Science
AI and memory deletion: Inside the medical quest to cure grief

When Cody Delistraty lost his mother in 2014, he was surprised by the various ways that he, his brother and his father dealt with their grief. The journalist and speechwriter had expected his family’s experiences to be aligned, that there would be a, “homogeneity to grieving.” The differences led Delistraty to wonder whether loss was more complicated than advertised.
In America, grief is often framed as a journey from Point A to Point B, a linear path efficiently chugging through stages like denial and anger, ultimately heading toward acceptance. But anyone who has experienced a loss firsthand understands that it isn’t so simple. Grief can be isolating, confusing and unyielding.

Shelf Help is a new wellness column where we interview researchers, thinkers and writers about their latest books — all with the aim of learning how to live a more complete life.
In 2022, a new addition to the DSM-5 (“Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders”) caught Delistraty’s eye: prolonged grief disorder. It’s a rare condition in which grief becomes so severe that it interferes with daily life. The classification opens the door to medical solutions: pharmaceuticals are in early testing stages, and a slew of new digital, psychedelic and other treatments are emerging.
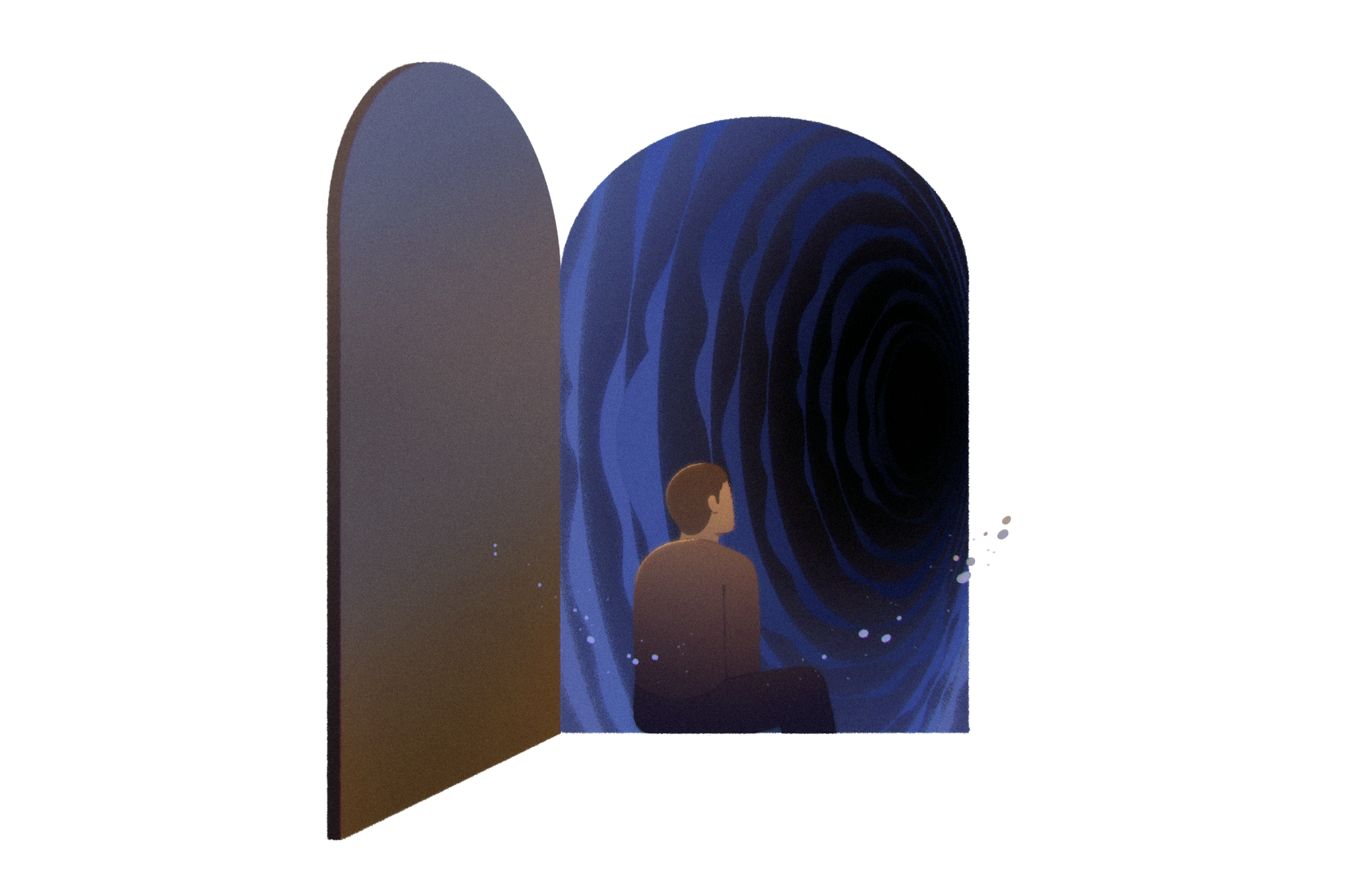
Delistraty’s new book, “The Grief Cure: Looking for the End of Loss,” (Harper) follows his inquisitive sampling of available and future therapies, all while wondering whether grief is a problem that needs to be solved.
