Science
Despite its 'nothingburger' reputation, COVID-19 remains deadlier than the flu
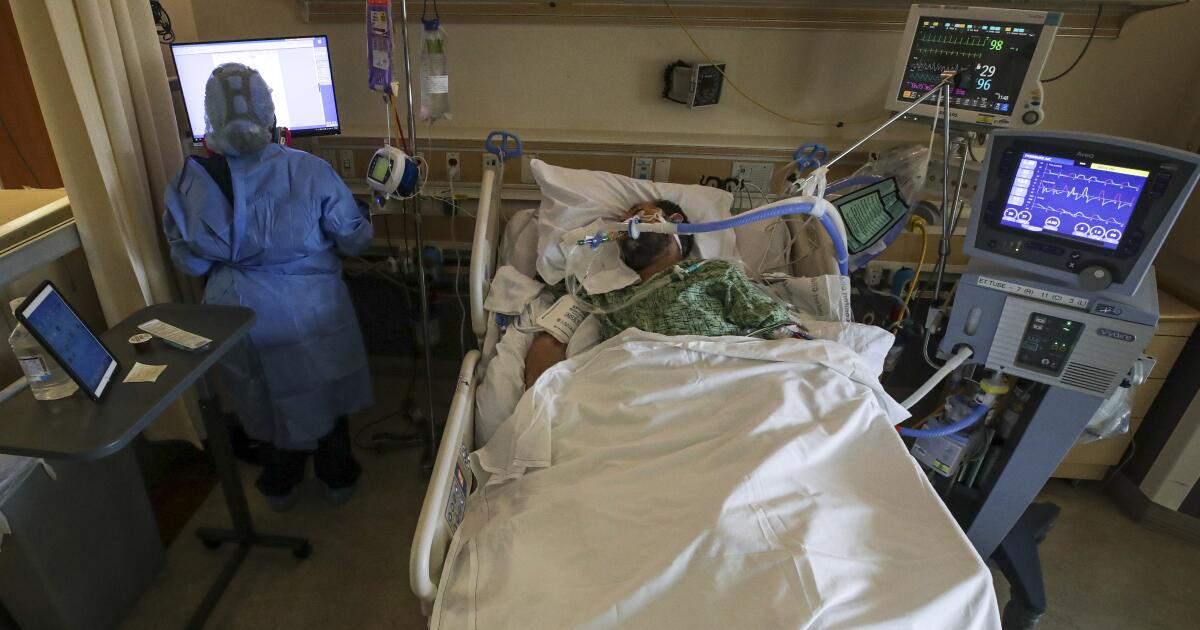
Since the earliest days of the pandemic, health officials have gauged the threat of COVID-19 by comparing it to the flu.
At first, it wasn’t even close. People hospitalized in 2020 with the then-novel respiratory disease were five times more likely to die of their illness than were patients who had been hospitalized with influenza during the preceding flu seasons.
Immunity from vaccines and past coronavirus infections has helped tame COVID-19 to the point that when researchers compared the mortality rates of hospitalized COVID-19 and seasonal influenza patients during the height of the 2022-23 flu season, they found that the pandemic disease was only 61% more likely to result in death.
Now the same researchers have analyzed data for the the fall and winter of 2023 and 2024. Dr. Ziyad Al-Aly, director of the Clinical Epidemiology Center at the VA St. Louis Health Care System, and his colleagues expected to find that the two respiratory diseases had finally equalized.
“There’s a narrative out there that the pandemic is over, that it’s a nothingburger,” Al-Aly said. “We came into this thinking we would do this rematch and find it would be like the flu from now on.”
The VA team examined electronic health records of patients treated in Veterans Affairs hospitals in all 50 states between Oct. 1 and March 27. They zeroed in on patients who were admitted because they had fevers, shortness of breath or other symptoms due to either COVID-19 or influenza. (People who were admitted for another reason, such as a heart attack, and were then found to have a coronavirus infection weren’t included in the analysis.)
The COVID-19 patients were a little older, on average, than the flu patients (73.9 versus 70.2 years old), and they were less likely to be current or former smokers. They were also more likely to have received at least three doses of COVID-19 vaccine and less likely to have shunned the shots altogether.
Yet after Al-Aly and his colleagues accounted for these differences and a host of other factors, they found that 5.7% of the COVID-19 patients died of their disease, compared with 4.2% of the influenza patients.
In other words, the risk of death from COVID-19 was still 35% greater than it was for the flu. The findings were published Wednesday in the Journal of the American Medical Assn.
“There is undeniably an impression out there that [COVID-19] is no longer a major threat to human health,” Al-Aly said. “I think it’s largely driven by opinion and an emotional itch to move beyond the pandemic, to put it all behind us. We want to believe that it’s like the flu, and we did — until we saw the data.”
Dr. Peter Chin-Hong, an infectious diseases specialist at UC San Francisco, said the study results are right in line with what he sees in his hospital.
“COVID continues to make some people in our community very ill and die — even in 2024,” he said. “Although most will not get seriously ill from COVID, for some people it is like 2020 all over again.”
