Science
Failure to Slow Warming Will Set Off Climate ‘Tipping Points,’ Scientists Say

Failure to restrict international warming to the targets set by worldwide accords will more than likely set off a number of local weather “tipping factors,” a group of scientists stated on Thursday, with irreversible results together with the collapse of the Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets, abrupt thawing of Arctic permafrost and the demise of coral reefs.
The researchers stated that even on the present stage of warming, about 1.1 levels Celsius (2 levels Fahrenheit) above preindustrial ranges, a few of these self-sustaining adjustments may need already begun. But when warming reached above 1.5 levels Celsius, the extra bold of two targets set by the 2015 Paris Settlement, the adjustments would turn into rather more sure.
And on the larger Paris goal, 2 levels Celsius, much more tipping factors would seemingly be set off, together with the lack of mountain glaciers and the collapse of a system of deep mixing of water within the North Atlantic.
The adjustments would have important, long-term results on life on Earth. The collapse of the Greenland and West Antarctic ice sheets, for instance, would result in unrelenting sea stage rise, measured in ft, not inches, over centuries. The thawing of permafrost would launch extra heat-trapping gases into the ambiance, hindering efforts to restrict warming. A shutdown of ocean mixing within the North Atlantic may have an effect on international temperatures and produce extra excessive climate to Europe.
Johan Rockström, the director of the Potsdam Institute for Local weather Influence Analysis in Germany and one of many researchers, stated the group had “come to the very dire conclusion that 1.5 levels Celsius is a threshold” past which a few of these results would begin. That makes it all of the extra crucial, he and others stated, for nations to rapidly and drastically lower emissions of carbon dioxide and different heat-trapping gases to curb international warming.
The analysis is in step with current assessments by the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change, a bunch of consultants convened by the United Nations, that past 1.5 levels of warming, the threats of local weather change develop significantly.
“It actually offers sturdy scientific help for fast emission cuts in step with the Paris Settlement,” stated David Armstrong McKay, a local weather scientist on the College of Exeter in Britain and the lead creator of a paper describing the researchers’ work, revealed in Science. Limiting warming to 1.5 levels “doesn’t assure we don’t see tipping factors,” Dr. McKay stated. “Nevertheless it reduces the probability.”
And as with the U.N. panel’s assessments, overshooting the 1.5 diploma goal doesn’t imply all is misplaced. “Each tenth of a level counts,” Dr. Rockström stated. “So 1.6 is best than 1.7 and so forth” in decreasing the tipping-point dangers.
International locations haven’t pledged to chop greenhouse fuel emissions sufficient to satisfy both Paris goal, though the local weather and power laws handed by Congress final month strikes america a lot nearer to its personal targets. Present insurance policies put the world on tempo for almost 3 levels Celsius of warming by the top of the century. At that stage of warming, much more tipping factors could be set off, the researchers stated.
The idea of local weather tipping factors has been round for many years. Nevertheless it has additionally been accompanied by a excessive diploma of uncertainty and debate, together with in regards to the threshold temperatures past which some adjustments would start, and whether or not a few of these occasions even meet the definition of adjustments that may be self-sustaining it doesn’t matter what occurs with future warming.
A significant research in 2008 recognized greater than a dozen elements of Earth’s system that would attain a tipping level. The brand new analysis eradicated just a few and added a number of extra, figuring out a complete of 16 elements, together with 9 that may have international results.
Amongst these eradicated, Dr. McKay stated, was summer time Arctic sea ice. Though ice extent has been steadily declining for many years, he stated there was not any clear threshold past which the decline would turn into self-sustaining.
However the primary aim of the brand new analysis, which reviewed research that had used information from previous climates, present observations and pc simulations, was to cut back the uncertainty about when the tipping factors is likely to be reached.
The research “places temperature thresholds on all of the tipping components,” Dr. Rockström stated. “That has by no means been carried out earlier than.”
Invoice Hare, who’s the chief government of Local weather Analytics, a nonprofit analysis and coverage group, and who was not concerned within the research, stated, “It systematically places collectively and synthesizes the state of scientific data about essential Earth system tipping factors.”
“It reinforces the urgency of the worldwide group working collectively to halve emissions by 2030 and get to web zero by 2050,” he stated.
