World
China supported sanctions on North Korea’s nuclear program. It’s also behind their failure
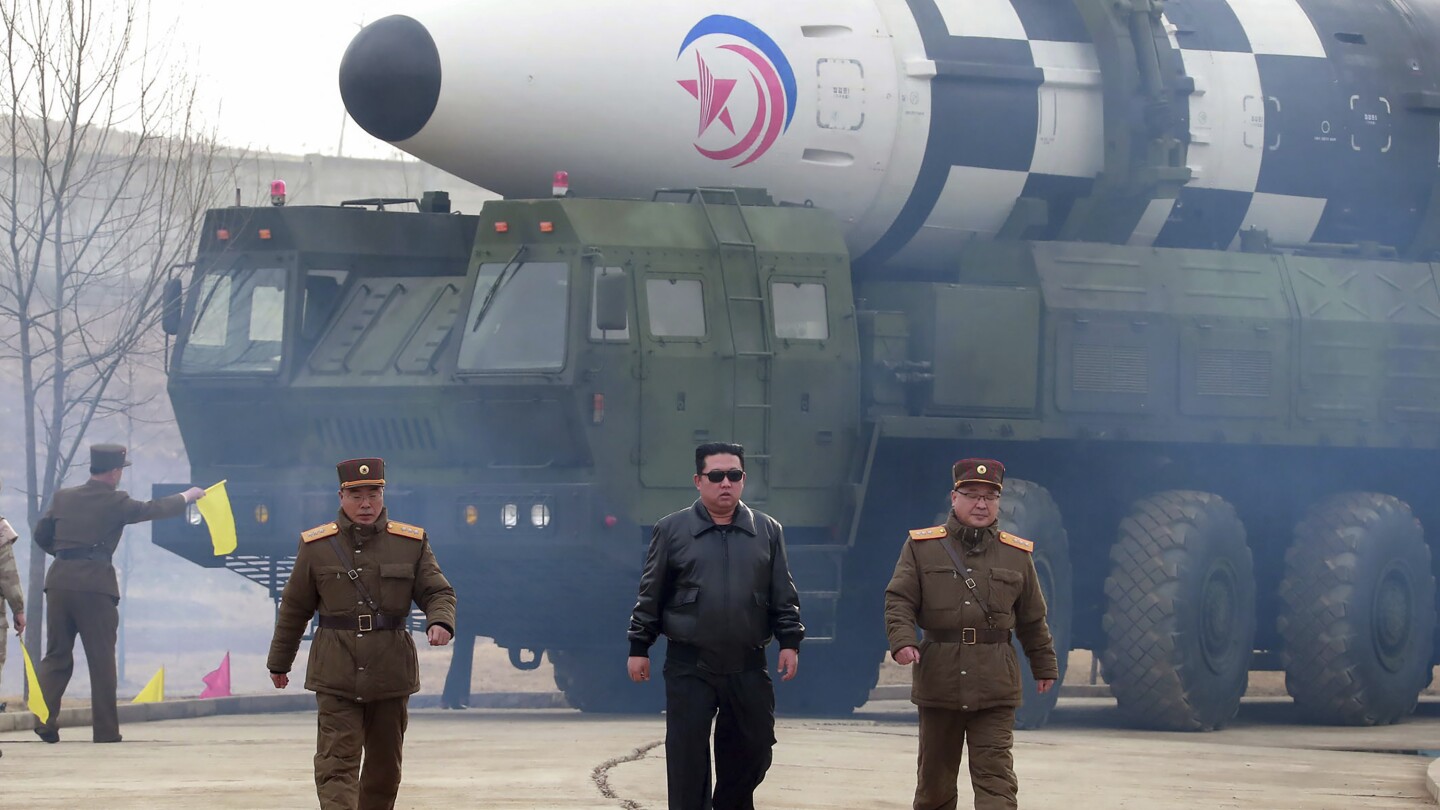

WASHINGTON (AP) — Chinese middlemen launder the proceeds of North Korean hackers’ cyber heists while Chinese ships deliver sanctioned North Korean goods to Chinese ports.