That’s particularly true for people who are older, who haven’t received their most recent recommended COVID-19 booster, and who haven’t taken full advantage of antivirals such as Paxlovid. Chin-Hong noted that only 5% of the COVID-19 patients in the study had been treated with antivirals before they were hospitalized.
Even if the mortality rates for the COVID-19 and flu patients had been equal, COVID-19 would still be the bigger health threat because it is sending more people to the hospital, Al-Aly said.
Between Oct. 1 and the end of March, 75.5 out of every 100,000 Americans had been hospitalized with influenza, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. During that same period, the hospitalization rate for COVID-19 was 122.9 per 100,000 Americans, the CDC says.
“COVID still carries a higher risk of hospitalization,” Al-Aly said. “And among those hospitalized, more will die as a result.”
Yet Al-Aly noted with frustration that while 48% of adults in the U.S. received a flu shot this year, only 21% of adults are up to date with their COVID-19 vaccinations, according to the CDC.
Chin-Hong added that more than 95% of adults hospitalized with COVID-19 this past fall and winter had not received the latest booster shot, according to the CDC.
Considering all the tools available to prevent hospitalizations and deaths — and especially the fact that they are readily available to patients in the VA system — the 35% relative risk of death from COVID-19 compared with the flu was “surprisingly high,” Chin-Hong said.
And it’s not like the flu is a trivial health threat, especially for senior citizens and people who are immunocompromised. It routinely kills tens of thousands of Americans each year, CDC data show.
“Influenza is a consequential infection,” Al-Aly said. “Even when COVID becomes equal to the flu, it’s still sobering and significant.”
The researchers also compared the mortality rates of VA COVID-19 patients before and after Dec. 24, when the Omicron subvariant known as JN.1 became the dominant strain in the United States. The difference was not statistically significant.
In just the last two weeks, JN.1 appears to have been overtaken by one of its descendants, a subvariant known as KP.2. It’s part of a family of subvariants that’s taken on the nickname “FLiRT,” a moniker that references some of the mutations that have cropped up on the viruses’ spike proteins.
So far, there’s no indication that KP.2 is any more dangerous than JN.1, Al-Aly said.
“Are the hospitals filling up? No,” he said. “Are ER rooms all over the country flooded with respiratory illness? No.” Nor are there worrying changes in the amount of coronavirus detected in wastewater.
“When you look at all these data streams, we’re not seeing ominous signs that KP.2 is something the general public should worry about,” Al-Aly said.
It’s also too early to tell whether KP.2 — or whatever comes after it — will finally erase the mortality gap between COVID-19 and the flu, he added.
“Maybe when we do a rematch in 2025, that will be the case,” he said.

