New York
Where Jazz Lives Now

Surfacing
The jazz membership, with its dim lighting and intently packed tables, looms massive in our collective creativeness. However at the moment, the music is prospering in a bunch of various areas.
A disco ball threw beads of sunshine throughout a crowded dance flooring on a current Monday night time in Decrease Manhattan whereas outdated movie footage rolled throughout a wall by the stage. A half-dozen musicians had been up there, churning waves of rhythm that reshaped over time: A transition would possibly begin with a double-tap of chords, reggae-style, from the keyboardist Ray Offended, or with a brand new vocal line, improvised and looped by the singer Kamilah.
A classically skilled pianist who’s logged time with D’Angelo and the Roots, Offended doesn’t “name tunes,” within the jazzman’s parlance. As standard, his group was cooking up grooves from scratch, treating the viewers as a participant. Collectively they stuffed the slender, two-story membership with rhythm and physique warmth until effectively previous midnight.
Since earlier than the coronavirus pandemic, Offended has led his Producer Mondays jam periods each week (Covid restrictions allowing) at Nublu, an Alphabet Metropolis venue that feels extra like a small European discothèque than a New York jazz membership. With a various clientele and a diversified slate of exhibits, Nublu’s administration retains one foot within the jazz world whereas reserving digital music and rock, too. On Mondays, all of it comes collectively.
As New York nightlife has bubbled again up over the previous few months, it’s been a significant consolation to return to the legacy jazz rooms, just like the Village Vanguard or the Blue Word, most of which survived the pandemic. However the true blood-pumping moments — the exhibits the place you may sense that different musicians are within the room listening for brand spanking new tips, and it feels just like the script continues to be being written onstage — have been occurring most frequently in venues that don’t appear to be typical jazz golf equipment. They’re areas the place jazz bleeds outward, and converses with a much less regimented viewers.
“The scene has began to fracture,” the drummer and producer Kassa Total, 39, mentioned in a current interview, admitting that he didn’t know precisely what venue would grow to be floor zero for the following era of innovators. “I don’t suppose it’s actually discovered a house but. And that’s good, truly.”
It’s an uncommonly thrilling time for stay jazz. Younger bandleaders have vast followings once more — Makaya McCraven, Esperanza Spalding, Robert Glasper and Christian Scott aTunde Adjuah every rack up hundreds of thousands of performs on streaming companies — and a era of musicians and listeners is lined as much as comply with their lead, or break free. This 12 months, for the primary time, the most-nominated artist on the Grammys is a jazz musician who crossed over: Jon Batiste.
These gamers’ music has by no means actually appeared at residence in jazz golf equipment, nor has the extra avant-garde and spiritual-leaning work of artists like James Brandon Lewis, Shabaka Hutchings, Angel Bat Dawid, Kamasi Washington, Nicole Mitchell or the Solar Ra Arkestra, all of whom are in excessive demand lately.
Possibly it’s a case of coincidental timing. A confluence of forces — the pandemic, the volatility of New York actual property, an more and more digital tradition — has upset the panorama, and with the music mutating quick, it additionally appears to be discovering new houses.
Jazz is a music of stay embodiment. A part of its energy has all the time been to alter the best way that we assemble (jazz golf equipment had been among the first actually built-in social areas in northern cities), and performers have all the time responded to the atmosphere the place they’re being heard. So updating our sense of the place this music occurs is likely to be basic to re-establishing jazz’s place in tradition, particularly at a second when the tradition appears prepared for a brand new wave of jazz.
FIFTY-NINE YEARS in the past, the poet and critic Amiri Baraka (writing then as LeRoi Jones) reported in DownBeat journal that New York’s main golf equipment had misplaced curiosity in jazz’s “new factor.” The freer, extra confrontational and Afrocentric types of improvising that had taken maintain — Ornette Coleman, John Coltrane and Cecil Taylor’s revolution, for brief — had been not welcome in industrial golf equipment. So artists began reserving themselves in downtown espresso outlets and their very own lofts as a substitute.
The music has by no means stopped churning and evolving, however because the Nineteen Sixties, jazz golf equipment — a vestige of the Prohibition period, with their windowless intimacy and intently clustered tables — have not often felt like an ideal residence for the music’s future improvement. On the similar time, it’s been unattainable to shake our attachment to the notion that golf equipment are the “genuine” residence of jazz, a jealously guarded idyll in any American creativeness.
