Science
How many COVID deaths are ‘acceptable’? Decision necessary to move to post-pandemic world
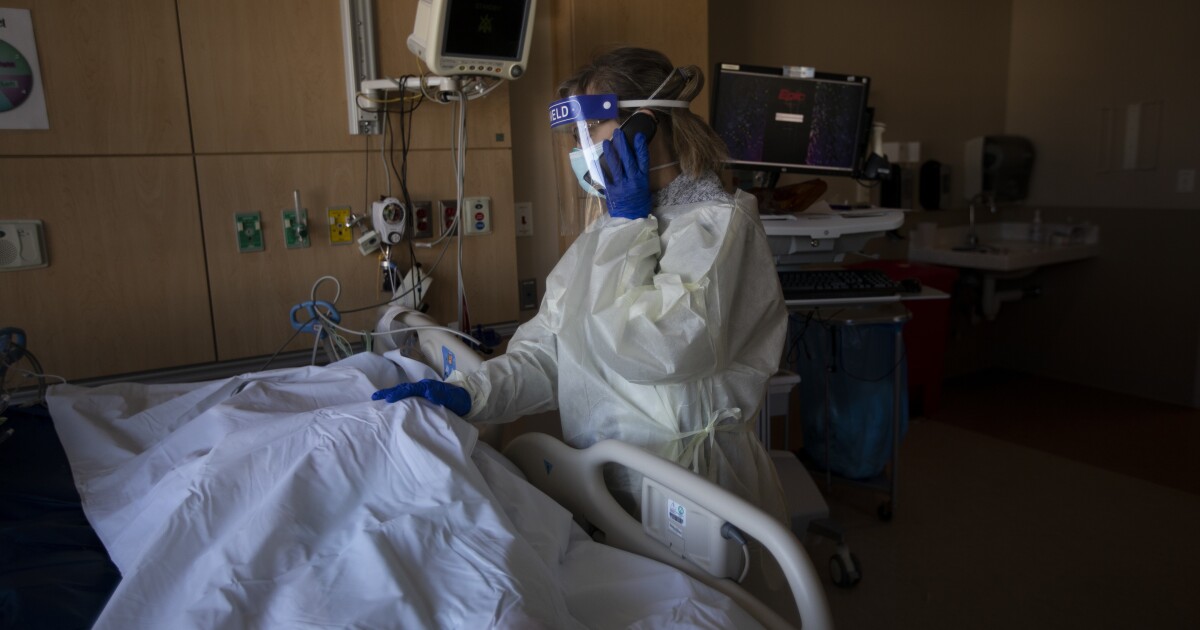
Within the post-pandemic world the USA is struggling to carry forth, how many individuals are we prepared to let die of COVID-19 annually?
Yep, let’s go there.
Ought to your vaccinated grandmother’s demise from COVID-19 be thought of a suitable loss? Ought to seasonal spikes in casualties among the many unvaccinated elicit greater than a shrug? Ought to life go on with out disruption if a brand new coronavirus variant begins killing as many kids as childhood cancers?
You gained’t see politicians calling press conferences to acknowledge that some deaths are inevitable and a few lives aren’t price what it could price to save lots of them.
The Path From Pandemic
That is the second in an occasional collection of tales concerning the transition out of the COVID-19 pandemic and the way life within the U.S. can be modified in its wake.
However acceptable numbers of deaths are the frequent foreign money of public well being professionals. And they’re a central consider each debate over when — and after what expenditure of cash and energy — the time has come to maneuver on.
Declaring an finish to the pandemic is about deciding how a lot sickness, demise and disruption is “accepted and acceptable as part of regular life,” stated Erica Charters, a historian with Oxford College’s “How Epidemics Finish” venture.
Setting an higher sure on the variety of COVID-19 deaths the nation will tolerate annually is the premise for selections about when it will likely be OK to drop pandemic security guidelines, and when it is perhaps essential to reinstate them.
A rising variety of People have concluded the time to maneuver on from the pandemic is now. In mid-March, 64% of adults who took an Axios-Ipsos ballot stated they’re in favor of lifting all federal, state and native COVID-19 restrictions — up from 44% in early February.
That sentiment isn’t essentially reckless. This week’s common each day demise charge is simply over a 3rd of what it was a month in the past, and has declined greater than 75% since Omicron deaths peaked in early February. Basically the entire coronaviruses in circulation listed below are variations of the Omicron variant, which causes milder illness than the strains that preceded it. Plus, not less than 95% of People have some immunity to the virus on account of vaccination, previous an infection or each, in line with estimates from the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention.