Thomas Stocker, a local weather scientist on the College of Bern in Switzerland who was not concerned within the research, cautioned that rather more analysis was wanted with reference to tipping factors. “It’s not the final word phrase,” he stated of the research’s findings. “It’s a contribution to an necessary dialog that’s ongoing.”
What is required, Dr. Stocker stated, is a complete evaluation by the Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Change, maybe as a part of the subsequent spherical of assessments, which is due within the second half of this decade.
Dr. Rockström agreed that extra analysis was wanted. “I’m hoping that the I.P.C.C. will take this scientific evaluation on board,” he stated.
The Potsdam institute and the College of Exeter are additionally sponsoring a convention subsequent week designed to encourage extra work on the topic. Amongst different initiatives, Dr. Rockström stated, is one to enhance modeling of those cataclysmic occasions.
“We’re in a significantly better place now than just some years again to advance an actual initiative on tipping level analysis,” he stated.

Science
Are 'deaths of despair' really more common for white Americans? A UCLA report says no
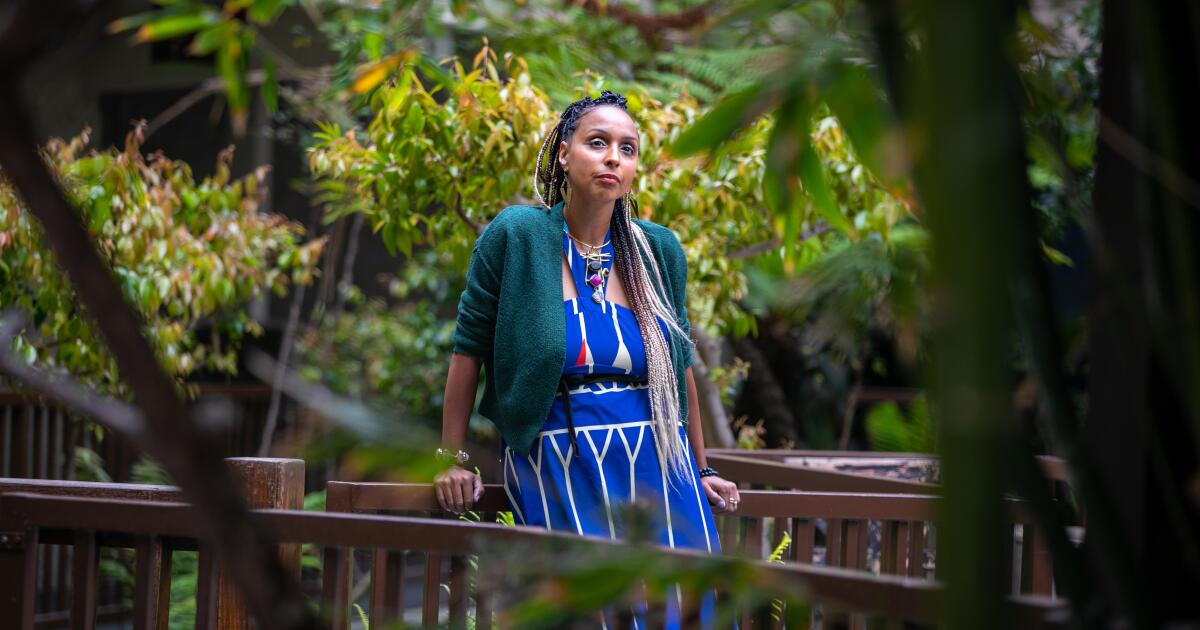

Nakeya Fields has seen how the stresses that come with being Black — racial injustice, financial strain, social isolation — can leave people feeling hopeless and push some into substance abuse.
It’s one of the reasons the Pasadena social worker started offering “therapeutic play” gatherings for Black mothers like herself and children.
“I’m trying to host more safe spaces for us to come and share that we’re suffering,” the 32-year-old said. “And honestly, the adults need play more than kids.”
Yet while Black and brown mental health practitioners such as Fields have labored to address these issues within their communities, a very different conversation has been occurring in the nation at large.