However Joel Ross, 26, a celebrated vibraphonist dwelling in Brooklyn, mentioned that particularly within the two years since coronavirus shutdowns started, many younger musicians have grow to be unstuck from the behavior of creating the rounds to typical jazz venues. “Cats are simply enjoying in random eating places and random spots,” he mentioned, naming a couple of musician-run periods which have began up in Brooklyn and Manhattan, however not in conventional golf equipment.
Generally it’s not a public factor in any respect. “Persons are getting collectively in their very own houses extra, and piecing music collectively,” Ross mentioned.
The vocalist, flutist and producer Melanie Charles, 34, has made her Bushwick residence right into a rehearsal area, recording studio and gathering spot. And when she performs, it’s normally not at straight-ahead jazz golf equipment. Her music makes use of electronics and requires one thing heavier than an upright bass, so these venues simply may not have what’s wanted. “Musicians like me and my friends, we’d like some bump on the underside,” she mentioned. “Our materials received’t work in these areas the best way we wish to do it.”
Excessive amongst Charles’s most well-liked locations to play is Cafe Erzulie, a Haitian restaurant and bar tucked alongside the border between the Bushwick and Bedford-Stuyvesant neighborhoods of Brooklyn. With bluish-green partitions painted with palm-leaf patterns and bistro tables arrayed across the room and the patio, the membership hosts a variety of music, together with R&B jams; album launch exhibits and birthday events for genre-bending artists like KeiyaA and Pink Siifu; and a weekly Jazz Night time on Thursdays.
Jazz Night time returned this month after a late-pandemic-induced hiatus, and demand had not ebbed: The room was near capability, with a crowd of younger, colorfully dressed patrons seated at tables and wrapped across the bar.
Jonathan Michel, a bassist and musical confidante of Charles, was joined by the keyboardist Axel Tosca and the percussionist Bendji Allonce, enjoying rumba-driven rearrangements of Gnarls Barkley’s “Loopy,” jazz requirements and conventional Caribbean songs. The group was tuned in all the best way, which didn’t all the time imply quiet. However when Allonce and Tosca dropped out and Michel took a considerate, not overly insistent bass solo, the room hushed.
Charles sat in with the trio partway via its set, singing a heart-aching authentic, “Symphony,” and an outdated Haitian tune, “Lot Bo.” Nearly instantly, she had 90 p.c of the place silent, and one hundred pc paying consideration. With the band galloping over “Lot Bo,” she took a pause from improvising in flowing, diving, melismatic runs to clarify what the tune’s lyrics imply: “I’ve to cross that river; once I get to the opposite aspect, I’ll relaxation,” she mentioned. “It’s been exhausting out right here in these streets,” she advised the gang, receiving a hum of recognition. “Relaxation is radical, low-key.”
Cafe Erzulie is only one of a handful of comparatively new venues in Brooklyn which have established their very own identities, impartial of jazz, however present the music an atmosphere to thrive. Public Data opened in Gowanus in 2019 with the first mission to current digital music in a hi-fi setting. It had initially deliberate to have improvising combos play in its cafe area, separate from the primary sound room, however its curators have just lately welcomed the music in additional absolutely.
Wild Birds, a Crown Heights eatery and venue, has made jazz a part of its common programming alongside cumbia, Afrobeat and different stay music. It’s going to typically begin a given night time with a stay band and viewers seating, then transition to a dance flooring state of affairs with a D.J. In Greenpoint, IRL Gallery has been internet hosting experimental jazz usually alongside visible artwork exhibitions and electronic-music bookings. Due south, in Prospect Lefferts Gardens, the Owl Music Parlor hosts jazz in addition to chamber music and singer-songwriter fare; Zanmi, a couple of blocks away, is one other Haitian restaurant the place jazz performances typically really feel like a roux of associated musical cultures.
And jazz is proving to be greater than only a feather in a venue’s cultural cap. The rooms are literally filling up. “For one, we cater to a really particular kind of demographic: younger folks of colour, who I feel actually perceive and recognize jazz music,” mentioned Mark Luxama, the proprietor of Cafe Erzulie, explaining Jazz Night time’s success. “We’ve been capable of fill seats.”
Apart from, he added, “it’s actually not in regards to the cash on Jazz Night time. I feel it’s extra about creating neighborhood, and with the ability to create area for the musicians to do their factor and have a extremely good time.”