Science
Very little plastic being recycled in California as state efforts falter

California touts itself as a leader on the problem of plastic garbage, but recent developments suggest otherwise.
A new report issued by the state’s waste agency shows plastic yogurt containers, shampoo bottles and restaurant takeout trays are being recycled at rates only in the single digits.
-
Share via
Polypropylene, labeled as #5 on packaging, is used for yogurt containers, margarine tubs and microwavable trays. Only 2% of it is getting recycled. Colored shampoo and detergent bottles, made from polyethylene, or #1 plastic, are getting recycled at a rate of just 5%.
Other plastics, including ones promoted as highly recyclable, such as clear polyethylene bottles, which hold some medications, or hard water bottles, are being recycled at just 16%.
No plastic in the report exceeds a recycling rate of 23%, with the majority reported in just the single digits.
Adding to this disquieting assessment, CalRecycle also just pulled back regulations that were supposed to finalize a landmark single-use plastic law known as Senate Bill 54 — a law designed to make the majority of packaging waste in the state recyclable or compostable by working with the plastic and packaging industries.
The report and delay have sparked a wide variety of reactions by those who have closely watched the law as it was written and implemented.
The proposed regulations were regarded as friendly to industry. As a result, some are hopeful that CalRecycle’s decision to pull them back for tweaking means the agency will make the law stronger. Others say the two developments just show the state has never really been serious about plastic recycling.
“California’s SB 54 … will NEVER increase the recycling rates of these items … because cartons and plastic packaging are fundamentally not technically or economically recyclable,” said Jan Dell, the founder of Orange County-based Last Beach Cleanup, an anti-plastic organization.
Industry representatives are also expressing disappointment, saying the more delays and changes the state makes, the harder it is “for California businesses to comply with the law and implement the resulting changes,” said John Myers, a spokesman for the California Chamber of Commerce, which represents companies that will be affected.
Reports on abysmally low rates of recycling for milk cartons and polystyrene have been widely shared and known. But the newest numbers were still a grim confirmation that there are few options for dealing with these materials.
According to one state analysis, 2.9 million tons of single-use plastic and 171.4 billion single-use plastic components were sold, offered for sale or distributed in California in 2023.
Single-use plastics and plastic waste more broadly are considered a growing environmental and health problem. In recent decades, plastic waste has overwhelmed waterways and oceans, sickening marine life and threatening human health.
Last spring, the Newsom administration was accused of neutering the regulations that CalRecycle had initially proposed to implement the law. The changes excluded all packaging material related to produce, meat, dairy products, dog food, toothpaste, condoms, shampoo and cereal boxes, among other products. These are all products that might fall under the purview of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
It also opened the door to “alternative” recycling, such as chemical recycling, which environmentalists say is polluting, and was banned in the language of the law.
The waste agency then submitted those draft regulations to the Office of Administrative Law, whose lawyers and staff review proposed regulations to ensure they are “clear, necessary, legally valid, and available to the public” before finalizing them. They were set to release their determination on Friday; CalRecycle pulled the regulations back before the office issued its determination.
Neither the law office nor governor’s office responded to requests for comment.
Melanie Turner, CalRecycle’s spokeswoman, said the agency withdrew its proposed regulations “to make changes … to improve clarity and support successful implementation of the law,” and its revisions were focused on areas that dealt with “food and agricultural commodities.”
California State Sen. Ben Allen (D-Santa Monica), author of the original legislation, called the delay “entirely avoidable” in a statement, but said it would allow CalRecycle an “opportunity to ensure the regulations truly follow the law as it was signed.”
He urged the waste agency and Newsom’s administration not to “allow broad, sweeping exemptions that would undermine the program and increase costs for ratepayers.”
Critics of the watered-down regulations, such as Anja Brandon, the director of plastics policy for the Ocean Conservancy, said she wasn’t surprised by the withdrawal.
The proposed regulations “would have gone beyond CalRecycle’s authority by creating a sweeping categorical exclusion for food and agricultural packaging — effectively a loophole that would have allowed producers to continue putting vast amounts of plastic packaging into the marketplace, completely undermining SB 54’s goals and success,” she said in a text message.
Turner said CalRecycle will conduct a 15-day comment period — although when that begins has not yet been divulged.
Science
Cancer survival rates soar nationwide, but L.A. doctors warn cultural and educational barriers leave some behind

