Health
A new study is the first to document likely cat-to-human virus transmission, but risks are low overall, experts say.

A veterinarian in Thailand seemingly contracted the coronavirus from an contaminated pet cat final 12 months, researchers concluded in a brand new examine. It’s the first documented case of suspected cat-to-human transmission, though specialists stress that the danger of cats infecting people with the virus stays low total.
One of many cat’s two house owners, who each had Covid-19, in all probability handed the virus to the cat, which then sneezed within the veterinarian’s face, in accordance with the paper, which was written by scientists at Thailand’s Prince of Songkla College. Genomic sequencing confirmed that the cat and all three folks have been contaminated with an similar model of the virus, which was not widespread within the native inhabitants on the time.
Cats are way more more likely to catch the virus from folks than to transmit it to them, scientists say. However the case is a reminder that people who find themselves contaminated with the virus ought to take precautions round their pets — and that veterinarians and shelter staff who could come into contact with contaminated animals ought to do the identical, mentioned Dr. Scott Weese, an infectious illnesses veterinarian on the College of Guelph in Ontario.
“When issues develop into human illnesses, we too usually neglect every part else,” he mentioned. “I believe it’s necessary for us to acknowledge this virus nonetheless can transfer between species.”
Earlier analysis has proven that pet house owners can infect their cats and that, in sure situations, cats can transmit the virus to one another. But it surely has been tough to show that cat-to-human transmission occurs in pure settings. (Mink, hamsters and deer have been reported to unfold the virus to people.)
The brand new paper appeared this week within the journal Rising Infectious Ailments, which is revealed by the U.S. Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention. It makes a powerful case for cat-to-human transmission, Dr. Weese mentioned: “They’ve acquired a reasonably good story right here.”
On Aug. 4, a father and son in Bangkok developed signs of Covid-19 and subsequently examined optimistic for the virus. Due to a scarcity of hospital beds in Bangkok, the 2 males have been transported on Aug. 8 to a hospital in Songkhla, a province in southern Thailand, by way of a 20-hour ambulance experience. For causes which can be unclear, they introduced their pet cat.
When the lads have been admitted to the hospital, the cat was despatched to a veterinary hospital for an examination. Though the cat gave the impression to be wholesome, the veterinarian, a 32-year-old girl, collected nasal and rectal swabs, which examined optimistic for the virus. Whereas the veterinarian was swabbing the cat’s nostril, the animal sneezed in her face. (The veterinarian was sporting gloves and a masks in the course of the examination, however no face protect or eye safety.)
On Aug. 13, the veterinarian developed Covid-19 signs, together with a fever and a cough. Shortly thereafter, she examined optimistic for the virus.
Genomic sequencing revealed that the cat’s house owners, the cat and the veterinarian have been all contaminated with the identical model of the Delta variant, which was distinct from viral samples taken from different sufferers in Songkhla on the time.
P.C.R. testing means that the cat had a excessive viral load on the time of its veterinary examination. Not one of the veterinarian’s shut contacts are identified to have had Covid-19 on the time, and he or she had no prior encounters with the pet’s house owners, including assist to the idea that the cat was the supply of the veterinarian’s an infection. (It was not clear whether or not she met with the house owners later.)
The C.D.C. recommends that people who find themselves contaminated with the virus keep away from contact with their pets. “For those who’re making an attempt to avoid folks since you’re doubtlessly infectious,” Dr. Weese mentioned, “simply attempt to avoid animals on the similar time.”

