Science
Opinion: How measles reemerged as a threat in California and elsewhere
The measles virus is resurging in the U.S. despite the long-standing availability of a vaccine that provides nearly life-long immunity. In the past few weeks, hundreds of people were exposed to a child with the virus in a Northern California healthcare facility; our state is one of 17 jurisdictions with reported measles cases in 2024, higher than seen in recent years.
Measles is an extremely transmissible pathogen: On average, one infected person infects 12 to 18 unvaccinated people. The airborne virus can linger in floating aerosols long after someone has left a room, and the common symptoms, which include rash, a high fever, watery eyes, cough and a runny nose, typically take a week or two to appear.
Infections can also cause immune amnesia, in which your immune system becomes better at fighting measles and worse at fighting other infections you were previously protected against. In rare cases it also leads to death, more often in children than adults, from respiratory or neurological complications, including a type of brain swelling in young children that can appear years after the initial measles infection.
Before the measles vaccine was introduced and licensed in 1963, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention cites an annual average of 549,000 cases (with likely millions more going unreported), 48,000 hospitalizations, nearly 500 deaths and 1,000 people with chronic disability. By 2000, thanks to vaccination, measles was declared eliminated in the U.S. But because of cases from people arriving here from other countries, combined with pockets of low vaccination, we are seeing outbreaks among unvaccinated people.
Policy can worsen the issue. Last month in Florida, following an outbreak at an elementary school, the state’s surgeon general left the decision to parents whether to send their children to school, citing high levels of community immunity as the rationale for not following the usual protocols. That cavalier response risked a much worse outbreak. A more standard response would have called for unvaccinated students and staff to be vaccinated and quarantine for 21 days (the time frame in which the disease could develop).
It might be tempting to Californians to dismiss this as a Florida problem. But our state has a measles time bomb on our hands. Ideally communities should hit at least 95% vaccination to achieve herd immunity. But a recent nationwide survey found that Southern California alone has 350 schools falling short of the desired vaccination threshold, meaning a single measles case in these schools could easily become an outbreak among the unvaccinated.
Misinformation around the measles vaccine has been an issue for years. A debunked but influential 1998 research paper in the Lancet, a British medical journal, suggested a link between the vaccine, which babies can receive starting at the age of 12 months, and autism. The paper was retracted in 2010 (and the authors were later reported to have committed fraud). But measles vaccine rates dropped in England throughout the early 2000s.
In California, a 2014 outbreak at Disneyland was connected to more than 140 cases in North America, with declining vaccination rates one contributing factor. A recent systematic review of the reasons why parents reject measles vaccination for their children found fear of autism the most cited concern. Those who were hesitant more frequently cited the internet and social media as information sources on vaccines than those who were not hesitant.
In recent years hesitancy has grown as misinformation about the COVID vaccine has made some parents doubtful of routine inoculations. Vaccination exemptions during the 2022-23 school year reached the highest level ever reported in the U.S., increasing in 40 states and Washington, D.C., and 10 states reaching exemption rates of above 5%. According to the CDC, the 93.1% vaccination rate among eligible children puts about 250,000 kindergarten students at risk for measles.
Encouragingly, we’ve seen in our own state that vaccine hesitancy can be reversed. Marin County had among the lowest measles vaccination rates in the state in 2011 and now has coverage close to 99% among children entering school. State contact tracing efforts that were strengthened during COVID-19, including the California Connected program, have been useful to track the contacts of measles cases.
But as the recent scares remind us, we still aren’t where we need to be with vaccination. Following the Disneyland outbreak, in 2015 California passed a law to remove the “personal belief” exemption from required childhood vaccines, meaning people must provide a medical reason to decline it. The law broadened the criteria for medical exemptions, which increased the year after it passed. Although the state tightened up medical exemptions with a new law in 2019, with the pandemic disrupting routine vaccinations and increasing homeschooling, the percentage of kindergarteners not up to date on vaccinations went up by 2021.
Vaccine exemption laws vary widely across the U.S., with some states allowing only medical exemptions, some also allowing religious exemptions and others permitting philosophical exemptions too. And outbreaks from one state can spill over across borders quickly.
