Science
Ever see a star explode? You're about to get a chance very soon
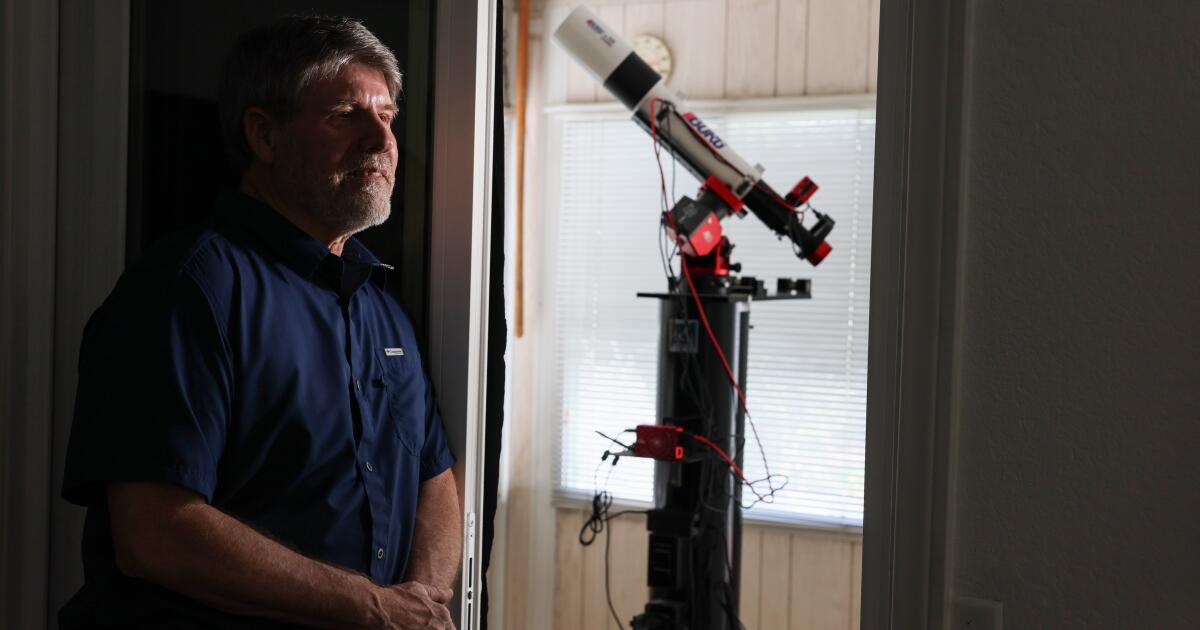

Every clear night for the last three weeks, Bob Stephens has pointed his home telescope at the same two stars in hopes of witnessing one of the most violent events in the universe — a nova explosion a hundred thousand times brighter than the sun.
The eruption, which scientists say could happen any day now, has excited the interest of major observatories worldwide, and it promises to advance our understanding of turbulent binary star systems.
Yet for all the high-tech observational power that NASA and other scientific institutions can muster, astrophysicists are relying on countless amateur astronomers like Stephens to spot the explosion first.
The reason? It’s just too costly to keep their equipment focused on the same subject for months at a time.
“I think everyone will look at it while it happens, but sitting there just looking at it isn’t going to make it happen,” said Tom Meneghini, the director of telescope operations and executive director emeritus at the Mt. Wilson Observatory. “It’s like a watched pot,” he joked.
The star is so far away that it takes 3,000 years for its light to reach the Earth, meaning the explosion occurred before the last of the Egyptian pyramids were built. It will appear about as bright as the North Star for just a few days before fading into the darkness.
Once it’s spotted, some of the most advanced observatories on Earth and in space will join in watching, including NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope.
“A lot of people are eagerly waiting to spot the new jewel in the crown,” said Mansi Kasliwal, the Caltech astronomy professor who is planning to use the Palomar Observatory in northeast San Diego County to observe the event. The nova will erupt in the Corona Borealis, or Northern Crown, constellation.