The American Cancer Society’s 2026 Cancer Statistics report, released Tuesday, marks a major milestone for U.S. cancer survival rates. For the first time, the annual report shows that 70% of Americans diagnosed with cancer can expect to live at least five years, compared with just 49% in the mid-1970s.
The new findings, based on data from national cancer records and death statistics from 2015 to 2021, also show promising progress in survival rates for people with the deadliest, most advanced and hardest-to-treat cancers when compared with rates from the mid-1990s. The five-year survival rate for myeloma, for example, nearly doubled (from 32% to 62%). The survival rate for liver cancer tripled (from 7% to 22%), for late-stage lung cancer nearly doubled (from 20% to 37%), and for both melanoma and rectal cancer more than doubled (from 16% to 35% and from 8% to 18%, respectively).
For all cancers, the five-year survival rate more than doubled since the mid-1990s, rising from 17% to 35%.
This also signals a 34% drop in cancer mortality since 1991, translating to an estimated 4.8 million fewer cancer deaths between 1991 and 2023. These significant public health advances result from years of public investment in research, early detection and prevention, and improved cancer treatment, according to the report.
“This stunning victory is largely the result of decades of cancer research that provided clinicians with the tools to treat the disease more effectively, turning many cancers from a death sentence into a chronic disease,” said Rebecca Siegel, senior scientific director at the American Cancer Society and lead author of the report.
As more people survive cancer, there is also a growing focus on the quality of life after treatment. Patients, families and caregivers face physical, financial and emotional challenges. Dr. William Dahut, the American Cancer Society’s chief scientific officer, said that ongoing innovation must go hand in hand with better support services and policies, so all survivors — not just the privileged — can have “not only more days, but better days.”
Indeed, the report also shows that not everyone has benefited equally from the advances of the last few decades. American Indian and Alaska Native people now have the highest cancer death rates in the country, with deaths from kidney, liver, stomach and cervical cancers about double that of white Americans.
Additionally, Black women are more likely to die from breast and uterine cancers than non-Black women — and Black men have the highest cancer rates of any American demographic. The report connects these disparities in survival to long-standing issues such as income inequity and the effects of past discrimination, such as redlining, affecting where people live — forcing historically marginalized populations to be disproportionately exposed to environmental carcinogens.
Dr. René Javier Sotelo, a urologic oncologist at Keck Medicine of USC, notes that the fight against cancer in Southern California, amid long-standing disparities facing vulnerable communities, is very much about overcoming educational, cultural and socioeconomic barriers.
While access to care and insurance options in Los Angeles are relatively robust, many disparities persist because community members often lack crucial information about risk factors, screening and early warning signs. “We need to insist on the importance of education and screening,” Sotelo said. He emphasized that making resources, helplines and culturally tailored materials readily available to everyone is crucial.
He cites penile cancer as a stark example: rates are higher among Latino men in L.A., not necessarily due to lack of access, but because of gaps in awareness and education around HPV vaccination and hygiene.
Despite these persisting inequities, the dramatic nationwide improvement in cancer survival is unquestionably good news, bringing renewed hope to many individuals and families. However, the report also gives a clear warning: Proposed federal cuts to cancer research and health insurance could stop or even undo these important gains.
“We can’t stop now,” warned Shane Jacobson, the American Cancer Society’s chief executive.
“We need to understand that we are not yet there,” Sotelo concurred. ”Cancer is still an issue.”
Science
Clashing with the state, L.A. City moves to adopt lenient wildfire ‘Zone Zero’ regulations