Chinese companies help North Koreans workers — from cheap laborers to well-paid IT specialists — find work abroad. A Beijing art gallery even boasts of North Korean artists working 12-hour days in its heavily surveilled compound, churning out paintings of idyllic visions of life under communism that each sell for thousands of dollars.
That’s all part of what international authorities say is a growing mountain of evidence that shows Beijing is helping cash-strapped North Korea evade a broad range of international sanctions designed to hamper Pyongyang’s nuclear weapons program, according to an Associated Press review of United Nations reports, court records and interviews with experts.
“It’s overwhelming,” Aaron Arnold, a former member of a U.N. panel on North Korea and a sanctions expert at the Royal United Services Institute, said of the links between China and sanctions evasion. “At this point, it’s very hard to say it’s not intentional.”
China has had a complicated relationship with Pyongyang since the 1950-53 Korean War. Though uneasy with a nuclear menace at its doorstep, China doesn’t want its neighbor’s government to collapse, experts say. China views North Korea as a buffer against the U.S., which maintains a significant troop presence in South Korea.
Beijing has long maintained it enforces the sanctions it has supported since North Korea started testing nuclear weapons and forcefully pushed back on any suggestions to the contrary. “China has been fully and strictly implementing the (U.N. Security Council) resolutions,” a Chinese ambassador said in a recent letter to the U.N, adding that his country had “sustained great losses” in doing so.
But in recent years, Beijing has sought to weaken those very sanctions and last year vetoed new restrictions on Pyongyang after it conducted a nuclear test.
This summer a top ruling Chinese party official provided a vivid example of China’s ambiguity on sanctions as he stood clapping next to North Korean Leader Kim Jong Un during a Pyongyang military parade. Rolling past the two men were trucks carrying nuclear-capable missiles and other weapons the regime isn’t supposed to have.
They were joined by Russia’s defense minister, apparently part of a new effort by the Kremlin, struggling in its invasion of Ukraine, to strength ties with North Korea. The U.S. has accused North Korea of supplying artillery shells and rockets to Russia, while new evidence shows Hamas fighters likely fired North Korean weapons during their Oct. 7 assault on Israel.
But while Russia and a handful of other countries have been accused of helping North Korea evade sanctions, none has been as prolific as China, according to court records and international reports.
“China violates North Korea sanctions it voted for and says won’t work because it’s afraid they’ll work. And, also, says it isn’t violating them” said Joshua Stanton, a human rights advocate and attorney who has helped write U.S. sanction laws against North Korea.
A review by the AP found a majority of the people placed on the U.S. government’s sanctions list related to North Korea in recent years have ties to China. Many are North Koreans working for alleged Chinese front companies while others are Chinese citizens who U.S. authorities say launder money or procure weapons material for North Korea.
Besides sanctions, U.S. criminal prosecutions against individuals or entities assisting North Korea’s regime often have links to China.
That’s especially true for cases related to North Korea’s sophisticated hackers, who experts believe have stolen upwards of $3 billion in digital currency in recent years. That windfall has coincided with the speedy growth of the country’s missile and weapons program.
An indictment filed earlier this year alleges that a Chinese middleman helped launder cryptocurrency stolen by the regime’s top hackers into U.S. dollars. And a similar case was filed in 2020 that accused two Chinese brokers of laundering more than $100 million in digital currencies stolen by North Korea.
Such “over-the-counter” brokers allow North Korean hackers to bypass know-your-customer rules governing banks and other financial exchanges.
North Korea depends heavily on China’s financial system and Chinese companies to obtain prohibited technology and goods, as well as to acquire U.S. dollars and gain access to the global financial system, records show.
“The (Chinese) banks are less rigorous because the Chinese government is not pushing them,” said former top U.S. Treasury official Anthony Ruggiero.
North Korea imported more than $250,000 worth of aluminum oxide, which can be used in processing nuclear weapons fuel, from a Chinese company in 2015, according to customs records cited in a think tank report. U.S. prosecutors have alleged the same company accounted for a significant share of overall trade between North Korea and China; its customers included the Chinese government’s Ministry of Commerce, which was bidding on North Korean projects.
