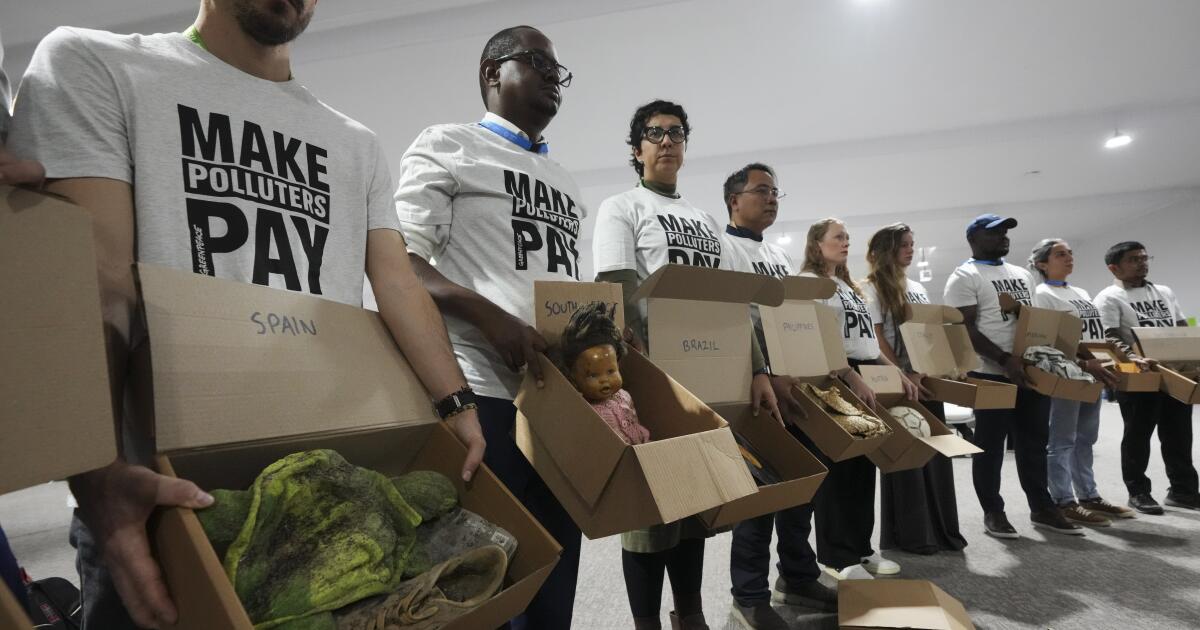
- Banks back accounting for 33% of capital market-linked emissions
- Environmental advocates push for 100% attribution
- PCAF board expected to back the 33% weighting, ending delays
World
Exclusive: Banks vote to limit accounting of emissions in bond and stock sales
/cloudfront-us-east-2.images.arcpublishing.com/reuters/6RA7EWG2UBLL5AKNETNZSGC3RI.jpg)
LONDON, July 30 (Reuters) – Banks working to develop global standards on accounting for carbon emissions in bond or stock sale underwriting have voted to exclude most of these emissions from their own carbon footprint, three people familiar with the matter said.
The majority of banks comprising an industry working group backed a plan earlier this month to exclude two-thirds of the emissions linked to their capital markets businesses from being attributed to them in carbon accounting, the sources said, following months of discord over the issue.
If upheld, the decision would pit banks against environmental advocates, many of whom say the banking industry should assume full responsibility for the emissions generated by activities financed through bonds and stock sales, as it already does with loans.
Almost half of the financing provided by the six biggest U.S. banks for top fossil fuel companies came from capital markets rather than direct lending between 2016 and 2022, according to environmental group Sierra Club.
Banks’ accounting of these emissions will impact their targets for becoming carbon-neutral. Major lenders have pledged to bring their emissions down to zero on a net basis by 2050, and have set interim targets for this decade.
Banks with big capital markets operations in the working group argued that they should assume responsibility for only 33% of the emissions of activities financed through bonds and stock sales because they do not have control over the borrowers as they do with loans. The banks have also expressed concern about capital market-related emissions dwarfing their lending-related emissions, the sources said.
Those pushing for a low accounting threshold say assuming responsibility for 100% of the emissions would lead to double-counting across the financial system, because bond and stock investors will also separately account for some of the emissions generated by the financing activities in their own carbon footprints.
The majority of the banks in the working group backed the 33% threshold but at least two dissented, with one advocating for 100%, the sources said, requesting anonymity because the deliberations were confidential.