Your understanding of grief initially centered on a concept known as the five stages: denial, anger, bargaining, depression and acceptance. How did that shift?

Cody Delistraty (Grace Ann Leadbeater)
When Elisabeth Kübler-Ross came up with the five stages, she was talking to patients who were coming to terms with their own deaths, not with their own grief, which is similar but also very different. There was a study that tracked grievers from various demographics and found that most people actually experience a progression, but my issue with the typical interpretation of the five stages is that it’s presented as the right way to grieve, that there’s a method you can master and that the end game is acceptance.
America has a culture of individuality and mastery — we want to achieve, we want to overcome, we want to bootstrap our way to success. But in grief, we only set ourselves back trying to do this. After a loss is the time to pause and reflect, and even if you do go through these stages to some degree, trying to rush through them or extract value in order to get to acceptance and move on is a fundamentally wrong way of looking at it.
“America has a culture of individuality and mastery — we want to achieve, we want to overcome, we want to bootstrap our way to success. But in grief, we only set ourselves back trying to do this.”
— Cody Delistraty, author of “The Grief Cure.”
Your book confronts the isolation of grieving and how it’s so often considered unseemly or inappropriate when done publicly. Grief is culturally framed as an individual journey, and yet it’s a universal fact of life. What do you think accounts for this disconnect?
This paradigm shift from public to private grieving is a relatively recent phenomenon. Americans, especially, are weary of talking or asking about loss. This is a symptom of “happiness culture,” where grief is considered a burden and you don’t want to seem unhappy or bring others down. The disintegration of local communities exacerbates this. And then this false idea that closure marks a victory over grief. Keeping grief private implies that you did your job. There’s morally valuable willpower. You did it. You got over it.
I think self-care has been the problematic marketing breakthrough of the 21st century, in which the more challenging aspects of being a human, like disappointment, sadness and grief, get pushed out of the frame. They’re not within our consumption narrative, and they’re not within the way we want to present to others.
What surprised me while researching is that it seems like people are actually bubbling with the desire to talk about these things. When I was researching for the book, I got sick of holing up in hotels, so I went to a bar and ended up talking with someone who told me about her recent divorce, which she called the greatest loss of her life. She hadn’t really talked to anybody about it, and it was so nice to connect over loss. When people are open, it can snowball into greater openness.
Our society can place varying value on different types of loss, resulting in some to fall through the cracks, like that woman with her divorce. But grief exists on a spectrum. In the book, you discuss ambiguous loss. Can you tell me more?

(Courtesy of Harper Collins)
The term ambiguous loss was coined by Pauline Boss at the University of Minnesota, who worked with the families of soldiers who went missing in Vietnam. Boss defined it as “a relational disorder caused by the lack of facts surrounding the loss of a loved one,” but today, it encompasses a wide variety of loss.