Health
Is Okra Nature’s Ozempic? Learn the Truth About This Weight Loss Hack

Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Health
Two cancer drugs show promise in reversing Alzheimer's devastating effects

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Two cancer drugs could potentially slow or even reverse the effects of Alzheimer’s disease, a new study suggests.
Researchers at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) explored how the common dementia changes gene expression (which genes are turned on or off) in certain brain cells, according to a press release from the university.
Next, they looked at which existing FDA-approved drugs might counteract, or reverse, those changes.
ALZHEIMER’S RISK COULD RISE WITH SPECIFIC SLEEP PATTERN, EXPERTS WARN
In analyzing millions of electronic medical records of adults over 65, the researchers identified two medications that appeared to reduce the likelihood of Alzheimer’s in the patients who took them.
The medications — letrozone and irinotecan — are both approved to treat cancer. Letrozole is a breast cancer medication and irinotecan treats colon and lung cancer.
When the scientists tested a combination of both medications in mice, they noted a reversal of the gene expression changes that were initiated by Alzheimer’s.
Two cancer drugs could potentially slow or even reverse the effects of Alzheimer’s disease, a new study suggests. (iStock)
They also discovered a reduction in tau protein clumps in the brain — a key marker of Alzheimer’s — and an improvement in learning and memory.
“Alzheimer’s disease comes with complex changes to the brain, which has made it tough to study and treat, but our computational tools opened up the possibility of tackling the complexity directly,” said co-senior author Marina Sirota, PhD, the interim director of the UCSF Bakar Computational Health Sciences Institute and professor of pediatrics, in the press release.
EATING THESE COMMON FOODS COULD REDUCE ALZHEIMER’S RISK, EXPERTS SAY
“We’re excited that our computational approach led us to a potential combination therapy for Alzheimer’s based on existing FDA-approved medications.”
The results of the study, which was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and the National Science Foundation, were published in the journal Cell on July 21.

In analyzing millions of electronic medical records of adults over 65, the researchers identified two medications that appeared to reduce the likelihood of Alzheimer’s in the patients who took them. (iStock)
While the study’s outcome was promising, the researchers acknowledged several limitations, including the fact that the database they used to identify possible drugs was built from cancer cells, not brain cells.
They also noted that animal models were used.
“Although necessary, validation in animal models may not fully recapitulate human biology,” the researchers wrote.
MEN FACE DOUBLE DEMENTIA RISK IF THEY HAVE A HIDDEN GENETIC MUTATION
There was also a noticeable gender difference in response to the medications, with male mice responding better than females.
“As a hormone modulator, letrozole might contribute to this sex difference,” the team noted. “However, the analysis remains inconclusive due to the small number of male letrozole users.”
The electronic medical records could also present limitations, “as data tend to be sparse and are not collected with specific research in mind.”
“We’re hopeful this can be swiftly translated into a real solution for millions of patients with Alzheimer’s.”
More than seven million people in the U.S. are currently living with Alzheimer’s, according to the Alzheimer’s Association.
This number is expected to approach 13 million by the year 2050.