The accounting standard will not be mandatory. The Partnership for Carbon Accounting Financials (PCAF), an association of banks seeking to harmonise carbon accounting across the industry, formed the working group comprising major banks in the hope that others will follow the standard that emerges.
PCAF’s board will now have the final say on whether to adopt the 33% accounting share for capital markets. Two of the sources said no decision had been made but it was reluctant to override the working group.
A PCAF spokesperson did not respond to a request for comment.
The working group’s members are Morgan Stanley (MS.N), Barclays (BARC.L), Bank of America (BAC.N) Citigroup (C.N), HSBC (HSBA.L), BNP Paribas (BNPP.PA), NatWest (NWG.L) and Standard Chartered (STAN.L). Officials from all but two either declined to comment or did not respond to requests for comment.
A Barclays spokesperson said the bank supported PCAF’s work to establish standards for emissions and declined to comment further. A Standard Chartered spokesperson said the bank was comfortable with any emissions accounting threshold and declined to comment further.
The sources said PCAF had become frustrated at how much energy had been spent arguing over the right number, and believed any percentage was better than further delays. Publication of PCAF’s final methodology has been delayed since last year because of the disagreements.
BUNDLING EMISSIONS
Campaign group ShareAction said the 33% weighting had been “plucked out of thin air.”
“PCAF has the responsibility to publish guidance that enables a transparent and unbiased assessment of banks’ climate risks and impacts,” its research manager Xavier Lerin said.
It is not yet clear whether banks will have to bundle together their capital market-related emissions and their lending-related emissions into a single target, or separate them.
Having a single target but two accounting approaches for the different emissions could prove challenging, one of the sources said.
The Science Based Targets initiative, a separate body backed by the United Nations and environmental groups, is in the process of developing net-zero standards which will include whether banks should have different or combined targets.
Reporting by Tommy Reggiori Wilkes in London; Editing by Greg Roumeliotis and Rosalba O’Brien
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles.

Continue Reading
World
Fact-check: What do we know about Russia’s nuclear arsenal?

Moscow has lowered the bar for using nuclear weapons and fired a missile capable of carrying a nuclear warhead into Ukraine, heightening tensions with the West.
Russia’s nuclear arsenal is under fresh scrutiny after an intermediate-range ballistic missile capable of carrying an atomic warhead was fired into Ukrainian territory.
President Vladimir Putin says the unprecedented attack using the so-called “Oreshnik” missile is a direct response to Ukraine’s use of US and UK-made missiles to strike targets deep in Russian territory.
He has also warned that the military facilities of Western countries allowing Ukraine to use their weapons to strike Russia could become targets.
The escalation comes days after the Russian President approved small but significant changes to his country’s nuclear doctrine, which would allow a nuclear response to a conventional, non-nuclear attack on Russian territory.
While Western officials, including US defence secretary Lloyd Austin, have dismissed the notion that Moscow’s use of nuclear weapons is imminent, experts warn that recent developments could increase the possibility of nuclear weapons use.
Here’s what we know about Russia’s inventory of atomic weapons.
How big is Russia’s nuclear arsenal?
Russia holds more nuclear warheads than any other nation at an estimated 5,580, which amounts to 47% of global stockpiles, according to data from the Federation of American Scientists (FAS).
But only an estimated 1,710 of those weapons are deployed, a fraction more than the 1,670 deployed by the US.
Both nations have the necessary nuclear might to destroy each other several times over, and considerably more atomic warheads than the world’s seven other nuclear nations: China, France, India, Israel, North Korea, Pakistan and the United Kingdom.
Of Moscow’s deployed weapons, an estimated 870 are on land-based ballistic missiles, 640 on submarine-launched ballistic missiles, and potentially 200 at heavy bomber bases.
According to FAS, there are no signs Russia is significantly scaling up its nuclear arsenal, but the federation does warn of a potential surge in the future as the country replaces single-warhead missiles with those capable of carrying multiple warheads.
Russia is also steadily modernising its nuclear arsenal.
What could trigger a Russian nuclear response?
Moscow’s previous 2020 doctrine stated that its nuclear weapons could be used in response to an attack using nuclear or other weapons of mass destruction “when the very existence of the state is put under threat.”
Now, the conditions under which a nuclear response could be launched have changed in three crucial ways:
- Russia will consider using nuclear weapons in the case of a strike on its territory using conventional weapons, such as cruise missiles, drones and tactical aircraft.
- It could launch a nuclear attack in response to an aggression by a non-nuclear state acting “with the participation or support of a nuclear state”, as is the case for Ukraine.