Climate grief is a big and very modern one. There was a European study that found a third of respondents are extremely worried about climate change. That’s a huge instance of ambiguous grief because there’s disappearance of species and landscapes, there’s an increase in climate refugees, but you can’t really point to a body in a casket and say this is what I’m grieving.
Relationships are another big example. In the book, I went to breakup boot camp to explore losing a loved one outside of death. Friend breakups can be devastating. I really push against the idea of hierarchies and grief. There isn’t a fundamental ranking within grief, and it is subjective to the relationship you had to that person or thing.
Your experiences brought you to the cutting edge of grief research. What do you make of the future of grief treatments?
When I was writing the AI [artificial intelligence] chapter of re-creating technologically deceased loved ones, it was super cutting-edge and wild. Then, of course, it all hit the news cycle pretty intensely with Chat-GPT. Optogenetics for memory deletion could be something we’re faced with in another decade or two. There will be medical technologies where we can take a lot of the pain and burden out of loss. My book questions whether that’s really for the best. We should be thinking about this now before the time comes.
TAKEAWAYS
from “The Grief Cure”
Psilocybin is a huge scientific breakthrough for grief. I talked to one of the most renowned psilocybin researchers, Robin Carhart-Harris, who told me about this guy, Kirk Rutter, whose mother had died, he’d been in this terrible car accident and then he went through a romantic breakup all in the span of about a year. Carhart-Harris’ team gave him just two pills of synthesized psilocybin, donned him with an eye mask and calm music, and he had this incredible perspective shift. He cycled through memories of his mom and realized he didn’t have to maintain the most painful parts, but he could still hold onto her and respect her memory. That treatment made him look at grief differently.
What is your best advice for somebody really stuck in their grief?
There’s no right way of doing it, but don’t rush it. As awful as this time is, there’s so much to be gleaned from really looking inward, reflecting on yourself and your feelings, and thinking about the person you’ve lost. I rushed after my mom died, trying to push past the pain, and here I am, a decade later, writing a book about it. These things really do take time.
I also recommend telling your people what you need from them. The vast majority of people want to talk about these things, they want to be helpful, but especially in the U.S., we are very bad at knowing what that looks like. To the degree that you can, communicate your needs. I think you’d be surprised by the degree to which people will be there for you.
Should someone in grief be aiming for closure?
I think closure is a mythical idea. Nancy Berns, a professor at Drake University, has done a lot of great work on closure and how it’s a social construct. We too often skip over the grappling-with and reflecting-on of grief in order to get to this mythical place of closure when really the truest value is being able to hold that loss in one part of your life while holding a future-looking part in another.
We see this push for closure reified across American culture. One of the biggest shocks for me was bereavement leave, where the median is only five days according to a 2024 study, and this only applies to a close family death. There’s no U.S. federal law requiring leave. This bolsters the idea that closure is part and parcel of productivity, of getting back to normal, of getting back to work.
Our rituals around grief are one-off. We go to a funeral, and that’s it. You get support for an hour, and then it’s over. We’d do well to really reflect on more personal, creative rituals that have more intimate meaning and can be continued over a longer period. This shift would help people with the understanding of time lines around grief. It all takes so much longer than we think. You miss so much when you rush through to tick the box of closure, and frankly, when you do so, you’re really not grieving at all.
(Maggie Chiang / For The Times)
Endicott is a writer and multi-disciplinary artist based in Denver. Her work has appeared in a number of publications including the New York Times, Scientific American, the Guardian, Elle, Electric Lit and Bomb Magazine. You can find her on Instagram @weirdbirds.
Shelf Help is a new wellness column where we interview researchers, thinkers and writers about their latest books — all with the aim of learning how to live a more complete life. Want to pitch us? Email alyssa.bereznak@latimes.com.

Science
What a Speech Reveals About Trump’s Plans for Nuclear Weapons

Within hours of the expiration last week of the final arms control treaty between Moscow and Washington, the State Department sent its top arms diplomat, Thomas G. DiNanno, to Geneva to lay out Washington’s vision for the future. His public address envisioned a future filled with waves of nuclear arms buildups and test detonations.