Steve Flanders, outreach coordinator for Palomar Observatory, shows the observatory’s Gattini-IR telescope, which Caltech professor Mansi Kasliwal’s team will use to observe the Blaze star explosion.
(Hayne Palmour IV/For The Times)
T Coronae Borealis, also called the Blaze Star, is actually two stars — a hot, dense white dwarf, and a cooler red giant.
The dwarf star, which ran out of fuel long ago and collapsed to roughly the size of Earth, has been siphoning hydrogen gas from its larger neighbor for about a human lifetime.
This stolen gas has accumulated in a disk around the dwarf like a hot, messy version of Saturn’s rings. Soon, the disk will grow so heavy that it will become violent and unwieldy, and inevitably, explode like a thermonuclear bomb.
Neither star is destroyed however, and the process repeats itself roughly every 80 years.
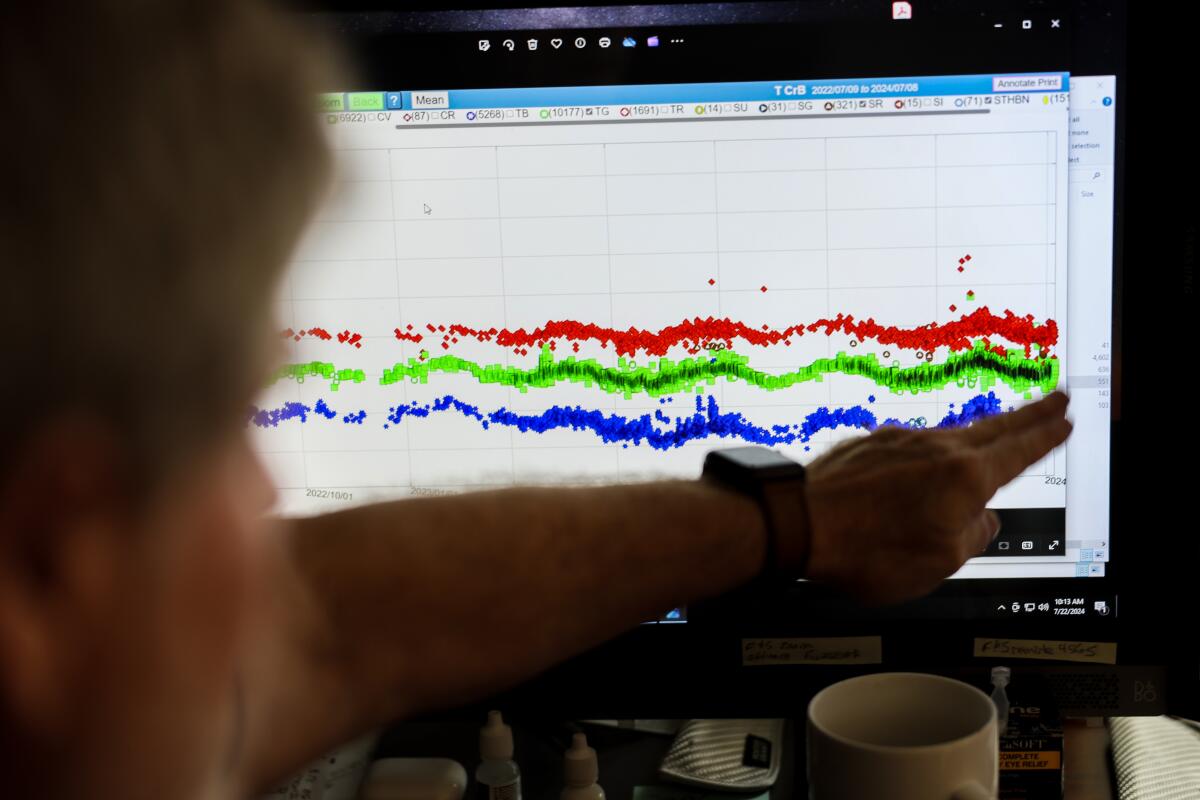
Stephens has data from T Coronae Borealis going back years. The oscillations in the data represent the two stars orbiting around each other.
