Science
The Animal Translators

The bare mole rat might not be a lot to take a look at, however it has a lot to say. The wrinkled, whiskered rodents, which reside, like many ants do, in giant, underground colonies, have an elaborate vocal repertoire. They whistle, trill and twitter; grunt, hiccup and hiss.
And when two of the voluble rats meet in a darkish tunnel, they change a regular salutation. “They’ll make a gentle chirp, after which a repeating gentle chirp,” mentioned Alison Barker, a neuroscientist on the Max Planck Institute for Mind Analysis, in Germany. “They’ve somewhat dialog.”
Hidden on this on a regular basis change is a wealth of social data, Dr. Barker and her colleagues found once they used machine-learning algorithms to research 36,000 gentle chirps recorded in seven mole rat colonies.
Not solely did every mole rat have its personal vocal signature, however every colony had its personal distinct dialect, which was handed down, culturally, over generations. Throughout instances of social instability — as within the weeks after a colony’s queen was violently deposed — these cohesive dialects fell aside. When a brand new queen started her reign, a brand new dialect appeared to take maintain.
“The greeting name, which I assumed was going to be fairly primary, turned out to be extremely sophisticated,” mentioned Dr. Barker, who’s now finding out the numerous different sounds the rodents make. “Machine-learning form of remodeled my analysis.”
Machine-learning programs, which use algorithms to detect patterns in giant collections of knowledge, have excelled at analyzing human language, giving rise to voice assistants that acknowledge speech, transcription software program that converts speech to textual content and digital instruments that translate between human languages.
In recent times, scientists have begun deploying this expertise to decode animal communication, utilizing machine-learning algorithms to determine when squeaking mice are confused or why fruit bats are shouting. Much more formidable initiatives are underway — to create a complete catalog of crow calls, map the syntax of sperm whales and even to construct applied sciences that permit people to speak again.
“Let’s attempt to discover a Google Translate for animals,” mentioned Diana Reiss, an knowledgeable on dolphin cognition and communication at Hunter Faculty and co-founder of Interspecies Web, a suppose tank dedicated to facilitating cross-species communication.
The sphere is younger and lots of initiatives are nonetheless of their infancy; humanity just isn’t on the verge of getting a Rosetta Stone for whale songs or the power to chew the fats with cats. However the work is already revealing that animal communication is much extra complicated than it sounds to the human ear, and the chatter is offering a richer view of the world past our personal species.
“I discover it actually intriguing that machines would possibly assist us to really feel nearer to animate life, that synthetic intelligences would possibly assist us to note organic intelligences,” mentioned Tom Mustill, a wildlife and science filmmaker and the writer of the forthcoming ebook, “How you can Converse Whale.” “That is like we’ve invented a telescope — a brand new device that enables us to understand what was already there however we couldn’t see earlier than.”
Superior eavesdropping
Research of animal communication are usually not new, however machine-learning algorithms can spot delicate patterns which may elude human listeners. As an illustration, scientists have proven that these applications can inform aside the voices of particular person animals, distinguish between sounds that animals make in several circumstances and break their vocalizations down into smaller elements, an important step in deciphering that means.
Learn Extra on Synthetic Intelligence
“One of many issues that’s actually nice about animal sound is that there are nonetheless so many mysteries and that these mysteries are issues which we will apply computation to,” mentioned Dan Stowell, an knowledgeable in machine listening at Tilburg College and Naturalis Biodiversity Heart within the Netherlands.
A number of years in the past, researchers on the College of Washington used machine studying to develop software program, referred to as DeepSqueak, that may routinely detect, analyze and categorize the ultrasonic vocalizations of rodents.
It could additionally distinguish between the complicated, songlike calls that the animals make once they’re feeling good and the lengthy, flat ones they make when they aren’t. “You may simply get a direct, subjective, from the animal’s mouth how-are-they-feeling,” mentioned Kevin Coffey, a behavioral neuroscientist on the College of Washington, who was a part of the workforce that developed DeepSqueak.
DeepSqueak has been repurposed for different species, together with lemurs and whales, whereas different groups have developed their very own programs for routinely detecting when clucking chickens or squealing pigs are in misery.
Decoding that means
Decoding the that means of animal calls additionally requires giant quantities of knowledge in regards to the context surrounding every squeak and squawk.
To be taught extra in regards to the vocalizations of Egyptian fruit bats, researchers used video cameras and microphones to file teams of the animals for 75 days. Then they reviewed the recordings, painstakingly noting a number of necessary particulars, similar to which bat was vocalizing and in what context, for every of practically 15,000 calls.
The bats are pugilistic, incessantly quarreling of their crowded colonies, and the overwhelming majority of their vocalizations are aggressive. “Principally, they’re pushing one another,” mentioned Yossi Yovel, a neuroecologist at Tel Aviv College who led the analysis. “Think about a giant stadium and everyone desires to discover a seat.”