Images from North Korean military parades have shown the regime’s nuclear missiles being transported on launchers made with Chinese heavy-duty truck chassis. China told the U.N. panel of experts that North Korea had promised it would use the trucks to move timber.
China regularly ignores reams of satellite photos and vessel tracking data compiled by a U.N. panel of experts showing Chinese-flagged vessels docking with North Korean ships and transferring goods. North Korean ships are banned by U.N. sanctions from participating in ship-to-ship transfers, which are often done to obscure the flow of sanctioned goods like coal exports and oil imports.
The U.S. and other leading democracies sent China a letter this summer saying they were “disappointed” that satellite photos continue to show cargo ships that have allegedly been documented breaking sanctions operating in Chinese ports and territorial waters.
“The international community is closely watching China’s commitment to upholding its UN obligations,” the letter warns.
China dismisses such findings, frequently saying that its own investigations uncovered no evidence of wrongdoing, without providing any alternative information or explanation.
Beijing said last year it couldn’t provide Chinese port of call records for several North Korean ships because the U.N. panel hadn’t provided the ships’ IMO number, a unique identifier painted on large vessels. Those numbers can easily be looked up using a ship’s name.
Eric Penton-Voak, the former coordinator of the U.N. panel of experts, said such excuses were ludicrous in light of China’s vast surveillance powers and showed the ruling communist party’s contempt for enforcing the sanctions it agreed to.
“It’s just grasping at any straw“ to avoid providing an answer, he said.
When the U.N. panel urged Beijing to investigate Chinese garment companies that were likely employing North Korean workers, China said there was nothing it could do because the tip was too vague. The U.N. panel, Beijing said, had only provided the company names in Korean and English. China told the U.N. panel in a letter that its “business registration system uses only the Chinese language.”
___
Associated Press writer Dake Kang in Beijing contributed.
___
The Associated Press receives support for nuclear security coverage from the Carnegie Corporation of New York and Outrider Foundation. The AP is solely responsible for all content.
Contact AP’s global investigative team at Investigative@ap.org

World
Zelenskiy, NATO boss and European leaders discuss Ukraine security guarantees

World
Hamas' Gaza death toll questioned as new report says its led to 'widespread inaccuracies and distortion'

A new report cites a laundry list of alleged errors in the casualty tallies that the Hamas-run Gaza Ministry of Health has issued during the conflict in Gaza, and found that worldwide media widely report the inflated numbers with little or no scrutiny.
The Henry Jackson Society (HJS), a U.K. based think tank, found “widespread inaccuracies and distortion in the data collection process” for the Hamas-run Gaza Ministry of Health (MoH) which has resulted in a “misleading picture of the conflict.” The study also analyzed how journalists worldwide have spread misleading MoH data without noting its shortcomings or offering alternative information from Israeli sources.
The report’s author, Andrew Fox, a fellow at HJS said his team’s research is based on lists of casualty figures that the MoH has released through Telegram as well as lists released by the U.N. Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs. Fox said he and his team have been able to examine segments of the reporting, despite changeable MoH data being “really hard to interrogate.”
On Tuesday, Gaza health authorities updated its number of dead to what it said was more than 45,000.
ISRAEL TO CLOSE EMBASSY IN IRELAND OVER ‘ANTI-ISRAEL POLICIES’
A man walks past shelter tents erected near collapsed buildings in the Bureij camp for Palestinian refugees in the central Gaza Strip on Oct. 1, 2024. (Eyad Baba/AFP via Getty Images)
The report said the ministry’s reporting long indicated that women and children made up more than half of the war dead, leading to accusations that Israel intentionally kills civilians in Gaza.
“If Israel was killing indiscriminately, you would expect deaths to roughly match the demographic proportions pre-war,” Fox said. At the time, adult men made up around 26% of the Gazan population. “The number of adult males that have died is vastly in excess of 26%,” he said.
Within accessible reporting, Fox and his team also found instances of casualty entries being recorded improperly, “artificially increas[ing] the numbers of women and children who are reported as killed.” This has included people with male names being listed as females, and grown adults being recorded as young children.