That means decisions by Florida’s public health department, and vaccine hesitancy anywhere, can affect us all. California has to close the gap for communities that are not well-protected against measles.
Abraar Karan is an infectious disease doctor and researcher at Stanford University, where Julie Parsonnet is a professor of infectious diseases and of epidemiology and population health.

Science
Diablo Canyon clears last California permit hurdle to keep running

Central Coast Water authorities approved waste discharge permits for Diablo Canyon nuclear plant Thursday, making it nearly certain it will remain running through 2030, and potentially through 2045.
The Pacific Gas & Electric-owned plant was originally supposed to shut down in 2025, but lawmakers extended that deadline by five years in 2022, fearing power shortages if a plant that provides about 9 percent the state’s electricity were to shut off.
In December, Diablo Canyon received a key permit from the California Coastal Commission through an agreement that involved PG&E giving up about 12,000 acres of nearby land for conservation in exchange for the loss of marine life caused by the plant’s operations.
Today’s 6-0 vote by the Central Coast Regional Water Board approved PG&E’s plans to limit discharges of pollutants into the water and continue to run its “once-through cooling system.” The cooling technology flushes ocean water through the plant to absorb heat and discharges it, killing what the Coastal Commission estimated to be two billion fish each year.
The board also granted the plant a certification under the Clean Water Act, the last state regulatory hurdle the facility needed to clear before the federal Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) is allowed to renew its permit through 2045.
The new regional water board permit made several changes since the last one was issued in 1990. One was a first-time limit on the chemical tributyltin-10, a toxic, internationally-banned compound added to paint to prevent organisms from growing on ship hulls.
Additional changes stemmed from a 2025 Supreme Court ruling that said if pollutant permits like this one impose specific water quality requirements, they must also specify how to meet them.
The plant’s biggest water quality impact is the heated water it discharges into the ocean, and that part of the permit remains unchanged. Radioactive waste from the plant is regulated not by the state but by the NRC.
California state law only allows the plant to remain open to 2030, but some lawmakers and regulators have already expressed interest in another extension given growing electricity demand and the plant’s role in providing carbon-free power to the grid.
Some board members raised concerns about granting a certification that would allow the NRC to reauthorize the plant’s permits through 2045.
“There’s every reason to think the California entities responsible for making the decision about continuing operation, namely the California [Independent System Operator] and the Energy Commission, all of them are sort of leaning toward continuing to operate this facility,” said boardmember Dominic Roques. “I’d like us to be consistent with state law at least, and imply that we are consistent with ending operation at five years.”
Other board members noted that regulators could revisit the permits in five years or sooner if state and federal laws changes, and the board ultimately approved the permit.
Science
Deadly bird flu found in California elephant seals for the first time

The H5N1 bird flu virus that devastated South American elephant seal populations has been confirmed in seals at California’s Año Nuevo State Park, researchers from UC Davis and UC Santa Cruz announced Wednesday.
The virus has ravaged wild, commercial and domestic animals across the globe and was found last week in seven weaned pups. The confirmation came from the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s National Veterinary Services Laboratory in Ames, Iowa.
“This is exceptionally rapid detection of an outbreak in free-ranging marine mammals,” said Professor Christine Johnson, director of the Institute for Pandemic Insights at UC Davis’ Weill School of Veterinary Medicine. “We have most likely identified the very first cases here because of coordinated teams that have been on high alert with active surveillance for this disease for some time.”
Since last week, when researchers began noticing neurological and respoiratory signs of the disease in some animals, 30 seals have died, said Roxanne Beltran, a professor of ecology and evolutionary biology at UC Santa Cruz. Twenty-nine were weaned pups and the other was an adult male. The team has so far confirmed the virus in only seven of the dead pups.
Infected animals often have tremors convulsions, seizures and muscle weakness, Johnson said.
Beltran said teams from UC Santa Cruz, UC Davis and California State Parks monitor the animals 260 days of the year, “including every day from December 15 to March 1” when the animals typically come ashore to breed, give birth and nurse.
The concerning behavior and deaths were first noticed Feb. 19.
“This is one of the most well-studied elephant seal colonies on the planet,” she said. “We know the seals so well that it’s very obvious to us when something is abnormal. And so my team was out that morning and we observed abnormal behaviors in seals and increased mortality that we had not seen the day before in those exact same locations. So we were very confident that we caught the beginning of this outbreak.”