- Moscow will also apply the same conditions to an attack on Belarus’ territory, in agreement with President Lukashenko.
Is there a rising nuclear threat?
The size of the world’s nuclear stockpiles has rapidly decreased amid the post-Cold War détente. The Soviet Union had some 40,000 warheads, and the US around 30,000, when stockpiles peaked during the 1960s and 70s.
But FAS warns that while the overall number is still in decline, operational warheads are on the rise once again. More countries are also upgrading their missiles to deploy multiple warheads.
“In nearly all of the nuclear-armed states there are either plans or a significant push to increase nuclear forces,” Hans M. Kristensen, Director of the Nuclear Information Project at the Federation of American Scientists (FAS), said in June this year.
Is the West reacting?
When Putin approved the updated nuclear protocol last week, many Western leaders dismissed it as sabre rattling.
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock said Germany and its partners would “not be intimidated” and accused Putin of “playing with our fear.”
But since Russia used a hypersonic ballistic missile capable of carrying a nuclear warhead in an attack on Dnipro, European leaders have raised the alarm.
“The last few dozen hours have shown that the threat is serious and real when it comes to global conflict,” Polish Prime Minister Donald Tusk said on Friday.
According to Dutch media reports, NATO’s secretary-general Mark Rutte is in Florida to urgently meet President-elect Donald Trump, potentially to discuss the recent escalation.
NATO and Ukraine will hold an extraordinary meeting in Brussels next Tuesday to discuss the situation and the possible allied reaction, according to Euronews sources.
World
Rental home investors poised to benefit as mortgage rates, high home prices sideline buyers in 2025
LOS ANGELES (AP) — Rental homes will remain an attractive option next year to would-be homebuyers sidelined by high mortgage rates and rising home prices, analysts say.
American Homes 4 Rent and Invitation Homes are two big real estate investment trusts poised to benefit from the trend, say analysts at Mizuho Securities USA and Raymond James & Associates.
Their outlooks boil down to a simple thesis: Many Americans will continue to have a difficult time finding a single-family home that they can afford to buy, which will make renting a house an attractive alternative.
It starts with mortgage rates. While the average rate on a 30-year mortgage fell to a two-year low of 6.08% in late September, it’s been mostly rising since then, echoing moves in the 10-year Treasury yield, which lenders use as a guide to pricing home loans.
The yield, which has hovered around 4.4% this week, surged after the presidential election, reflecting expectations among investors that President-elect Donald Trump’s proposed economic policies may widen the federal deficit and crank up inflation.
Analysts at Raymond James and Associates say they see mortgage rates remaining “higher for longer,” given the outcome of the election. Last week, they reiterated their “Outperform” ratings on American Homes 4 Rent and Invitation Homes, noting “we are increasingly confident in the longer-term outlook for single-family rental fundamentals and the industry’s growth prospects.”
They also believe the two companies will continue to benefit from “outsized demographic demand for suburban homes,” and the monthly payment gap between renting and owning a home, which they estimate can be as much as 30% less to rent.
Analysts at Mizuho also expect that homeownership affordability hurdles will maintain “a supportive backdrop” and stoke demand for rental houses, helping American Homes 4 Rent and Invitation Homes to maintain their tenant retention rates.
The companies are averaging higher new and renewal tenant lease rates when compared to several of the largest U.S. apartment owners, including AvalonBay, Equity Residential and Camden Property Trust, according to Mizuho. It has an “Outperform” rating on American Homes 4 Rent and a “Neutral” rating on Invitation Homes.
Shares in Invitation Homes are down 1.2% so far this year, while American Homes 4 Rent is up 4.4%. That’s well below the S&P 500’s 24% gain in the same period.
While individual homeowners and mom-and-pop investors still account for the vast majority of single-family rental homes, homebuilders have stepped up construction of new houses planned for rental communities.
In the third quarter, builders broke ground on about 24,000 single-family homes slated to become rentals. That’s up from 17,000 a year earlier. In the second quarter, single-family rental starts climbed to 25,000, the highest quarterly total going back to at least 1990, according to an analysis of U.S. Census data by the National Association of Home Builders.
World
US briefed Ukraine ahead of Putin's 'experimental Intermediate-range ballistic' attack

A U.S. official on Thursday confirmed to Fox News Digital that Ukrainian authorities were briefed ahead of Russia’s “experimental Intermediate-range ballistic missile” attack that this type of weapon may be used against Ukraine in order to help it prepare.
