News
Why the era of ageing wine in concrete may finally have come
Frog’s Leap has all the time been an exception amongst Napa Valley wineries. The Williams household, who based it, had been preaching the natural gospel lengthy earlier than most of their neighbours. They’ve treasured previous vine varieties which can be much less trendy and extra obscure than essentially the most worthwhile Cabernet Sauvignon. They even appear to have managed an amicable and profitable transition from one technology to a different. And John Williams and his son Rory had been Napa’s first to undertake a winemaking observe that has been spreading everywhere in the world.
Wooden, particularly oak, has lengthy been the fabric of selection for ageing and, usually, fermenting wine in. It clearly has an affinity with the flavours of wine and, most significantly, encourages simply the correct quantity of oxygen wanted to stabilise and make clear it. Historic civilisations could have used clay pots and the like, however picket barrels succeeded amphorae as containers for each storage and transport as way back because the third century AD.
In direction of the tip of the twentieth century, it turned a badge of honour among the many world’s wine producers to boast about what number of new French oak barrels they purchased every year. Certainly, for a lot of wine producers the world over, the best annual value is their funding in new barrels, which maintain the equal of about 300 bottles. They’ll value $1,000 every and could also be used for not more than three years.
Up to now, an oak barrel — certainly, ageing wine in any respect — was considered a luxurious in poorer components of Europe. In direction of the tip of the final century, they usually hoped to interchange their previous concrete vats, usually as massive as a room, with new stainless-steel tanks which can be a lot simpler to wash. The deserted wine co-ops that now dot the Languedoc, as an example, are full of those ghostly vessels, usually nonetheless encrusted with the purple tartrate crystals deposited by pink winemaking. A few of the extra energetic wine farmers would use dynamite to rid themselves of those concrete dinosaurs.
But concrete has turn into more and more à la mode in wine manufacturing. This century many wineries have experimented with big concrete egg-shaped containers, that are alleged to encourage motion and helpful contact with the lees. And glamorous new wineries, equivalent to these designed for the glitzy likes of Château Cheval Blanc in St-Emilion and Masseto in Bolgheri, boast concrete fermentation vessels in all sizes and styles. Maybe the truth that, regardless of the prevailing trend elsewhere, Bordeaux’s most costly wine, Petrus, has all the time been fermented in concrete has performed a small half in encouraging this phenomenon.
Nevertheless it applies solely to fermentation. Most advantageous wine continues to be aged in wooden, even when producers and shoppers have broadly taken towards the pronounced “oaky” flavours related to new, small barrels so the dimensions and common age of the oak barrel or vat has been rising.
At Frog’s Leap, they’re flying within the face of present observe in northern California, the place demand for brand spanking new French oak barrels has lengthy been so nice that the most important French coopers established outposts there a few years in the past.
In addition to utilizing an array of concrete eggs, which John Williams describes as “space-eaters”, they’ve put in two 13,000-US gallon concrete “rooms” during which they age their Chardonnay and Sauvignon Blanc. They’re thrilled by the extra texture of their wines. Certainly, so happy are they by this retro materials that they’ve additionally invested in 100 small, sq. 240-US gallon concrete cubes for his or her unusually zesty Zinfandel, with “tremendously thrilling” outcomes, says John Williams. (The outcomes for Cabernet Sauvignon are much less conclusive; it appears the Bordeaux pink wine grape actually appreciates its keep in oak, maybe as a result of it permits extra oxygen ingress.)
One in every of concrete’s nice benefits over oak is its regular temperature, however its attraction to the Williamses can also be each monetary and ecological. “It takes one 75-year-old oak tree to supply two barrels for wine use and people barrels have a usable lifetime of three to 5 years,” says John Williams.
Against this, the lifespan of a concrete container is limitless, decreasing their carbon footprint.
In reality, producing the cement for concrete is comparatively heavy on sand and greenhouse gasoline emissions however a minimum of the Williams are sourcing their new vessels near residence — from Sonoma Solid Stone, whose principal enterprise is producing sinks, simply over the hill in Petaluma. The Frog’s Leap concrete containers need to be rinsed every year with a heavy answer of tartaric acid (the most typical acid in wine) however are nonetheless simpler to keep up than oak.
