Over the weekend, DC Studios’ new Superman feature became this year’s third-biggest box-office debut in the US. The movie’s success is a sign that theatergoers might actually not be quite as tired of superheroes as people tend to think, and that’s particularly notable for Warner Bros., given the studio’s plan to build a new cinematic universe of DC Comics adaptations for the big screen. But making interconnected film franchises work is easier said than done. And even though Superman is putting up numbers, DC might have a much harder time doing the same with its next couple of cape movies.
Technology
New Harry Potter-named malware strikes, revealing global espionage campaign

A new malware has been detected by security researchers that is suspected of conducting espionage. Hackers infect devices by impersonating government agencies, usually tax agencies such as the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). Once the malicious software is on a PC, it can gather intelligence (collecting personal data, passwords and more), download additional malicious software and upload data to the hacker’s server. It does all this while using Google Sheets to avoid suspicion and store data.
GET SECURITY ALERTS, EXPERT TIPS – SIGN UP FOR KURT’S NEWSLETTER – THE CYBERGUY REPORT HERE
Illustration of computer being hacked by malware (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
It all starts with a fake email
The hackers behind the malware, called “Voldemort,” have cleverly designed it to avoid getting caught. Just like the name Voldemort spelled trouble in J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series, it’s causing issues in the cybersecurity world, too.
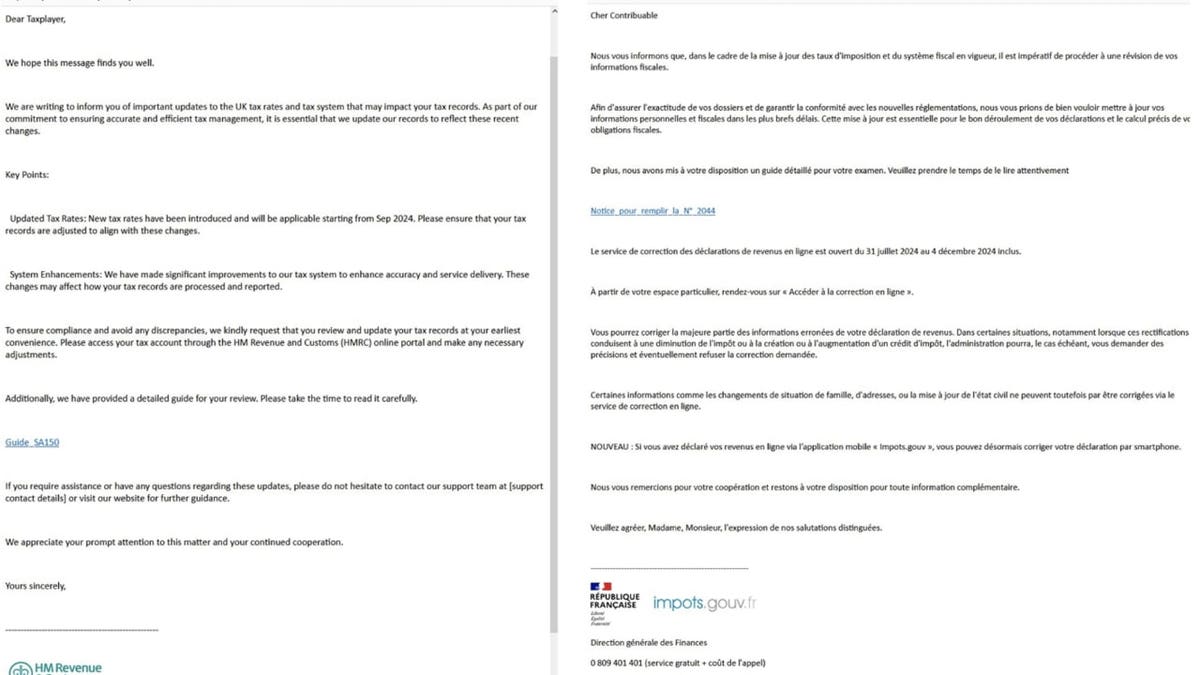
The cyberattack kicks off when you receive an email that looks like it’s from a government tax agency. According to Proofpoint, the hackers behind this campaign have been impersonating tax agencies in various countries, including the U.S. (IRS), the U.K. (HM Revenue & Customs), France (Direction Générale des Finances Publiques), Germany (Bundeszentralamt für Steuern), Italy (Agenzia delle Entrate) and, as of Aug. 19, India (Income Tax Department) and Japan (National Tax Agency). Each email lure was customized and written in the language of the tax authority being impersonated.
Proofpoint analysts found that the hackers tailored their phishing emails to match the target’s country of residence based on publicly available information rather than the organization’s location or the language suggested by the email address. For example, some targets in a European organization received emails impersonating the IRS because they were linked to the U.S. in public records. In some cases, the hackers mixed up the country of residence when the target shared a name with a more prominent individual.
The email also tries to mimic the email of the government agency. For example, the U.S. folks were sent fake emails using “no_reply_irs[.]gov@amecaindustrial[.]com.”
Email that tries to mimic the email of a government agency (Proofpoint) (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
The attack cleverly unfolds on your device
In the fake email, hackers impersonating the government warn you about changes in the tax rates and tax systems and ask you to click a link to read a detailed guide. Clicking on the link brings you to a landing page, which uses Google AMP Cache URLs to redirect you to a page with a “Click to view document” button.