More than seven million people in the U.S. are currently living with Alzheimer’s, according to the Alzheimer’s Association. (iStock)
There are currently only two disease-modifying medications that have been FDA-approved to treat Alzheimer’s, UCSF states.
Lecanemab (Leqembi) and donanemab (Kisunla) are both monoclonal antibodies that are administered via IV infusions.
They work by reducing the build-up of amyloid plaques in the brain, but they are only effective for those with early-stage Alzheimer’s and have the potential for some serious side effects, according to experts.
(Other Alzheimer’s medications help with symptoms, but don’t treat the underlying disease.)
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“Alzheimer’s is likely the result of numerous alterations in many genes and proteins that, together, disrupt brain health,” said co-senior study author Yadong Huang, M.D., PhD, professor of neurology and pathology at UCSF, in the release.
“This makes it very challenging for drug development — which traditionally produces one drug for a single gene or protein that drives disease.”
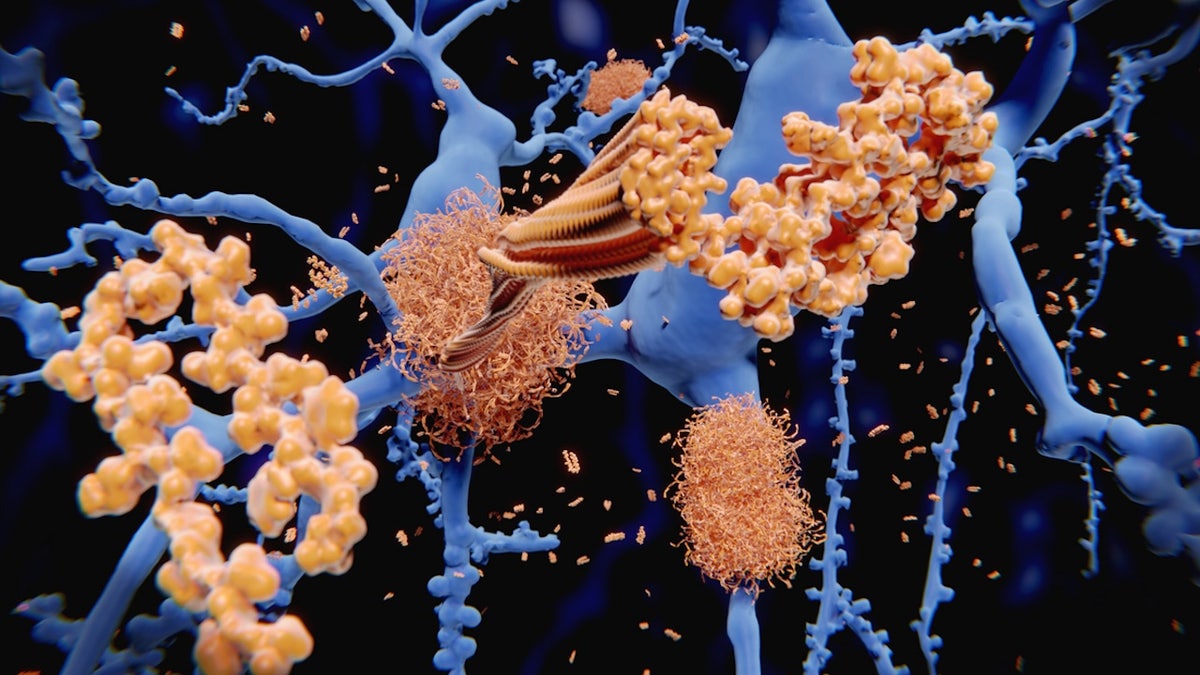
Existing Alzheimer’s drugs work by reducing the build-up of amyloid plaques in the brain, but they are only effective for those with early-stage disease. (iStock)
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to start a clinical trial to explore the combined drugs’ impact on human patients with Alzheimer’s.
“If completely independent data sources, such as single-cell expression data and clinical records, guide us to the same pathways and the same drugs, and then resolve Alzheimer’s in a genetic model, then maybe we’re onto something,” Sirota said in the release.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“We’re hopeful this can be swiftly translated into a real solution for millions of patients with Alzheimer’s.”
Health
Video: How the Organ Donation System Let These Patients Down

Under pressure from the federal government to increase organ transplants, hospitals and organ procurement organizations across the country are rushing people toward donation, and some patients have been harmed. Brian M. Rosenthal explains how and where this is happening.
-
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoNew weekly injection for Parkinson's could replace daily pill for millions, study suggests
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoConstitutional scholar uses Biden autopen to flip Dems’ ‘democracy’ script against them: ‘Scandal’
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoTest Your Knowledge of French Novels Made Into Musicals and Movies
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoDOJ rejects Ghislaine Maxwell’s appeal in SCOTUS response
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoShould You Get a Heat Pump? Take Our 2-Question Quiz.
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoEx-MLB pitcher Dan Serafini found guilty of murdering father-in-law
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSCOTUS allows dismantling of Education Dept. And, Trump threatens Russia with tariffs
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoJohn Goodman, 72, Says His 200-Lb. Weight Loss Helps Him ‘Live Life Better’