(Robert Gauthier/Los Angeles Times)
This time around, there’s an army of enthusiasts like Stephens ready to sound the alarm when the star goes nova.
Far from mere hobbyists, a number of these amateur observers have published their own scientific research. Stephens even built his own observatory as an addition to his house in Rancho Cucamonga.
“The city thinks it’s a sunroom,” Stephens said. After the inspector stopped by, he removed the screws securing the roof, allowing him to roll it off to reveal the clear sky to his telescope.
Every night, he turns on the telescope and spends more than an hour taking data, which he later posts to an online community of amateur astronomers who monitor the star almost nonstop.
Major observatories simply cannot keep such constant watch. Hundreds of scientists compete for time to look at a wide range of astronomical targets every night. For them, keeping these telescopes glued to the Blaze Star is a waste of valuable observation time.
Estimates on when the nova will occur vary, but most astrophysicists agree it will happen before the end of the year, and likely by the end of August.
Once it blows, there are a few alert systems set up to notify amateurs and professionals. Some observatories have even programmed their telescopes to autonomously ditch their current observation plan and look at the star when the notification comes in, Stephens said.
Major observatories also face another complication. Many of their telescopes are designed to look at the faintest and dimmest targets, but the Blaze Star nova will be anything but faint. Pointing these telescopes at the nova would overwhelm sensors, resulting in a washed-out, overexposed picture.
That’s why Palomar Observatory, Caltech’s research station in north San Diego County, isn’t using its iconic 16-foot-wide Hale telescope under its massive white dome. Instead, it’s using a much smaller telescope, called Gattini-IR, located in a small brick building about a quarter mile down the road.
Once the nova happens, Gattini-IR will go from observing the Blaze Star every couple nights to every couple hours.
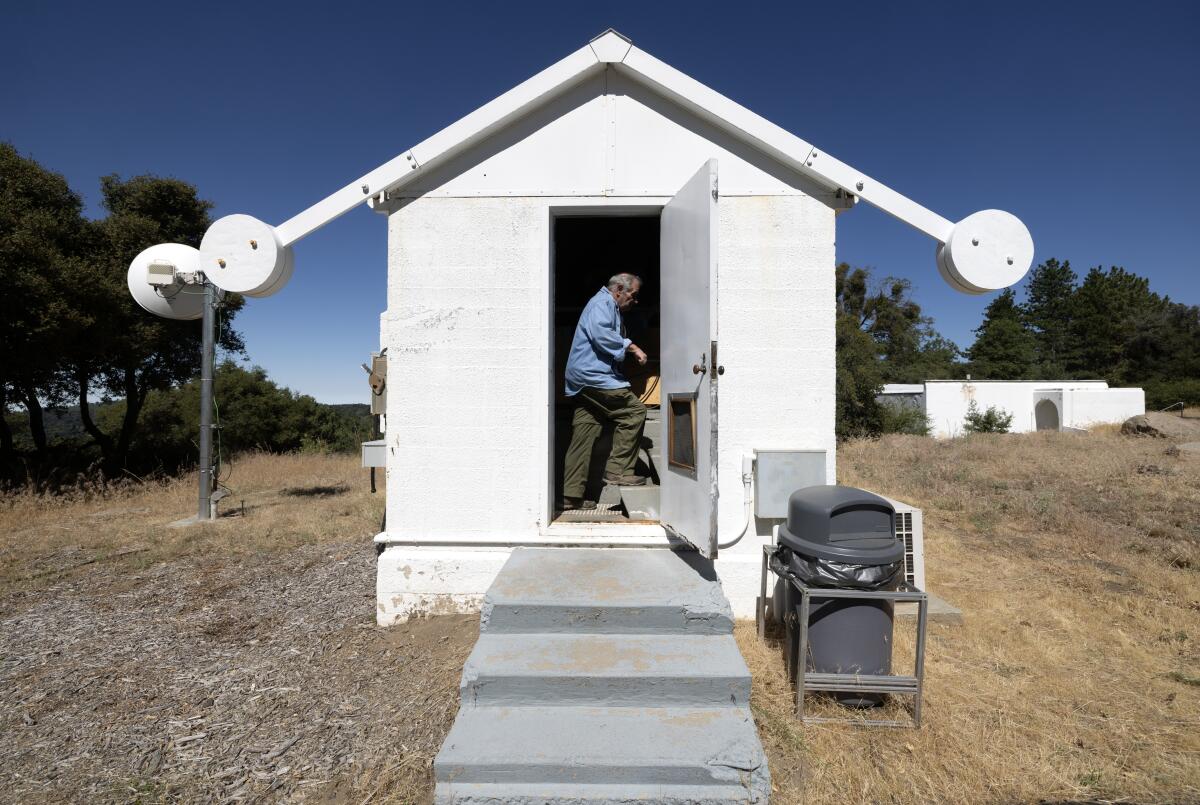

Steve Flanders enters the small building on the Palomar Observatory grounds where the Gattini-IR telescope is set up. The Gattini-IR telescope is monitoring the Blaze Star, which is expected to go nova.
(Hayne Palmour IV/For The Times)
Scientists say they still have a lot to learn about novas. For example, physicists are still unsure why some erupt every decade while others likely don’t for millennia.