FROM THE START, the story of jazz golf equipment in New York has been a narrative of white artists receiving preferential therapy. The primary time historical past remembers jazz being performed in a New York institution was winter 1917, when the Dixieland Authentic Jass Band — all white, and dishonestly named (so little about their sound was authentic) — traveled up from New Orleans to play at Reisenweber’s Café in Columbus Circle. The performances led to a document deal, and the Dixieland band had quickly recorded the world’s first commercially distributed jazz sides, for the Victor label.
Throughout Prohibition, jazz turned the popular leisure in speakeasies and mob-run joints. The enterprise of the scene remained principally in white arms, even in Harlem. However many golf equipment served a blended clientele, and jazz venues had been among the first public institutions to serve Black and white folks collectively within the Twenties and ’30s. (After all, there have been notable exceptions.) In interviews for the archivist Jeff Gold’s current ebook, “Sittin’ In: Jazz Golf equipment of the Forties and Nineteen Fifties,” Quincy Jones and Sonny Rollins every remembered the town’s postwar jazz golf equipment as a type of oasis. “It was a spot of neighborhood and pure love of the artwork,” Jones mentioned. “You couldn’t discover that wherever else.”
However when jazz grew too radical for commerce, the avant-garde was booted from the golf equipment, and up sprang a loft scene. Artists discovered themselves without delay empowered and impoverished. They had been reserving their very own exhibits and advertising themselves. However Baraka, writing about one of many first cafes to current Cecil Taylor’s trio, famous a deadly flaw. “No matter this espresso store is paying Taylor,” he wrote, “it’s definitely not sufficient.”
The cash piece by no means fairly shook out on the avant-garde, and by the Nineteen Eighties the lofts had principally closed amid rising rents and unfriendlier civic attitudes towards semi-legal meeting. Nonetheless, that form-busting, take-no-prisoners custom — whether or not you name it avant-garde, free jazz or hearth music — continues.
In current a long time, it has had a pair of fierce defenders within the bassist William Parker and the dancer Patricia Nicholson Parker, a husband-and-wife duo of organizers. The Parkers run the nonprofit Arts for Artwork, and because the Nineteen Nineties they’ve introduced the standard-bearing Imaginative and prescient Competition, typically on the Brooklyn performing arts area Roulette. They’ve additionally lengthy introduced music to the Clemente, a cultural heart on the Decrease East Facet, and in the course of the pandemic they’ve added digital live shows to their programming.
It’s exhausting to argue with outcomes, and if Arts for Artwork has by no means constructed an enormous viewers, it has retained a constant one whereas nurturing among the most expansive minds in improvised music. James Brandon Lewis, the tenor saxophonist whose album “Jesup Wagon” topped many jazz critics’ value determinations of final 12 months’s releases, has that inventive neighborhood partly to thank for shepherding his profession. Zoh Amba, one other uncompromising younger saxophonist, is slicing a powerful path for herself thanks largely to Arts for Artwork’s assist.
“What Arts for Artwork asks of individuals is that they actually simply play their greatest,” Nicholson Parker mentioned. “In case your music is about getting folks to eat alcohol, then that’s completely different.”
“you want locations and individuals who assist that type of inventive freedom,” she added.
AT SMALLS JAZZ Membership, the storied West Village basement, purebred jazz jam periods nonetheless stretch into the wee hours on a nightly foundation, inheriting among the infectious, insidery power that existed in its truest kind into the Nineteen Nineties at golf equipment like Bradley’s. However at the moment it’s exhausting to argue that Smalls is the correct vacation spot for listening to essentially the most cutting-edge sounds.
And though they don’t normally say it publicly, seasoned gamers have come to agree that the code of conduct at Smalls’ jam periods went a bit of flimsy after the 2018 demise of Roy Hargrove. His frequent presence as an elder there had helped to maintain the bar excessive, even because the room had come to be crammed with musicians whose hands-on expertise of jazz arrived principally via the distorted lens of formal schooling.
The Jazz Gallery, a nonprofit membership 10 blocks north of Union Sq., has mixed the Bradley’s legacy with a dedication to bringing ahead new works by progressive younger bandleaders, and it’s grow to be an important hub. Rio Sakairi, the Gallery’s inventive director, cultivates rising expertise and encourages mentorship between generations, typically by providing focused grants and commissions of recent work.