Such enthusiasm for ageing wine in concrete could also be uncommon in Napa Valley but it surely has turn into more and more widespread in Spain the place some see concrete (and, in some areas, clay tinajas) as a healthful revival of native custom.
Extremely revered vintner Telmo Rodriguez determined that his new Lanzaga vineyard in Rioja can be all-concrete, reproducing how wine was made there within the Thirties. He was inspired by his companion Pablo Eguzkiza, who had expertise of creating wine in concrete when working at Petrus in Bordeaux. “I actually like picket tanks,” Eguzkiza admits, “however they’re very tough to preserve in good situation (they all the time need to be full).” Lanzaga’s concrete cylinders maintain as much as 100 hectolitres (2,640 US gallons).
Different outstanding followers of concrete embrace Michel Chapoutier of France and Australia, who has lengthy favoured it for grape varieties significantly liable to oxidation equivalent to Grenache, and Sebastian Zuccardi of Argentina. When Zuccardi constructed a brand new vineyard in Valle de Uco, excessive in Argentine wine nation, he intentionally centered on concrete vessels as a result of he wished to precise native characters unaffected by the flavour of oak. He too factors out that he’s merely reviving a fabric that was widespread domestically within the Thirties.
But not everyone seems to be satisfied. On the opposite aspect of the Andes in Chile, Burgundy-trained winemaker François Massoc is very sceptical of what he describes as “concrete tanks in every kind of shapes rising like mushrooms everywhere in the world”. Whereas concrete evangelists argue that wine can “breathe” in concrete, he claims “they neglect that the internal pores [of the concrete tank] aren’t linked with the outside pores, so that is unattainable”.
Williams and Chapoutier counter that so long as the concrete is unlined, it isn’t oxygen outdoors wine containers that works its magic however minute quantities of oxygen trapped within the skinny layers of the inside of the container. Concrete-aged wines definitely don’t seem like starved of oxygen, and sometimes appear to have freshness and extra texture, although maybe I’m imagining a sure graininess.
Massoc can also be involved about potential contamination from chemical compounds utilized in making them, noting that, “Cheval Blanc made a big research earlier than selecting their concrete, and we have to keep in mind that Kees [this famous château’s chief adviser] is a geologist, so he knew what he was doing. That’s the explanation why they’ve an exquisite and technically extraordinary vineyard. Others? I don’t know.”
Ageing in concrete could be very a lot in keeping with the present vogue for pure fruit flavours. It appears to be nicely suited to many a energetic white wine and to reds for comparatively early consumption. However for complicated reds designed for lengthy ageing, the coopers in all probability want lose no sleep.
Concrete suggestions
Whites
-
M Chapoutier, Bila-Haut Occultum Lapidem 2017 Côtes du Roussillon 13%. £15 Frazier’s, £16.99 Noble Grape, £19.99 Flagship Wines
-
Gerard & Pierre Morin, Cuvée Ovide 2018 Sancerre 13%. £21 The Sourcing Desk
-
Frog’s Leap, Shale & Stone Chardonnay 2019 Napa Valley 13.2%. £25 VINUM, £27.17 Justerini & Brooks, £27.90 Hedonism and from $23.95 from many US retailers
Reds
-
Bertrand-Bergé, Origines 2019 Fitou 14.5%. £9.50 The Wine Society
-
Alto las Hormigas, Clasico Malbec 2018/9 Mendoza 13.5%. £12ish broadly accessible
-
Dom des Espiers 2020 Côtes-du-Rhône 14.5%. £12.82 Stone, Vine & Solar
-
Lanzaga, Corriente 2017 Rioja 14%. £16.20 Sincere Grapes
-
Frontonio, Microcosmico Garnacha 2018 IGP Valdejálon 13.5%. £17.95 Winedirect.co.uk, £17.99 NYWines
-
Zuccardi, Concreto Malbec 2018 Mendoza 14%. £28.75 Frazier’s, £29.95 Winedirect.co.uk
Tasting notes on Purple Pages of JancisRobinson.com. Extra stockists from Wine-searcher.com
Observe Jancis on Twitter @JancisRobinson
Observe @FTMag on Twitter to search out out about our newest tales first

News
SCOTUS allows dismantling of Education Dept. And, Trump threatens Russia with tariffs

Good morning. You’re reading the Up First newsletter. Subscribe here to get it delivered to your inbox, and listen to the Up First podcast for all the news you need to start your day.