The views of President Trump’s administration articulated in Mr. DiNanno’s speech represent a stark break with decades of federal policy. In particular, deep in the speech, he describes a U.S. rationale for going its own way on the global ban on nuclear test detonations, which had been meant to curb arms races that in the Cold War had raised the risk of miscalculation, and war.
This annotation of the text of his remarks aims to offer background information on some of the specialized language of nuclear policymaking that Mr. DiNanno used to make his points, while highlighting places where outside experts may disagree with his and the administration’s claims.
What remains unknown is the extent to which Mr. DiNanno’s presentation represents a fixed policy of unrestrained U.S. arms buildups, or more of an open threat meant to spur negotiations toward new global accords on ways to better manage the nuclear age.
Read the original speech.
New York Times Analysis
Next »
1
Established in 1979 as Cold War arsenals grew worldwide, the Conference on Disarmament is a United Nations arms reduction forum made up of 65 member states. It has helped the world negotiate and adopt major arms agreements.
2
In his State Department role, working under Secretary of State Marco Rubio, Mr. DiNanno is Washington’s top diplomat for the negotiation and verification of international arms accords. Past holders of that office include John Bolton during the first term of the George W. Bush administration and Rose Gottemoeller during Barack Obama’s two terms.
3
This appears to be referring to China, which has 600 nuclear weapons today. By 2030, U.S. intelligence estimates say it will have more than 1,000.
4
Here he means Russia, which is conducting tests to put a nuclear weapon into space as well as to develop an underwater drone meant to cross oceans.
New York Times Analysis
« Previous Next »
5
In this year’s federal budget, the Trump administration is to spend roughly $90 billion on nuclear arms, including basic upgrades of the nation’s arsenal and the replacement of aging missiles, bombers and submarines that can deliver warheads halfway around the globe.
6
A chief concern of many American policymakers is that Washington will soon face not just a single peer adversary, as in the Cold War, but two superpower rivals, China and Russia.
New York Times Analysis
« Previous Next »
7
The 1987 Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty or I.N.F. banned all weapons capable of traveling between 500 and 5,500 kilometers, or 310 and 3,420 miles, whether armed with nuclear or conventional warheads. The Trump administration is now deploying a number of conventionally armed weapons in that range, including a cruise missile and a hypersonic weapon.
8
The destructive force of the relatively small Russian arms can be just fractions of the Hiroshima bomb’s power, perhaps making their use more likely. The lesser warheads are known as tactical or nonstrategic nuclear arms, and President Vladimir V. Putin of Russia has repeatedly threatened to use them in Ukraine.
9
Negotiators of arms control treaties have mostly focused on long-range weapons because the delivery vehicles and their deadly warheads are considered planet shakers that could end civilization.
New York Times Analysis
« Previous Next »
10
This underwater Russian craft is meant to cross an ocean, detonate a thermonuclear warhead and raise a radioactive tsunami powerful enough to shatter a coastal city.
11
The nuclear power source of this Russian weapon can in theory keep the cruise missile airborne far longer than other nuclear-armed missiles.
12
Russia has conducted test launches for placing a nuclear weapon into orbit, which the Biden administration quietly warned Congress about two years ago.
13
The term refers to the five permanent members of the United Nations Security Council—China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States.
New York Times Analysis
« Previous Next »
14
A top concern of American officials is that Beijing and Moscow might form an alliance to coordinate their nuclear forces. Their joint program to develop fuel for atom bombs is seen as an indication of this emerging threat.
15
This Trump administration plan is dated November but was made public in December.
16
Released last year, this Chinese government document sought to portray Beijing as a leader in reducing the global threat of nuclear weapons.
17
Typically, arms control treaties have not required countries to destroy warheads so their keepers put them into storage for possible reuse. The United States retains something on the order of 20,000 small atom bombs meant to ignite the larger blasts of hydrogen bombs.
18
An imminent surge centers on the nation’s Ohio-class submarines. The Trump administration has called for the reopening of submarine missile tubes that were closed to comply with the New START limits. That will add as many 56 long-range missiles to the fleet. Because each missile can hold multiple arms, the additional force adds up to hundreds more warheads.