She’s come to phrases with the Gallery’s place on the receiving finish of jazz’s tutorial pipeline. “You can not take the truth that jazz is being taught at conservatory out of the equation,” she mentioned. “Youthful musicians which are popping out, all of them undergo college methods.”
Partly as an extension of the best way jazz conservatories work, jam session tradition doesn’t actually exist on the Gallery. Reveals finish after they’re scheduled to. To Charles, it feels “extra like a piece area” than a membership. “I’m glad these areas are there,” she mentioned.
Taking a look at a jazz scene in transition, a fan can solely hope that among the power accrued on the margins, in cross-pollinated golf equipment and extra experimental settings, would possibly stream again into areas the place the jazz custom is a standard forex: locations like Smalls, the Jazz Gallery and the Nationwide Jazz Museum in Harlem (all of which have nonprofit standing, and the financial flexibility related to it).
“It simply must be reconnected: The Smalls folks have to be speaking to the Jazz Gallery folks; the beat machine children have to be speaking to the Smalls folks,” mentioned Total, the drummer. “Possibly there must be an area that acknowledges all these completely different parts.”
For now, Charles mentioned, the outdated haunts nonetheless really feel wanted, and cherished. “On the finish of the day I nonetheless find yourself at Smalls,” she mentioned. “It’s like a church whose heyday is gone, however you continue to come and pay your respects.”
Surfacing is a visible column that explores the intersection of artwork and life, produced by Alicia DeSantis, Jolie Ruben, Tala Safie and Josephine Sedgwick.

New York
We Counted 22,252 Cars to See How Much Congestion Pricing Might Have Made This Morning

Today would have been the first Monday of New York City’s congestion pricing plan. Before it was halted by Gov. Kathy Hochul, the plan was designed to rein in some of the nation’s worst traffic while raising a billion dollars for the subway every year, one toll at a time.
A year’s worth of tolls is hard to picture. But what about a day’s worth? What about an hour’s?
To understand how the plan could have worked, we went to the edges of the tolling zone during the first rush hour that the fees would have kicked in.
Here’s what we saw:
Video by Noah Throop/The New York Times; animation by Ruru Kuo/The New York Times
You probably wouldn’t have seen every one of those cars if the program had been allowed to proceed. That’s because officials said the fees would have discouraged some drivers from crossing into the tolled zone, leading to an estimated 17 percent reduction in traffic. (It’s also Monday on a holiday week.)
The above video was just at one crossing point, on Lexington Avenue. We sent 27 people to count vehicles manually at four bridges, four tunnels and nine streets where cars entered the business district. In total, we counted 22,252 cars, trucks, motorcycles and buses between 8 a.m. and 9 a.m. on Monday.
We wanted to see how the dense flow of traffic into the central business district would have generated money in real time.
Though we can’t know that dollar amount precisely, we can hazard a guess. Congestion pricing was commonly referred to as a $15-per-car toll, but it wasn’t so simple. There were going to be smaller fees for taxi trips, credits for the tunnels, heftier charges for trucks and buses, and a number of exemptions.
To try to account for all that fee variance, we used estimates from the firm Replica, which models traffic data, on who enters the business district, as well as records from the Metropolitan Transportation Authority and city agencies. We also made a few assumptions where data wasn’t available. We then came up with a ballpark figure for how much the city might have generated in an hour at those toll points.
The total? About $200,000 in tolls for that hour.
Note: The Trinity Place exit from the Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel, which would have been tolled, is closed at this hour.
It’s far from a perfect guess. Our vehicle total is definitely an undercount: We counted only the major entrances — bridges, tunnels and 60th Street — which means we missed all the cars that entered the zone by exiting the Franklin D. Roosevelt Drive or the West Side Highway.
And our translation into a dollar number is rough. Among many other choices we had to make, we assumed all drivers had E-ZPass — saving them a big surcharge — and we couldn’t distinguish between transit buses and charter buses, so we gave all buses an exemption.
But it does give you a rough sense of scale: It’s a lot of cars, and a lot of money. Over the course of a typical day, hundreds of thousands of vehicles stream into the Manhattan central business district through various crossings.
Trips into tolling district, per Replica estimates Note: Data counts estimated entrances on a weekday in spring 2023. Source: Replica.