Some researchers suspect that novas like the Blaze Star could be precursors to supernovas. These explosions — billions of times brighter than the sun — destroy the star, often leaving behind a black hole. Supernovas are also a useful tool for astronomers to measure distance.
Studying similar events has already led to discoveries, however.
Recently, scientists determined that novas tend to fling material into space at faster speeds than what would be predicted based on the intensity of the explosion.
“We want to understand the physics of novae, so having a nova that’s as close as T Coronae Borelias, which will hopefully be very well studied by all telescopes … we can get a very full picture,” said Caltech professor Kasliwal.
Some of that understanding will be due in part to amateur astronomers.
Thanks to the rapid development of telescopes, amateurs are working with technology that professionals didn’t have just 20 years ago, let alone 80, said Forrest Sims, an amateur astronomer from Apache Junction, Ariz., who is also observing the star every clear night.
And the amateurs can achieve better coverage than the big telescopes because “we typically have complete control over when and where we can point [our telescopes],” said Sims. “A professional may have to write a grant to get a half hour or two hours time on a big telescope.”
That allows them to collect a lot of data. And with hundreds in the community observing from around the world, they can achieve almost continuous coverage of the Blaze Star. Many, including Sims and Stephens, post their data to the American Assn. of Variable Star Observers website, allowing everyone to use the data.
Stephens remembers reading a journal article from a professional who managed to observe five asteroids over two years. “I thought, I could do that in a month,” Stephens said. He went on to publish a paper with 10 observations.

In his at-home observatory, Bob Stephens is using a Borg 101 telescope. “Resistance is futile!” Stephens said when introducing the telescope, a reference to the phrase uttered by “the Borg” in “Star Trek.”
(Robert Gauthier/Los Angeles Times)
One professor was so shocked by the number Stephens was able to see that she reached out and agreed to fly to Puerto Rico for an asteroid conference just to meet him. They ended up working together — Stephens had the telescopes; she had the connections in the field.
Today, amateur astronomers’ work is getting so sophisticated, many in the field have a hard time calling them amateurs.
“We call ourselves ‘small telescope scientists,’ ” said Sims. “It sounds more fun, and in some respects, professionals — and not even grudgingly — will admit that the work we’re doing is often professional caliber.”

