Health
Potentially Deadly Bacteria Detected in U.S. Soil for First Time

A probably lethal micro organism was discovered for the primary time in water and soil samples in the USA, prompting the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention to alert medical doctors and public well being specialists all through the nation on Wednesday to take it into consideration when inspecting sufferers.
The micro organism, Burkholderia pseudomallei, was detected within the Gulf Coast area of Southern Mississippi. Publicity to the micro organism may cause melioidosis, a “uncommon and severe illness,” in line with the C.D.C.; about one in each 4,600 folks uncovered are discovered to have the illness, in line with a research from 2019. The research additionally discovered that about 90,000 folks die yearly from melioidosis.
“As soon as well-established within the soil, B. pseudomallei can not feasibly be faraway from the soil,” the C.D.C. wrote in its well being advisory. “Public well being efforts ought to focus totally on enhancing identification of circumstances in order that acceptable remedy could be administered.”
The samples present that the micro organism has been current within the Mississippi area since at the very least 2020, when one individual within the Gulf Coast area was discovered to have melioidosis, although it’s unclear precisely how lengthy Burkholderia pseudomallei, often known as B. pseudomallei, has been within the space.
The micro organism has beforehand been present in areas with tropical and subtropical climates world wide, like South and Southeast Asia, northern Australia and components of Central and South America. The C.D.C. stated that modeling confirmed that southern Mississippi’s local weather was additionally conducive to rising it.
The environmental sampling in Mississippi was performed after two sufferers within the space acquired diagnoses of melioidosis, two years aside — one in July 2020, the opposite in Could 2022. The unnamed people weren’t associated, the C.D.C. stated, however lived in “shut geographical proximity,” and had not not too long ago traveled out of the USA.
Genomic sequencing information confirmed that each folks had been contaminated by the identical novel pressure from the Western Hemisphere, officers stated. Each sufferers have been hospitalized and recovered after antibiotic remedy.
Final month, the Mississippi State Division of Well being and C.D.C. collected environmental samples of soil, water and plant matter from the sufferers’ properties, family merchandise and close by areas they frequented.
The micro organism can infect animals and folks by way of direct contact or by way of cuts and wounds. The chance of spreading from individual to individual is low, officers stated. Signs often happen between sooner or later to 3 weeks after publicity.
Most melioidosis circumstances happen exterior of the USA, the C.D.C. stated. However final yr, 4 folks in 4 completely different states have been contaminated with melioidosis after utilizing contaminated aromatherapy spray offered at Walmart. Two of the 4 folks died, officers stated.
Melioidosis signs are nonspecific and fluctuate from individual to individual, the C.D.C. stated, however signs embody fever, localized ache or swelling, chest ache and complications. Folks with diabetes, extreme alcohol use, continual lung illness, continual kidney illness and immunosuppressive circumstances are extra prone to the micro organism. Officers stated a fast analysis and antibiotics have been essential.
B. pseudomallei isn’t the one factor present in soil that may additionally trigger sickness.
Valley fever, additionally referred to as coccidioidomycosis, is an an infection brought on by a fungus that lives within the soil within the southwestern United States and components of Mexico and Central and South America. It’s contracted by respiration within the microscopic fungal spores from the air, though most individuals who breathe within the spores don’t get sick, the C.D.C. stated. In 2019, about 20,000 circumstances have been reported to the company, most from folks dwelling in Arizona or California.