For years, discussions about America’s substance-abuse crisis have focused almost exclusively on the narrative that it is white, middle-age adults who face the greatest risk of dying from drug overdoses, alcoholic liver disease and suicide.
The theory, which was presented by two Princeton economists in 2015 and based on data from 1999 to 2013, argued that despair was behind rising premature mortality rates among white Americans, especially those who were less educated.
Virtually overnight, the “deaths of despair” concept began to drive the national discourse over populist far-right politics; the rise of Donald Trump; and deepening political polarization over such topics as addiction treatment, law enforcement and immigration.
But after roughly a decade, researchers at UCLA and elsewhere have begun to dismantle this idea.
In a study published recently in the journal JAMA Psychiatry, authors found that deaths of despair rates for middle-age Black and Native Americans have surged past those of white Americans as the overdose crisis moves from being driven by prescription opioids to illegal drugs such as fentanyl and heroin.
While the opioid crisis did raise drug overdose deaths among white Americans for a time, it was an anomaly, said Joseph Friedman, a social medicine expert at UCLA’s David Geffen School of Medicine who was the lead author of the journal analysis. In fact, by 2022 the rate for white Americans had started to dip.
“What’s really important is that now, with these three causes of death, the gap has closed, and it’s moving in the other direction,” Friedman said.
Sandra Mims, a community health worker with Community Health Project L.A., puts out boxes of Narcan — a naloxone nasal spray that reverses the effects of opioid overdose — at an event at MacArthur Park in Los Angeles on International Overdose Awareness Day.
(Mel Melcon / Los Angeles Times)
The analysis found that deaths of despair for Black Americans hit a rate of 103.81 per 100,000 people in 2022, compared with 102.63 for white Americans. The rate for Native American and Alaska Native populations was even higher at 241.7 per 100,000 people in 2022.
The UCLA analysis doesn’t specify the midlife personal issues that might have led to addiction or suicide.
But the authors say that flaws in the methodology of the 2015 deaths of despair report skewed its conclusions about who was most at risk. Specifically, Friedman said that it failed to give enough consideration to long-standing racial inequities that Black Americans experience in income, educational attainment, incarceration and access to quality medical care, all of which can contribute to drug use and poor mental health outcomes. And statistics for Native Americans weren’t factored in at all.
“It was burned into the American psyche that it was white people in the rural U.S.,” Friedman said. “It was just a very small piece of the truth that was very interesting but was widely sold as something it wasn’t.”
Another recent worrying sign, Friedman says: Deaths of despair among Latinos are starting to catch up to those among Black and Native Americans.
Princeton professors Anne Case and her husband Angus Deaton, winner of the 2015 Nobel Prize in economic sciences, were thrust into the media spotlight when their deaths of despair findings were first published. Deaton told NPR that during a visit to the White House, even President Obama asked him about the phenomenon.
Their 2020 book, “Deaths of Despair and the Future of Capitalism,” was described by publisher Princeton University Press as “a troubling portrait of the American dream in decline.”
“For the white working class, today’s America has become a land of broken families and few prospects. As the college educated become healthier and wealthier, adults without a degree are literally dying from pain and despair,” the publisher said.
Fields, who employs yoga and pottery in her therapy, said this framing was misleading and racially biased.
“I’m actually flabbergasted that somebody has a term called ‘deaths of despair,’” Fields said. “It’s ‘despair’ when white people experience this suffering. But when we experience it, it’s just what we have to deal with.”