Implicit in a call to drop the final remaining security guidelines is a willingness to abide the present mortality charge. Over the past week, COVID-19 has claimed a mean of 626 lives within the U.S. every day. That’s fewer than the roughly 1,900 who die of coronary heart illness and the 1,650 who die of most cancers every day, on common, however properly above the 147 are misplaced to influenza and pneumonia mixed.
Juan Lopez removes the physique of a COVID-19 sufferer from a hospital in McAllen, Texas, in 2020.
(Carolyn Cole/Los Angeles Instances)
For public well being consultants, the calculus is extra specific. Mortality and morbidity — the phrases their occupation makes use of for demise and sickness — are on one facet of the equation, and instruments like seat belts, blood strain treatment, smoking-cessation packages and vaccines are on the opposite.
These instruments fluctuate in price, intrusiveness and political acceptability. Regardless of public well being campaigns and authorized mandates, People proceed to drive drunk and go away seatbelts unfastened. Tobacco kills greater than 480,000 folks a yr in the USA, but 34.2 million adults proceed to smoke. Diabetes claims greater than 100,000 lives a yr, however efforts to discourage the sale and consumption of sugary drinks — a major contributor — have met fierce resistance.
Sooner or later, all efforts to restrict preventable deaths will hit the arduous wall of funding constraints, treatment availability, and folks’s willingness to take steps to guard themselves and others. That’s the place the variety of deaths that’s “acceptable” comes into focus.
“We actually want a nationwide consensus on what the appropriate variety of deaths is” for COVID-19, stated Michael Osterholm, who directs the College of Minnesota’s Middle for Infectious Illness Analysis and Coverage.
It doesn’t matter what steps the nation takes, there’s no manner for that quantity to be zero.
In contrast to vaccines for illnesses like measles, polio and diphtheria, those out there now for COVID-19 don’t produce lifelong immunity. Nor does a previous an infection, even a extremely dangerous one. And contemplating that the coronavirus has established itself in animals like ferrets and white-tailed deer, the specter of resurgence will at all times be with us, Osterholm and two colleagues defined in a latest version of the Journal of the American Medical Assn.
The CDC and different federal businesses are nonetheless deciding on the standards they’ll use to find out when the pandemic has ended. There’s nonetheless time — Dr. Rochelle Walensky, the company’s director, stated as lately as final week that we’re not there but.
To date, the CDC’s recommendation on loosening COVID-19 restrictions has centered on native, not nationwide circumstances. The important thing indicator is the capability of a county’s hospitals to deal with a brand new inflow of sufferers.
Hospital employees put together to maneuver the physique of a COVID-19 sufferer to a morgue at Windfall Holy Cross Medical Middle in Mission Hills.
(Jae C. Hong/Related Press)
A gaggle of 23 outstanding public well being consultants from throughout the nation has made extra progress. Of their “Roadmap for Residing with COVID,” specialists in immunology, virology, healthcare economics and public well being element a litany of circumstances that can should be met to usher the USA safely right into a post-pandemic period.
In that “subsequent regular,” the roadmap explains, the coronavirus stays very a lot with us — an endemic virus that continues to flow into, sicken and kill, however at ranges properly beneath these of the final two years.
The consultants suggest that the nation deal with COVID-19 as one amongst a cluster of respiratory viruses — together with influenza, respiratory syncytial virus and different pathogens — that wreak a predictable stage of havoc yr in and yr out. Hospitals are ready to take care of these annual onslaughts of sickness, and People have accepted the quantity of illness and demise they trigger as regular.
One indication of our complacency: Even in a foul influenza season, near half of American adults gained’t take the difficulty to get a flu shot.
More often than not, hospitals can handle the inflow of sufferers with respiratory illnesses with out compromising the care of individuals with most cancers, coronary heart illness or different life-threatening circumstances. Nor do they defer or cancel the routine care that retains the sufferers with big selection of sicknesses from getting sicker.
With that in thoughts, the roadmap authors got here proper out with a steered variety of acceptable yearly deaths from COVID-19 and different respiratory sicknesses mixed: 60,225.
That determine works out to 1 demise per 2 million People, or 165 per day nationwide. Add all of them up and you’ve got the tough equal of an especially extreme season of influenza.
Relations load the casket their liked one, Charles Jackson Jr., right into a hearse on the Angelus Funeral House in Los Angeles. Jackson died of COVID-19.