However a machine-learning system might distinguish, with 61 p.c accuracy, between aggressive calls made in 4 totally different contexts, figuring out whether or not a selected name had been emitted throughout a combat associated to meals, mating, perching place or sleep. That’s not an ideal efficiency, Dr. Yovel famous, however it’s considerably higher than the 25 p.c accuracy related to random guessing.
Dr. Yovel was shocked to find that the software program might additionally determine, at ranges higher than probability guessing, which bat was on the receiving finish of the scolding.
“This suggests that an eavesdropping bat is theoretically in a position, to some extent at the very least, to determine if particular person A is addressing particular person B or particular person C,” the researchers wrote of their 2016 paper.
Though the concept stays unproven, the bats could differ their vocalizations relying on their relationship to and data of the offender, the identical method individuals would possibly use totally different tones when addressing totally different audiences.
“It’s a colony, they’re very social, they know one another,” Dr. Yovel mentioned. “Maybe after I shout at you for meals, it’s totally different from after I shout at any person else for meals. So the identical name could have barely totally different nuances, which we had been in a position to detect utilizing machine studying.”
Nonetheless, detecting patterns is simply the start. Scientists then want to find out whether or not the algorithms have uncovered one thing significant about real-world animal habits.
“You must be very cautious to keep away from recognizing patterns that aren’t actual,” Dr. Stowell mentioned.
After the algorithms instructed that bare mole rat colonies all had distinct dialects, Dr. Barker and her colleagues confirmed that the rodents had been way more seemingly to reply to gentle chirps from members of their very own colonies than these from overseas ones. To rule out the chance that the bare mole rats had been merely responding to particular person voices they acknowledged, the researchers repeated the experiment with synthetic gentle chirps they generated to match the dialect of a rat’s house colony. The outcomes held.
Within the wild, colony-specific dialects would possibly assist bare mole rats make sure that they aren’t sharing scarce sources with strangers, and could also be a method of implementing social conformity. “In these giant underground tunnels, you need to be sure that everybody’s following the foundations,” Dr. Barker mentioned. “And one very fast option to take a look at that’s to verify everyone seems to be talking very equally.”
Different main initiatives are underway. Undertaking CETI — brief for the Cetacean Translation Initiative — is bringing collectively machine-learning specialists, marine biologists, roboticists, linguists and cryptographers, amongst others, at greater than a dozen establishments to decode the communication of sperm whales, which emit bursts of clicks which can be organized into Morse code-like sequences referred to as codas.
The workforce is planning to put in its “core whale-listening stations,” every of which incorporates 28 underwater microphones, off the coast of Dominica this fall. It plans to make use of robotic fish to file audio and video of the whales, in addition to small acoustic tags to file the vocalizations and actions of particular person animals.
Then, the researchers will attempt to decipher the syntax and semantics of whale communication and probe larger scientific questions on sperm whale habits and cognition, similar to how giant teams coordinate their actions and the way whale calves be taught to speak.
“Each which method we flip there’s one other query,” mentioned David Gruber, a marine biologist at Baruch Faculty who leads Undertaking CETI. “If there was a giant occasion that occurred per week in the past, how would we all know that they’re nonetheless speaking about it? Do whales do arithmetic?”
The Earth Species Undertaking, a California-based nonprofit, can also be partnering with biologists to pilot an assortment of machine-learning approaches with whales and different species.
As an illustration, it’s working with marine biologists to find out whether or not machine-learning algorithms can routinely determine what behaviors baleen whales are participating in, based mostly on motion information collected by monitoring tags.
“Is there a selected signature within the information for when an animal takes a breath or when an animal is feeding?” mentioned Ari Friedlaender, a marine ecologist on the College of California, Santa Cruz, who’s collaborating on the venture.
The researchers hope to overlay that behavioral information with audio recordings to find out whether or not there are specific sounds that whales persistently make in sure contexts.
“Now you are able to do actually attention-grabbing issues, like, ‘Let’s take orcas, take a look at their movement, translate the movement into the sound that goes with it,’” mentioned Aza Raskin, the president and co-founder of the Earth Species Undertaking. “Or you can begin with the audio and say, ‘What habits goes with what they’re saying?’”
Speaking again
In one other line of analysis, Earth Species specialists are utilizing machine-learning algorithms to create a listing of all the decision sorts made by captive Hawaiian crows, which grew to become extinct within the wild 20 years in the past.
They are going to then examine the outcomes to historic recordings of untamed Hawaiian crows to determine particular name sorts the birds might need misplaced over their years in captivity.