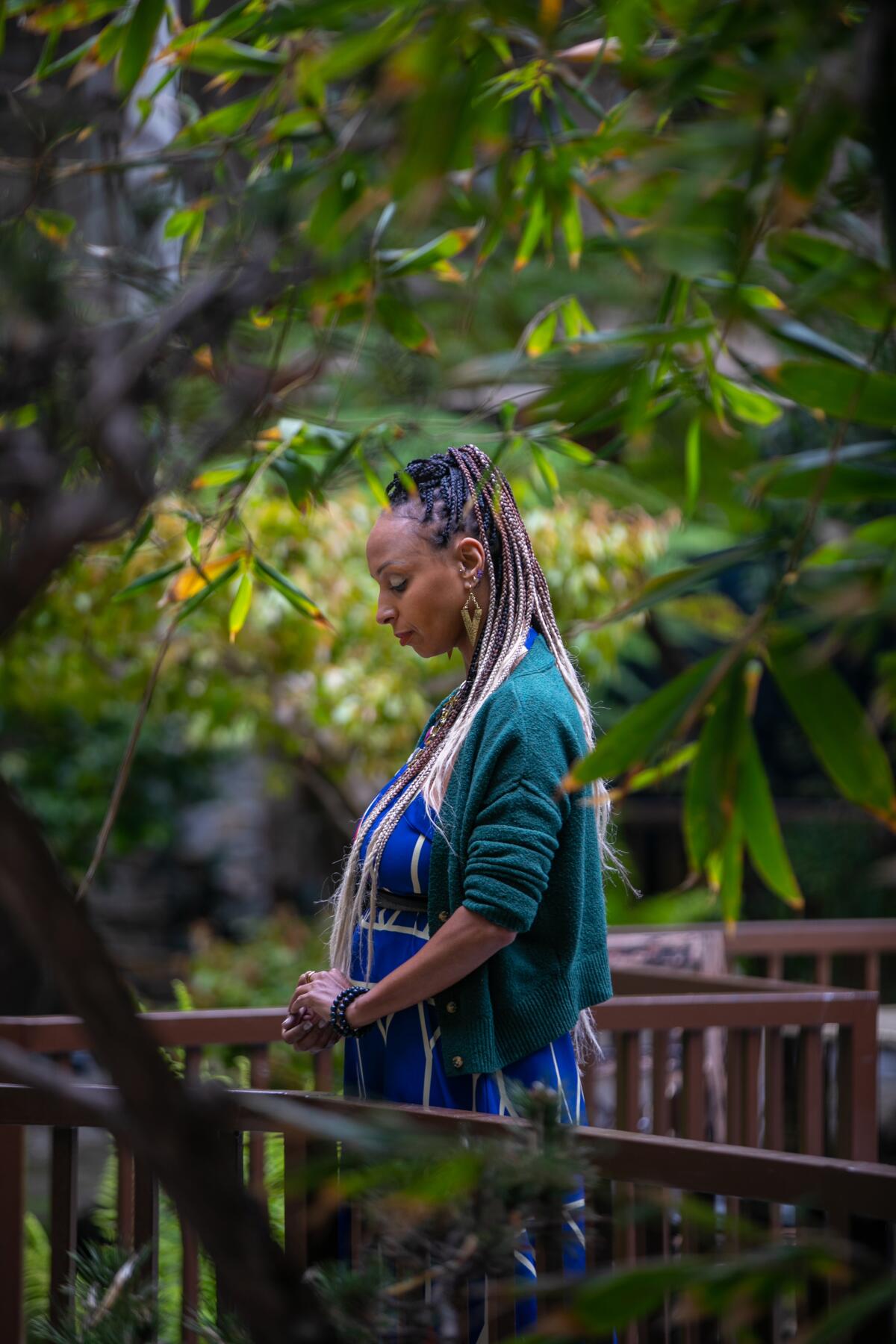

Nakeya Fields says it’s important to address mental wellness issues early, before people reach a crisis point and become another statistic.
(Jason Armond / Los Angeles Times)
Both Friedman and Fields say their critiques are not intended to minimize deaths among white Americans.
Still, Friedman wonders: “How do we empower Black and Native American communities in a way that enables them to treat these problems?”
Racism must be considered when trying to make sense of the crisis in premature deaths, says Dr. Helena Hansen, head of UCLA’s Department of Psychiatry and a senior author on Friedman’s analysis. Hansen, who is Black and specializes in addiction psychiatry, also co-authored the book “Whiteout: How Racial Capitalism Changed the Color of Opioids in America.”
For years, pharmaceutical companies steered expensive prescription pain medications, such as the opioid Oxycontin, as well as the most effective medications for opioid-use disorder, to white Americans with good access to healthcare, she said.
But at the same time, Black and brown Americans were unfairly subjected to law enforcement policies that prioritized incarceration for illegal drug use over increasing access to more humane medical strategies to help them, further harming already vulnerable communities, Hansen said.