After you click the button, the hackers check if you’re using a Windows device. If you are, you’ll be redirected to another page. When you interact with that page, it triggers a download that looks like a PDF file in your PC’s download folder, but it’s actually an LNK or ZIP file hosted on an external server.
When you open the file, it runs a Python script from another server without actually downloading the script to your computer. This script collects system information to profile you, while a fake PDF opens to hide the malicious activity.
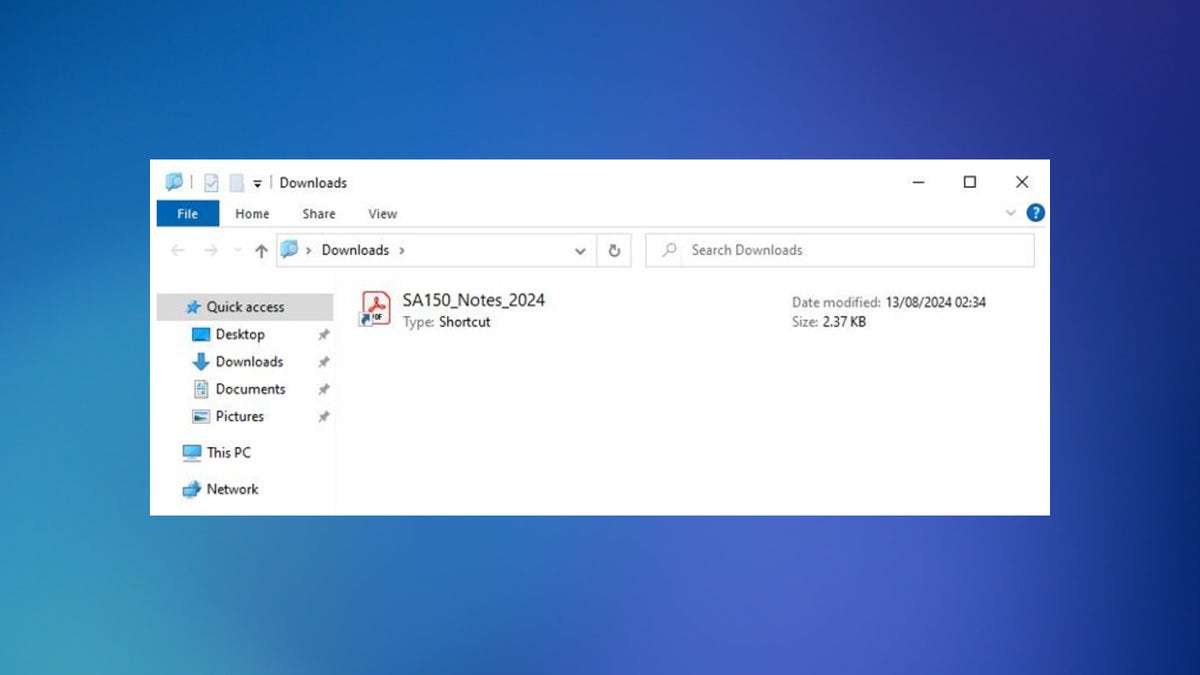
Download that looks like PDF file in your PC’s download folder (Proofpoint) (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
Voldemort uses Google Sheets to store data
Once the malware has successfully infected your Windows device, it can:
- Ping: Check if it’s still connected to its control server
- Dir: Get a list of files and folders on your system
- Download: Send files from your system to the control server
- Upload: Put files from the control server onto your system
- Exec: Run specific commands or programs on your system
- Copy: Copy files or folders on your system
- Move: Move files or folders around on your system
- Sleep: Pause its activity for a set time
- Exit: Stop running on your system
The malware uses Google Sheets as its command center, where it gets new instructions and stores stolen data. Each infected device sends its data to specific cells in the Google Sheet, marked by unique IDs to keep everything organized.
Voldemort interacts with Google Sheets through Google’s API, using an embedded client ID, secret and refresh token stored in its encrypted settings. This method gives the malware a reliable way to communicate without raising suspicion since Google Sheets is widely used in businesses, making it hard for security tools to block it.
HOW TO RECOGNIZE AND AVOID BEING A VICTIM OF VACATION RENTAL SCAMS
4 ways to protect yourself from malware attacks
Hackers are releasing increasingly sophisticated malware, but that doesn’t mean you’re defenseless. Below are some tips to help protect yourself from such attacks.
1) Read sensitive emails carefully: The best way to spot fake emails that deliver malware is to check them carefully. While hackers may be tech-savvy, their language skills often aren’t perfect. For example, in the screenshots above, you can see typos like “Taxplayers” instead of “Taxpayers.” Government agencies don’t usually make these kinds of mistakes.
2) Check email domain: Verify that the email domain matches the organization it claims to represent. For example, an email from the IRS should come from an address ending in “@irs.gov.” Be cautious of slight misspellings or variations in the domain.
3) Invest in data removal services: Hackers target you based on your publicly available information. That could be anything from your leaked info through a data breach to the information you provided to an e-commerce shop. Check out my top picks for data removal services here.
4) Have strong antivirus software: If you have strong antivirus software installed on your device, it can protect you when you receive these types of scam emails or accidentally open the attachment or click a link. The best way to protect yourself from clicking malicious links that install malware that may get access to your private information is to have antivirus protection installed on all your devices. This can also alert you of any phishing emails or ransomware scams. Get my picks for the best 2024 antivirus protection winners for your Windows, Mac, Android and iOS devices.