“Their vocal repertoire could have eroded over time, which is an actual conservation concern,” mentioned Christian Rutz, a behavioral ecologist on the College of St. Andrews in Scotland who’s working with Earth Species on the venture. “They preserve them in these aviaries to breed birds for future releases. However what if these crows not know learn how to converse crow?”
Scientists can then research the operate of any misplaced calls — and maybe even reintroduce essentially the most vital ones to captive colonies.
The Earth Species Undertaking has additionally partnered with Michelle Fournet, a marine acoustic ecologist on the College of New Hampshire, who has been attempting to decipher humpback whale communication by taking part in prerecorded whale calls via underwater audio system and observing how the whales reply.
Now, Earth Species scientists are utilizing algorithms to generate novel humpback whale vocalizations — that’s, “new calls that don’t exist however sound like they may,” Dr. Fournet mentioned. “I can’t say how cool it’s to think about one thing from nature that isn’t there after which to hearken to it.”
Enjoying these new calls to wild whales might assist scientists take a look at hypotheses in regards to the operate of sure vocalizations, she mentioned.
Given sufficient information about how whales converse with one another, machine-learning programs ought to be capable to generate believable responses to particular whale calls and play them again in actual time, specialists mentioned. That signifies that scientists might, in essence, use whale chatbots to “converse” with the marine mammals even earlier than they absolutely perceive what the whales are saying.
These machine-mediated conversations might assist researchers refine their fashions, and enhance their understanding of whale communication. “Sooner or later, it may be an actual dialogue,” mentioned Michael Bronstein, a machine-learning knowledgeable at Oxford and a part of Undertaking CETI.
He added, “As a scientist, that is in all probability the craziest venture I’ve ever participated in.”
Studying to hear
The prospect of ongoing, two-way dialogue with different species stays unknown. However true dialog would require quite a few “stipulations,” together with matching intelligence sorts, suitable sensory programs and, crucially, a shared want to talk, mentioned Natalie Uomini, an knowledgeable on cognitive evolution on the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
“There needs to be the motivation on either side to need to talk,” she mentioned.
Even then, some animals could have experiences which can be so totally different from our personal that some concepts merely get misplaced in translation. “For instance, we’ve got an idea of ‘getting moist,’” Dr. Bronstein mentioned. “I feel whales wouldn’t even give you the chance ever to know what it means.”
These experiments may elevate moral points, specialists acknowledge. “When you discover patterns in animals that help you perceive their communication, that opens the door to manipulating their communications,” Mr. Mustill mentioned.
However the expertise is also deployed for the good thing about animals, serving to specialists monitor the welfare of each wild and home fauna. Scientists additionally mentioned that they hoped that by offering new perception into animal lives, this analysis would possibly immediate a broader societal shift. Many pointed to the galvanizing impact of the 1970 album “Songs of the Humpback Whale,” which featured recordings of otherworldly whale calls and has been extensively credited with serving to to spark the worldwide Save the Whales motion.
The biologist Roger Payne, who produced that album, is now a part of Undertaking CETI. And lots of scientists mentioned they hoped these new, high-tech efforts to know the vocalizations of whales — and crows and bats and even bare mole rats — might be equally transformative, offering new methods to attach with and perceive the creatures with whom we share the planet.
“It’s not what the whales are saying that issues to me,” Dr. Gruber mentioned. “It’s the truth that we’re listening.”

Science
If you're living with a drug or mental health problem, here's where to look for help

Fatal overdoses in the U.S. fell for the first time in five years in 2023, according to preliminary estimates recently released by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, but UCLA researcher Joseph Friedman warns that the new findings should not be interpreted to mean that the nation’s drug and mental health crises are abating.
Friedman has analyzed “deaths of despair” that result from overdose, suicide and liver disease due to alcoholism and found that while death rates for white Americans have dipped, rates have risen in recent years among people of color in the U.S., especially among Native and Black Americans. Illegal opioids such as fentanyl have ravaged Black and low-income communities in Los Angeles.
While it’s difficult to pinpoint the exact reasons behind substance abuse or suicide, Friedman as well as other experts in addiction medicine and mental health say racial inequality, economic distress and historical trauma have aggravated those problems in marginalized communities.
If you or someone you know needs immediate help for a mental health, substance-use or suicidal crisis, call or text 988, or chat online by visiting the suicide and crisis line’s website. For mental health resources and referrals, call the Los Angeles County Department of Mental Health’s Help Line 24/7 at (800) 854-7771.
Here are other organizations that offer information, counseling and support services:
Nakeya Fields, a licensed clinical social worker in Pasadena, founded the Black Mental Health Task Force, a coalition that brings together mental health professionals, clients, nonprofits, community organizations, educators and others in California to raise awareness about mental wellness. Her Therapeutic Play Foundation offers activities designed to improve resilience and coping skills through creative arts, play and sports. It provides individual, couples, group and family therapy for Black, Latinx, LGBTQ+ and other members of marginalized populations.