“In our society, people with access to the new technologies and pharmaceuticals are more likely to be white,” Hansen says. “None of this is by accident. All of this is the direct result of careful racially and class-segmented marketing strategies by pharmaceutical companies.”
This two-tiered system arose because drug manufacturers, doctors and policymakers have for too long failed to see people from historically marginalized communities who live with addiction and mental health crises as worthy of the same sympathy and treatments that many white Americans receive, Hansen says.
Joseph Gone, a professor of anthropology at Harvard who has spent 25 years studying the intersection of colonialism, culture and mental health in Indigenous communities, agreed.
“Deaths of despair have been a reality for Indigenous communities since conquest and dispossession,” he said.
“It’s amazing how much grief our people contend with from early deaths — there are not that many communities in America that bear it quite the way we do,” said Gone, who is a member of the Aaniiih-Gros Ventre tribal nation of north-central Montana. “Until we acknowledge and take responsibility for the casualties of colonization, which endure to this day through deaths of despair, it’s going to be very hard to turn this around.”
Gone, who has collaborated with Friedman on previous research, says the mental health crisis in tribal nations is aggravated by widespread joblessness and generational poverty, and a lack of healthcare resources to treat people in need of immediate or long-term treatment.
Just one traveling psychiatrist serves reservations spread across both Montana and Wyoming — a region covering more than 243,300 square miles — mostly to manage patients’ prescriptions, he says.
And “for all of Indian country, we’re talking about a very small number of in-patient psychiatric facilities,” Gone says.
General practitioners can serve as a first line of defense, but they are not necessarily equipped to address the ongoing life crises that can lead to excessive drug and alcohol use, Gone says.
Fields says it’s important to address mental wellness issues early, before people reach a crisis point and become another statistic.
While her focus remains on Black women, she’s developed additional programming for adults, families and children, such as developmental screenings that measure for high stress levels. In June, Fields will co-present “Rap 4 Peace,” a conference and gala featuring hip-hop artists talking about mental health and reducing gun violence.
“This ‘tragedy of despair’ lives in us,” Fields says. “We breathe it. We go outside hoping that nobody will harm us or our children because they feel threatened by us. This is truly harmful to our bodies.”
Science
SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets from Vandenberg Space Force Base by 2026. Could that harm the coast?
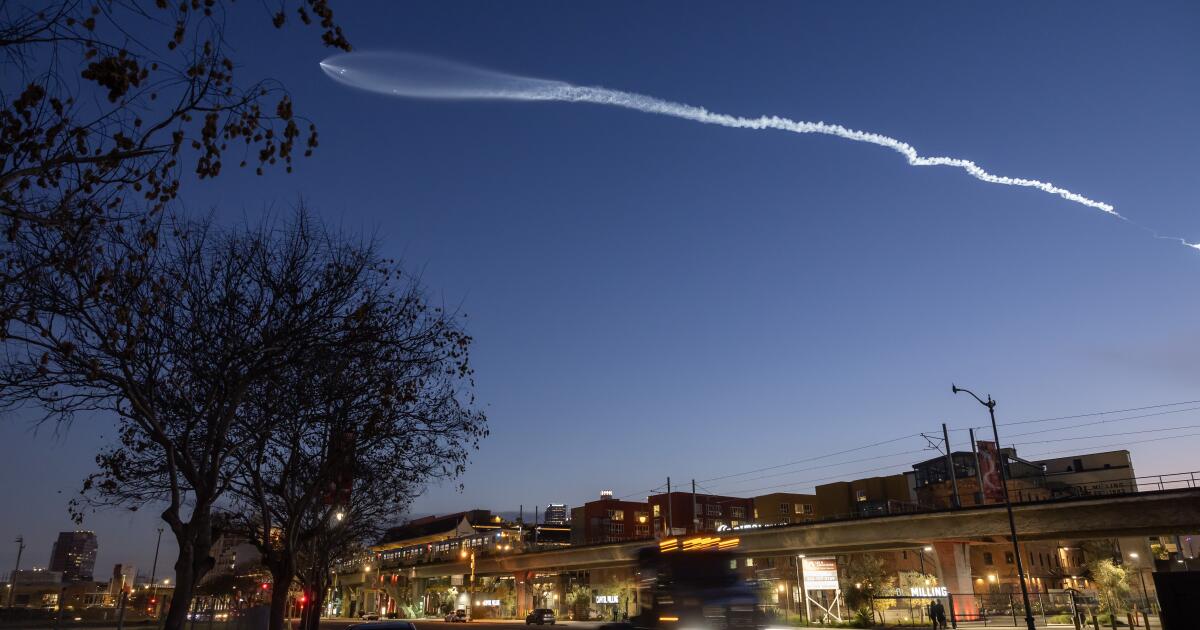

SpaceX plans to launch 90 rockets into space from a Santa Barbara County military base by 2026, tripling the number of blasts rocking the coastal community — and raising concerns from neighbors and environmental groups about the effects on marine life.