SUBSCRIBE TO KURT’S YOUTUBE CHANNEL FOR QUICK VIDEO TIPS ON HOW TO WORK ALL OF YOUR TECH DEVICES
Kurt’s key takeaway
While researchers can’t say for sure, many of the techniques used by the malware are similar to those employed by hackers suspected of espionage. Even if this assessment turns out to be incorrect, the scale and sophistication of the attack are concerning. Anyone without technical knowledge could easily fall victim and lose personal data and money. This attack specifically targets Windows users, which also raises questions about Microsoft’s security framework.
What measures do you think organizations should implement to better protect individuals from malware attacks? Let us know by writing us at Cyberguy.com/Contact.
For more of my tech tips and security alerts, subscribe to my free CyberGuy Report Newsletter by heading to Cyberguy.com/Newsletter.
Ask Kurt a question or let us know what stories you’d like us to cover.
Follow Kurt on his social channels:
Answers to the most asked CyberGuy questions:
New from Kurt:
Copyright 2024 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.

Technology
Superman is a box office hit, but the hard part comes next

Though it fell short of A Minecraft Movie’s and Lilo & Stitch’s domestic opening weekends, Superman raked in $125 million stateside and another $95 million internationally, making it WB’s strongest superhero debut since Matt Reeves’ The Batman in 2022. You can see those numbers reflected in the sheer amount of Superman hype (some of which has been weird and gross) that has overtaken social media since the movie first premiered. Because of Superman’s success, DC Studios co-CEO James Gunn is reportedly thinking about a couple of spinoff series revolving around Edi Gathegi‘s Mister Terrific and Skyler Gisondo‘s Jimmy Olsen. But before any of that comes to fruition, the studio first has to sell the public on its next two big tentpole features due out next year: Craig Gillespie’s Supergirl and James Watkins’ Clayface.
Following the disaster that became known as the DCEU, WB was in desperate need of a fresh start and a vision for how it could use DC characters in ways that audiences would actually like. That need led to the creation of DC Studios with Gunn and co-CEO Peter Safran guiding the whole endeavor. Though Gunn had worked on previous DC projects, his DC Studios’ appointment felt like a power move on WB’s part that spoke to its desire to push back against Marvel’s box-office dominance. And while it seemed a little odd that Gunn wanted to launch his new DC Universe with an animated Creature Commandos streaming series for (HBO) Max, it was easy to understand the logic behind his plan to make a new Superman the franchise’s centerpiece.
Superman has always been a pillar of the DC Comics brand and embodied much of what makes the company’s characters compelling across different mediums. In a universe full of gods, alien monsters, and supervillains, Superman represents hope and humanity at its best. He’s a near-indestructible powerhouse, but he’s also just a dork from Kansas who loves his family and believes in the importance of journalism. He’s got a bunch of superfriends, but he also has major beef with deranged billionaires who can’t wrap their minds around the concept of immigrants being people who make valuable contributions to society.
Those basic beats have defined Superman stories ever since the character first appeared back in 1938. And part of what makes Gunn’s new film so excellent is the way it weaves all of those ideas together into a colorful, optimistic joyride that feels nothing like WB’s other recent takes on the Man of Steel.
Some of Superman’s success can also be attributed to the basic fact that he’s a character whose lore most people are familiar with — something the movie acknowledges by glossing over Clark Kent’s tragic backstory and dropping you right into his life as an established superhero. But the same can’t exactly be said for Superman’s cousin, Kara / Supergirl, and B-tier Batman villain Clayface.
Thanks to CBS’s Supergirl and HBO Max’s Harley Quinn animated series, Kara and Clayface have had pretty big presences on the small screen in recent years. But the characters have always had somewhat lower profiles compared to DC’s other heroes and villains. Viewed through one lens, DC Studios following Superman up with Supergirl and Clayface reads as a calculated move to avoid following in the examples of the MCU and DCEU, which were both fleshed out with a series of features focused on the kinds of A-list characters you see on lunchboxes and bookbags. But the upcoming features also feel, at least on paper, informed by the way that studios like Marvel and Disney have gotten into the habit of expanding their genre franchises with ill-conceived spinoffs.
That’s kind of the general vibe you get from the full slate of DC Studio’s projects that are currently in development, which includes a stop-motion movie about two of Batman’s Robins, a True Detective-style Green Lantern show for HBO Max, and a feature about Bane and Deathstroke. A sequel to The Batman — which predates the DCU and exists in its own continuity — is also due out in 2027. And at some point down the line, the studio intends to introduce a new Bruce Wayne who will presumably link up with Superman and Wonder Woman (whose reboot is also in the pipeline) to form some sort of Justice League.

DC Studios
Most of DC Studios’ far-off films and series feel like the kinds of projects you would expect a studio to lead with — ones with instantly recognizable characters whose stories are well known enough to get audiences curious and excited about how they could be done differently. Milly Alcock’s Supergirl, who gets a brief and fantastic Superman cameo, seems a bit better suited to keep the franchise’s current momentum going. But given that we’re so early in this DCU’s existence, a body horror like Clayface, about an actor who becomes a murderous mud monster, feels like a tougher sell (even if Mike Flanagan is writing the script).