Queens-Midtown Tunnel
50,600
Lincoln Tunnel
49,200
Williamsburg Bridge
27,900
Manhattan Bridge
24,000
Brooklyn-Battery Tunnel
23,100
Queensboro Bridge
21,700
Brooklyn Bridge
17,100
Holland Tunnel
15,400
All other entrances
118,000
Total
347,000
The tolling infrastructure that was installed for the program cost roughly half a billion dollars.
The M.T.A. had planned to use the congestion pricing revenue estimates to secure $15 billion in financing for subway upgrades. Many of those improvement plans have now been suspended.
Methodology We stationed as many as five counters at some bridges and tunnels to ensure that we counted only cars that directly entered the tolling zone, not those that would have continued onto non-tolled routes.
Our count also excluded certain exempt vehicles like emergency vehicles.
We used estimates of the traffic into the district to make a best guess at how many of each kind of vehicle entered the zone. Most of our estimates came from the traffic data firm Replica, which uses a variety of data sources, including phone location, credit card and census data, to model transportation patterns. Replica estimated that around 58 percent of trips into the central business district on a weekday in spring 2023 were made by private vehicles, 35 percent by taxis or other for-hire vehicles (Uber and Lyft) and the remainder by commercial vehicles.
We also used data on trucks, buses, for-hire vehicles and motorcycles from the M.T.A., the Taxi and Limousine Commission and the Department of Transportation.
For simplicity, we assumed all vehicles would be equally likely to enter the zone from 8 a.m. to 9 a.m. as they would be in any other hour. We could not account for the other trips that a for-hire vehicle might make once within the tolled zone, only the initial crossing. And we did not include the discount to drivers who make under $50,000, because it would kick in only after 10 trips in a calendar month.
New York
Transcript of Trump Manhattan Trial, May 30, 2024

-
Jury Deliberation Re-charge
SUPREME COURT OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK
COUNTY OF NEW YORK CRIMINAL TERM
-
-
PART: 59
Χ
THE PEOPLE OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK,
-against-
DONALD J. TRUMP,
DEFENDANT.
BEFORE:
Indict. No.
71543-2023
CHARGE
4909
FALSIFYING BUSINESS
RECORDS 1ST DEGREE
JURY TRIAL
100 Centre Street
New York, New York 10013
May 30, 2024
HONORABLE JUAN M. MERCHAN
JUSTICE OF THE SUPREME COURT
APPEARANCES:
FOR THE PEOPLE:
ALVIN BRAGG, JR., ESQ.
DISTRICT ATTORNEY, NEW YORK COUNTY
One Hogan Place
New York, New York 10013
BY:
JOSHUA STEINGLASS, ESQ.
MATTHEW COLANGELO,
ESQ.
SUSAN HOFFINGER, ESQ.
CHRISTOPHER CONROY, ESQ.
BECKY MANGOLD, ESQ.
KATHERINE ELLIS, ESQ.
Assistant District Attorneys
BLANCHE LAW
BY:
TODD BLANCHE, ESQ.
EMIL BOVE, ESQ.
KENDRA WHARTON, ESQ.
NECHELES LAW, LLP
BY: SUSAN NECHELES, ESQ.
GEDALIA STERN, ESQ.
Attorneys for the Defendant
SUSAN PEARCE-BATES, RPR, CSR, RSA
Principal Court Reporter
LAURIE EISENBERG, RPR, CSR
LISA KRAMSKY
THERESA MAGNICCARI
Senior Court Reporters
Susan Pearce-Bates, RPR, CCR, RSA
Principal Court Reporter
New York
Transcript of Trump Manhattan Trial, May 29, 2024

SUPREME COURT OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK
COUNTY OF NEW YORK CRIMINAL TERM
-
THE PEOPLE OF THE STATE OF NEW YORK,
PART: 59
Indict. No.
71543-2023
CHARGE
-against-
DONALD J. TRUMP,
DEFENDANT.
BEFORE:
4815
FALSIFYING BUSINESS
RECORDS 1ST DEGREE
JURY TRIAL
X
100 Centre Street
New York, New York 10013
May 29, 2024
HONORABLE JUAN M. MERCHAN
JUSTICE OF THE SUPREME COURT
APPEARANCES:
FOR THE
PEOPLE:
ALVIN BRAGG, JR.,
ESQ.