In late 2022, the virus decimated southern elephant seal populations in South America and several sub-Antarctic Islands. At some colonies in Argentina, 97% of pups died, while on South Georgia Island, researchers reported a 47% decline in breeding females between 2022 and 2024. Researchers believe tens of thousands of animals died.
More than 30,000 sea lions in Peru and Chile died between 2022 and 2024. In Argentina, roughly 1,300 sea lions and fur seals perished.
At the time, researchers were not sure why northern Pacific populations were not infected, but suspected previous or milder strains of the virus conferred some immunity.
The virus is better known in the U.S. for sweeping through the nation’s dairy herds, where it infected dozens of dairy workers, millions of cows and thousands of wild, feral and domestic mammals. It’s also been found in wild birds and killed millions of commercial chickens, geese and ducks.
Two Americans have died from the virus since 2024, and 71 have been infected. The vast majority were dairy or commercial poultry workers. One death was that of a Louisiana man who had underlying conditions and was believed to have been exposed via backyard poultry or wild birds.
Scientists at UC Santa Cruz and UC Davis increased their surveillance of the elephant seals in Año Nuevo in recent years. The catastrophic effect of the disease prompted worry that it would spread to California elephant seals, said Beltran, whose lab leads UC Santa Cruz’s northern elephant seal research program at Año Nuevo.
Johnson, the UC Davis researcher, said the team has been working with stranding networks across the Pacific region for several years — sampling the tissue of birds, elephant seals and other marine mammals. They have not seen the virus in other California marine mammals. Two previous outbreaks of bird flu in U.S. marine mammals occurred in Maine in 2022 and Washington in 2023, affecting gray and harbor seals.
The virus in the animals has not yet been fully sequenced, so it’s unclear how the animals were exposed.
“We think the transmission is actually from dead and dying sea birds” living among the sea lions, Johnson said. “But we’ll certainly be investigating if there’s any mammal-to-mammal transmission.”
Genetic sequencing from southern elephant seal populations in Argentina suggested that version of the virus had acquired mutations that allowed it to pass between mammals.
The H5N1 virus was first detected in geese in China in 1996. Since then it has spread across the globe, reaching North America in 2021. The only continent where it has not been detected is Oceania.
Año Nuevo State Park, just north of Santa Cruz, is home to a colony of some 5,000 elephant seals during the winter breeding season. About 1,350 seals were on the beach when the outbreak began. Other large California colonies are located at Piedras Blancas and Point Reyes National Sea Shore. Most of those animals — roughly 900 — are weaned pups.
It’s “important to keep this in context. So far, avian influenza has affected only a small proportion of the weaned at this time, and there are still thousands of apparently healthy animals in the population,” Beltran said in a press conference.
Public access to the park has been closed and guided elephant seal tours canceled.
Health and wildlife officials urge beachgoers to keep a safe distance from wildlife and keep dogs leashed because the virus is contagious.