19
This refers to weapons meant for use on a battlefield or within a particular geographic region rather than for aiming at distant targets. It is often seen as synonymous with intermediate-range weapons.
20
Here, the talk turns to the explosive testing of nuclear weapons for safety, reliability and devising new types of arms. The United States last conducted such a test in 1992 and afterwards adopted a policy of using such nonexplosive means like supercomputer simulations to evaluate its arsenal. In 1996, the world’s nuclear powers signed a global ban on explosive testing. A number of nations, including the United States and China, never ratified the treaty, and it never officially went into force.
21
In new detail, the talk addresses what Mr. Trump meant last fall when he declared that he had instructed the Pentagon “to start testing our Nuclear Weapons on an equal basis” in response to the technical advances of unnamed foreign states.
22
Outside experts say the central issue is not whether China and Russia are cheating on the global test ban treaty but whether they are adhering to the U.S. definition. From the treaty’s start in 1996, Washington interpreted “zero” explosive force as the compliance standard but the treaty itself gives no definition for what constitutes a nuclear explosion. Over decades, that ambiguity led to technical disputes that helped block the treaty’s ratification.
23
By definition, all nuclear explosions are supercritical, which means they split atoms in chain reactions that become self-sustaining in sufficient amounts of nuclear fuel. The reports Mr. DiNanno refers to told of intelligence data suggesting that Russia was conducting a lesser class of supercritical tests that were too small to be detected easily. Russian scientists have openly discussed such small experiments, which are seen as useful for assessing weapon safety but not for developing new types of weapons.
24
This sounds alarming but experts note that the text provides no evidence and goes on to speak of preparations, not detonations, except in one specific case.
New York Times Analysis
« Previous
25
The talk gave no clear indication of how the claims about Russian and Chinese nuclear testing might influence U.S. arms policy. But it repeated Mr. Trump’s call for testing “on an equal basis,” suggesting the United States might be headed in that direction, too.
26
The talk, however, ended on an upbeat but ambiguous note, giving no indication of what Mr. DiNanno meant by “responsible.” Even so, the remark came in the context of bilateral and multilateral actions to reduce the number of nuclear arms in the world, suggesting that perhaps the administration’s aim is to build up political leverage and spur new negotiations with Russia, China or both on testing restraints.
Science
Notoriously hazardous South L.A. oil wells finally plugged after decades of community pressure

California Gov. Gavin Newsom announced this week that state oil and gas regulators have permanently closed one of the most infamous drill sites in Los Angeles, bringing an end to a decades-long community campaign to prevent dangerous gas leaks and spills from rundown extraction equipment.
A state contractor plugged all 21 oil wells at the AllenCo Energy drill site in University Park, preventing the release of noxious gases and chemical vapors into the densely populated South Los Angeles neighborhood. The two-acre site, owned by the Archdiocese of Los Angeles, is located across the street from several multifamily apartment buildings and less than 1,000 feet from St. Vincent School.
For years, residents and students had repeatedly complained about acrid odors from the site, with many suffering chronic headaches and nosebleeds. The health concerns prompted a community-driven campaign to shut down the site, with some residents even pleading (unsuccessfully) with the late Pope Francis to intervene.
AllenCo, the site’s operator since 2009, repeatedly flouted environmental regulations and defied state orders to permanently seal its wells.
This month, the California Department of Conservation’s Geologic Energy Management Division (CalGEM) finished capping the remaining unplugged wells with help from Biden-era federal funding.
“This is a monumental achievement for the community who have endured an array of health issues and corporate stalling tactics for far too long,” Newsom said in a statement Wednesday. “I applaud the tireless work of community activists who partnered with local and state agencies to finish the job and improve the health and safety of this community. This is a win for all Californians.”
The land was donated to the Catholic Archdiocese of Los Angeles in the 1950s by descendants of one of the city’s early oil barons. Over the decades, the archdiocese leased the land to several oil companies including Standard Oil of California.