Today’s top stories
The U.S. Supreme Court ruled yesterday that it will allow the Trump administration to resume dismantling the U.S. Department of Education. The Court overruled a lower court that temporarily paused massive cuts at the department. Congress created the department by law and President Trump promised to shut it down without any change in that law, which is why opponents sued.
The Washington, D.C., headquarters of the U.S. Department of Education shown in March.
Win McNamee/Getty Images North America
hide caption
toggle caption
Win McNamee/Getty Images North America
- 🎧 The court’s decision now means that roughly 1,400 Education Department workers will lose their jobs, NPR’s Cory Turner tells Up First. The work that those employees did, including helping local schools support kids with disabilities and children living in poverty, may also cease. The ruling isn’t the final word as the case continues to work its way through lower courts. The plaintiffs’ concern is that by the time they get a final ruling in court, it might not matter, as the harm to the department could be irreversible, Turner stated.
Some Trump supporters over the weekend were surprised when he urged them to move on from the Epstein files. The Justice Department and the FBI released a two-page memo last week stating they found no evidence to support conspiracy theories about the life and death of disgraced financier and convicted sex trafficker Jeffrey Epstein. They stated he really did kill himself in jail in 2019 and left no client list. This comes after Attorney General Pam Bondi previously said on Fox News that she had the list on her desk.
- 🎧 Heading into the last election, a central concept of Trump’s MAGA ideology was the belief that there was a deep state cabal of shadowy figures protecting pedophiles and unsavory people running the government and obstructing Trump’s agenda, says NPR’s Stephen Fowler. Now, Trump has a baseless theory about the files, suggesting Democrats created them to target him. Fowler says it is uncertain if Trump’s shift on the topic has hurt his favorability with his supporters, but it does reiterate the stranglehold the president has on the shape and direction of the GOP.
Trump yesterday threatened to implement heavy tariffs on countries that trade with Moscow if the Kremlin doesn’t reach a ceasefire deal with Ukraine by September. The president also promised Ukraine billions of dollars worth of U.S.-made military equipment, which NATO countries in Europe will pay for.
- 🎧 NPR’s Charles Maynes says the president’s change of tone on Russia was quite a shift. A big driver in this shift is Trump’s frustration with and even a sense of betrayal by Russian President Vladimir Putin. The president said he thought he had a peace deal with Putin four separate times, only to see Russian attacks in Ukraine continue. Some in Moscow see the 50-day grace period provided for the ceasefire as a sign that Trump isn’t ready to give up on Russia.
Living better

Frank Frost found camaraderie in a cycling group in the U.K. that his doctor recommended he try. They call themselves the “Chain Gang” and members look after each other, he said. “We’re all of a certain age,” says Frost. ” We don’t leave anybody.”
Frank Frost
hide caption
toggle caption
Frank Frost
Living Better is a special series about what it takes to stay healthy in America.
Doctors are writing “social prescriptions” to get people engaged with nature, art, exercise and volunteering in the same way they would prescribe pills or therapy. Research has shown it can help with mental health, chronic disease and dementia. The method worked for Frank Frost. He gained weight and was diagnosed with Type 2 diabetes in his 50s. A doctor found out he used to love riding a bike as a kid and gave him a prescription for a 10-week cycling course for adults getting back into cycling. The prescription led to Frost developing friends, losing 100 pounds and getting his diabetes under control. Julia Hotz, the author of The Connection Cure: The Prescriptive Power of Movement, Nature, Art, Service, and Belonging, shares details on the health approach:
- 🚲 Health providers in around 30 countries are practicing social prescribing to address symptoms of Type 2 diabetes, chronic pain, dementia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, anxiety and depression, and more. A growing number of U.S. providers are also embracing the approach.