Russian President Vladimir Putin confirmed the attack Thursday evening local time in an address to the nation and said it was in direct response to the U.S. and the U.K. jointly approving Ukraine’s use of Western-supplied long-range missiles to target Russia.
It remains unclear if there were any casualties in the attack on the city of Dnipro, which was originally reported as an Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) strike, and which would have marked the first time such a weapon had been used during a time of war, sending panic across the globe.
1,000 DAYS OF WAR IN UKRAINE AS ZELENSKYY DOUBLES DOWN ON AERIAL OPTIONS WITH ATACMS, DRONES AND MISSILES
Putin and U.S. sources have since confirmed the strike was not an ICBM, but the Kremlin chief also claimed that the weapon used poses a significant challenge for Western nations.
“The missiles attack targets at a speed of MACH 10. That’s 2.5 miles per second,” Putin said according to a translation. “The world’s current air defense systems and the missile defense systems developed by the Americans in Europe do not intercept such missiles.”
Fox News Digital could not immediately verify whether the U.S. or its NATO allies are capable of defending against this latest missile, dubbed the Oreshnik.
But according to one U.S. official, Putin may be playing up his abilities in a move to intimidate the West and Ukraine.
A Yars intercontinental ballistic missile is test-fired in northwestern Russia on Oct. 29. (Russian Defense Ministry Press Service via AP)
“While we take all threats against Ukraine seriously, it is important to keep a few key facts in mind: Russia likely possesses only a handful of these experimental missiles,” the official told Fox News Digital. “Ukraine has withstood countless attacks from Russia, including from missiles with significantly larger warheads than this weapon.
“Let me be clear: Russia may be seeking to use this capability to try to intimidate Ukraine and its supporters, or generate attention in the information space, but it will not be a game-changer in this conflict,” the official added.
US EMBASSY IN KYIV CLOSED AS ‘POTENTIAL SIGNIFICANT AIR ATTACK’ LOOMS
Following President Biden’s position reversal this week to allow Ukraine to use U.S.-supplied long-range Army Tactical Missile Systems (ATACMS) against the Russian homeland, Kyiv immediately levied strikes against a military arsenal in the Russian region of Bryansk, more than 70 miles from Ukraine’s border.
While Ukrainian troops are the ones to officially fire the sophisticated missiles, the weapons system still relies on U.S. satellites to hit its target — an issue Putin touched on in his unannounced speech Thursday.
“We are testing the Oreshnik missile systems in combat conditions in response to NATO countries’ aggressive actions against Russia. We will decide on the further deployment of intermediate-range and shorter-range missiles depending on the actions of the U.S. and its satellites,” he said.
CLICK TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP

Firefighters work at the site of a Russian missile strike in Dnipro, Ukraine, on Thursday. (Press service of the State Emergency Service of Ukraine in Dnipropetrovsk region/Handout via Reuters)
Putin claimed Russia will alert Ukrainian citizens of an impending attack like the strike he carried out on Thursday, though it remains unclear if he issued a warning to the Ukrainians living in Dnipro.
The Kremlin chief said the “defense industry” was targeted, though images released by the Ukrainian ministry of defense showed what appeared to be civilian infrastructure was also caught in the fray.
The Pentagon on Thursday confirmed that Russia informed the U.S. of the impending attack, which corresponds with information obtained by Fox News Digital, but it is unclear if Moscow clarified which Ukrainian city was the intended target.
A U.S. official told Fox News Digital that the U.S. is committed to helping Ukraine bolster its air defense systems and has done so already by supplying Ukraine with hundreds of additional Patriot and Advanced Medium-Range Air-to-Air Missiles.
-
Business1 week ago
Column: OpenAI just scored a huge victory in a copyright case … or did it?
-
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoBird flu leaves teen in critical condition after country's first reported case
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoColumn: Molly White's message for journalists going freelance — be ready for the pitfalls
-
World1 week ago
Sarah Palin, NY Times Have Explored Settlement, as Judge Sets Defamation Retrial
-

 Science3 days ago
Science3 days agoTrump nominates Dr. Oz to head Medicare and Medicaid and help take on 'illness industrial complex'
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoTrump taps FCC member Brendan Carr to lead agency: 'Warrior for Free Speech'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25739950/247386_Elon_Musk_Open_AI_CVirginia.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25739950/247386_Elon_Musk_Open_AI_CVirginia.jpg) Technology4 days ago
Technology4 days agoInside Elon Musk’s messy breakup with OpenAI
-

 Lifestyle5 days ago
Lifestyle5 days agoSome in the U.S. farm industry are alarmed by Trump's embrace of RFK Jr. and tariffs