Much of the community outcry over the site’s management occurred after AllenCo took over the site in 2009. The company drastically boosted oil production, but failed to properly maintain its equipment, resulting in oil spills and gas leaks.
In 2013, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency officials became sick while inspecting the site. The federal investigators encountered puddles of crude oil on the facility grounds, as well as caustic fumes emanating from the facility, resulting in violations for air quality and other environmental infractions.
In 2020, CalGEM ordered AllenCo to plug the wells after if determined the company had essentially deserted the site, leaving the wells unplugged and in an unsafe condition. AllenCo ignored the order.
In perhaps the most remarkable events in the site’s history, CalGEM officials in 2022 arrived on the site with a court order and used bolt cutters to enter the site to depressurize the poorly maintained oil wells.
The AllenCo wells were prioritized and plugged this week as part of a CalGEM program to identify and permanently cap high-risk oil and gas wells. Tens of thousands of unproductive and unplugged oil wells have been abandoned across California — many of which continue to leak potentially explosive methane or toxic benzene.
Environmental advocates have long fought for regulators to require oil and gas companies to plug these wells to protect nearby communities and the environment.
However, as oil production declines and fossil fuel companies increasingly become insolvent, California regulators worry taxpayers may have to assume the costs to plug these wells. Federal and state officials have put aside funding to deal with some of these so-called “orphaned” wells, but environmental advocates say it’s not enough. They say oil and gas companies still need to be held to account, so that the same communities that were subjected to decades of pollution won’t have to foot the bill for expensive cleanups.
“This is welcome news that the surrounding community deserves, but there is much more work to be done at a much faster pace,” said Cooper Kass, attorney at the Center for Biological Diversity’s Climate Law Institute. “There are still thousands of unplugged and hazardous idle wells threatening communities across the state, and our legislators and regulators should force polluters, not taxpayers, to pay to clean up these dangerous sites.”
Science
Newsom tells world leaders Trump’s retreat on the environment will mean economic harm

SACRAMENTO — Gov. Gavin Newsom told world leaders Friday that President Trump’s retreat from efforts to combat climate change would decimate the U.S. automobile industry and surrender the future economic viability to China and other nations embracing the transition to renewable energy.
Newsom, appearing at the Munich Security Conference in Germany, urged diplomats, business leaders and policy advocates to forcefully stand up to Trump’s global bullying and loyalty to the oil and coal industry. The California governor said the Trump administration’s massive rollbacks on environmental protection will be short-lived.
“Donald Trump is temporary. He’ll be gone in three years,” Newsom said during a Friday morning panel discussion on climate action. “California is a stable and reliable partner in this space.”
Newsom’s comments came in the wake of the Trump administration’s repeal of the endangerment finding and all federal vehicle emissions regulations. The endangerment finding is the U.S. government’s 2009 affirmation that planet-heating pollution poses a threat to human health and the environment.
Environmental Protection Agency administrator Lee Zeldin said the finding has been regulatory overreach, placing heavy burdens on auto manufacturers, restricting consumer choice and resulting in higher costs for Americans. Its repeal marked the “single largest act of deregulation in the history of the United States of America,” he said.
Scientists and experts were quick to condemn the action, saying it contradicts established science and will put more people in harm’s way. Independent researchers around the world have long concluded that greenhouse gases released by the burning of gasoline, diesel and other fossil fuels are warming the planet and worsening weather disasters.
The move will also threaten the U.S.’s position as a leader in the global clean energy transition, with nations such as China pulling ahead on electric vehicle production and investments in renewables such as solar, batteries and wind, experts said.
Newsom’s trip to Germany is just his latest international jaunt in recent months as he positions himself to lead the Democratic Party’s opposition to Trump and the Republican-led Congress, and to seed a possible run for the White House in 2028. Last month Newsom traveled to the World Economic Forum in Davos, Switzerland, and in November to the U.N. climate summit in Belém, Brazil — mocking and condemning Trump’s policies on Greenland, international trade and the environment.