- 🚲 Social prescribing can save money due to a reduction in emergency room visits and repeat visits to primary care physicians. Health care systems have acknowledged that it can be cheaper to cover weeks of Zumba classes than medication over the course of a lifetime.
- 🚲 People interested in social prescribing can visit the map on Social Prescribing USA’s website to find a list of organizations and health systems involved in this practice.
Picture show

Evelyn del Rosario Morán Cojoc, an artist from Guatemala, creates a mural that depicts traditional foods from her Mayan culture — like that floating ear of corn and three yellow beans. She teaches art to kids across the country, encouraging them to depict their indigenous traditions.
Ben de la Cruz/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ben de la Cruz/NPR
The theme of this year’s Smithsonian Folklife Festival in Washington, D.C., was youth and the future of culture. The event showcased a diverse range of talent. A 26-year-old Bolivian rapper infused his unique style into Spanish hip-hop by incorporating words from his father’s indigenous language. Two refugee weavers made a traditional bag as they work to revitalize their ancient art form. A Guatemalan artist created a mural that highlights her Mayan culture. A Mexican American dad and his two daughters demonstrated techniques for shaping a guitar passed down from their great-grandfather. The Goats and Soda team sat down with the four ensembles to talk about their craft, the youth they mentor and the cultural traditions they’re keeping alive. Read what they had to say and see photos of their craft.
3 things to know before you go

Andrew Cuomo speaks during an election party following the primaries at the Carpenters Union in New York City on June 24, 2025.
John Lamparski/AFP via Getty Images
hide caption
toggle caption
John Lamparski/AFP via Getty Images
- Former New York Gov. Andrew Cuomo announced yesterday that he is relaunching his campaign for New York City mayor, this time as an independent candidate. (via Gothamist)
- South African President Cyril Ramaphosa has suspended his police minister after serious allegations linking him to organized crime.
- Los Angeles is now three years away from the Olympic Games, and to commemorate the occasion, organizers yesterday released a preview of the competition schedule. (via LAist)
This newsletter was edited by Suzanne Nuyen.
News
Trump does deal with Nato allies to arm Ukraine and warns Russia of severe sanctions
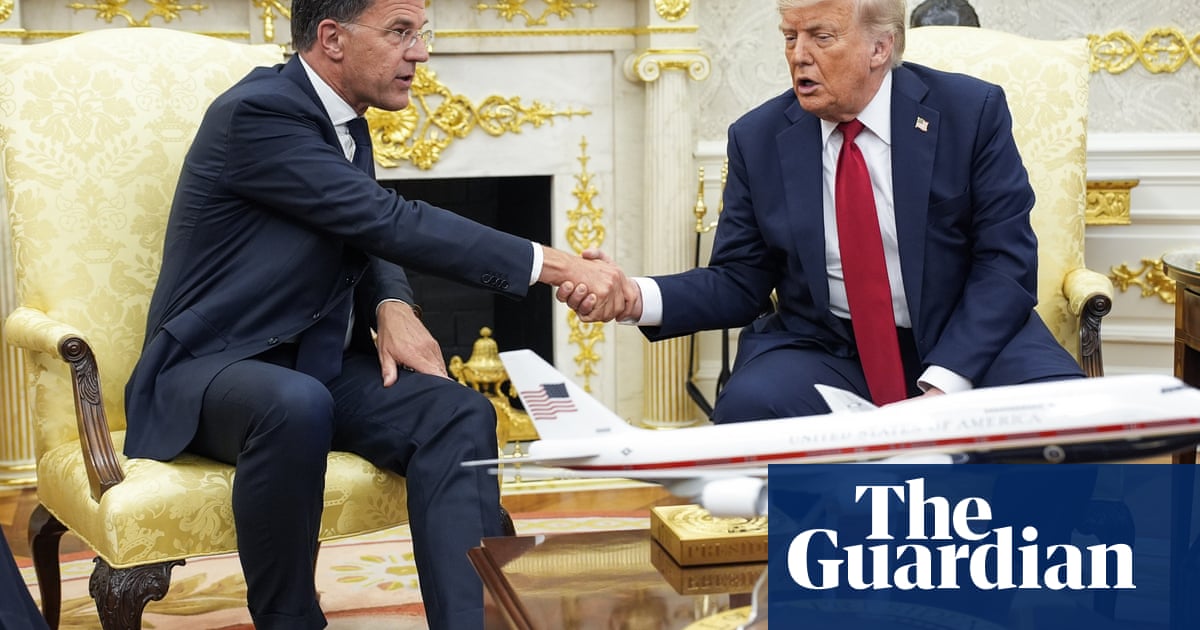

Donald Trump said he has sealed an agreement with Nato allies that will lead to large-scale arms deliveries to Ukraine, including Patriot missiles, and warned Russia that it will face severe sanctions if Moscow does not make peace within 50 days.