DISTRICT ATTORNEY, NEW YORK COUNTY
One Hogan Place
New York, New York 10013
BY:
JOSHUA STEINGLASS, ESQ.
MATTHEW COLANGELO,
ESQ.
SUSAN HOFFINGER, ESQ.
CHRISTOPHER CONROY, ESQ.
BECKY MANGOLD, ESQ.
KATHERINE ELLIS, ESQ.
Assistant District Attorneys
BLANCHE LAW
BY:
TODD BLANCHE, ESQ.
EMIL BOVE, ESQ.
KENDRA WHARTON, ESQ.
NECHELES LAW, LLP
BY: SUSAN NECHELES, ESQ.
Attorneys for the Defendant
SUSAN PEARCE-BATES, RPR, CSR, RSA
Principal Court Reporter
LAURIE EISENBERG, RPR, CSR
LISA KRAMSKY
THERESA MAGNICCARI
Senior Court Reporters
Susan Pearce-Bates,
RPR, CCR, RSA
Principal Court Reporter
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTension and stand-offs as South Africa struggles to launch coalition gov’t
-
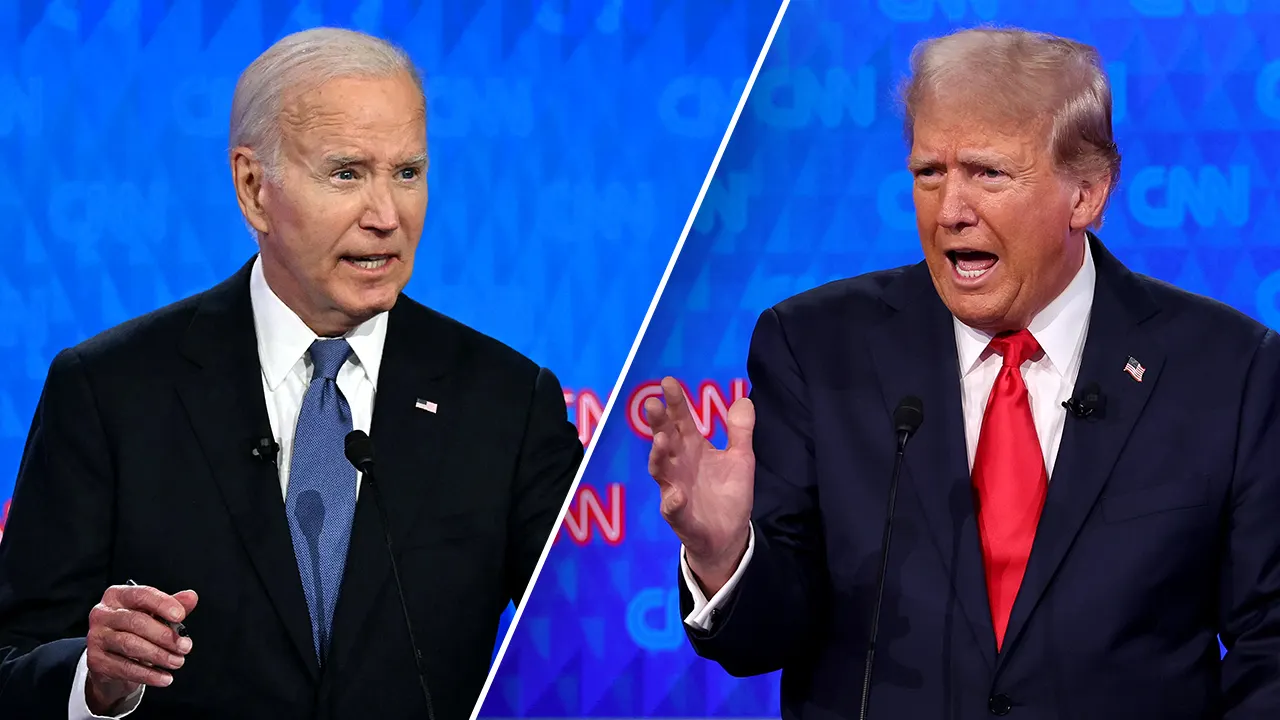

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFirst 2024 Trump-Biden presidential debate: Top clashes over issues from the border to Ukraine
-
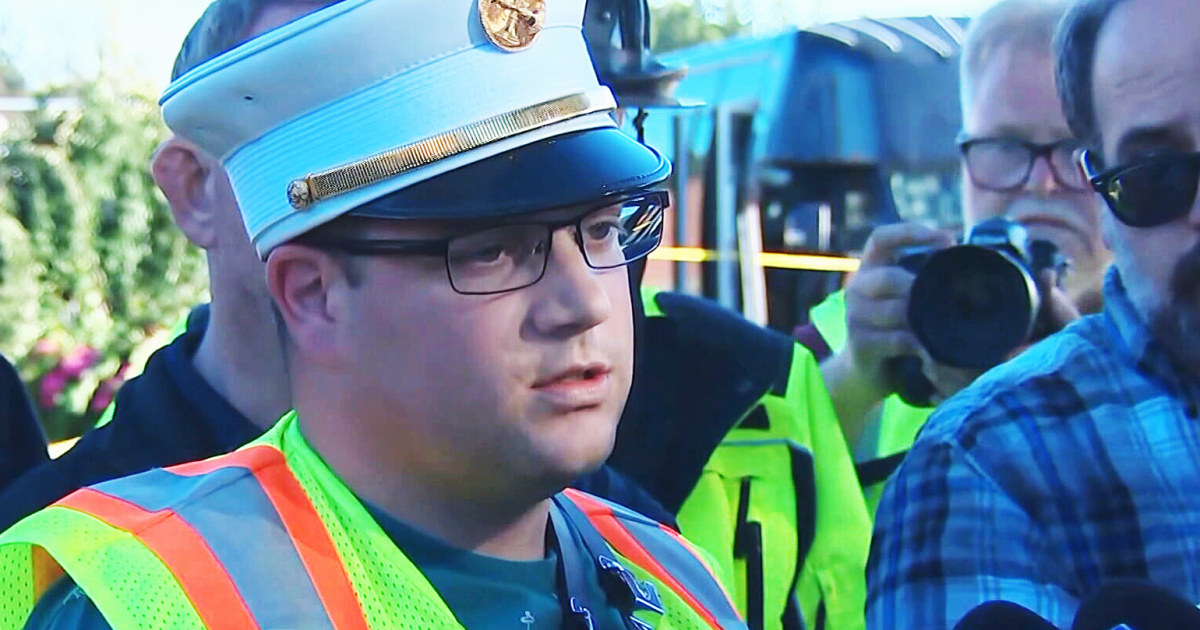

 News1 week ago
News1 week ago4 killed, 9 injured after vehicle crashes into Long Island nail salon
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSupreme Court denies Steve Bannon's plea to stay free while he appeals