When asked how he would restore the world’s confidence in the United States if he were to become president, Newsom sidestepped. Instead he offered a campaign-like soliloquy on California’s success on fostering Tesla and the nation’s other top electric vehicle manufacturers as well as being a magnet for industries spending billions of dollars on research and development for the global transition away from carbon-based economies.
The purpose of the Munich conference was to open a dialogue among world leaders on global security, military, economic and environmental issues. Along with Friday’s discussion on climate action, Newsom is scheduled to appear at a livestreamed forum on transatlantic cooperation Saturday.
Andrew Forrest, executive chairman of the Australia-based mining company giant Fortescue, said during a panel Friday his company is proof that even the largest energy-consuming companies in the world can thrive without relying on the carbon-based fuels that have driven industries for more than a century. Fortescue, which buys diesel fuel from countries across the world, will transition to a “green grid” this decade, saving the company a billion dollars a year, he said.
“The science is absolutely clear, but so is the economics. I am, and my company Fortescue is, the industrial-grade proof that going renewable is great economics, great business, and if you desert it, then in the end, you’ll be sorted out by your shareholders or by your voters at the ballot box,” Forrest said.
Newsom said California has also shown the world what can be done with innovative government policies that embrace electric vehicles and the transition to a non-carbon-based economy, and continues to do so despite the attacks and regressive mandates being imposed by the Trump administration.
“This is about economic prosperity and competitiveness, and that’s why I’m so infuriated with what Donald Trump has done,” Newsom said. “Remember, Tesla exists for one reason — California’s regulatory market, which created the incentives and the structure and the certainty that allowed Elon Musk and others to invest and build that capacity. We are not walking away from that.”
California has led the nation in the push toward EVs. For more than 50 years, the state enjoyed unique authority from the EPA to set stricter tailpipe emission standards than the federal government, considered critical to the state’s efforts to address its notorious smog and air-quality issues. The authority, which the Trump administration has moved to rescind, was also the basis for California’s plan to ban the sale of new gasoline-powered cars by 2035.
The administration again targeted electric vehicles in its announcement on Thursday.
“The forced transition to electric vehicles is eliminated,” Zeldin said. “No longer will automakers be pressured to shift their fleets toward electric vehicles, vehicles that are still sitting unsold on dealer lots all across America.”
But the efforts to shut down the energy transition may be too little, too late, said Hannah Safford, former director of transportation and resilience at the White House Climate Policy Office under the Biden administration.
“Electric cars make more economic sense for people, more models are becoming available, and the administration can’t necessarily stop that from happening,” said Safford, who is now associate director for climate and environment at the Federation of American Scientists.
Still, some automakers and trade groups supported the EPA’s decision, as did fossil fuel industry groups and those geared toward free markets and regulatory reform. Among them were the Independent Petroleum Assn. of America, which praised the administration for its “efforts to reform and streamline regulations governing greenhouse gas emissions.”
Ford, which has invested in electric vehicles and recently completed a prototype of a $30,000 electric truck, said in a statement to The Times that it appreciated EPA’s move “to address the imbalance between current emissions standards and consumer choice.”
Toyota, meanwhile, deferred to a statement from Alliance for Automotive Innovation president John Bozzella, who said similarly that “automotive emissions regulations finalized in the previous administration are extremely challenging for automakers to achieve given the current marketplace demand for EVs.”
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoWhite House says murder rate plummeted to lowest level since 1900 under Trump administration
-

 Alabama1 week ago
Alabama1 week agoGeneva’s Kiera Howell, 16, auditions for ‘American Idol’ season 24
-

 Ohio1 week ago
Ohio1 week agoOhio town launching treasure hunt for $10K worth of gold, jewelry
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoThe Long Goodbye: A California Couple Self-Deports to Mexico
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoVideo: Rare Giant Phantom Jelly Spotted in Deep Waters Near Argentina
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoVideo: Farewell, Pocket Books
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: Investigators Say Doorbell Camera Was Disconnected Before Nancy Guthrie’s Kidnapping
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoApple might let you use ChatGPT from CarPlay


