Science
When slowing down can save a life: Training L.A. law enforcement to understand autism
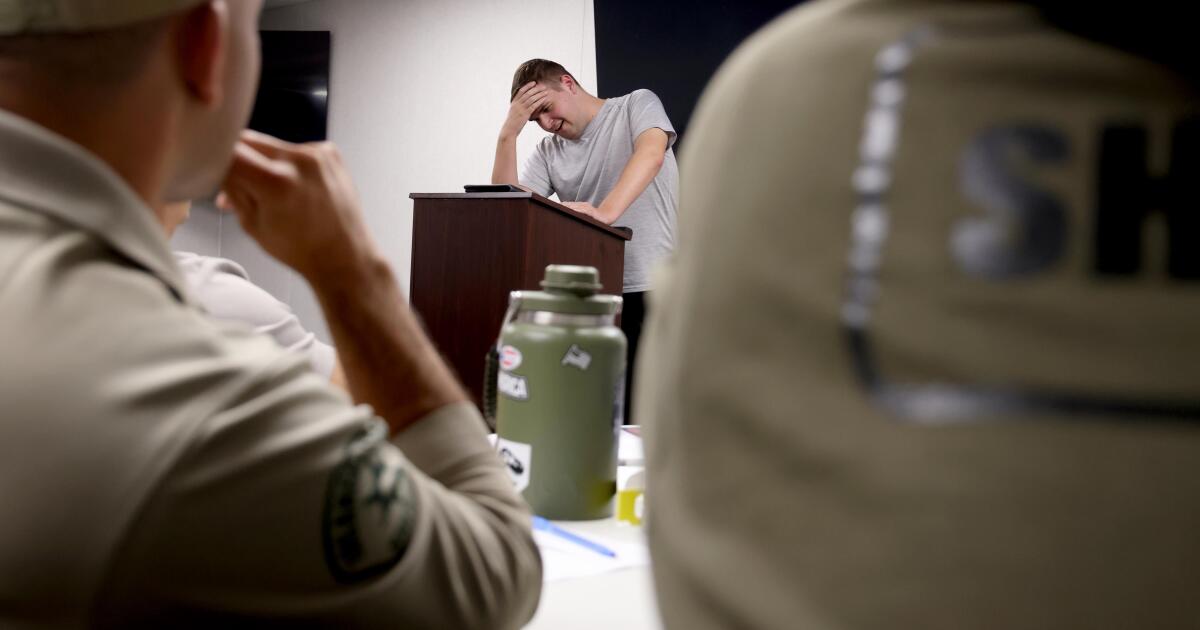

Kate Movius moved among a roomful of Los Angeles County sheriff’s deputies, passing out a pop trivia quiz and paper prism glasses.
She told them to put on the vision-distorting glasses, and to write with their nondominant hand. As they filled out the tests, Movius moved about the City of Industry classroom pounding abruptly on tables. Then came the cowbell. An aide flashed the overhead lights on and off at random. The goal was to help the deputies understand the feeling of sensory overwhelm, which many autistic people experience when incoming stimulation exceeds their capacity to process.
“So what can you do to assist somebody, or de-escalate somebody, or get information from someone who suffers from a sensory disorder?” Movius asked the rattled crowd afterward. “We can minimize sensory input. … That might be the difference between them being able to stay calm and them taking off.”
Movius, founder of the consultancy Autism Interaction Solutions, is one of a growing number of people around the U.S. working to teach law enforcement agencies to recognize autistic behaviors and ensure that encounters between neurodevelopmentally disabled people and law enforcement end safely.
She and City of Industry Mayor Cory Moss later passed out bags filled with tools donated by the city to aid interactions: a pair of noise-damping headphones to decrease auditory input, a whiteboard, a set of communication cards with words and images to point to, fidget toys to calm and distract.
“The thing about autistic behavior when it comes to law enforcement is a lot of it may look suspicious, and a lot of it may feel very disrespectful,” said Movius, who is also the parent of an autistic 25-year-old man. Responding officers, she said, “are not coming in thinking, ‘Could this be a developmentally disabled person?’ I would love for them to have that in the back of their minds.”
A sheriff’s deputy reads a pamphlet on autism during the training program.
(Genaro Molina / Los Angeles Times)
Autism spectrum disorder is a developmental condition that manifests differently in nearly every person who has it. Symptoms cluster around difficulties in communication, social interaction and sensory processing.
An autistic person stopped by police might hold the officer’s gaze intensely or not look at them at all. They may repeat a phrase from a movie, repeat the officer’s question or temporarily lose their ability to speak. They might flee.
All are common involuntary responses for an autistic person in a stressful situation, which a sudden encounter with law enforcement almost invariably is. To someone unfamiliar with the condition, all could be mistaken for intoxication, defiance or guilt.
Autism rates in the U.S. have increased nearly fivefold since the Centers for Disease Control began tracking diagnoses in 2000, a rise experts attribute to broadening diagnostic criteria and better efforts to identify children who have the condition.
The CDC now estimates that 1 in 31 U.S. 8-year-olds is autistic. In California, the rate is closer to 1 in 22 children.
As diverse as the autistic population is, people across the spectrum are more likely to be stopped by law enforcement than neurotypical peers.
About 15% of all people in the U.S. ages 18 to 24 have been stopped by police at some point in their lives, according to federal data. While the government doesn’t track encounters for disabled people specifically, a separate study found that 20% of autistic people ages 21 to 25 have been stopped, often after a report or officer observation of a person behaving unusually.