It’s easy to imagine Supergirl and Clayface revealing that what audiences have grown weary of isn’t comics-inspired narratives, but sprawling, interconnected franchises more concerned with growth than being made up of good movies. That energy is what dragged the MCU into its flop era and made most of Disney Plus’ Star Wars series slogs to get through, and DC Studios clearly doesn’t want to wind up in a similar position. Turning Clark’s cousin and a lesser-known DC villain into box-office juggernauts might be an even bigger challenge — but Superman at least shows that Gunn and Safran know where to start. And if the studio plays its cards right, this really might be the start of a new golden age for DC.
Technology
How to disable Gemini AI on Android and keep control of your apps

NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
Google is making a push to ensure its AI, Gemini, is tightly integrated with Android systems by granting it access to core apps like WhatsApp, Messages, and Phone. The rollout of this change started on July 7, 2025, and it may override older privacy configurations unless you know how to disable Gemini on Android. Here’s what you need to know.
Sign up for my FREE CyberGuy Report
Get my best tech tips, urgent security alerts, and exclusive deals delivered straight to your inbox. Plus, you’ll get instant access to my Ultimate Scam Survival Guide – free when you join my CYBERGUY.COM/NEWSLETTER.
A woman looking surprised at her Android phone’s screen. (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
What’s changing with Gemini on Android
Currently, the official email and support pages aren’t providing consistent information on Gemini’s true behavior regarding this change and how to disable it. However, we do know that Gemini will be able to interact with other apps. For instance, it would be able to make calls through the Phone app or send messages through WhatsApp.
Gemini will still be able to interact with your Android apps even if you turned off Gemini Apps Activity in the Gemini Apps setting. This setting allows Google to save your interactions with Gemini apps. These are used to train the AI by allowing “human reviewers (including service providers)” to “read, annotate, and process your Gemini Apps conversations,” according to the Google support page.
What to know before you disable Gemini on Android
Settings location may vary. Not all users will see the same options in the Gemini app or Google app, as settings can differ based on device model, region, or update status. If you don’t see a particular setting, it may be due to these factors.
How to stop the Gemini app from accessing your Android apps
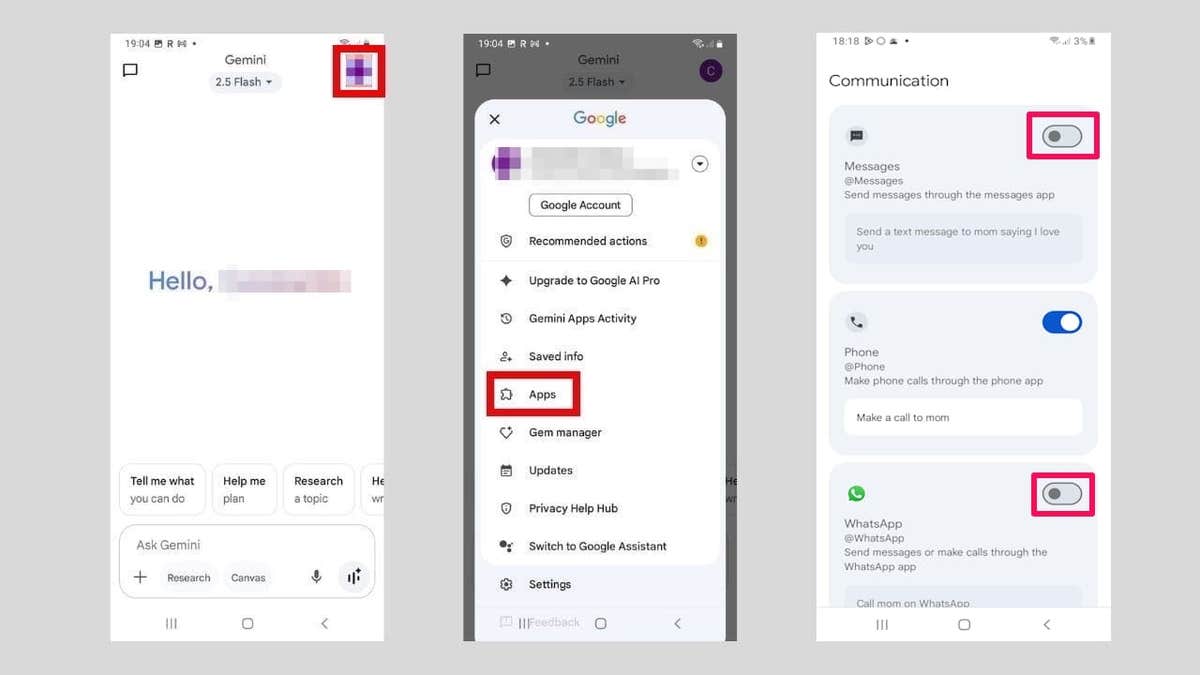
Google made it vague in the email by saying you can block Gemini from interacting with other apps in the Apps settings. That means if you have Gemini installed on your phone as a separate app, you need to do the following:
- Open the Google Gemini app on your Android phone.
- Tap your profile picture icon in the top-right corner of the screen.
- Tap Apps in the menu.
- Turn off the toggles for the apps you don’t want Gemini to access, which will then disable Gemini’s ability to interact with those specific apps and change the switch from blue to grey.