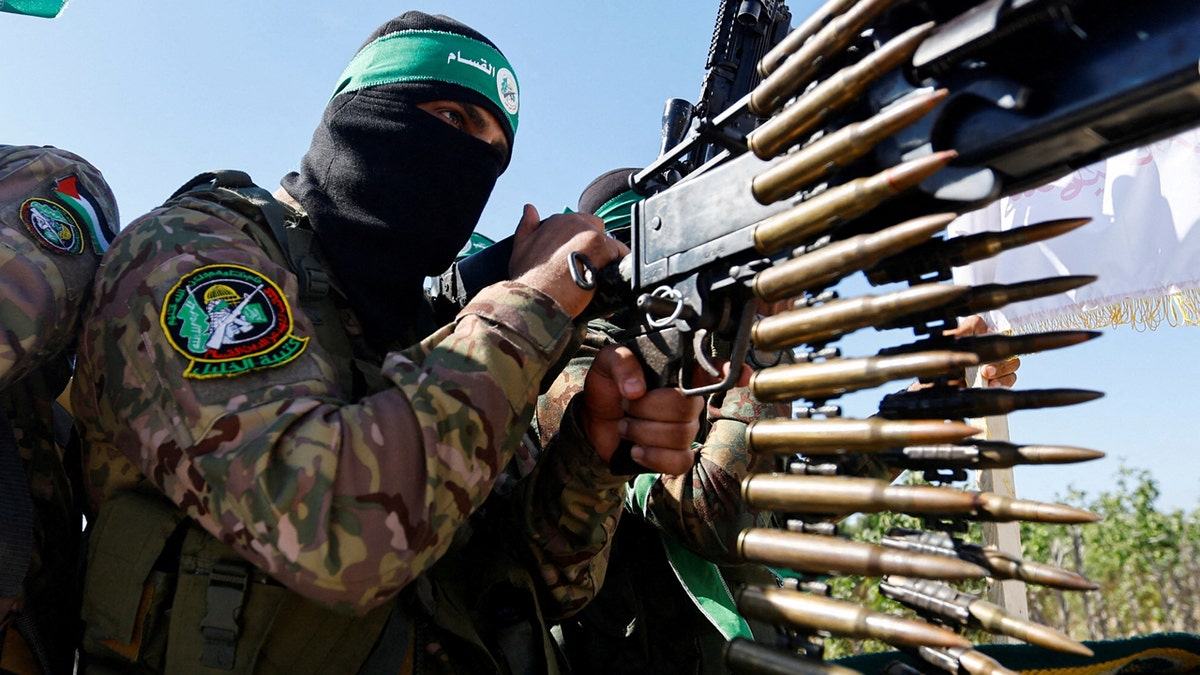

A terrorist from Hamas takes part in a military parade. (Reuters/Ibraheem Abu Mustafa/File Photo)
Analyzing data by category has further highlighted biases within reporting. There are three kinds of entries within MoH’s casualty figures: entries collected by hospitals prior to the breakdown of networks in November 2023, entries submitted by family members of the deceased, and entries collected through “media sources,” whose veracity researchers like Dr. David Adesnik, vice president of research at the Foundation for Defense of Democracies, has previously questioned.
Analysis of gender breakdowns among these groupings shows that hospital records “are distorted,” with a higher percentage of women and children among hospital-reported casualties than in those reported by family members.
