up in other states. In Ohio, for example, a menu of alternative math “pathways” in high school has been touted as providing entry into a variety of appealing and lucrative careers. But the pathways labeled for data science and computer science remove many Algebra II skills; the fine print reveals that the pathways are inadequate for students who might want college degrees in those fields. School officials in Middletown, Connecticut, have proposed to revamp the traditional calculus track by scaling back on preparations for eighth-grade Algebra I and introducing mash-up algebra-and-geometry courses that would magically pack three years of instruction into two.
Unfortunately, not every state has a critical mass of academic experts and private-sector tech practitioners to push back when school systems try to rebrand an inferior math education as something new and innovative. The students who are most reliant upon public schools are the most harmed when districts embrace policies based on superficial appeals to equity or false promises about future job opportunities. When only the children of families with resources beyond the public schools are gaining preparation for the lucrative degrees and secure jobs of the future, public education is failing in a primary duty.

California
California man beheaded his 1-year-old son with a knife, authorities say

SACRAMENTO, Calif. — A man has been arrested on suspicion of beheading his 1-year-old son, Northern California authorities said.
The Sacramento County Sheriff’s Office said in a statement Friday that deputies responding to an early morning family disturbance call found a woman outside a home who told deputies that her husband Andrey Demskiy, 28, assaulted her and her mother.
Deputies forced their way into the house in northern Sacramento County when they learned Demskiy was inside with the boy. As they took him into custody, they found a “severed child’s head” in the bedroom where Demskiy was detained.
Detectives said Demskiy used a knife to behead his son after his wife and mother-in-law left the house, according to the statement. He was in custody and ineligible for bail, and was scheduled to appear in court Tuesday.
The sheriff’s department and the county public defenders office did not respond to emails seeking information on whether Demskiy had an attorney who could speak on his behalf.
California
Protests Swept California Campuses Last Year. Schools Are Now Blocking Them | KQED
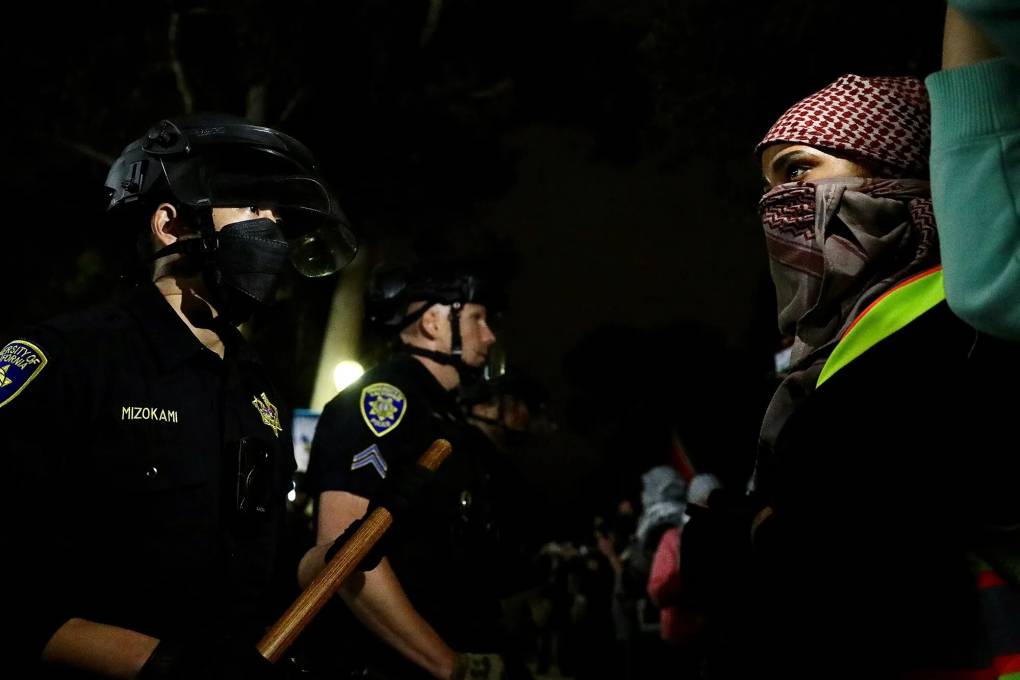