Steps to stop the Gemini app from accessing your Android apps. (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
Alternatively, you can just uninstall the Gemini app from your Android phone.
- Long-press the Google Gemini app.
- Tap Remove in the menu.
If your device doesn’t have Gemini installed already, the recent changes won’t secretly install it. You’re likely safe for now. However, you need to stay vigilant in case future updates try to sneak in Gemini functionality without your knowledge.
How to disable Gemini in the Google app on Android
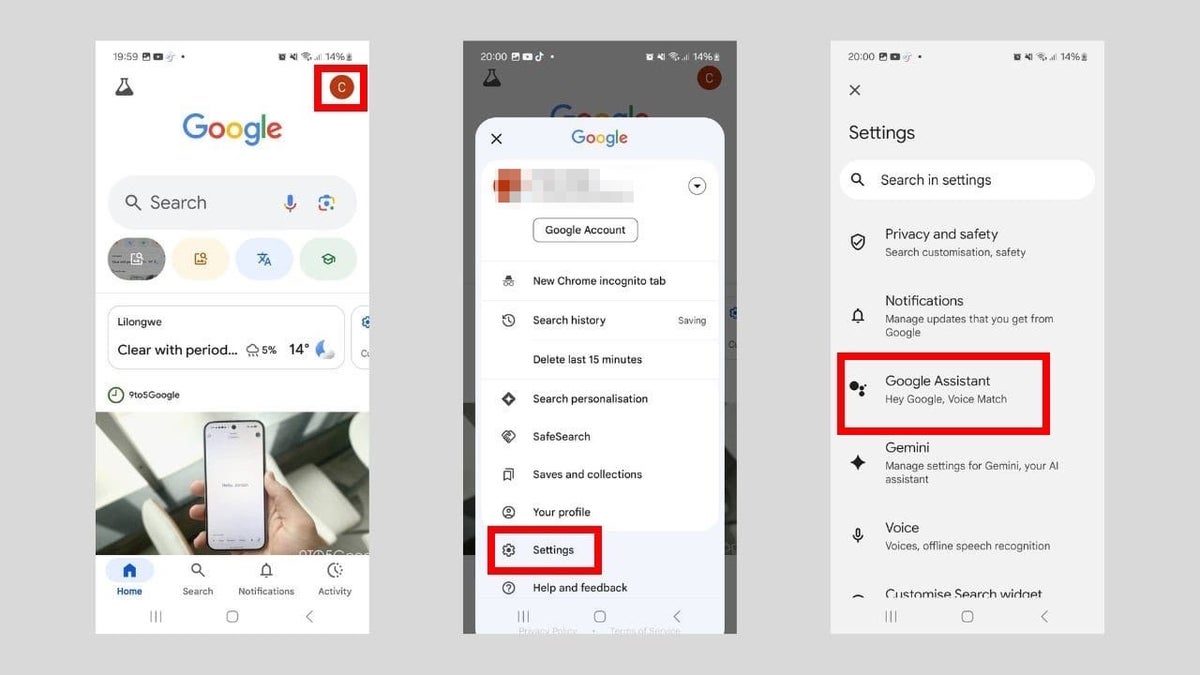
Gemini can also interact with other apps through the Google app on Android. So it makes sense to disable Gemini on Android in that app as well. Here’s how to do that:
- Tap your profile picture in the top-right corner.
- Tap Settings in the menu.
- Tap Google Assistant.
Steps to stop the Gemini app from accessing your Android apps. (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
- Tap Digital assistants from Google.
- If it’s set to Gemini, select Google Assistant.
- Tap Switch in the pop-up.
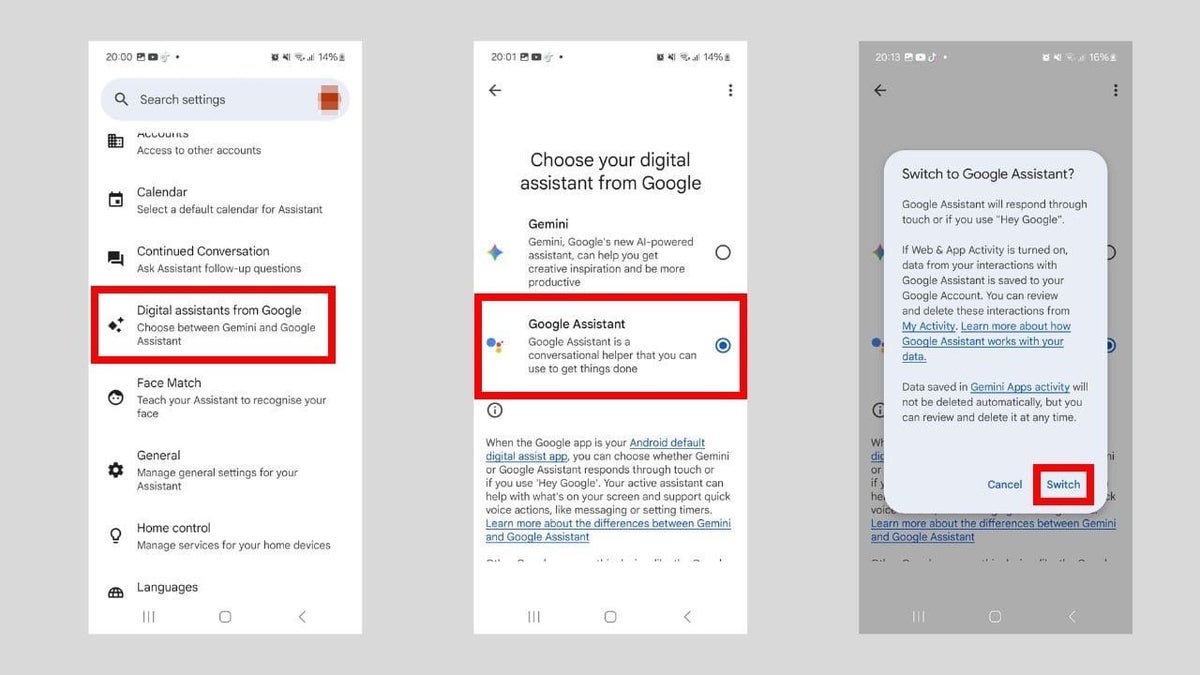
Steps to stop the Gemini app from accessing your Android apps. (Kurt “CyberGuy” Knutsson)
What happens after you disable Gemini on Android
Even after you disable Gemini on Android, there are a few key things to understand about how your data is handled and what settings might still require your attention:
If you have already disabled Gemini features, they should remain off: Google states that if you previously turned off Gemini’s access to apps, those privacy settings will persist after the update. However, it’s wise to double-check your settings to ensure nothing has changed.