(Jason Armond/Los Angeles Instances)
“There was no magic to it in any respect,” stated Osterholm, who contributed to the roadmap. “Our aim was to say that at these numbers and beneath, you’re a lot much less more likely to be stressing the healthcare system.”
That’s necessary as a result of “deaths enhance when hospitals can not present optimum care,” the roadmap authors wrote. An awesome inflow of sufferers with respiratory sicknesses can lead to fatalities from every kind of illnesses.
It additionally issues who dies, stated Jeffrey Kahn, director of the Berman Institute of Bioethics at Johns Hopkins College. When deaths are concentrated amongst a stigmatized minority, as they had been when the HIV/AIDS epidemic struck, the world was slower to reply. However, when kids are the principal victims, as with polio within the Nineteen Fifties, the nation was united in its dedication to cease unfold.
“It very a lot issues which slice of the inhabitants is most affected by this or different infectious illnesses,” Kahn stated.
Equally, when opioid overdose deaths started to precise a heavy toll on white folks within the Nineteen Nineties, the general public well being response got here extra shortly than with other forms of drug deaths that fell closely on Black People. However which may be altering, Kahn stated. The pandemic’s disproportionate toll on communities of coloration has drawn consideration to longstanding racial and ethnic disparities in well being and prompted concerted campaigns to deal with them.
Along with counting deaths, an excellent “dashboard” of the nation’s post-pandemic well-being would account for the way a lot of the inhabitants has immunity to circulating respiratory illnesses, and the way a lot virus is detected in wastewater. If these indicators get too excessive, they’d set off “circuit breakers” equivalent to a renewed masks mandate and limits on social gatherings, the authors wrote.
These circuit breakers replicate a fundamental precept of moral decision-making in democracies, stated Kahn, who was not concerned within the Roadmap. As soon as folks have the data and instruments they should shield themselves from hurt, they need to be free to go about their enterprise with out the interference of public well being strictures.
Nonetheless, it’s affordable to position limits on these freedoms when their train injures too many individuals, together with vaccinated grandmothers and not less than a smattering of kids.
“That’s the push-pull of public well being,” Kahn stated.

Science
U.S. Efforts to Cut Emissions Stalled in 2024 as Power Demand Surged

America’s efforts to cut its climate change pollution stalled in 2024, with greenhouse gas emissions dropping just a fraction, 0.2 percent, compared to the year before, according to estimates published Thursday by the Rhodium Group, a research firm.
Despite continued rapid growth in solar and wind power, emissions levels stayed relatively flat last year because demand for electricity surged nationwide, which led to a spike in the amount of natural gas burned by power plants.
The fact that emissions didn’t decline much means the United States is even further off-track from hitting President Biden’s goal of slashing greenhouse gases 50 percent below 2005 levels by 2030. Scientists say all major economies would have to cut their emissions deeply this decade to keep global warming at relatively low levels.
Since 2005, United States emissions have fallen roughly 20 percent, a significant drop at a time when the economy has also expanded. But to meet its climate goals, U.S. emissions would need to decline nearly 10 times as fast each year as they’ve fallen over the past decade. That seems increasingly unlikely, experts say, especially since President-elect Donald J. Trump has promised to dismantle Mr. Biden’s climate policies and promote the production of fossil fuels, the burning of which generates greenhouse gases.
“On the one hand, it is notable that we’ve now seen two years in a row where the U.S. economy grew but emissions went down,” said Ben King, an associate director at the Rhodium Group. “But it’s far from enough to achieve our climate targets.”
The biggest reason that U.S. emissions have fallen in recent years is that electric utilities have been retiring their older, dirtier coal-fired power plants and replacing them with cheaper and less-polluting natural gas, wind and solar power. That trend mostly continued last year, with a few unexpected ups and downs.
The nation’s demand for electricity, which has stayed more or less flat for two decades, suddenly jumped by roughly 3 percent in 2024, in large part because scorching heat during the summer caused many Americans to crank up their air-conditioners. A smaller factor was that tech companies have been building more energy-hungry data centers in states like Virginia and Texas.
While power companies installed large numbers of wind turbines, solar panels and batteries last year to meet rising demand, natural gas use also rose to record highs, while coal use declined only slightly. The net result was that emissions from the power sector increased an estimated 0.2 percent, according to the Rhodium Group.
At the same time, transportation, the nation’s largest source of greenhouse gases, saw an 0.8 percent rise in emissions last year. Gasoline and jet fuel consumption both increased as Americans continued to drive and fly more after the pandemic. Nearly 10 percent of new car sales in 2024 were less-polluting electric vehicles, but those models still make up a small fraction of total cars on the road and have yet to put a major dent in transportation emissions.