UN ACCUSED OF DOWNPLAYING HAMAS TERRORISTS’ USE OF GAZA HOSPITALS AS NEW REPORT IGNORES IMPORTANT DETAILS
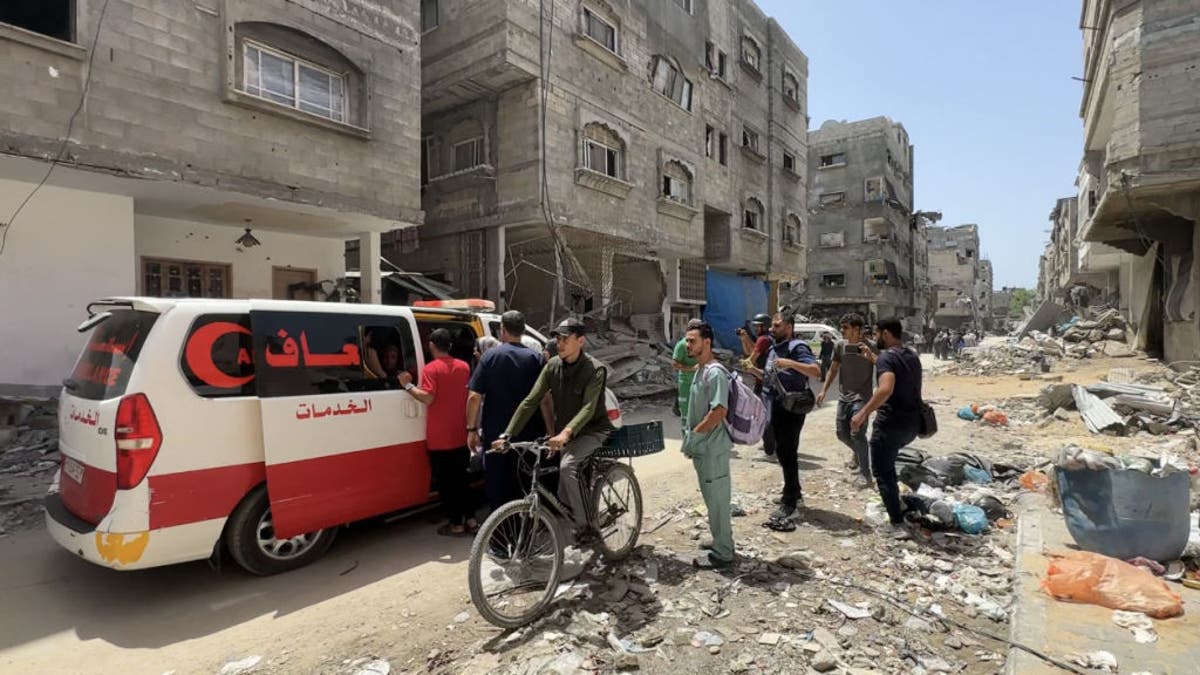

Kamal Adwan hospital’s health team evacuate Palestinian patients after Israeli airstrikes damaged the hospital in Gaza Strip on May 21, 2024. (Karam Hassan/Anadolu via Getty Images)
Though around 5,000 natural deaths typically occur in Gaza each year, the study found that MoH casualty figures do not account for natural deaths. It claims that it also fails to exclude deaths unassociated with Israeli military action from its count. This includes individuals believed to have been killed by Hamas, like 13-year-old Ahmed Shaddad Halmy Brikeh, who appears on a casualty list from August despite reports indicating he had “been shot dead by Hamas” while trying to get food from an aid shipment in December 2023. The list also excludes individuals killed by Hamas’ rockets, about 1,750 of which “fell short within the Gaza strip” between October 2023 and July 2024.
Fox and his team also found individuals who died before the conflict began had been added to MoH casualty counts. In addition, at least three cancer patients whose names were included in lists to leave the Gaza Strip for treatment in April had been listed as dead during the month of March.