After a meeting with the Nato secretary general, Mark Rutte, Trump said they had agreed “a very big deal”, in which “billions of dollars’ worth of military equipment is going to be purchased from the United States, going to Nato … And that’s going to be quickly distributed to the battlefield.”
Speaking in the White House alongside a clearly delighted Rutte, the US president said the arms deliveries would be comprehensive and would include the Patriot missile batteries that Ukraine desperately needs for its air defences against a daily Russian aerial onslaught.
“It’s everything: it’s Patriots. It’s all of them. It’s a full complement, with the batteries,” Trump said.
He did not go into any more detail, but made clear the weapons would be entirely paid for by Washington’s European allies, and that initial missile deliveries would come “within days” from European stocks, on the understanding they would be replenished with US supplies.
At a White House lunch with religious leaders later in the day, Trump said the deal was “fully approved, fully done”.
“We’ll send them a lot of weapons of all kinds and they’re going to deliver those weapons immediately … and they’re going to pay,” he said.
At his meeting with Trump, Rutte said there was a significant number of Nato allies – including Germany, Finland, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands and Canada – ready to rearm Ukraine as part of the deal.
“They all want to be part of this. And this is only the first wave. There will be more,” he said.
The German chancellor, Friedrich Merz, said last week that Berlin was ready to acquire additional Patriot systems.
Trump claimed there was one country, which he did not name, but which had “17 Patriots getting ready to be shipped”. Monday’s deal would include that stockpile, or “a big portion of the 17”, he said.
Such an arms delivery would represent a significant reinforcement of Ukraine’s air defences. Kyiv is currently thought to have only six Patriot batteries, at a time when it is coming under frequent and intense Russian drone and missile bombardments.
At the same time, Trump expressed increased frustration with Vladimir Putin, whom he accused of giving the impression of pursuing peace while intensifying attacks on Ukrainian cities. He gave the Russian president a new deadline of 50 days to end the fighting or face 100% tariffs on Russian goods, and more importantly, sweeping “secondary tariffs”, suggesting trade sanctions would be imposed on countries who continue to pay for Russian oil and other commodities.
“The secondary tariffs are very, very powerful,” the president said.
The announcement marked a dramatic change for the administration, both in substance and tone.
The Trump White House had not only made clear it would continue its predecessor’s policy of continuing to supply Ukraine out of US stocks, but the president and his top officials have been derisive about Kyiv’s chances of prevailing.
On Monday, Trump delivered his most admiring language on Ukraine and its European backers to date, with Rutte on one side and the US vice-president, JD Vance, the administration’s biggest sceptic on US involvement in Europe, on the other.
“They fought with tremendous courage, and they continue to fight with tremendous courage,” Trump said of the Ukrainians.
“Europe has a lot of spirit for this war,” he said, suggesting he had been taken by surprise by the level of commitment shown by European allies at the Nato summit in The Hague last month. “The level of esprit de corps spirit that they have is amazing,” he said. “They really think it’s very, very important.
“Having a strong Europe is a very good thing. It’s a very good thing. So I’m okay with it,” he said.