The American Indian Counseling Center, a division of the Los Angeles County Mental Health Department, offers crisis intervention, 24/7 intensive mental health services and counseling for all ages, as well as physician consultations for medications and referrals to culturally relevant support groups. Call (562) 402-0677 and ask to speak with the on-duty worker.
United American Indian Involvement’s behavioral health program provides outpatient substance use disorder treatment and mental health services to American Indians and Alaska Natives living throughout Los Angeles County. Visit the website or call (213) 202-3970.
Melanin and Mental Health offers an online network of Black and brown mental healthcare providers that is searchable by geographic area, issue type and treatment sought. It’s also possible to filter results by therapists’ racial background and specialty, as well as by insurance carrier.
The Black Mental Health Alliance offers confidential referrals to culturally competent mental health professionals who are in its database of licensed therapists.
Painted Brain advocates for mental wellness in underserved L.A. communities by offering self-care, relaxation and therapeutic art and play sessions, support groups and trainings for mental health professionals. As part of its peer-led model, many of the staff have experienced mental health issues themselves. Its community center and art space is located at 5980 W. Pico Blvd. in Los Angeles.
The Los Angeles LGBT Center offers individual, couples, family, group therapy and psychiatric care, as well as support for people struggling with substance use. The center has locations in West Hollywood, at Mi Centro in East L.A., at its Trans Wellness Center near MacArthur Park and in South L.A.’s Leimert Park neighborhood.
The Community Health Project Los Angeles provides services to people who use drugs by way of a harm-reduction approach that emphasizes offering clean needles as well as education on how to respond to an overdose.
Science
Are 'deaths of despair' really more common for white Americans? A UCLA report says no
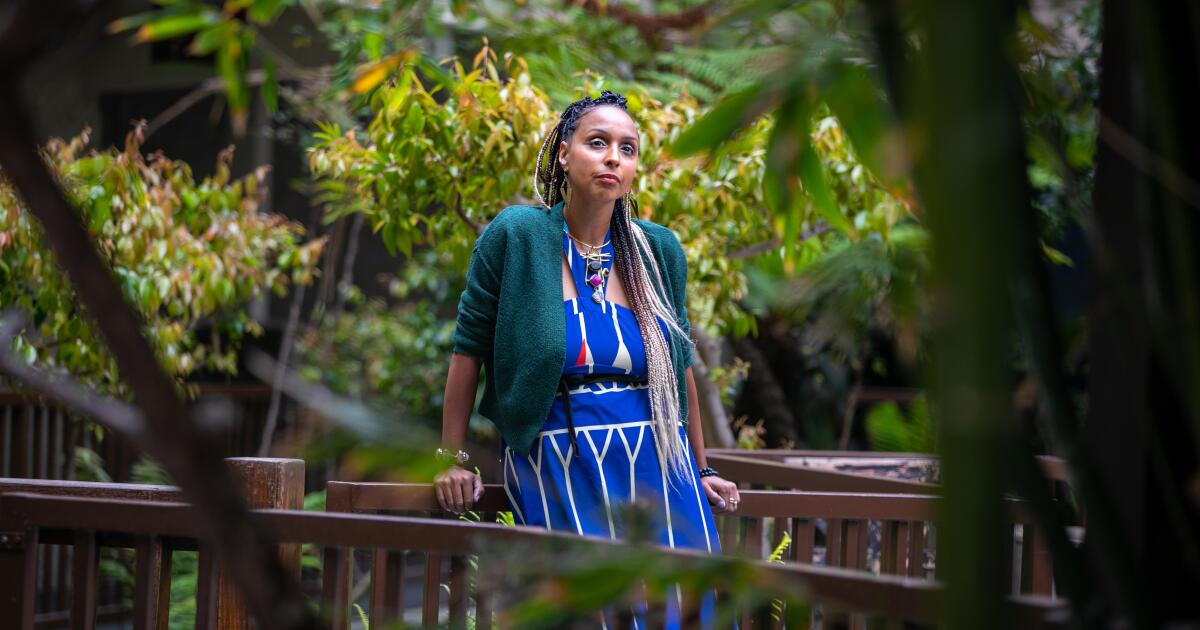

Nakeya Fields has seen how the stresses that come with being Black — racial injustice, financial strain, social isolation — can leave people feeling hopeless and push some into substance abuse.
It’s one of the reasons the Pasadena social worker started offering “therapeutic play” gatherings for Black mothers like herself and children.
“I’m trying to host more safe spaces for us to come and share that we’re suffering,” the 32-year-old said. “And honestly, the adults need play more than kids.”