As the state continues multiyear marathon discussions on rules for what residents in wildfire hazard zones must do to make the first five feet from their houses — an area dubbed “Zone Zero” — ember-resistant, the Los Angeles City Council voted Tuesday to start creating its own version of the regulations that is more lenient than most proposals currently favored in Sacramento.
Critics of Zone Zero, who are worried about the financial burden and labor required to comply as well as the detrimental impacts to urban ecosystems, have been particularly vocal in Los Angeles. However, wildfire safety advocates worry the measures endorsed by L.A.’s City Council will do little to prevent homes from burning.
“My motion is to get advice from local experts, from the Fire Department, to actually put something in place that makes sense, that’s rooted in science,” said City Councilmember John Lee, who put forth the motion. “Sacramento, unfortunately, doesn’t consult with the largest city in the state — the largest area that deals with wildfires — and so, this is our way of sending a message.”
Tony Andersen — executive officer of the state’s Board of Forestry and Fire Protection, which is in charge of creating the regulations — has repeatedly stressed the board’s commitment to incorporating L.A.’s feedback. Over the last year, the board hosted a contentious public meeting in Pasadena, walking tours with L.A. residents and numerous virtual workshops and hearings.
-
Share via
Some L.A. residents are championing a proposed fire-safety rule, referred to as “Zone Zero,” requiring the clearance of flammable material within the first five feet of homes. Others are skeptical of its value.
With the state long past its original Jan. 1, 2023, deadline to complete the regulations, several cities around the state have taken the matter into their own hands and adopted regulations ahead of the state, including Berkeley and San Diego.
“With the lack of guidance from the State Board of Forestry and Fire Protection, the City is left in a precarious position as it strives to protect residents, property, and the landscape that creates the City of Los Angeles,” the L.A. City Council motion states.
However, unlike San Diego and Berkeley, whose regulations more or less match the strictest options the state Board of Forestry is considering, Los Angeles is pushing for a more lenient approach.
The statewide regulations, once adopted, are expected to override any local versions that are significantly more lenient.
The Zone Zero regulations apply only to rural areas where the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection responds to fires and urban areas that Cal Fire has determined have “very high” fire hazard. In L.A., that includes significant portions of Silver Lake, Echo Park, Brentwood and Pacific Palisades.
Fire experts and L.A. residents are generally fine with many of the measures within the state’s Zone Zero draft regulations, such as the requirement that there be no wooden or combustible fences or outbuildings within the first five feet of a home. Then there are some measures already required under previous wildfire regulations — such as removing dead vegetation like twigs and leaves, from the ground, roof and gutters — that are not under debate.
However, other new measures introduced by the state have generated controversy, especially in Los Angeles. The disputes have mainly centered around what to do about trees and other living vegetation, like shrubs and grass.
The state is considering two options for trees: One would require residents to trim branches within five feet of a house’s walls and roof; the other does not. Both require keeping trees well-maintained and at least 10 feet from chimneys.
On vegetation, the state is considering options for Zone Zero ranging from banning virtually all vegetation beyond small potted plants to just maintaining the regulations already on the books, which allow nearly all healthy vegetation.
Lee’s motion instructs the Los Angeles Fire Department to create regulations in line with the most lenient options that allow healthy vegetation and do not require the removal of tree limbs within five feet of a house. It is unclear whether LAFD will complete the process before the Board of Forestry considers finalized statewide regulations, which it expects to do midyear.
The motion follows a pointed report from LAFD and the city’s Community Forest Advisory Committee that argued the Board of Forestry’s draft regulations stepped beyond the intentions of the 2020 law creating Zone Zero, would undermine the city’s biodiversity goals and could result in the loss of up to 18% of the urban tree canopy in some neighborhoods.
The board has not decided which approach it will adopt statewide, but fire safety advocates worry that the lenient options championed by L.A. do little to protect vulnerable homes from wildfire.
Recent studies into fire mechanics have generally found that the intense heat from wildfire can quickly dry out these plants, making them susceptible to ignition from embers, flames and radiant heat. And anything next to a house that can burn risks taking the house with it.
Another recent study that looked at five major wildfires in California from the last decade, not including the 2025 Eaton and Palisades fires, found that 20% of homes with significant vegetation in Zone Zero survived, compared to 37% of homes that had cleared the vegetation.
-

 Montana4 days ago
Montana4 days agoService door of Crans-Montana bar where 40 died in fire was locked from inside, owner says
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoPower bank feature creep is out of control
-

 Delaware6 days ago
Delaware6 days agoMERR responds to dead humpback whale washed up near Bethany Beach
-

 Dallas, TX6 days ago
Dallas, TX6 days agoAnti-ICE protest outside Dallas City Hall follows deadly shooting in Minneapolis
-

 Dallas, TX1 week ago
Dallas, TX1 week agoDefensive coordinator candidates who could improve Cowboys’ brutal secondary in 2026
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: This Organizer Reclaims Counter Space
-

 Virginia4 days ago
Virginia4 days agoVirginia Tech gains commitment from ACC transfer QB
-

 Iowa1 week ago
Iowa1 week agoPat McAfee praises Audi Crooks, plays hype song for Iowa State star


