Science
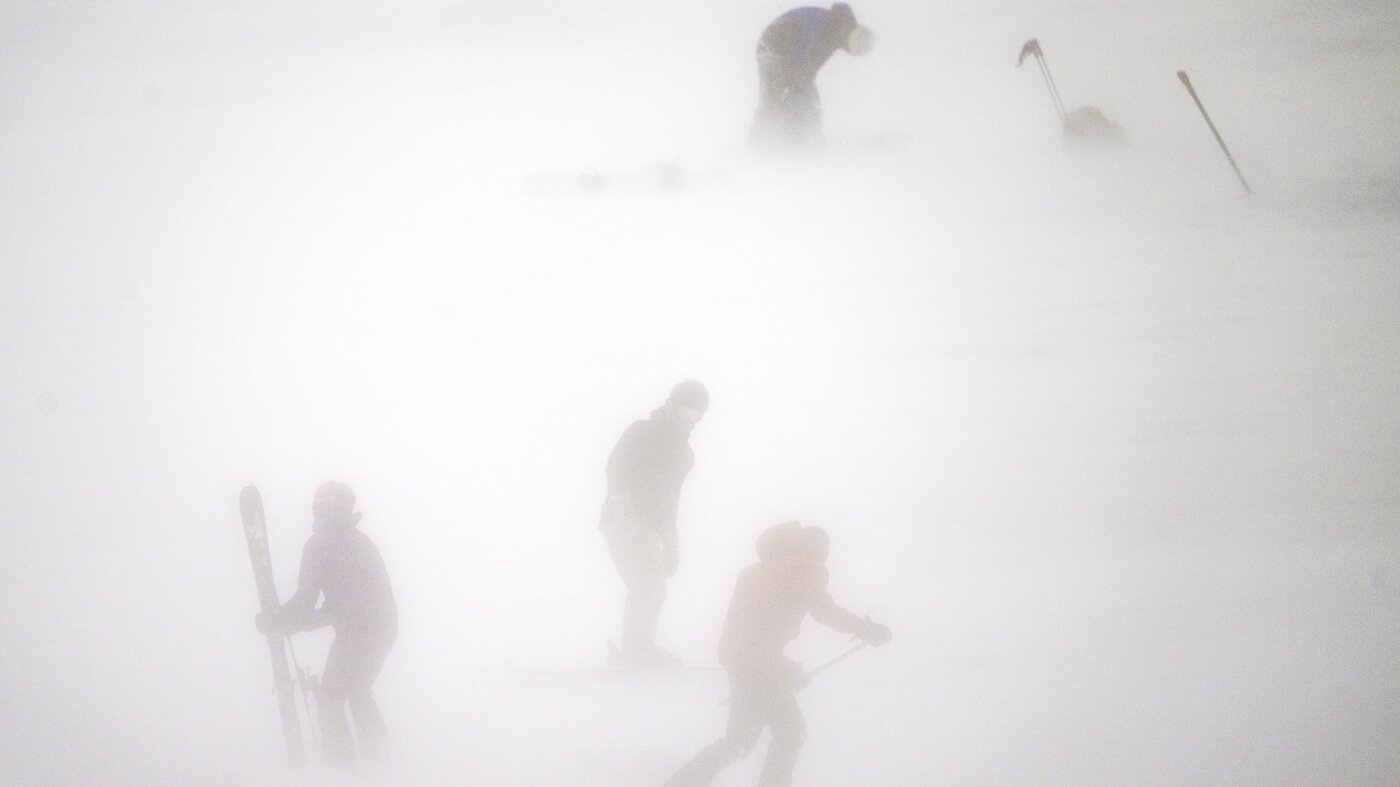
Bodies of all 9 skiers killed in devastating avalanche recovered by authorities
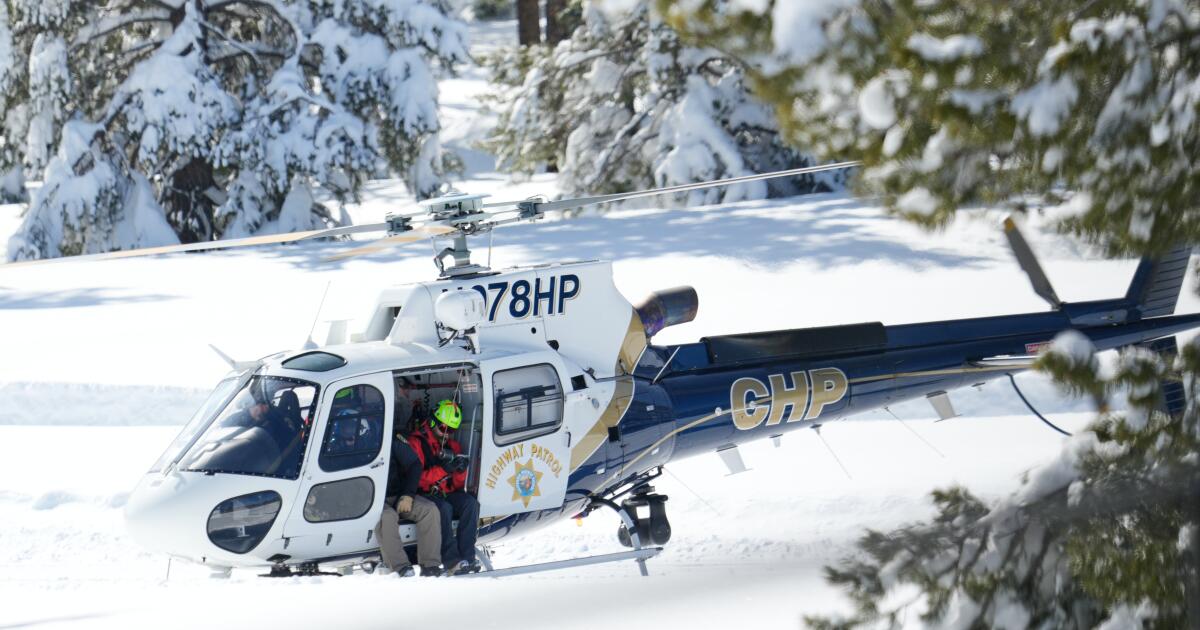

California search-and-rescue teams have recovered the bodies of all nine missing skiers killed Tuesday in a devastating avalanche in a remote region of Sierra Nevada north of Lake Tahoe.
When a catastrophic avalanche rumbled over a stretch of the High Sierra, dozens of law enforcement officers scoured the mountainside for a group of 15 skiers, including four mountain guides.
Within hours, crews rescued six survivors and discovered eight deceased skiers near the Frog Lake Backcountry Huts. Another skier was still missing, but was presumed dead.
After five days of navigating deep snowpack and treacherous weather conditions, authorities announced they had found the body of the ninth victim.
During a press conference on Saturday afternoon, Nevada County identified the victims as six skiers and three professional mountain guides:
- Andrew Alissandratos, 34, of Verdi, Nev., a Blackbird Mountain Guide
- Carrie Atkin, 46, of Soda Springs, Calif.
- Nicole Choo, 42, of South Lake Tahoe, Calif., Blackbird Mountain Guide
- Lizabeth Clabaugh, 52, of Boise, Idaho
- Michael Henry, 30, from Soda Springs, Calif., a Blackbird Mountain Guide
- Danielle Keatley, 44, of Soda Springs and Larkspur, Calif.
- Kate Morse, 45, of Soda Springs and Tiburon, Calif.
- Caroline Sekar, 45, of Soda Springs and San Francisco, Calif.
- Katherine Vitt, 43, of Greenbrae, Calif.
Authorities lamented the fast-moving disaster as the deadliest avalanche in modern California history.
“There are no words that truly capture the significance of this loss and our hearts mourn alongside the families of those affected by this catastrophic event,” Nevada County Sheriff Shannan Moon said in a statement on Saturday. “The weight of this event is felt across many families, friends, and colleagues, and we stand together with them during this difficult time.” Moon said.
The avalanche occurred amid a powerful atmospheric river storm that unleashed several feet of snow onto the Sierra Nevada mountains. First responders maneuvered through the blizzard on snowcats and skis to rescue the survivors.