Yet while Black and brown mental health practitioners such as Fields have labored to address these issues within their communities, a very different conversation has been occurring in the nation at large.
For years, discussions about America’s substance-abuse crisis have focused almost exclusively on the narrative that it is white, middle-age adults who face the greatest risk of dying from drug overdoses, alcoholic liver disease and suicide.
The theory, which was presented by two Princeton economists in 2015 and based on data from 1999 to 2013, argued that despair was behind rising premature mortality rates among white Americans, especially those who were less educated.
Virtually overnight, the “deaths of despair” concept began to drive the national discourse over populist far-right politics; the rise of Donald Trump; and deepening political polarization over such topics as addiction treatment, law enforcement and immigration.
But after roughly a decade, researchers at UCLA and elsewhere have begun to dismantle this idea.
In a study published recently in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, authors found that deaths of despair rates for middle-age Black and Native Americans have surged past those of white Americans as the overdose crisis moves from being driven by prescription opioids to illegal drugs such as fentanyl and heroin.
While the opioid crisis did raise drug overdose deaths among white Americans for a time, it was an anomaly, said Joseph Friedman, a social medicine expert at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine who was the lead author of the journal analysis. In fact, by 2022 the rate for white Americans had started to dip.
“What’s really important is that now, with these three causes of death, the gap has closed, and it’s moving in the other direction,” Friedman said.
Sandra Mims, a community health worker with Community Health Project L.A., puts out boxes of Narcan — a naloxone nasal spray that reverses the effects of opioid overdose — at an event at MacArthur Park in Los Angeles on International Overdose Awareness Day.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
The analysis found that deaths of despair for Black Americans hit a rate of 103.81 per 100,000 people in 2022, compared with 102.63 for white Americans. The rate for Native American and Alaska Native populations was even higher at 241.7 per 100,000 people in 2022.
The UCLA analysis doesn’t specify the midlife personal issues that might have led to addiction or suicide.
But the authors say that flaws in the methodology of the 2015 deaths of despair report skewed its conclusions about who was most at risk. Specifically, Friedman said that it failed to give enough consideration to long-standing racial inequities that Black Americans experience in income, educational attainment, incarceration and access to quality medical care, all of which can contribute to drug use and poor mental health outcomes. And statistics for Native Americans weren’t factored in at all.
“It was burned into the American psyche that it was white people in the rural U.S.,” Friedman said. “It was just a very small piece of the truth that was very interesting but was widely sold as something it wasn’t.”
Another recent worrying sign, Friedman says: Deaths of despair among Latinos are starting to catch up to those among Black and Native Americans.
Princeton professors Anne Case and her husband Angus Deaton, winner of the 2015 Nobel Prize in economic sciences, were thrust into the media spotlight when their deaths of despair findings were first published. Deaton told NPR that during a visit to the White House, even President Obama asked him about the phenomenon.
Their 2020 book, “Deaths of Despair and the Future of Capitalism,” was described by publisher Princeton University Press as “a troubling portrait of the American dream in decline.”
“For the white working class, today’s America has become a land of broken families and few prospects. As the college educated become healthier and wealthier, adults without a degree are literally dying from pain and despair,” the publisher said.
Fields, who employs yoga and pottery in her therapy, said this framing was misleading and racially biased.
“I’m actually flabbergasted that somebody has a term called ‘deaths of despair,’” Fields said. “It’s ‘despair’ when white people experience this suffering. But when we experience it, it’s just what we have to deal with.”