No forced installation: The Gemini app will not be installed automatically if it isn’t already present on your device. You remain in control of whether or not to add it.
Data review by humans: Conversations with Gemini may be reviewed and annotated by human reviewers for quality control and AI training purposes. Even if your activity is deleted, data reviewed by humans can be retained for up to three years, and this data is disconnected from your Google Account before review. Avoid sharing confidential or sensitive information in Gemini chats, as Google explicitly advises against it.
Kurt’s key takeaways
While some users may welcome this change, if you value control and transparency over your data, limiting its access is the best option. Unfortunately, Google’s guidance on the subject is murky, and you can’t fully disable Gemini on Android unless you root your Android phone. But by proactively reviewing and tweaking a few settings, you can regain some control.
As AI systems become more powerful, do you trust companies to put your privacy before their profits? Let us know by writing us at Cyberguy.com/Contact.
Sign up for my FREE CyberGuy Report
Get my best tech tips, urgent security alerts, and exclusive deals delivered straight to your inbox. Plus, you’ll get instant access to my Ultimate Scam Survival Guide – free when you join my CYBERGUY.COM/NEWSLETTER.
Copyright 2025 CyberGuy.com. All rights reserved.
Technology
Foldables are in and suddenly really thin

Hi! Welcome to Installer No. 89, your guide to the best and Verge-iest stuff in the world. My name is Jay Peters, and I will be taking care of Installer while David is on parental leave. All of us here at The Verge are very excited for him and his family, and he’ll be back later this year.
It’s a huge honor to be writing this. I look forward to Installer every week to see what awesome things David is obsessed with and what you all are into. (Thanks to everyone who sent over their favorite non-famous apps to get me started. Keep reading for some of those!) I’m really excited to keep the party going. (If you’re new here, welcome, and also you can read all the old editions at the Installer homepage.)
This week, as I am at around this time every year, I’ve been obsessed with the annual Summer Games Done Quick speedrunning marathon. If you’ve never watched, the event is an annual, weeklong, always-on livestream of people playing video games at an extremely high level to raise money for charity. Throughout the week, I’ll tune in when I have a moment and then find myself watching somebody obliterate a beloved classic or a game that I’ve never heard of.
The show, which you can watch for free on Twitch, typically ends very early in the morning on Sunday, and you can watch replays on the Games Done Quick YouTube channel. My two favorite runs so far have been a Beat Saber showcase and a nail-biter Cuphead race. (If you have any suggested runs I should watch, let me know — maybe I’ll feature them in a future Installer!)
Anyway, let’s dive in. This week, I have for you some new Samsung foldable phones, a check-in with the developer of one of the great Reddit apps, and more.
(As always, the best part of Installer is your ideas and tips. What do you want to know more about? What awesome tricks do you know that everyone else should? What app should everyone be using? Tell me everything: installer@theverge.com. And if you know someone else who might enjoy Installer, tell them to subscribe here. It’s free, and you get it a full day early!)
- Samsung Galaxy Z Fold 7: Foldables have never really interested me, but even I am extremely impressed by just how thin the Z Fold 7 looks. But then I look at the price: $1,999, a $100 increase from the Z Fold 6! Too rich for my blood. The Z Flip 7, with its edge-to-edge cover display, also seems like a good upgrade.
- Samsung Galaxy Watch 8: As Victoria Song said, “the squircle has taken over”: Samsung’s new Galaxy Watch 8 and Watch 8 Classic now have circle faces set in rounded square bodies. The change means the watches can sit flatter on your wrist, which sounds like a good thing to me; I’ll always take a thinner watch over a bulkier one.
- Nothing Phone 3: This was technically announced last week, but Installer took the week off for the July 4th holiday in the US, so I’m including it now. Nothing is touting this phone as its “first true flagship” — though perhaps the most noticeable thing about it is its unusual camera layout.
- Nothing Headphone 1: Nothing announced its first pair of over-ear headphones last week, too, and they seem like a decent pair of cans. The translucent design isn’t my cup of tea, but props to Nothing for trying something funky and new.