On the flip side, emissions from America’s industrial sector — which includes steel, cement and chemicals — fell by 1.8 percent in 2024. Some of that may have been the result of lost output, as two hurricanes and a strike at the nation’s ports disrupted some factory activity in the fall, Mr. King said.
“It’s a reminder that there’s always some bumpiness in emissions,” Mr. King said. “It’s not just a question of how many electric vehicles are on the road or how much solar we’ve installed. A big portion of our economy still relies on fossil fuels.”
One of the most striking findings in this year’s data was that emissions from oil and gas operations dropped roughly 3.7 percent in 2024. Even though the United States produced record amounts of oil and near-record amounts of natural gas last year, many companies appear to have curbed leaks of methane, which is the main ingredient in natural gas and which can seep into the atmosphere and contribute significantly to global warming.
Over the past few years, the Biden administration and several states have adopted new regulations that require oil and gas producers to detect and fix methane leaks. Many companies also have financial incentives to capture methane to sell rather than vent it into the air.
Between 2014 and 2024, U.S. companies appear to have reduced the amount of methane that escaped, per each cubic feet of gas they produced, by 40 percent, according to the Rhodium Group.
Several experts have estimated that greenhouse gases generated in the United States could start dropping sharply in the years ahead if many clean energy policies stay in place, particularly the 2022 Inflation Reduction Act that pumped hundreds of billions of dollars into low-carbon energy technologies such as electric vehicles, wind turbines, solar panels, nuclear reactors, green hydrogen and batteries.
While Mr. Trump has pledged to scrap many of Mr. Biden’s subsidies and tax credits for electric vehicles and low-carbon energy, it remains to be seen whether Congress will agree.
That law has not yet had a major impact on the country’s emissions, said Mr. King, since it takes time for new factories to open and power plants to get built. But, he said, data shows that low-carbon energy and transportation now make up fully 5 percent of total U.S. private investment.
“That’s a leading indicator that things are changing quickly,” he said.
Science
How to protect yourself from the smoke caused by L.A. wildfires

You don’t have to live close to a wildfire to be affected by its smoke. With severe winds fanning the fires in and around Pacific Palisades, the Pasadena foothills and Simi Valley, huge swaths of the Southland are contending with dangerous air quality.
Wildfire smoke can irritate your eyes, nose, throat and lungs. The soot may contain all kinds of dangerous pollutants, including some that may cause cancer. The tiniest particles in smoke can travel deep into your lungs or even enter your bloodstream.
Conditions like these aren’t good for anyone, but they’re particularly bad for people in vulnerable groups, including children, those with asthma or other respiratory conditions, people with heart disease and those who are pregnant.
Here’s what you should know to keep yourself safe.
Stay indoors
Minimize your exposure to unhealthy air by staying inside and keeping your doors and windows shut.
If you have a central heating and air conditioning system, you can keep your indoor air clean by turning it on and keeping it running. Make sure the fresh-air intake is closed so that you’re not drawing in outdoor air.
Keep your pets inside
They shouldn’t breathe the unhealthy air either.
Check your air filters
Clean filters work better than dirty ones, and high-efficiency filters work better than regular ones. The California Air Resources Board and the South Coast Air Quality Management District recommend filters with a MERV rating of 13 or higher.
You might consider using portable high-efficiency air cleaner in a room where you spend the most time. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency has information about them here, and CARB has a list of certified cleaning devices here.
Don’t pollute your indoor air
That means no burning candles or incense. If your power is out and you need to see in the dark, you’re much better off with a flashlight or headlamp.
If you’re cold, bundle up. This is not the time to start a cozy fire in the fireplace. Don’t use a gas stove or wood-fired appliances, since these will make your indoor air quality worse, not better, the AQMD says.
The CDC also advises against vacuuming, since it can stir up dust and release fine particles into the air.
Take care when cleaning up
You don’t want your skin to come into contact with wildfire ash. That means you should wear long sleeves, pants, gloves, socks and shoes. The AQMD even wants you to wear goggles.
If you’re sweeping up ash outdoors, get a hose and mist it with water first. That will keep it from flying up in the air as you move it around. Once the ash is wet, sweep it up gently with a broom or mop. Bag it up in a plastic bag and throw it away.
It’s a good idea to wash your vehicles and outdoor toys if they’re covered in ash. Try not to send ashy water into storm drains. Direct the dirty water into ground areas instead, the AQMD advises.