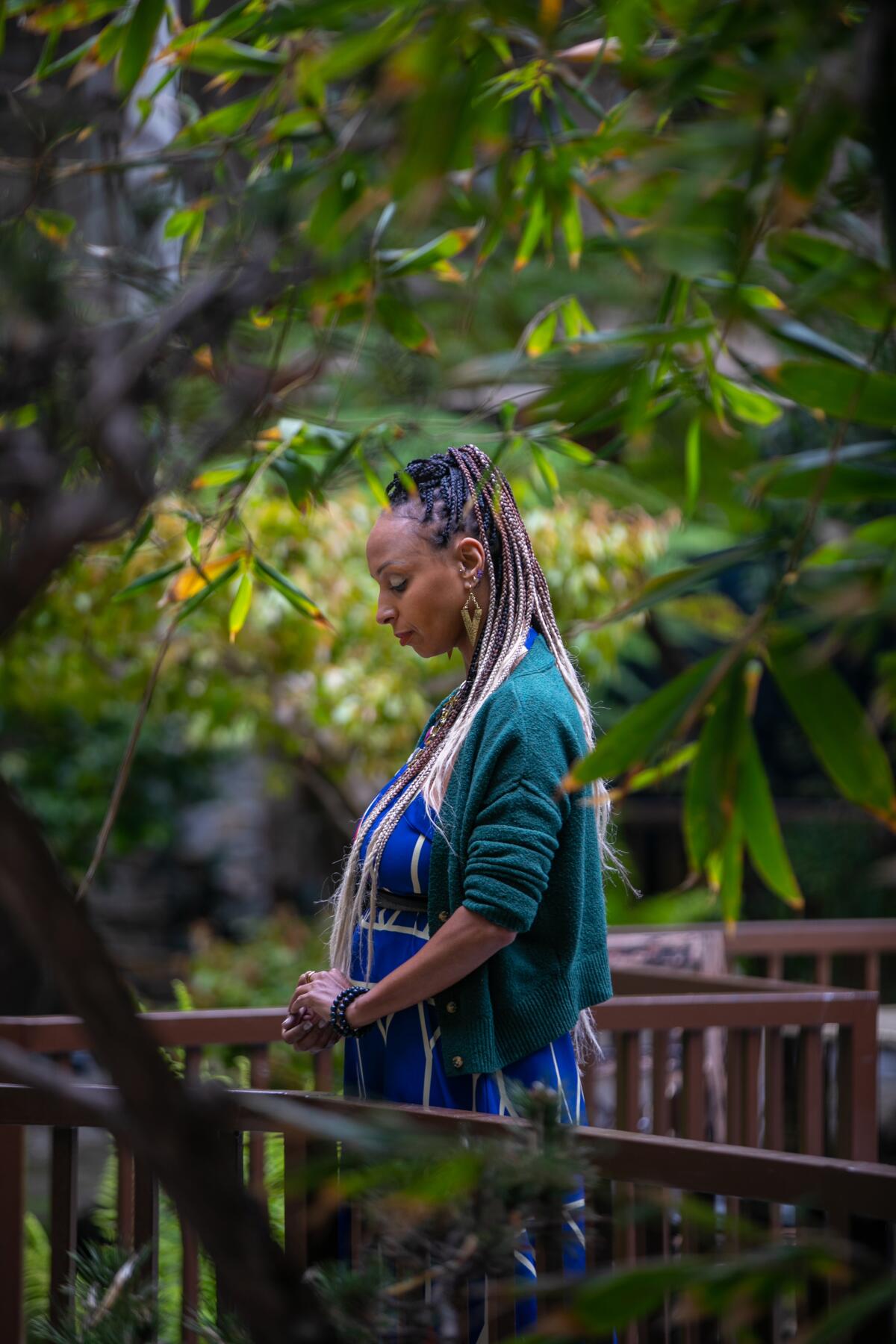

Nakeya Fields says it’s important to address mental wellness issues early, before people reach a crisis point and become another statistic.
(Jason Armond / Los Angeles Times)
Both Friedman and Fields say their critiques are not intended to minimize deaths among white Americans.
Still, Friedman wonders: “How do we empower Black and Native American communities in a way that enables them to treat these problems?”
Racism must be considered when trying to make sense of the crisis in premature deaths, says Dr. Helena Hansen, head of UCLA’s Department of Psychiatry and a senior author on Friedman’s analysis. Hansen, who is Black and specializes in addiction psychiatry, also co-authored the book “Whiteout: How Racial Capitalism Changed the Color of Opioids in America.”
For years, pharmaceutical companies steered expensive prescription pain medications, such as the opioid Oxycontin, as well as the most effective medications for opioid-use disorder, to white Americans with good access to healthcare, she said.
But at the same time, Black and brown Americans were unfairly subjected to law enforcement policies that prioritized incarceration for illegal drug use over increasing access to more humane medical strategies to help them, further harming already vulnerable communities, Hansen said.
“In our society, people with access to the new technologies and pharmaceuticals are more likely to be white,” Hansen says. “None of this is by accident. All of this is the direct result of careful racially and class-segmented marketing strategies by pharmaceutical companies.”
This two-tiered system arose because drug manufacturers, doctors and policymakers have for too long failed to see people from historically marginalized communities who live with addiction and mental health crises as worthy of the same sympathy and treatments that many white Americans receive, Hansen says.
Joseph Gone, a professor of anthropology at Harvard who has spent 25 years studying the intersection of colonialism, culture and mental health in Indigenous communities, agreed.
“Deaths of despair have been a reality for Indigenous communities since conquest and dispossession,” he said.
“It’s amazing how much grief our people contend with from early deaths — there are not that many communities in America that bear it quite the way we do,” said Gone, who is a member of the Aaniiih-Gros Ventre tribal nation of north-central Montana. “Until we acknowledge and take responsibility for the casualties of colonization, which endure to this day through deaths of despair, it’s going to be very hard to turn this around.”
Gone, who has collaborated with Friedman on previous research, says the mental health crisis in tribal nations is aggravated by widespread joblessness and generational poverty, and a lack of healthcare resources to treat people in need of immediate or long-term treatment.