But the unstable snowpack, high winds and whiteout conditions made search-and-recovery efforts too perilous, prompting first responders to leave behind the bodies of deceased skiers and suspend operations on Wednesday and Thursday.
Authorities carved paths through the deep snow to eventually continue the search, and California Highway Patrol officers found the ninth victim.
The Nevada County Sheriff‘s Office was also assisted by California National Guard, California State Parks, Placer County Sheriff’s Office, Washoe County Sheriff’s Office, California Governor’s Office of Emergency Services, Truckee Police Department and the United States Forest Service.
Science
Video: ‘Very Successful Day’: NASA Completes Artemis II Launchpad Test

new video loaded: ‘Very Successful Day’: NASA Completes Artemis II Launchpad Test
transcript
transcript
‘Very Successful Day’: NASA Completes Artemis II Launchpad Test
NASA successfully completed a rehearsal to launch the Artemis II rocket on Thursday. The mission would send astronauts around the Moon’s orbit for the first time in more than 50 years.
-
“Very successful day. I’m very proud of this team and all that they accomplished to get us to yesterday, and then to go execute with such precision.” “Following that successful wet dress yesterday, we’re now targeting March 6 as our earliest launch attempt. I am going to caveat that — I want to be open, transparent with all of you, that there is still pending work.”

By Jorge Mitssunaga
February 20, 2026
Science
Fourth measles case confirmed in L.A. County; person visited LAX, restaurants while infectious
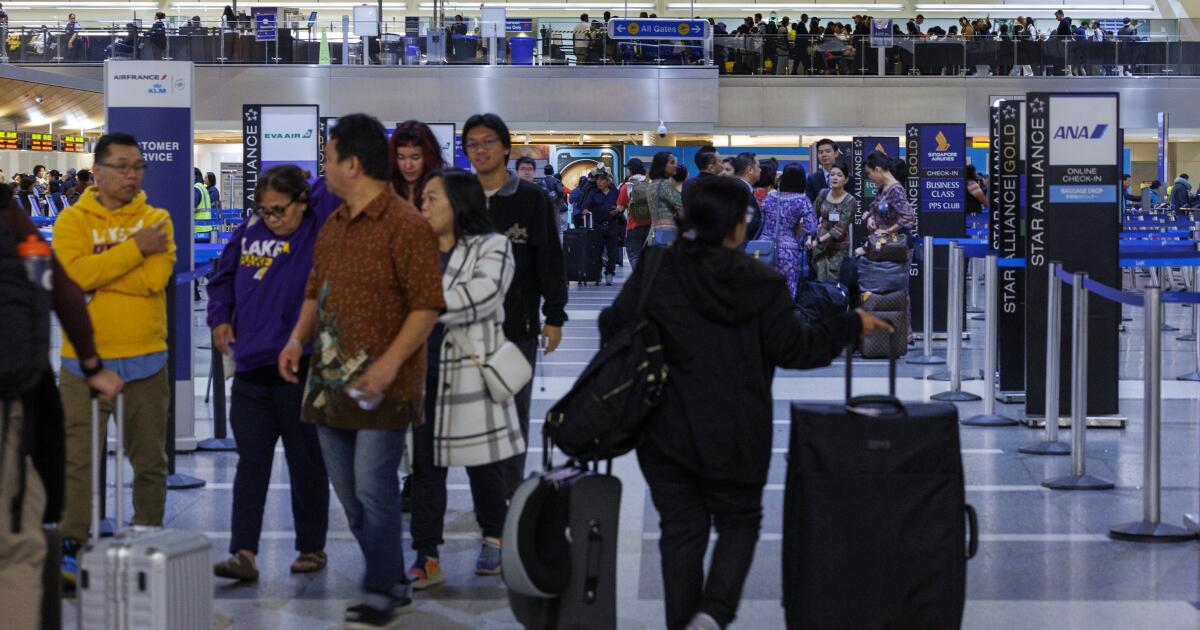

A fourth measles case has been confirmed in Los Angeles County, prompting renewed calls from health officials for residents to ensure they are protected against the highly contagious virus.