- Tony Hawk’s Pro Skater 3 + 4: This game puts remakes of two classics into one package, and it’s awesome. I’ve been playing on my Switch 2 — where it runs pretty well! — and have had a blast reliving my youth. Turns out that I’m pretty rusty now, but thankfully, the game has some helpful settings to make things easier for the less skilled among us.
- HBO Max: Max is HBO Max again, like it probably always should have been, even though HBO Max isn’t a great name, either.
- Perplexity’s Comet browser: The AI “answer” engine’s new browser naturally uses Perplexity as its main search engine but also has an AI assistant built in. Browsers could be the next big turf war for AI companies, and Perplexity is beating OpenAI to the punch. There is a catch, though: right now, it’s only available to subscribers of Perplexity’s $200-per-month subscription.
- Anker’s Nano Wireless Car Charger: This new car charger with a long, flexible arm looks like a super useful and malleable way to mount your phone inside your car. I don’t even own a car and I want this.
- Superman: I don’t have any strong feelings about Superman or DC Comics, but it seems like James Gunn’s new
DC cinematic universe Hail Maryfilm is actually pretty good. The Fantastic Four: First Steps looks great, too — 2025 is shaping up to be a big superhero summer.
If you followed the Reddit protests in 2023, then you probably recognize the name Christian Selig. He was the developer of the beloved Apollo for Reddit iOS app, but he became a central figure of the protests because Reddit’s API changes were going to be so cost-prohibitive that they forced him to shut Apollo down.
I’ve gotten to know Selig, and nowadays, he works on an app called Pixel Pals, is an advisor to the new Digg, and recently posted a great PC build video that has more than 2.5 million views. (Yes, he does poke fun at another, let’s say, infamous PC build video.) I got to catch up with him to learn about his homescreen and what he’s into.
Image: Christian Selig
The phone: iPhone 15 Pro Blue Titanium 128 GB
The wallpaper: I’m pretty sure it’s just something random someone posted on Twitter ages ago that I saved. But I love how simple it is, and I love how it looks on the home screen with the default iOS blur applied.
The apps: I try to keep things simple and positioned in an easy-to-reach area. I don’t keep social media apps on my phone in an attempt to be healthier, so it’s mostly things that are useful: vehicle apps (still a bit cold in Canada, so gotta love being able to preheat your vehicle), with Overcast for podcasts, Microsoft To Do (née Wunderlist) for my to-dos, ChatGPT because it’s 2025, YouTube because I spend way too much time there, Pixel Pals because it’s an app I build so I like to have it nice and handy, the Chess.com app for passing some time, and the alpha for Digg, which has been a ton of fun to use.
I also asked Christian to share a few things he’s into right now:
- I’ve gotten into chess lately, and that’s been a ton of fun to play around with and learn as a total noob.
- I’ve been digitizing old VHS and Hi8 tapes from my childhood and that has been such a massive rabbit hole to go down, but so, so cool and satisfying to see the results of.
- I’m super into all things solar and battery technology. I have a very amateur setup at my apartment with our very limited space, but my partner and I bought land recently and are excited to go down the solar route and hopefully gain some energy independence.
And about his role at Digg:
- What an advisor means in this case is basically just being brutally honest with the team on what I think about their mobile app (what is great, what sucks, what could be improved) as well as advising on their developer strategy as they get into that in the future. No bullshit, they’ve been phenomenally receptive and humble in getting feedback.
- As for why I got on board, I’ve just kind of been sad about the modern state of community in social networks. Even outside of the Reddit API stuff, Reddit itself just feels more and more lately like a corporate shell of its former fun, vibrant community-based self. Kevin Rose seemed so jazzed about the possibility of imagining a community for the people of the future, and that really spoke to me as something that I also wanted to see exist in the world.
- As you can imagine, a lot of folks have pitched me on “Reddit but better!” pie-in-the-sky ideas over the years. Kevin was the first one to come to me with concrete plans for a modern, community-based platform that felt like it had actual wood behind the arrow. And having now talked to the folks that make up the team at “New Digg,” I feel that even more so. They’ve got some really bright people.
Here’s what the Installer community is into this week. I want to know what you’re into right now as well! Email installer@theverge.com with your recommendations for anything and everything, and we’ll feature some of our favorites here every week. For even more great recommendations, check out the replies to this post on The Verge, this post on Threads, and this post on Bluesky.
This week’s section is a mix of everyone’s favorite non-famous apps and some more typical recommendations.