Just one traveling psychiatrist serves reservations spread across both Montana and Wyoming — a region covering more than 243,300 square miles — mostly to manage patients’ prescriptions, he says.
And “for all of Indian country, we’re talking about a very small number of in-patient psychiatric facilities,” Gone says.
General practitioners can serve as a first line of defense, but they are not necessarily equipped to address the ongoing life crises that can lead to excessive drug and alcohol use, Gone says.
Fields says it’s important to address mental wellness issues early, before people reach a crisis point and become another statistic.
While her focus remains on Black women, she’s developed additional programming for adults, families and children, such as developmental screenings that measure for high stress levels. In June, Fields will co-present “Rap 4 Peace,” a conference and gala featuring hip-hop artists talking about mental health and reducing gun violence.
“This ‘tragedy of despair’ lives in us,” Fields says. “We breathe it. We go outside hoping that nobody will harm us or our children because they feel threatened by us. This is truly harmful to our bodies.”
Science
SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets from Vandenberg Space Force Base by 2026. Could that harm the coast?
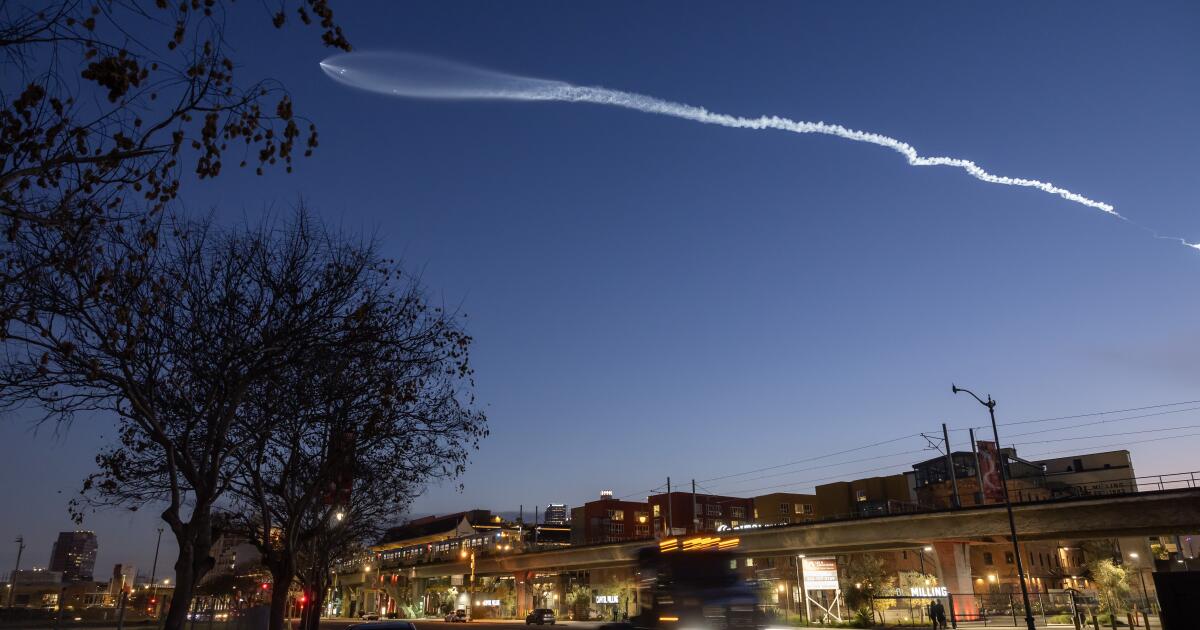

SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets into space from a Santa Barbara County military base by 2026, tripling the number of blasts rocking the coastal community — and raising concerns from neighbors and environmental groups about the effects on marine life.
Founded by billionaire Elon Musk, SpaceX has ramped up the number of rocket launches from Vandenberg Space Force Base in recent years, and it has made clear its desire to increase the frequency of blastoffs. But during a California Coastal Commission hearing Friday, U.S. Space Force officials outlined for the first time its own plans to multiply the number of launches from the base, from 37 in 2023 to more than 120 a year by 2026.
The overwhelming majority of those rocket liftoffs would be conducted by SpaceX, which has already done more launches from the base than the commission has approved.
Last year SpaceX breached an agreement with the commission that limited the number of launches to six, sending 28 rockets into space.
It is seeking an agreement with the commission to do 36 launches a year, increasing to 90 in 2026.
The decision by the commission, which was created to protect the state’s coastal resources, will directly affect residents and marine life near the military base that hear and feel the rockets’ sonic booms.
It could also redirect the future of SpaceX, whose pursuit to redefine space exploration is already closely tied with U.S. military interests, given its work as a military contractor.