RETURN OF TRUMP GIVES FAMILIES OF GAZA HOSTAGES NEW HOPE
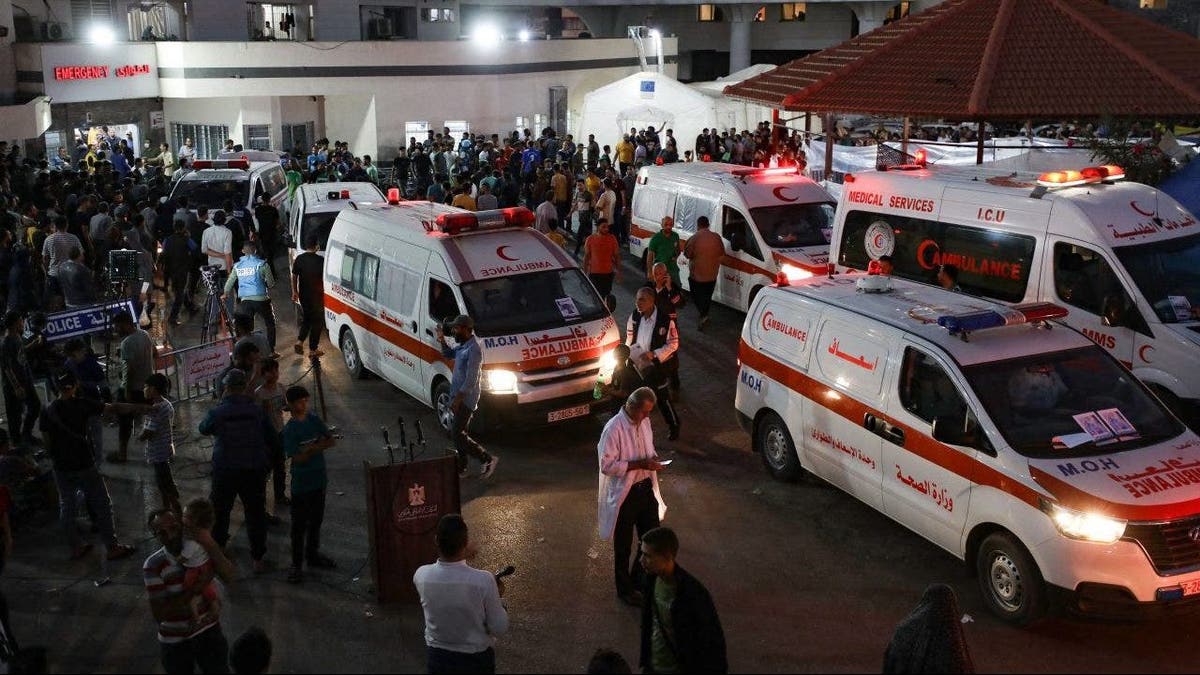

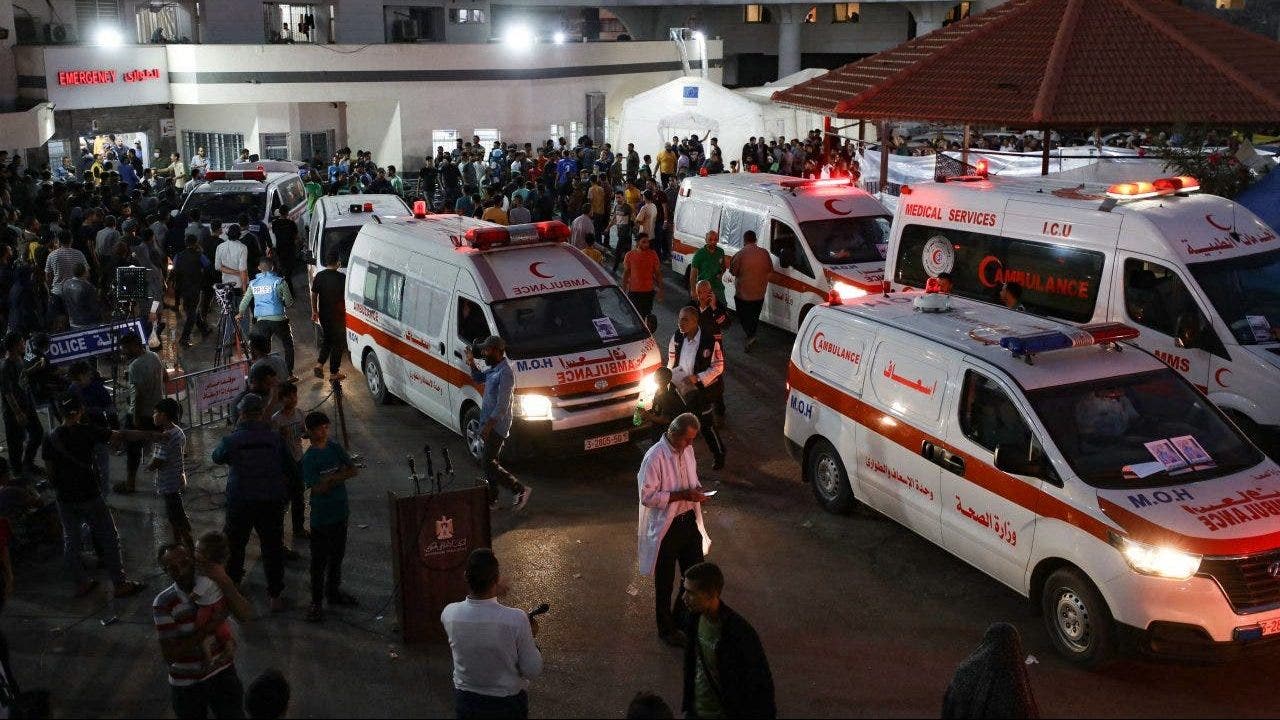
Ambulances carrying victims of Israeli strikes crowd the entrance to the emergency ward of the Al-Shifa hospital in Gaza City on Oct. 15, 2023. (Dawood Nemer/AFP via Getty Images)
The ministry does not separate combatants and civilians in its casualty figures. Though the study states that Israeli forces have killed around 17,000 Hamas terrorists, Fox said that his research indicated the death toll may include as many as 22,000 members of Hamas. He said his research supports the fact that around 15,000 of the dead in Gaza are women and children, and 7,500 are non-combatant adult males.
“Collecting these sorts of lists in a war zone is a hugely challenging thing,” Fox admitted, but he stated that the MoH’s mistakes, whether innocent or deliberate, show that the institution is “really unreliable.”