Health
This Big-Breakfast Fasting Trick Melts Belly Fat and Curbs Hunger

Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Health
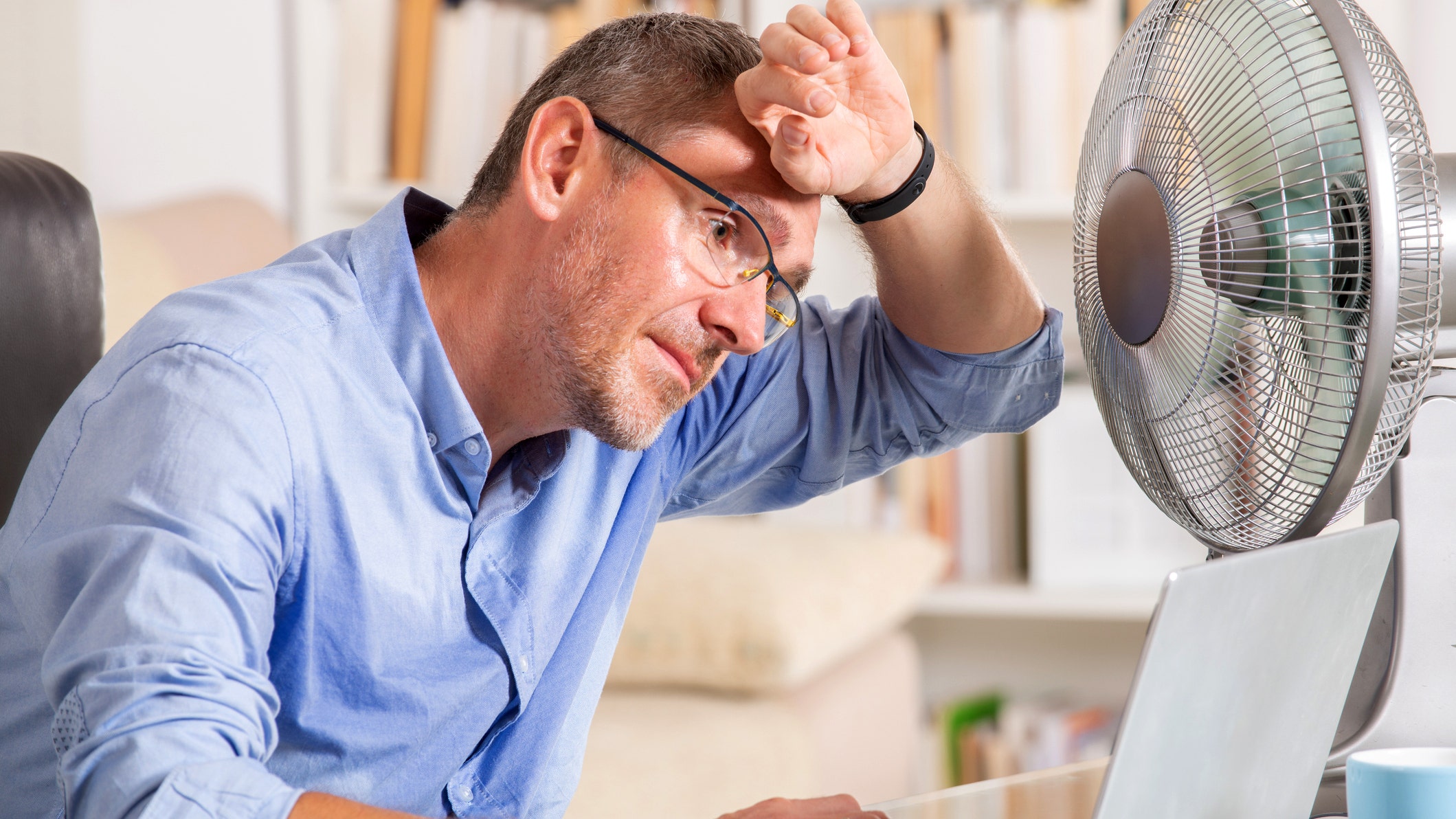
The heat has a surprising effect on the brain — here's what doctors want you to know

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Summer heat has swept the U.S., with warnings issued across the East Coast and Midwest.
In addition to putting stress on the body, hot weather can also take a toll on the brain and mental health.
Dr. Jace Reed, director of emergency psychiatry at Cedars-Sinai Hospital in Los Angeles, emphasized in an interview with Fox News Digital that the brain is a major organ that can be greatly affected by heat.
AMERICANS TOLD TO AVOID COFFEE DURING EXTREME HEAT WARNING IN 3 STATES
Extreme heat can cause mental health changes like increased irritability and anxiety, along with decreased memory, attention and reaction time.
This can affect daily interactions socially and professionally, the expert cautioned.