Some of these encounters have ended in tragedy.
In 2021, Los Angeles County sheriff’s deputies shot and permanently paralyzed a deaf autistic man after family members called 911 for help getting him to a hospital.
Isaias Cervantes, 25, had become distressed about a shopping trip and started pushing his mother, his family’s attorney said at the time. He resisted as two deputies attempted to handcuff him and one of the deputies shot him, according to a county report.
In 2024, Ryan Gainer’s family called 911 for support when the 15-year-old became agitated. Responding San Bernardino County sheriff‘s deputies shot and killed him outside his Apple Valley home.
Last year, police in Pocatello, Idaho, shot Victor Perez, 17, through a chain-link fence after the nonspeaking teenager did not heed their shouted commands. He died from his injuries in April.

Sheriff’s deputies take a trivia quiz using their non-writing hands, while wearing vision-distorting glasses, as Kate Movius, standing left, and Industry Mayor Cory Moss, right, ring cowbells. The idea was to help them understand the sensory overwhelm some autistic people experience.
(Genaro Molina / Los Angeles Times)
As early as 2001, the FBI published a bulletin on police officers’ need to adjust their approach when interacting with autistic people.
“Officers should not interpret an autistic individual’s failure to respond to orders or questions as a lack of cooperation or as a reason for increased force,” the bulletin stated. “They also need to recognize that individuals with autism often confess to crimes that they did not commit or may respond to the last choice in a sequence presented in a question.”
But a review of multiple studies last year by Chapman University researchers found that while up to 60% of officers have been on a call involving an autistic person, only 5% to 40% had received any training on autism.
In response, universities, nonprofits and private consultants across the U.S. have developed curricula for law enforcement on how to recognize autistic behaviors and adapt accordingly.
The primary goal, Movius told deputies at November’s training session, is to slow interactions down to the greatest extent possible. Many autistic people require additional time to process auditory input and verbal responses, particularly in unfamiliar circumstances.
If at all possible, Movius said, wait 20 seconds for a response after asking a question. It may feel unnaturally long, she acknowledged. But every additional question or instruction fired in that time — what’s your name? Did you hear me? Look at me. What’s your name? — just decreases the likelihood that a person struggling to process will be able to respond at all.
Moss’ son, Brayden, then 17, was one of several teenagers and young adults with autism who spoke or wrote statements to be read to the deputies. The diversity of their speech patterns and physical mannerisms showed the breadth of the spectrum. Some were fluently verbal, while others communicated through signs and notes.
“This population is so diverse. It is so complicated. But if there’s anything that we can show [deputies] in here that will make them stop and think, ‘Hey, what if this is autism?’ … it is saving lives,” Moss said.

Mayor Cory Moss, left, and Kate Movius hug at the end of the training program last November. Movius started Autism Interaction Solutions after her son was born with profound autism.
(Genaro Molina / Los Angeles Times)
Some disability advocates cautioned that it takes more than isolated training sessions to ensure encounters end safely.
Judy Mark, co-founder and president of the nonprofit Disability Voices United, says she trained thousands of officers on safe autism interactions but stopped after Cervantes’ shooting. She now urges families concerned about an autistic child’s safety to call an ambulance rather than law enforcement.
“I have significant concern about these training sessions,” Mark said. “People get comfort from it, and the Sheriff’s Department can check the box.”
While not a panacea, supporters argue that a brief course is better than no preparation at all. Some years ago, Movius received a letter from a man whose profoundly autistic son slipped away as the family loaded their car at the beach. He opened the unlocked door of a police vehicle, climbed into the back and began to flail in distress.
Though surprised, the officer seated at the wheel de-escalated the situation and helped the young man find his family, the father wrote to Movius. He had just been to her training.
-

 World2 days ago
World2 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts3 days ago
Massachusetts3 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Louisiana5 days ago
Louisiana5 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Denver, CO3 days ago
Denver, CO3 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoOpenAI didn’t contact police despite employees flagging mass shooter’s concerning chatbot interactions: REPORT




