Despite this unreliability, the Henry Jackson Society’s survey of reporting of the conflict found that 98% of media organizations it looked at utilized fatality data from MoH versus 5% who cited Israeli figures. Fox found that “fewer than one in every 50 articles [about the conflict] mentioned that the figures provided by the MoH were unverifiable or controversial,” though “Israeli statistics had their credibility questioned in half of the few articles that incorporated them.”
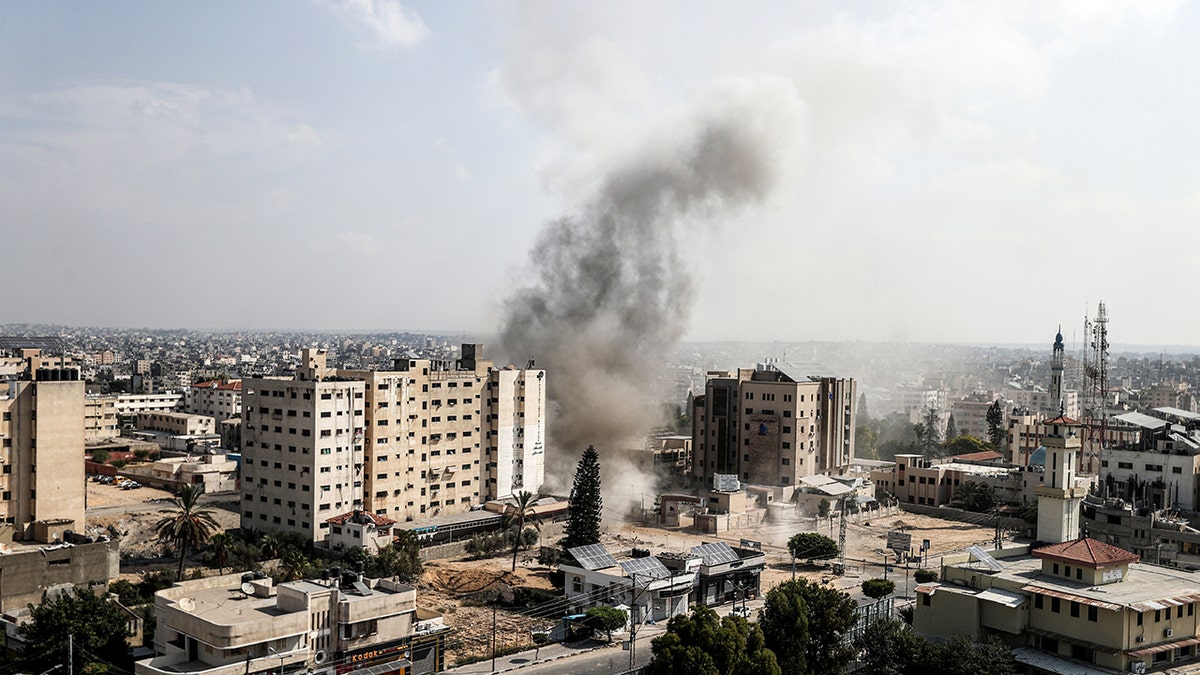

Smoke rises near the al-Wafa hospital from Israeli airstrike in Gaza City on Oct. 24, 2023. (Ali Jadallah/Anadolu via Getty Images)
As an illustration of the phenomenon witnessed in the survey, Fox pointed out what he called an “incredibly biased” article from a British broadcaster that recently emerged citing MoH data claiming that there have been more than 45,000 deaths in Gaza. Though its report mentions MoH data, it does not break down the numbers of combatants and civilians, and does not mention the questionable veracity of MoH reporting. Instead, it parrots MoH claims, reporting that women and children make up for over half of the fatalities.