Extreme heat can cause mental health changes like increased irritability and anxiety, along with decreased memory, attention and reaction time. (iStock)
“You may be slower at completing your task or remembering what someone just told you,” he told Fox News Digital. “Those can be initial early signs that the heat is affecting your brain and your mental abilities.”
Symptoms like extreme confusion could mark the beginning of a heat stroke, which could require hospitalization, the psychiatrist warned.
YOUR BRAIN PHYSICALLY CHANGES WHEN YOU WORK TOO MUCH, SCIENTISTS WARN
In a separate interview with Fox News Digital, Thea Gallagher, a doctor of psychology and director of wellness programs at NYU Langone Health, noted that when the body overheats, it struggles to regulate internal balance.
This can lead to disrupted sleep, fatigue and poor concentration, as well as impaired cognitive function, slow reaction times and struggles with decision-making.
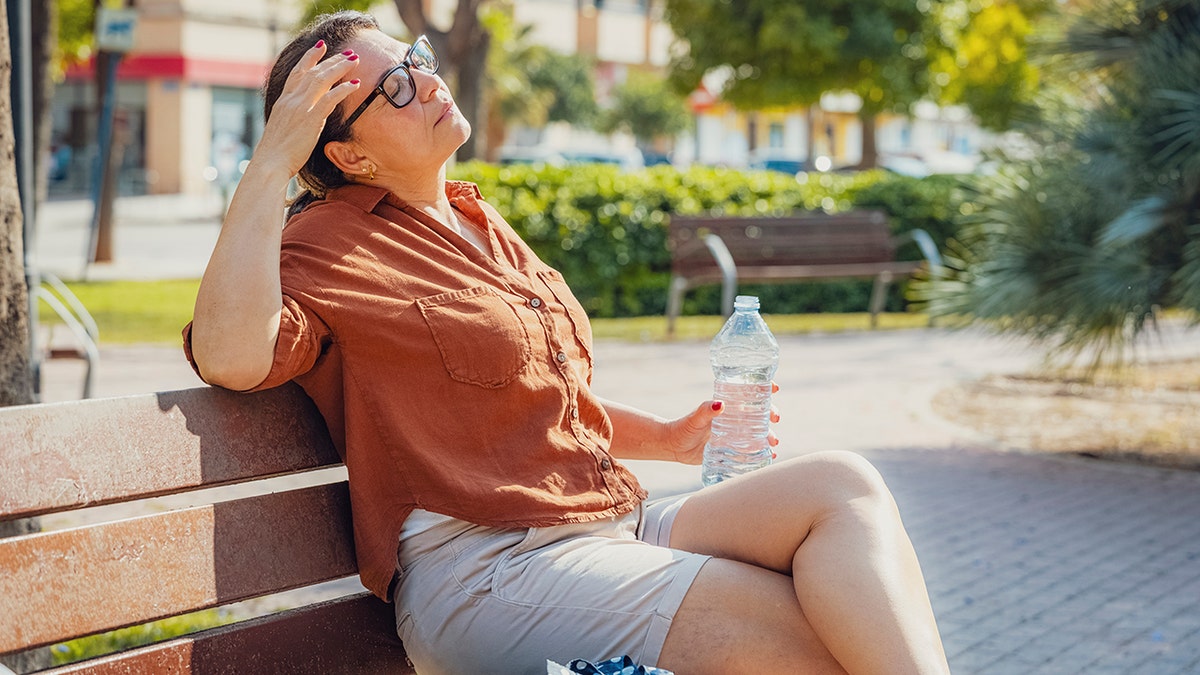

Extreme heat can cause slower cognitive function, along with delays in reaction times and decision-making. (iStock)
The heat can also increase oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, Gallagher added, which can potentially damage neurons, worsen existing neurological conditions and raise stroke risk.
“Heat exposure may trigger an inflammatory response in the brain,” she said. “In cases like heatstroke, inflammation is believed to contribute to symptoms such as confusion and delirium.”
NEGATIVE THOUGHTS MIGHT BE CHANGING YOUR BRAIN IN SURPRISING WAYS, STUDY SUGGESTS
Excessive heat can also weaken the protective blood-brain barrier, according to the expert, which makes the brain more vulnerable to toxins and pathogens.