Trump described his deepening disillusion with Putin, and suggested his wife, Melania, may have played a role in pointing out the Russian leader’s duplicity in talks over a peace deal.
“My conversations with him are always very pleasant. I say, isn’t that a very lovely conversation? And then the missiles go off that night,” Trump said. “I go home, I tell the first lady: I spoke with Vladimir today. We had a wonderful conversation. She said: Really? Another city was just hit.”
Ukrainian regional officials reported at least six civilians killed and 30 injured by Russian bombing in the past 24 hours. The country’s air force said Moscow had attacked with 136 drones and four S-300 or S-400 missiles.
“Look, I don’t want to say he’s an assassin, but he’s a tough guy. It’s been proven over the years. He’s fooled a lot of people,” Trump said, listing his predecessors in the White House.
“He didn’t fool me. But what I do say is that at a certain point, ultimately talk doesn’t talk. It’s got to be action,” he said.
Russian officials and pro-war bloggers on Monday largely shrugged off Trump’s announcement, declaring it to be less significant than anticipated.
Konstantin Kosachev, a senior Russian lawmaker, wrote on Telegram that it amounted to “hot air”.
It was broadly welcomed in Kyiv, where there has been longstanding and deep anxiety about Trump’s intentions. Andrii Kovalenko, a member of Ukraine’s national security and defence council, posted a one-word response: “Cool.”
There was still scepticism however, over whether even the promise of new weaponry for Ukraine combined with the threat of trade sanctions would be enough to halt Russia’s offensive.
Illia Ponomarenko, a Ukrainian journalist and blogger wrote: “How many Ukrainian lives could have been saved if, from the very beginning, Trump had listened to wise and honest people about helping Ukraine, instead of the artful lies of that cannibal Putin on the phone?”.
News
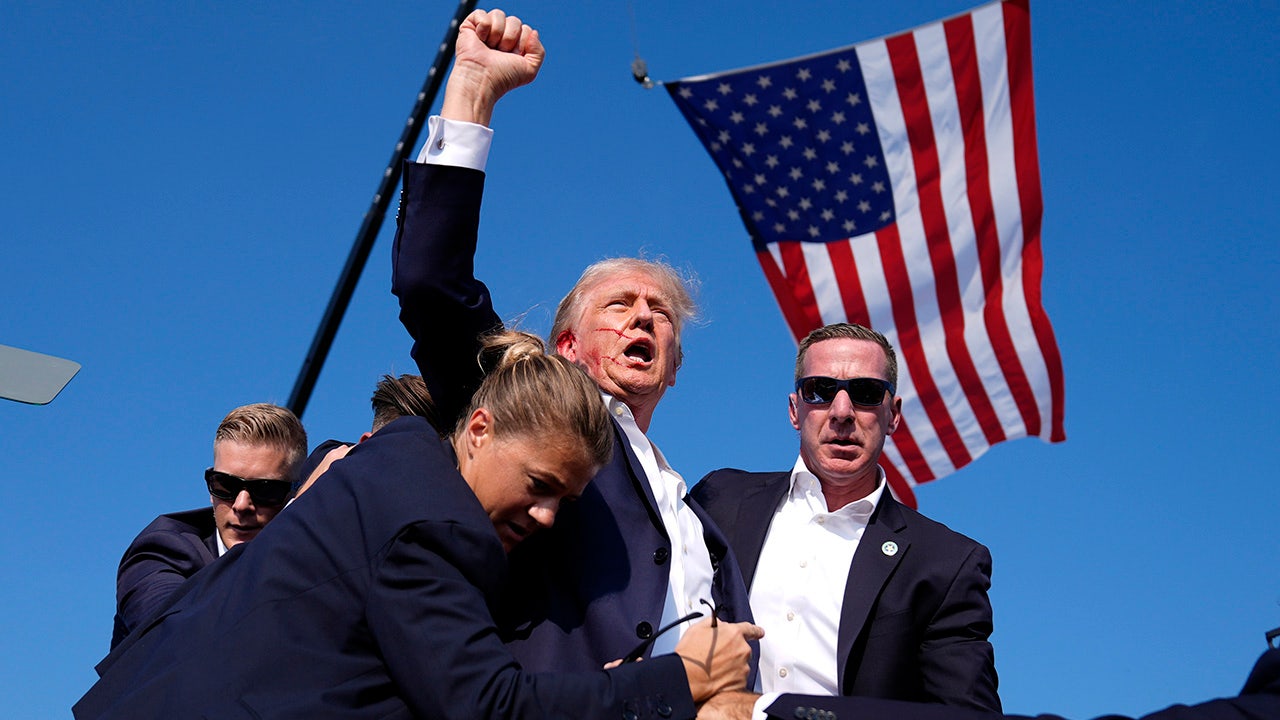
Senate committee details failures by Secret Service in preventing Trump shooting

Then-candidate Donald Trump is rushed offstage by U.S. Secret Service agents after being struck by a bullet during a rally on July 13, 2024, in Butler, Pa.