Founded by billionaire Elon Musk, SpaceX has ramped up the number of rocket launches from Vandenberg Space Force Base in recent years, and it has made clear its desire to increase the frequency of blastoffs. But during a California Coastal Commission hearing Friday, U.S. Space Force officials outlined for the first time its own plans to multiply the number of launches from the base, from 37 in 2023 to more than 120 a year by 2026.
The overwhelming majority of those rocket liftoffs would be conducted by SpaceX, which has already done more launches from the base than the commission has approved.
Last year SpaceX breached an agreement with the commission that limited the number of launches to six, sending 28 rockets into space.
It is seeking an agreement with the commission to do 36 launches a year, increasing to 90 in 2026.
The decision by the commission, which was created to protect the state’s coastal resources, will directly affect residents and marine life near the military base that hear and feel the rockets’ sonic booms.
It could also redirect the future of SpaceX, whose pursuit to redefine space exploration is already closely tied with U.S. military interests, given its work as a military contractor.
“The ultimate goal is for this to be more routine and not a huge deal,” said Space Force Col. Bryan Titus, operations vice commander at the base.
Formed in 2019, the U.S. Space Force has been looking to improve its ability to send rockets into space, Titus said, so SpaceX’s ability to launch with more frequency is a benefit to the U.S. military.
SpaceX launched 96 rockets in 2023 from Vandenberg and three other facilities: Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Merritt Island, Fla., and SpaceX Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas.
Environmental groups argue that turning launches into a routine event could affect marine life.
“We’re concerned that more frequent launches will result in permanent changes,” said Ana Citrin, legal and policy director for the Gaviota Coast Conservancy.
Federal agencies, including the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and National Marine Fisheries Service, monitor the effects of the liftoffs on such animals as sea otters, bats, western snowy plovers, California least terns and California red-legged frogs.
Thus far, the monitoring has shown that some of the animals might react to the blastoff by flushing, or fleeing from their nests and homes, but they return soon after, according to U.S. Space Force officials. No long-term effects have been seen, they said.
SpaceX did not respond to a request for comment.
Flushing or hunkering down after a blast are already signs of wildlife exhibiting signs of stress, said Duncan Leitch, a professor of integrative biology at UCLA.
Most animals can adapt to infrequent incidents, but exposure to more frequent stressful incidents can change their biology as well as their behavior, he said.
In the worst-case scenarios, he said, the ability of birds to communicate could be impeded, and migratory birds could avoid the area. Fish and other animals that use sound to communicate and navigate underwater — including whales — could be affected too.
“Over a longer period of time, there may be reductions in the population of fish as they move away from the sound, or they may be affected to the point that it affects their health,” Leitch said. “It would change the ecosystem as far as other animals that rely on the fish.
“Having sounds that are well into the damaging, or painful, range of decibels now occurring [100] times a year, the animals might not have the ability to change their behavior or accommodate these types of sounds.”
Some environmental groups, including the Surfrider Foundation, are asking the commission to reject the increase.
SpaceX “intends to begin increasing very rapidly, so we’re very concerned about this,” said Mandy Sackett, senior California policy coordinator for the Surfrider Foundation.
More frequent launches could change the way wildlife in the area responds in the long term, environmental groups said.
Members of the California Coastal Commission are also asking whether SpaceX should be entitled to circumvent the permit process, as federal agencies are.