“The ultimate goal is for this to be more routine and not a huge deal,” said Space Force Col. Bryan Titus, operations vice commander at the base.
Formed in 2019, the U.S. Space Force has been looking to improve its ability to send rockets into space, Titus said, so SpaceX’s ability to launch with more frequency is a benefit to the U.S. military.
SpaceX launched 96 rockets in 2023 from Vandenberg and three other facilities: Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Fla., and SpaceX Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas.
Environmental groups argue that turning launches into a routine event could affect marine life.
“We’re concerned that more frequent launches will result in permanent changes,” said Ana Citrin, legal and policy director for the Gaviota Coast Conservancy.
Federal agencies, including the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, monitor the effects of the liftoffs on such animals as sea otters, bats, western snowy plovers, California least terns and California red-legged frogs.
Thus far, the monitoring has shown that some of the animals might react to the blastoff by flushing, or fleeing from their nests and homes, but they return soon after, according to U.S. Space Force officials. No long-term effects have been seen, they said.
SpaceX did not respond to a request for comment.
Flushing or hunkering down after a blast are already signs of wildlife exhibiting signs of stress, said Duncan Leitch, a professor of integrative biology at UCLA.
Most animals can adapt to infrequent incidents, but exposure to more frequent stressful incidents can change their biology as well as their behavior, he said.
In the worst-case scenarios, he said, the ability of birds to communicate could be impeded, and migratory birds could avoid the area. Fish and other animals that use sound to communicate and navigate underwater — including whales — could be affected too.
“Over a longer period of time, there may be reductions in the population of fish as they move away from the sound, or they may be affected to the point that it affects their health,” Leitch said. “It would change the ecosystem as far as other animals that rely on the fish.
“Having sounds that are well into the damaging, or painful, range of decibels now occurring [100] times a year, the animals might not have the ability to change their behavior or accommodate these types of sounds.”
Some environmental groups, including the Surfrider Foundation, are asking the commission to reject the increase.
SpaceX “intends to begin increasing very rapidly, so we’re very concerned about this,” said Mandy Sackett, senior California policy coordinator for the Surfrider Foundation.
More frequent launches could change the way wildlife in the area responds in the long term, environmental groups said.
Members of the California Coastal Commission are also asking whether SpaceX should be entitled to circumvent the permit process, as federal agencies are.
Federal entities negotiate agreements with the commission but ultimately can move ahead even without commission approval. In such cases, the commission’s recourse would be through mediation or the courts.
Because SpaceX is a U.S. Space Force contractor, military officials argue that all launch operations at the base by the company are “federal activities.”
But U.S. Space Force officials said only 25% of the rockets launched into space by SpaceX are carrying payloads for the Department of the Defense.
The vast majority of the liftoffs are for the company’s private benefit, raising questions about why SpaceX can dispense with permits when 75% of its blasts from the base don’t involve the U.S. government.
“That is still pretty skewed for me,” Commissioner Mike Wilson said during a meeting Friday.
Some commissioners — whose focus is usually on environmental protection, development and water issues during their monthly meetings — also brought up the war in Ukraine during Friday’s discussion.
“I question the national security public benefit of concentrating that much power, literally communication power, in one company that we’re enabling in this case,” Wilson said. “[SpaceX] has already showed that it will play in international conflicts at the will of one human being.”
Wilson was referring to reports that Musk’s company refused to allow Ukraine to use satellite internet service from Starlink, a subsidiary of SpaceX, to help it carry out an attack against Russia in September 2022.
“If the idea is that we’re supporting these permits on the side that we’re promoting national defense, and then a single company is able to dismantle our allies during armed conflict — that really doesn’t align,” Commissioner Justin Cummings said.
“I suspect that would violate our strategies around national defense.”
Titus declined to address the question, saying it was “out of my lane,” but he said he would try to get answers to address the commissioners’ concerns.
Some commissioners on Friday also argued that SpaceX, not U.S. military officials, should be making the company’s case in front of the agency.
“When this comes back, I think it would be really important that a representative from SpaceX comes to the meeting,” Cummings said.
Cummings said it was “ridiculous” for SpaceX not to appear at the meeting, despite multiple efforts from the agency to have SpaceX officials speak.
“They obviously refuse to because they’ve never shown up,” he said.
On Friday, Commission Chair Caryl Hart suggested an agreement might not be possible unless SpaceX changes its stance.
“From my perspective,” Hart said, “I think we’re going to continue to hit significant obstacles in achieving a federal consistency ruling without having SpaceX.”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoAavesham Movie Review
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTrump, Reciting Songs And Praising Cannibals, Draws Yawns And Raises Eyebrows
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoUnfrosted Movie Review: A sweet origins film which borders on the saccharine