Anna Moneymaker/Getty Images
hide caption
toggle caption
Anna Moneymaker/Getty Images
A Senate committee report released Sunday blames the U.S. Secret Service for a “cascade of preventable failures” that led up to the assassination attempt against then-presidential candidate Donald Trump during a rally in Butler, Pa., last summer.
Trump was injured in the shooting when a bullet whizzed past his head, grazing his ear. Two attendees were wounded, and rally-goer and former fire chief Corey Comperatore was killed.
A Secret Service sniper shot and killed the perpetrator, 20-year-old Thomas Matthew Crooks of Bethel Park, Pa.

In its report, the Senate Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs Committee said the Secret Service’s “lack of structured communication was likely the greatest contributor to the failures” on the day of the rally. The report was released by the committee’s chairman, Sen. Rand Paul, R-Ky.
For instance, the Secret Service security room agent, who is responsible for collecting and disseminating information, learned about a suspicious person with a rangefinder from a counterpart in the Pennsylvania State Police roughly 25 minutes before the shooting. That agent relayed the report to a fellow Secret Service agent in the room, but the information did not go out over the radio or make it to Trump’s security detail in time for them to prevent him from taking the stage.
There were communication gaps both within the Secret Service hierarchy, and also among the agency and the state and federal law enforcement agencies on scene, the committee said.
There were organizational mistakes, too. The committee noted that one of the Secret Service countersniper teams protecting Trump at the Butler rally had an obstructed view of the roof of the nearby American Glass Research building where Crooks was located.
The report, released one year to the day after the shooting, also found that the Secret Service had denied some resources to Trump’s detail during the 2024 presidential election and said former Secret Service Director Kimberly Cheatle had falsely testified to Congress when she said no requests were denied for the Butler rally.

In a statement on Sunday, Secret Service Director Sean Curran said the agency “took a serious look at our operations” following last year’s shooting and “implemented substantive reforms to address the failures that occurred that day.”
The agency announced last week that it had put in place 21 of 46 recommendations made by congressional oversight bodies, including streamlining communication procedures and clarifying the responsibilities of advance teams.
The Secret Service also said it had disciplined six employees in relation to the Butler shooting, with suspensions ranging from 10 to 42 days without pay. Still, the committee said in its report that “not a single person has been fired.”
Curran, who was one of the agents who surrounded Trump as shots were fired in Butler, added in his statement that the Secret Service will “continue to work cooperatively with the committee as we move forward in our mission.”
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoTry to Match These Snarky Quotations to Their Novels and Stories
-

 News5 days ago
News5 days agoVideo: Trump Compliments President of Liberia on His ‘Beautiful English’
-
Business1 week ago
Companies keep slashing jobs. How worried should workers be about AI replacing them?
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoTexas Flooding Map: See How the Floodwaters Rose Along the Guadalupe River
-
Finance1 week ago
Do you really save money on Prime Day?
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoVideo: Clashes After Immigration Raid at California Cannabis Farm
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoApple’s latest AirPods are already on sale for $99 before Prime Day
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoJournalist who refused to duck during Trump assassination attempt reflects on Butler rally in new book