Those with lung or heart problems should avoid clean-up activities.
Discard spoiled food…
If you lost power for a significant length of time, the food in your refrigerator or freezer may be spoiled.
Food kept in a fridge should stay safe for up to four hours if you’ve kept the door closed. If you’ve been without power for longer than that, you’ll need to toss all perishable items, including meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk and cut fruits and vegetables. Anything with “an unusual smell, color, or texture” should be thrown out as well, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease and Control Prevention.
Refrigerated medicines should be OK unless the power was out for more than a day. Check the label to make sure.
…even if it was in the freezer
Your freezer may be in better shape, especially if it’s well-stocked. Items in a full freezer may be safe for up to 48 hours if it’s been kept shut, and a half-full freezer may be OK for up to 24 hours. (The frozen items help keep each other cold, so the more the better.)
If items have remained below 40 degrees Fahrenheit (4 degrees Celsius) or you can still see ice crystals in them, they may be OK to use or refreeze, according to the federal government’s food safety website.
Ice cream and frozen yogurt should be thrown out if the power goes out for any amount of time. Meat, poultry, seafood, eggs, milk and most other dairy products need to go if they were exposed to temperatures above 40 degrees F for two hours or longer. The same goes for frozen meals, casseroles, soups, stews and cakes, pies and pastries with custard or cheese fillings.
Fruit and fruit juices that have started to thaw can be refrozen unless they’ve started to get moldy, slimy or smell like yeast. Vegetables and vegetable juices should be discarded if they’ve been above 40 degrees F for six hours or more, even if they look and smell fine.
Breakfast items like waffles and bagels can be refrozen, as can breads, rolls, muffins and other baked goods without custard fillings.
Consider alternative shelter
If you’ve done everything you can but your eyes are still watering, you can’t stop coughing, or you just don’t feel well, seek alternative shelter where the air quality is better.
Hold off on vigorous exercise
Doing anything that would cause you to breathe in more deeply is a bad idea right now.
Mask up outdoors
If you need to be outside for an extended time, be sure to wear a high-quality mask. A surgical mask or cloth mask won’t cut it — health authorities agree that you should reach for an N95 or P-100 respirator with a tight seal.
Are young children at greater risk of wildfire smoke?
Very young children are especially vulnerable to the effects of wildfire smoke because their lungs are still rapidly developing. And because they breathe much faster than adults, they are taking in more toxic particulate matter relative to their tiny bodies, which can trigger inflammation, coughing and wheezing.
Any kind of air pollution can be dangerous to young children, but wildfire smoke is about 10 times as toxic for children compared to air pollution from burning fossil fuels, said Dr. Lisa Patel, clinical associate professor of pediatrics at Stanford Children’s Health. Young children with preexisting respiratory problems like asthma are at even greater risk.
Patel advises parents to keep their young children indoors as much as possible, create a safe room in their home with an air purifier, and try to avoid using gas stoves to avoid polluting the indoor air.
Children over the age of 2 should also wear a well-fitting KN95 mask if they will be outdoors for a long period of time. Infants and toddlers younger than that don’t need to mask up because it can be a suffocation risk, Patel said.
What are the risks for pregnant people?
Pregnant people should also take extra precautions around wildfire smoke, which can cross the placenta and affect a developing fetus. Studies have found that exposure to wildfire smoke during pregnancy can increase the risk of premature birth and low birth weight. Researchers have also linked the toxic chemicals in smoke with maternal health complications including hypertension and preeclampsia.
What about other high-risk populations?
Certain chronic diseases including asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or other respiratory conditions can also make you particularly vulnerable to wildfire smoke. People with heart disease, diabetes and chronic kidney disease should take extra care to breathe clean air, the CDC says. The tiny particles in wildfire smoke can aggravate existing health problems, and may make heart attacks or strokes more likely, CARB warns.
Get ready for the next emergency
Living in Southern California means another wildfire is coming sooner or later. To prepare for the bad air, you can:
- Stock up on disposable respirators, like N95 or P-100s.
- Have clean filters ready for your A/C system and change them out when things get smoky.
- Know how to check the air quality where you live and work. The AQMD has an interactive map that’s updated hourly. Just type in an address and it will zoom in on the location. You can also sign up to get air quality alerts by email or on your smartphone.
- Know where your fire extinguisher is and keep it handy.
- If you have a heart or lung condition, keep at least five days’ worth of medication on hand.
Times staff writer Karen Garcia contributed to this report.