“It’s just a great example of everything we’ve written in the report,” Fox said.
World
Arson at karaoke bar in Vietnam’s Hanoi kills 11, police say

Vietnam’s Ministry of Public Security says suspected perpetrator confessed to starting blaze after dispute with staff.
A suspected arson attack at a cafe and karaoke bar in Vietnam’s Hanoi has killed 11 people and injured two others, police have said.
Vietnam’s Ministry of Public Security said on Thursday that it had arrested a man who confessed to starting the blaze on the ground floor of the building following a dispute with staff.
Rescue workers who rushed to the scene brought seven people out of the building alive, two of whom were rushed to hospital, police said.
Footage that circulated on social media showed a multistorey building engulfed in flames as firefighters worked at the scene while surrounded by a crowd of onlookers.
“At that time, we saw many people screaming for help but could not approach because the fire spread very quickly, and even with a ladder, we could not climb up,” the Lao Dong newspaper quoted a witness as saying.
The Tien Phong newspaper quoted a witness as saying there was a strong smell of petrol at the scene.
“Everyone shouted for those inside to run outside, but no one called for help,” the witness said.
CCTV footage published by the VnExpress news site appeared to show a man carrying a bucket towards the cafe seconds before the blaze began shortly after 11pm (16:00 GMT) on Wednesday.
Fires are a common hazard in Vietnam’s tightly packed urban centres.
Between 2017 and 2022, 433 people were killed in some 17,000 house fires in the country, most of them in urban areas, according to the Ministry of Public Security.
In September last year, 56 people, including four children, were killed and dozens injured in a fire at an apartment block in Hanoi.
This October, a court in southern Binh Duong province jailed six people, including four police officers, over safety lapses related to a fire at a karaoke complex that killed 32 people in 2022.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoOpenAI's controversial Sora is finally launching today. Will it truly disrupt Hollywood?
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoCanadian premier threatens to cut off energy imports to US if Trump imposes tariff on country
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782636/247422_ChatGPT_anniversary_CVirginia.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25782636/247422_ChatGPT_anniversary_CVirginia.jpg) Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoInside the launch — and future — of ChatGPT
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25789444/1258459915.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25789444/1258459915.jpg) Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoOpenAI cofounder Ilya Sutskever says the way AI is built is about to change
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoU.S. Supreme Court will decide if oil industry may sue to block California's zero-emissions goal
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25546252/STK169_Mark_Zuckerburg_CVIRGINIA_D.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25546252/STK169_Mark_Zuckerburg_CVIRGINIA_D.jpg) Technology5 days ago
Technology5 days agoMeta asks the US government to block OpenAI’s switch to a for-profit
-

 Politics6 days ago
Politics6 days agoConservative group debuts major ad buy in key senators' states as 'soft appeal' for Hegseth, Gabbard, Patel
-

 Business3 days ago
Business3 days agoFreddie Freeman's World Series walk-off grand slam baseball sells at auction for $1.56 million