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: How Blast Waves Can Injure the Brain
-
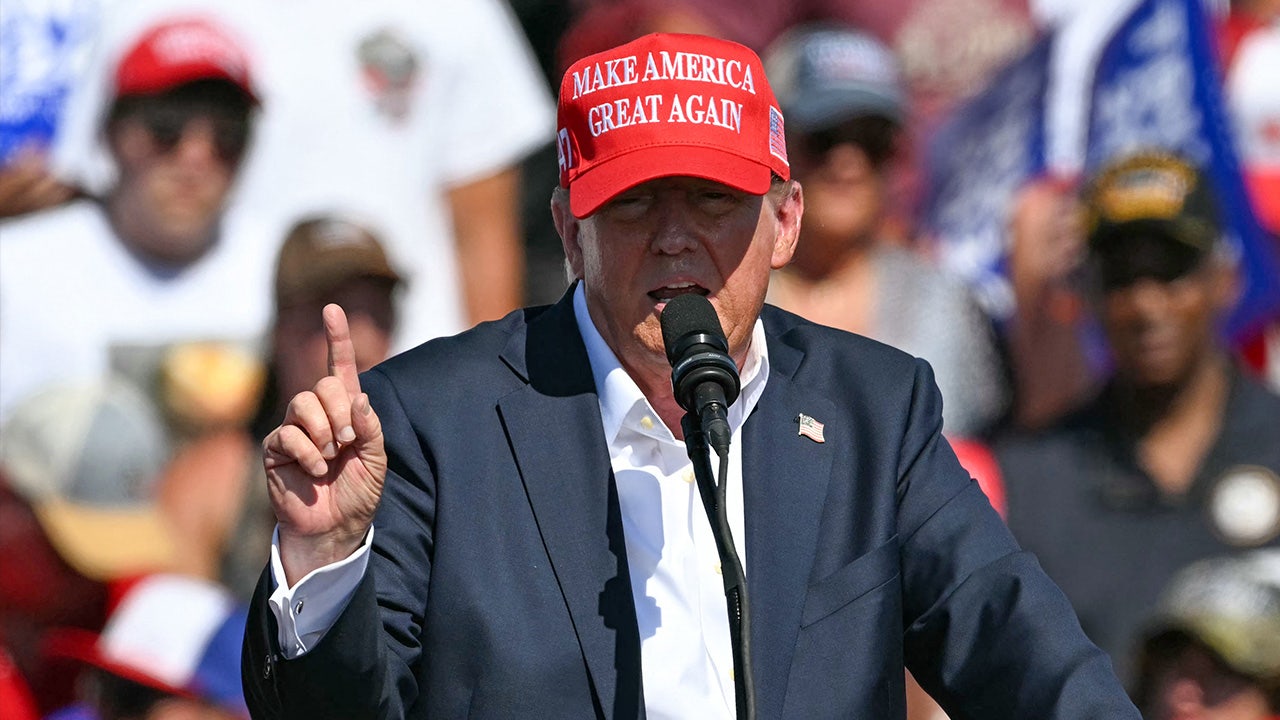

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump says 'biggest problem' not Biden's age, 'decline,' but his policies in first appearance since debate
-
 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIncreasing numbers of voters don’t think Biden should be running after debate with Trump — CBS News poll
-
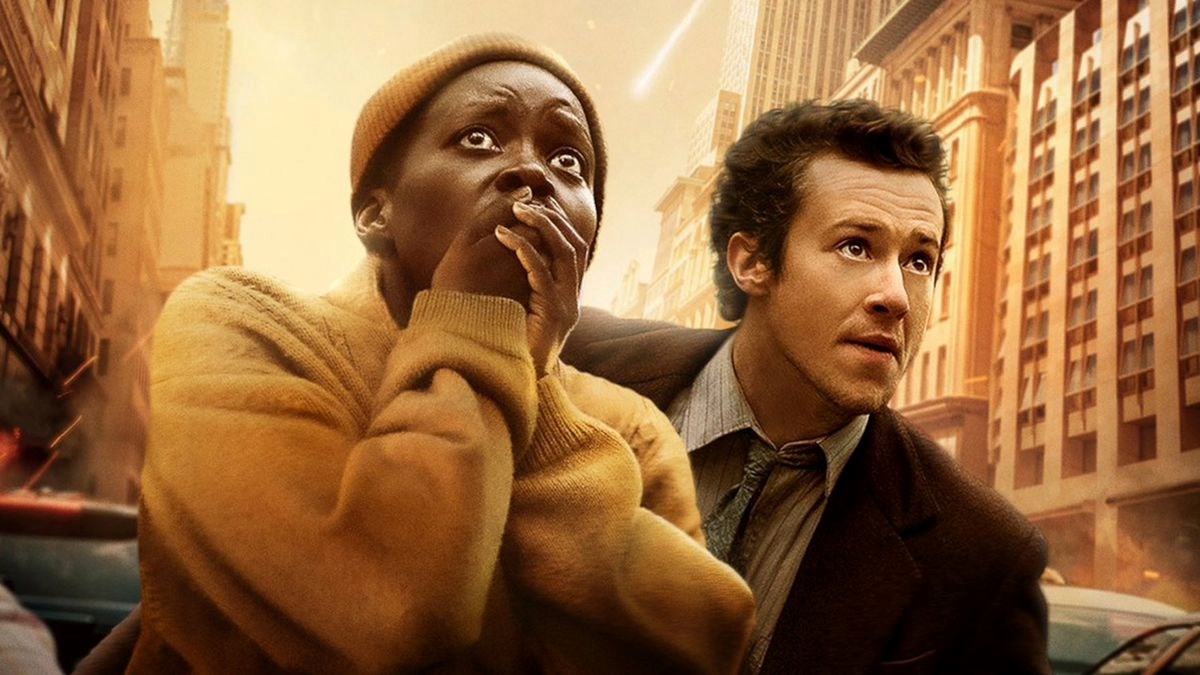

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie review: A Quiet Place, quivering since Day One