Federal entities negotiate agreements with the commission but ultimately can move ahead even without commission approval. In such cases, the commission’s recourse would be through mediation or the courts.
Because SpaceX is a U.S. Space Force contractor, military officials argue that all launch operations at the base by the company are “federal activities.”
But U.S. Space Force officials said only 25% of the rockets launched into space by SpaceX are carrying payloads for the Department of the Defense.
The vast majority of the liftoffs are for the company’s private benefit, raising questions about why SpaceX can dispense with permits when 75% of its blasts from the base don’t involve the U.S. government.
“That is still pretty skewed for me,” Commissioner Mike Wilson said during a meeting Friday.
Some commissioners — whose focus is usually on environmental protection, development and water issues during their monthly meetings — also brought up the war in Ukraine during Friday’s discussion.
“I question the national security public benefit of concentrating that much power, literally communication power, in one company that we’re enabling in this case,” Wilson said. “[SpaceX] has already showed that it will play in international conflicts at the will of one human being.”
Wilson was referring to reports that Musk’s company refused to allow Ukraine to use satellite internet service from Starlink, a subsidiary of SpaceX, to help it carry out an attack against Russia in September 2022.
“If the idea is that we’re supporting these permits on the side that we’re promoting national defense, and then a single company is able to dismantle our allies during armed conflict — that really doesn’t align,” Commissioner Justin Cummings said.
“I suspect that would violate our strategies around national defense.”
Titus declined to address the question, saying it was “out of my lane,” but he said he would try to get answers to address the commissioners’ concerns.
Some commissioners on Friday also argued that SpaceX, not U.S. military officials, should be making the company’s case in front of the agency.
“When this comes back, I think it would be really important that a representative from SpaceX comes to the meeting,” Cummings said.
Cummings said it was “ridiculous” for SpaceX not to appear at the meeting, despite multiple efforts from the agency to have SpaceX officials speak.
“They obviously refuse to because they’ve never shown up,” he said.
On Friday, Commission Chair Caryl Hart suggested an agreement might not be possible unless SpaceX changes its stance.
“From my perspective,” Hart said, “I think we’re going to continue to hit significant obstacles in achieving a federal consistency ruling without having SpaceX.”
Science
Pregnant? Researchers want you to know something about fluoride

Adding fluoride to drinking water is widely considered a triumph of public health. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says the cavity-prevention strategy ranks alongside the development of vaccines and the recognition of tobacco’s dangers as signal achievements of the 20th century.
But new evidence from Los Angeles mothers and their preschool-age children suggests community water fluoridation may have a downside.
A study published Monday in JAMA Network Open links prenatal exposure to the mineral with an increased risk of neurobehavioral problems at age 3, including symptoms that characterize autism spectrum disorder. The association was seen among women who consumed fluoride in amounts that are considered typical in Los Angeles and across the country.
The findings do not show that drinking fluoridated water causes autism or any other behavioral conditions. Nor is it clear whether the relationship between fluoride exposure and the problems seen in the L.A.-area children — a cohort that is predominantly low-income and 80% Latino — would extend to other demographic groups.
However, the results are concerning enough that USC epidemiologist Tracy Bastain said she would advise pregnant people to avoid fluoridated water straight from the tap and drink filtered water instead.
“This exposure can impact the developing fetus,” said Bastain, the study’s senior author. “Eliminating that from drinking water is probably a good practice.”
About 63% of Americans receive fluoridated water through their taps, including 73% of those served by community water systems, according to the CDC. In Los Angeles County, 62% of residents get fluoridated water, the Department of Public Health says.
The data analyzed by Bastain and her colleagues came from participants in an ongoing USC research project called Maternal and Developmental Risks from Environmental and Social Stressors, or MADRES. Women receiving prenatal care from clinics in Central and South Los Angeles that cater to low-income patients with Medi-Cal insurance were invited to join.
Between 2017 and 2020, 229 mothers took a test to measure the concentration of fluoride in their urine during their third trimester of pregnancy. Then, between 2020 and 2023, they completed a 99-question survey to assess their child’s behavior when their sons and daughters were 3 years old.