Science
Punk and Emo Fossils Are a Hot Topic in Paleontology

Mark Sutton, an Imperial College London paleontologist, is not a punk.
“I’m more of a folk and country person,” he said.
But when Dr. Sutton pieced together 3-D renderings of a tiny fossil mollusk, he was struck by the spikes that covered its wormlike body. “This is like a classic punk hairstyle, the way it’s sticking up,” he thought. He called the fossil “Punk.” Then he found a similar fossil with downward-tipped spines reminiscent of long, side-swept “emo” bangs. He nicknamed that specimen after the emotional alt-rock genre.
On Wednesday, Dr. Sutton and his colleagues published a paper in the journal Nature formally naming the creatures as the species Punk ferox and Emo vorticaudum. True to their names, these worm-mollusks are behind something of an upset (if not quite “anarchy in the U.K.”) over scientists’ understanding of the origins of one of the biggest groups of animals on Earth.
In terms of sheer number of species, mollusks are second only to arthropods (the group that contains insects, spiders and crustaceans). The better-known half of the mollusk family tree, conchiferans, contains animals like snails, clams and octopuses. “The other half is this weird and wacky group of spiny things,” Dr. Sutton said. Some animals in this branch, the aculiferans, resemble armored marine slugs, while others are “obscure, weird molluscan worms,” he said.
Punk and Emo, the forerunners of today’s worm-mollusks, lived on the dark seafloor amid gardens of sponges, nearly 200 million years before the first dinosaurs emerged on land. Today, their ancient seafloor is a fossil site at the border between England and Wales.
The site is littered with rounded rocky nodules that “look a bit like potatoes,” Dr. Sutton said. “And then you crack them open, and some of them have got these fossils inside. But the thing is, they don’t really look like much at first.”
While the nodules can preserve an entire animal’s body in 3-D, the cross-section that becomes visible when a nodule is cracked open can be difficult to interpret “because you’re not seeing the full anatomy,” Dr. Sutton said.
Paleontologists can use CT scans to see parts of fossils still hidden in rock, essentially taking thousands of X-rays of the fossil and then stitching those X-ray slices together into one digital 3-D image. But in these nodules, the fossilized creatures and the rock surrounding them are too similar in density to be easily differentiated by X-rays. Instead, Dr. Sutton essentially recreated this process of slicing and imaging by hand.
“We grind away a slice at a time, take a photo, repeat at 20-micron intervals or so, and basically destroy but digitize the fossil as we go,” Dr. Sutton said. At the end of the process, the original fossil nodule is “a sad-looking pile of dust,” but the thousands of images, when painstakingly digitally combined, provide a remarkable picture of the fossil animal.
Punk and Emo’s Hot Topic-worthy spikes set them apart from other fossils from the aculiferan branch of the mollusk family. “We don’t know much about aculiferans, and it’s unusual to find out we’ve suddenly got two,” Dr. Sutton said.
Stewart Edie, the curator of fossil bivalves at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History, said that Punk and Emo’s bizarre appearances shook up a long-held understanding of how mollusks evolved. Traditionally, scientists thought that the group of mollusks containing snails, clams and cephalopods “saw all of the evolutionary action,” said Dr. Edie, who was not involved with the new discovery. “And the other major group, the aculiferans, were considerably less adventurous.” But Punk and Emo “buck that trend,” he said.
The new alt-rock aculiferans reveal the hidden diversity of their group in the distant past and raise questions about why their descendants make up such a small part of the mollusk class today. “This is really giving us an almost unprecedented window into the sorts of things that were actually around when mollusks were getting going,” Dr. Sutton said. “It’s just this little weird, unexpected, really clear view of what was going on in the early history of one of the most important groups of animals.”
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoThese are the top 7 issues facing the struggling restaurant industry in 2025
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoThe 25 worst losses in college football history, including Baylor’s 2024 entry at Colorado
-

 Sports1 week ago
Sports1 week agoThe top out-of-contract players available as free transfers: Kimmich, De Bruyne, Van Dijk…
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoNew Orleans attacker had 'remote detonator' for explosives in French Quarter, Biden says
-

 Politics7 days ago
Politics7 days agoCarter's judicial picks reshaped the federal bench across the country
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoWho Are the Recipients of the Presidential Medal of Freedom?
-

 Health4 days ago
Health4 days agoOzempic ‘microdosing’ is the new weight-loss trend: Should you try it?
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoIvory Coast says French troops to leave country after decades