At UC Santa Cruz, police arrested one student who was using a megaphone during a demonstration on Oct. 7, according to an eyewitness who spoke to LookOut Santa Cruz. Santa Cruz County Sheriff’s Office public arrest reports show one person was arrested on the Santa Cruz campus for obstruction of a public officer and battery without injury that day.
While no arrests were made, Pomona College has suspended 12 students for the remainder of the 2024–25 academic year following an Oct. 7 demonstration in which they entered, damaged and vandalized a restricted building, according to the student newspaper. The college also banned dozens of students from the four other campuses of the Claremont Colleges, a consortium that includes Pomona.
Private colleges have implemented their own policy changes. Pomona College now requires students and faculty to swipe their ID cards to enter academic buildings. Since last semester, students and visitors entering USC are also required to show a school or photo ID.
Some students are still facing charges from last year’s protests
Few charges have been filed after UCLA’s encampment made headlines in April when counterprotesters led an attack on encampment protesters while law enforcement did not intervene for several hours. The following day, 254 people were arrested on charges related to the protest encampment. In October, two additional people were also arrested for participating in the counter-protester violence.
The Los Angeles County District Attorney’s office is pursuing three felony cases against individuals arrested at UCLA in relation to violence during last spring’s protests.
Meanwhile, the city attorney’s office is reviewing 93 misdemeanor cases from USC and 210 from UCLA, according to information it provided to CalMatters last month.
Lilyan Zwirzina, a junior at Cal Poly Humboldt, was among the students arrested in the early morning of April 30 following protesters occupying a campus building and ignoring orders to disperse from the university. Law enforcement took her to Humboldt County Correctional Facility, where she faced four misdemeanor charges, including resisting arrest. Zwirzina thought she’d have to cancel her study abroad semester, which conflicted with the court date she was given.
“I was pretty frustrated and kind of freaked out,” Zwirzina said. Authorities dropped the charges against her in July.
The Humboldt County District Attorney’s Office didn’t pursue charges against 27 of the 39 people arrested, citing insufficient evidence. The 12 remaining cases were referred to the Cal Poly Humboldt Police Department for investigation. Those cases remain under investigation, according to the university.
For 13 people, including students, arrested at Stanford University in June, the Santa Clara County District Attorney Jeff Rosen has not pressed charges as of Nov. 20, according to information his office provided CalMatters.
Elsewhere across the state, some district attorneys are pursuing misdemeanor and felony charges against student protesters. Orange County District Attorney Todd Spitzer is pursuing misdemeanor charges against 50 people, including two UCI professors, a teaching assistant, and 26 students, stemming from a protest at UC Irvine on Oct. 22, 2023. Charges include failure to disperse, resisting arrest and vandalism.
At Pomona College, 19 students were arrested on April 5 on charges of trespassing after some protesters entered and refused to leave an administrative building. Students arrested either had their cases dismissed or have accepted community service in lieu of further legal action. James Gutierrez, the attorney representing the arrested students, said he asked that the college drop charges against its students, citing their right to protest the use of paid tuition dollars.
“They are righteously demanding that their colleges, the ones they pay tuition to and housing fees and pour a lot of money into, that that university or college stop investing in companies that are directly supporting this genocide and indirectly supporting it,” he said.
Students fight back against campus protest policies
As administrators face the challenge of applying protest policies more uniformly and swiftly, the truer test of California public higher education institutions’ protest rules will be playing out in court.
In one already resolved case, UC leadership agreed in August to comply with a court order requiring the campus to end programs or events that exclude Jewish students. A federal judge ruled some Jewish students in support of Israel who were blocked from entering the encampment had their religious liberties violated — though some Jewish students did participate in UCLA’s protest encampment.
Now, students have filed at least two lawsuits against their campuses and the UC system for violating their rights while ending student encampments last spring. In September, ACLU NorCal filed suits against the UC and UC Santa Cruz for not providing students due process when they immediately barred arrested students from returning to campus.
“Those students should have gotten a hearing, an opportunity to defend themselves or to explain themselves, and the school would have shown evidence of why they created a risk of disturbance on campus,” Chessie Thacher, senior staff attorney at ACLU of Northern California, said.
UC Santa Cruz spokesperson Scott Hernandez-Jason said the university “appreciates the court’s careful deliberation” and that the university “is committed to upholding the right to free expression while also protecting the safety of its campus community.”
In October, ACLU SoCal filed lawsuits on behalf of two students and two faculty members against the UC and UCLA, alleging the actions the university took to break down the encampment violated their free speech rights.
UCLA spokesperson Ricardo Vazquez told CalMatters via email that the university would respond in court and that UCLA “fully supports community members expressing their First Amendment rights in ways that do not violate the law, our policies, jeopardize community safety, or disrupt the functioning of the university.”
“The encampment that arose on campus this spring became a focal point for violence, a disruption to campus, and was in violation of the law,” Vazquez said in the email statement. “These conditions necessitated its removal.”
California
Southern California hiring in November runs 47% below average

A record 8.11 million at work in Los Angeles, Orange, Riverside and San Bernardino counties in November.
Subscribe to continue reading this article.
Already subscribed? To login in, click here.
Originally Published:
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCanadian premier threatens to cut off energy imports to US if Trump imposes tariff on country
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782636/247422_ChatGPT_anniversary_CVirginia.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782636/247422_ChatGPT_anniversary_CVirginia.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoInside the launch — and future — of ChatGPT
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25789444/1258459915.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25789444/1258459915.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoOpenAI cofounder Ilya Sutskever says the way AI is built is about to change
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoU.S. Supreme Court will decide if oil industry may sue to block California's zero-emissions goal
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25546252/STK169_Mark_Zuckerburg_CVIRGINIA_D.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25546252/STK169_Mark_Zuckerburg_CVIRGINIA_D.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta asks the US government to block OpenAI’s switch to a for-profit
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoConservative group debuts major ad buy in key senators' states as 'soft appeal' for Hegseth, Gabbard, Patel
-

 Business7 days ago
Business7 days agoFreddie Freeman's World Series walk-off grand slam baseball sells at auction for $1.56 million
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23951353/STK043_VRG_Illo_N_Barclay_3_Meta.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/23951353/STK043_VRG_Illo_N_Barclay_3_Meta.jpg) Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoMeta’s Instagram boss: who posted something matters more in the AI age


