Among other things, the survey asked mothers whether their children were restless, hyperactive, impatient, clingy or accident-prone. It also asked about specific behaviors, such as resisting bedtime or sleeping alone, chewing on things that aren’t edible, holding their breath, and being overly concerned with neatness or cleanliness.
Some of the questions the mothers answered addressed health problems with no obvious medical cause, including headaches, cramps, nausea and skin rashes.
Among the 229 children — 116 girls and 113 boys — 35 were found to have a collection of symptoms that put them in the clinical or borderline clinical range for inward-focused problems such as sadness, depression and anxiety. In addition, 23 were in the clinical or borderline clinical range for behaviors directed at others, such as shouting in a classroom or attacking other kids, and 32 were deemed at least borderline clinical for a combination of inward and outward problems.
What interested the researchers was whether there was any correlation between a child’s risk of having clinical or borderline clinical behavioral problems and the amount of fluoride in his or her mother’s urine during pregnancy.
They found that compared to women whose fluoride levels placed them at the 25th percentile — meaning 24% of women in the study had levels lower than theirs — women at the 75th percentile were 83% more likely to have their child score in the “clinical” or “borderline clinical” range for inward and outward problems combined. When the researchers narrowed their focus to children in the clinical range only, that risk increased to 84%, according to the study.
The researchers also found that the same increase in fluoride levels was associated with an 18.5% increase in a child’s symptoms related to autism spectrum disorder, as well as an 11.3% increase in symptoms of anxiety.
The amount of fluoride needed for mothers to go from the 25th to the 75th percentile was 0.68 milligrams per liter. As it happens, that’s nearly identical to the 0.7 mg per liter standard that federal regulators say is optimal for preventing tooth decay.
Bastain said that allowed the researchers to compare what might happen to children in two parallel universes: a typical one where their mothers consumed fluoridated water during pregnancy, and an alternate one where they didn’t.
“You can use it as a proxy for if they lived in a fluoridated community or not,” she said.
What that thought experiment shows is that children in the fluoridated community face a higher level of risk. That said, it’s not clear when that risk becomes high enough to be worrisome.
“We don’t know what the safe threshold is,” Bastain said. “It’s not like you can say that as long as you’re under the 75th percentile, there are no effects.”
The study authors’ concerns about the effects of fluoride on developing brains didn’t come out of nowhere.
The National Toxicology Program — a joint effort of the CDC, the National Institutes of Health, and the Food and Drug Administration — has been investigating the issue since 2016. In a report last year that reviewed an array of evidence from humans and laboratory animals, a working group concluded “with moderate confidence” that overall fluoride exposure at levels at or above 1.5 mg per liter “is consistently associated with lower IQ in children.”
The working group added that “more studies are needed to fully understand the potential for lower fluoride exposure to affect children’s IQ.”
A 2019 study of hundreds of mothers in Canada — where 39% of residents have fluoridated water — found that a 1-mg increase in daily fluoride intake during pregnancy was associated with a 3.7-point reduction in IQ scores in their 3- and 4-year-old children.
And among hundreds of pregnant women in Mexico, a 0.5-mg-per-liter increase in urinary fluoride went along with a 2.5-point drop in IQ scores for their 6- to 12-year-old children, researchers reported in 2017.
Bastain and her colleagues write their study is the first they are aware of that examines the link between prenatal fluoride exposure and neurobehavioral outcomes in children in the United States. The results are sure to be controversial, Bastain said, but there’s a straightforward way for pregnant people to reduce the possible risk.
“It’s a pretty easy intervention to get one of those tabletop plastic pitchers” that filter out metals, she said. “Most of them do a pretty good job of filtering out fluoride.”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSkeletal remains found almost 40 years ago identified as woman who disappeared in 1968
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago“Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes”: Disney's New Kingdom is Far From Magical (Movie Review)
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIndia Lok Sabha election 2024 Phase 4: Who votes and what’s at stake?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoUkraine’s military chief admits ‘difficult situation’ in Kharkiv region
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCatalans vote in crucial regional election for the separatist movement
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNorth Dakota gov, former presidential candidate Doug Burgum front and center at Trump New Jersey rally
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoAavesham Movie Review
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTrump, Reciting Songs And Praising Cannibals, Draws Yawns And Raises Eyebrows