Higher temperatures are also associated with disturbances in mood and violent behavior, especially during prolonged heatwaves.
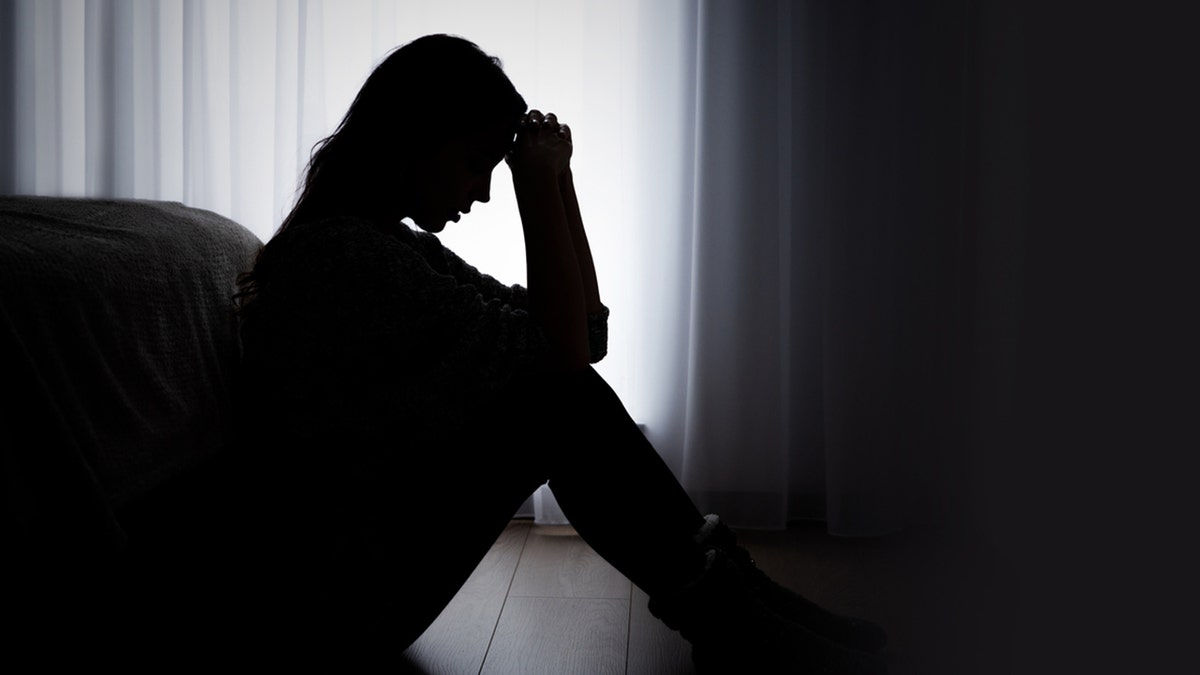

Emergency visits for mental health concerns rise during hotter days, according to experts. (iStock)
Psychiatric emergency visits for anxiety, depression and substance use also rise significantly on the hottest days, Gallagher confirmed.
Below are some of the main mental symptoms that can worsen in hot weather, experts cautioned.
- Irritability, anxiety or mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating, or “brain fog”
- Increased impulsivity or aggression
- Worsening of psychiatric symptoms like depression or psychosis
- Confusion or delirium, particularly during heat stroke
People who suffer from mental health conditions such as mood disorders, schizophrenia, anxiety or even dementia are more vulnerable in hot weather.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Some psychiatric medications could make it difficult for the body to regulate temperature or stay hydrated, Gallagher noted, while heat can “intensify” symptoms like agitation or paranoia.
“People with cognitive impairments may not recognize the signs of overheating,” she added.