The infected individual flew from Singapore to Los Angeles International Airport on Feb. 9 aboard Singapore Airlines Flight 38. The plane landed at about 7 p.m. following a 14-hour journey, according to the L.A. County Department of Public Health.
Over the following days, the individual visited a few San Gabriel Valley fast food restaurants, potentially exposing others to the measles virus.
“As measles cases increase, it is important that residents take steps to make sure they are fully protected,” L.A. County Health Officer Dr. Muntu Davis said in a statement. “The [measles-mumps-rubella] vaccine is the safest and most reliable way to prevent measles and protect yourself, your family, and your community.”
The health department did not respond to questions from The Times regarding the sex or age of the infected individual, who was described in a statement as “a resident who recently traveled internationally.”
After arriving at and leaving the Tom Bradley International Terminal, the individual visited restaurants and convenience stores throughout Whittier and Montebello.
The individual ate at a Burger King in Montebello, 1212 West Beverly Blvd., on Feb. 10 between 5:30 and 7 p.m. The next day, the person dined at Taqueria El Atacor, 11156 1/2 Whittier Blvd. in Whittier, between 3 and 5 p.m.
The final two stops in Montebello were at Domino’s Pizza, 803 West Whittier Blvd., between 4 p.m. and 5:15 p.m. on Feb. 12; and 7-Eleven, 1106 West Beverly Blvd., on Feb. 13 between 4:30 p.m. and 5:45 p.m.
Those who were in the Bradley Terminal (Terminal B) on Feb. 9 from 7:30 p.m. to 9:40 p.m., or in the eateries above during the aforementioned time windows, may have been exposed to the measles virus.
Symptoms typically develop anywhere from seven to 21 days after exposure, according to the health department.
Concerned individuals should confirm whether they have protection against the virus, either through past measles vaccinations or infections.
Those who are not immunized or are unsure of their status should monitor themselves closely for signs of infection. Common symptoms include fever, cough, runny nose or red eyes, as well as a rash.
Those with such symptoms are encouraged to stay home and avoid school, work and any gatherings. They should also call a healthcare provider immediately, but not go into a healthcare facility without informing them.
The monitoring deadline for symptoms ranges from March 2 at LAX until March 6 at 7-Eleven for individuals who visited those spaces around the same time as the infected person.
Davis said the most effective way to protect against measles is to take the MMR vaccine. Children age 1 year and older are considered fully immunized after receiving two doses.
“Measles spreads easily and can lead to serious complications, including pneumonia, brain swelling, and even death,” Davis said. “We urge everyone to confirm their immunity and get the MMR vaccine if needed, especially before traveling. Taking this simple step helps safeguard your health and strengthens protection for our entire community.”
Previous cases confirmed in L.A. County so far this year also involved individuals who had traveled internationally. One of those individuals ventured to Sherman Oaks on Jan. 24, another to Woodland Hills on Jan. 30. The first case had no identified public exposure locations in L.A. County.
Measles cases have increased in the United States as vaccination rates have fallen in recent years, allowing the highly contagious virus to spread in communities with lower vaccine coverage.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there were 2,280 confirmed measles cases in the U.S. last year, the highest annual total since 1991. As of Feb. 12, 910 cases had already been confirmed nationwide this year — including 15 in California.
-

 Montana4 days ago
Montana4 days ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoWhat a Speech Reveals About Trump’s Plans for Nuclear Weapons
-

 Oklahoma6 days ago
Oklahoma6 days agoWildfires rage in Oklahoma as thousands urged to evacuate a small city
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoThe DJI Romo robovac had security so poor, this man remotely accessed thousands of them
-

 Technology3 days ago
Technology3 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoNotoriously hazardous South L.A. oil wells finally plugged after decades of community pressure
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Secret New York City Passage Linked to Underground Railroad
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoAU calls for end to ‘extermination’ of Palestinians, decries African wars



