“I want to give a shoutout to my favorite mobile game designer who’s based here in Germany: Arnold Rauers and his little studio Tiny Touchtales develop some beautiful, addictive light strategy games. My favorites are Card Thief, Geo Gods, and Miracle Merchant.” — Nick
“I use Panic’s Nova to make websites and truly love it. Probably my favorite app. Mimestream is also fantastic! Can’t wait for the iPhone version.” — Jeanne
“My favorite non-famous app is Live Soccer TV. Shows you the complete worldwide soccer schedule, and the list of broadcast networks/platforms in each county airing the game. Been on my home screen for ages now. It simply does what it says it does. No fluff and for 5 dollars a year, I pay for the ad free upgrade. Perfect app. Hope it never changes.” — Dustin
“Obsidian and Anybox.” — Peter
“I’m constantly shocked whenever recommendations come up for recipe apps that Crouton is not mentioned. To me, if Apple were to have made a recipe app themselves, this would be it. Even better, it’s cheap — only $14.99/yr and has some incredibly cool features like ‘hands free’ mode that allows you to simply blink your eyes to move to the next step of a recipe for those times when you have chicken juice all over your fingers.” — Justin
“All of Claire North’s books are fantastic! Her stuff is super original: sci-fi-ish but more about big ideas like time, memory, and identity. She does a really good job of bringing out the nuances and real-life feelings and consequences of the roles her characters have. It’s smart and emotional without being heavy, and her characters always stick with me. The First Fifteen Lives of Harry August or Touch are great places to start.” — Dave
“I know it’s been out for a while, but my whole family is addicted to Marvel Snap. The new season with The Fantastic Four is really fun so far and this gives my kids things that help them tickle their brain with logic. Also, all the different variants for the cards are really cool to see.” — WALL-E
“Been using Folio as my Pocket replacement and have been quite happy.” — Carter
“All four The Trip movies are streaming on Criterion Channel. Very funny, very mean comedies — and the longer BBC episodic cuts are also available too, if you want the extended play version (which you will).” — Kevin
“Despite my backlog, I’m checking out A Solitaire Mystery, as I have no choice but to play anything from the Baba Is You developer.” — Tristan
“Just made the switch to the Pixel line from iOS, and I’m really digging trying a new OS. Outside of that, I’ve been taking a slight tech break and going back to physically painting, reading paperbacks, and being present.” — EmpireStrikesBacktotheFuture
All week, I have been mourning the recent end of the latest series of Taskmaster, a British comedy show where five comedians must all complete absurd tasks and be graded on them by the show’s mercurial host. This batch of episodes, series 19, was my favorite set yet: the cast of comedians (the first to feature an American, Jason Mantzoukas) were all hilarious, and the tasks were ridiculous.
If you’re looking for something new and funny to watch, I can’t recommend series 19 enough. Best of all, you can watch every series of the show for free on YouTube. Your time starts now.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoVideo: Trump Signs the ‘One Big Beautiful Bill’ Into Law
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoOpinion | The Ugliness of the ‘Big, Beautiful’ Bill, in Charts
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoRussia-Ukraine war: List of key events, day 1,227
-

 News4 days ago
News4 days agoVideo: Trump Compliments President of Liberia on His ‘Beautiful English’
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoCyberpunk Edgerunners 2 will be even sadder and bloodier
-
Business1 week ago
Companies keep slashing jobs. How worried should workers be about AI replacing them?
-

 News1 week ago
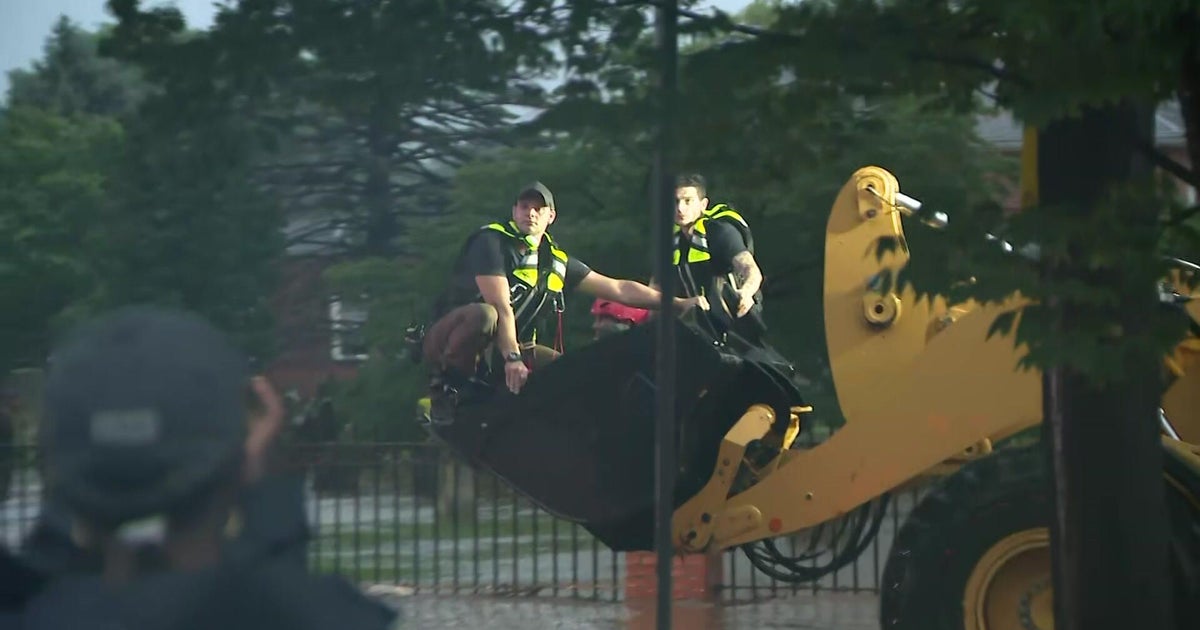
News1 week agoTexas Flooding Map: See How the Floodwaters Rose Along the Guadalupe River
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoDeath toll from Texas floods rises to 24 as search underway for more than 20 girls unaccounted for | CNN