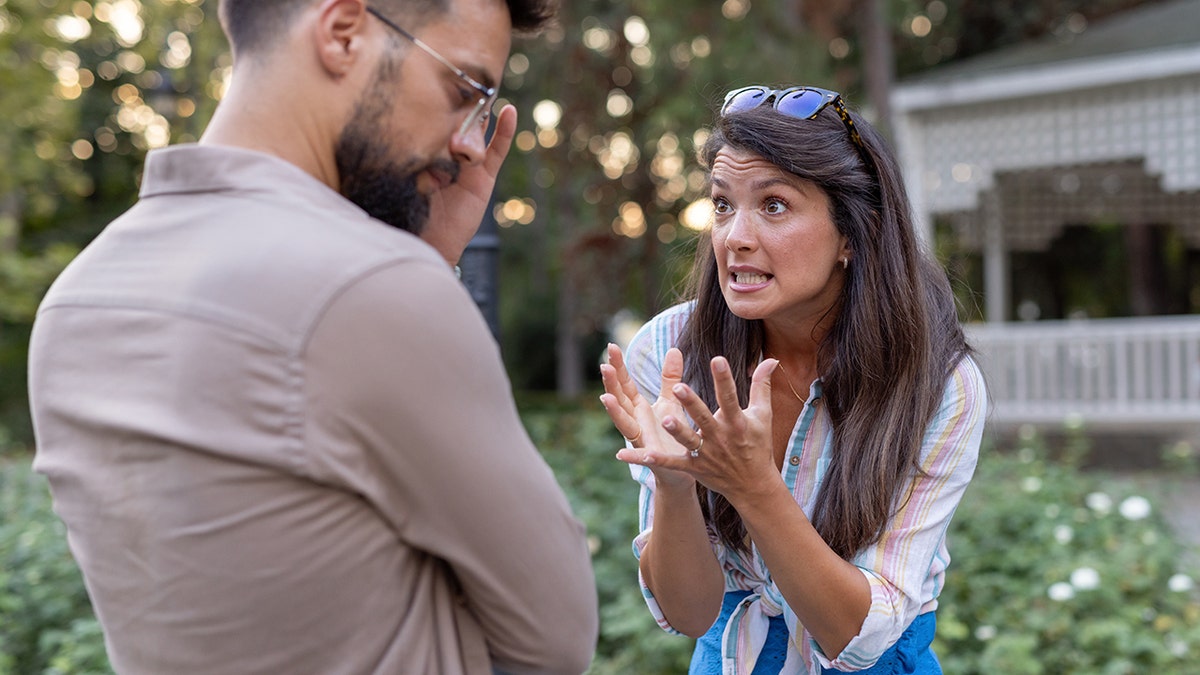

It’s important to have patience with yourself and others on hot days, one psychologist advised. (iStock)
“Some SSRIs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) can suppress sweat production, which is the body’s primary cooling mechanism. This raises the risk of overheating, dehydration and even heat stroke.”
“Paradoxically, SSRIs can also cause excessive sweating in some individuals — a side effect known as ‘SSRI sweats,’” she went on. “While this might seem like it would help with cooling, it can actually lead to dehydration if fluid intake doesn’t keep up.”
Protecting brain health
The experts recommended the following practices to protect brain health in extreme heat.
- Stay hydrated, as dehydration worsens cognitive decline
- Avoid peak heat hours; stay indoors or in shaded areas from 11 a.m. to 4 p.m.
- Use fans, air conditioning or cool showers
- Use blackout curtains and cooling bedding to ensure restful sleep
- Ask your doctor if any medications may increase heat sensitivity
- Use deep breathing and relaxation techniques to help manage heat-induced stress
- Stay socially connected; check in with friends and family
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“Days are also longer and there are more activities, which can be exhausting,” Gallagher noted. “Therefore, it is good to prioritize sleep and rest … and [find] ways to slow down when you can.”
Health
Lose Weight for Less With Hacks Like the Ozempic Click Chart + Microdosing

Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoHeart attack deaths have plummeted in US, but new cardiovascular threats emerge
-
 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoElon Musk scam tricks victims on Facebook with Tesla hoax
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoWhite House drops 'Daddy's Home' meme after viral NATO summit moment
-
World1 week ago
Protecting children online: The time to act is now
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week ago16 billion passwords leaked in massive data breach
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoSearching for healing: Inside one of the last hospitals in Haiti’s capital
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week ago'South Park' dispute escalates as creators accuse Paramount's buyers of meddling
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMeta wins artificial intelligence copyright case in blow to authors















