Health
Most notable drug and vaccine approvals of 2023, according to pharmacists

Each year, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approves hundreds of new drugs and therapeutic products for use by the American public.
GoodRx Health, an American health care company and telemedicine platform, has compiled and published a list of some of the most influential drug and vaccine approvals of 2023, selected by its team of pharmacists.
The list only includes products that were approved through Dec. 8.
ANTI-AGING DRUG FOR DOGS FROM SAN FRANCISCO FIRM MOVES CLOSER TO GAINING FDA APPROVAL
Below are the medications that represent “meaningful steps forward,” the firm believes, in terms of improving human health.
1. Paxlovid for COVID-19
After initially granting emergency use authorization (EUA) in late 2021, the FDA fully approved this antiviral medication on May 25, 2023.
It is intended for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 illness for people who are considered at high risk for severe effects.
Paxlovid is intended for the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19 illness for people who are considered at high risk for severe effects. (Getty Images)
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) recommends Paxlovid as the preferred treatment option for adults and teens who are not hospitalized, GoodRx noted.
“Paxlovid has been a mainstay of COVID therapeutic management since its initial EUA designation in Dec. 2021,” Christina Madison, a Nevada pharmacist who is the founder and CEO of The Public Health Pharmacist, told GoodRx.
COVID DRUG PAXLOVID, WHICH HELPS PREVENT SEVERE SYMPTOMS, WILL DOUBLE IN PRICE AS PANDEMIC EBBS
“Having full FDA approval also helps us with hesitant patients not wanting to take a medication that isn’t FDA approved,” she added.
“It’s great news that this [medication] has gone through the rigorous approval process and has been found to be safe and effective.”
2. Arexvy, Abrysvo and Beyfortus for RSV
Each year, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes approximately 60,000 to 160,000 hospitalizations and 6,000 to 10,000 deaths among adults ages 65 years and older, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
It also causes 58,000 to 80,000 hospitalizations and 100 to 300 deaths in children 5 years of age and younger.
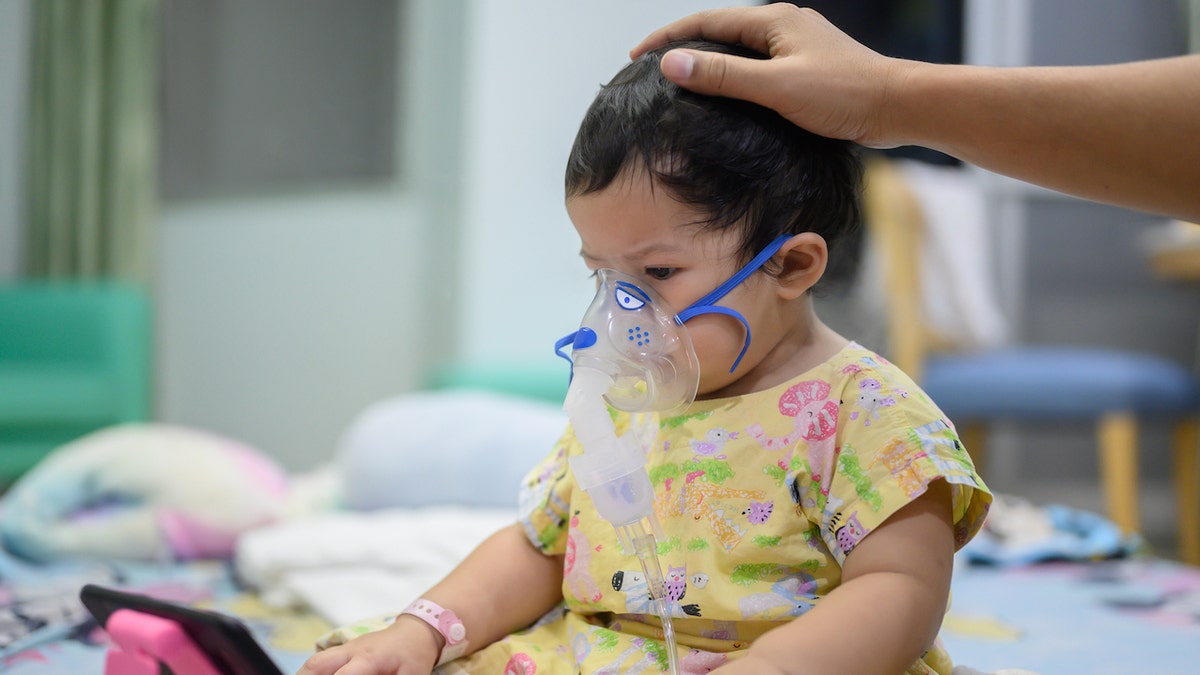
Each year, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) causes some 58,000 to 80,000 hospitalizations and 100 to 300 deaths in children 5 years and younger. (iStock)
To help prevent RSV illness, the FDA approved three medications in 2023, GoodRx reported.
COLD, FLU, COVID-19 AND RSV: HOW TO IDENTIFY THE DIFFERING SYMPTOMS AND STAY SAFE
Arexvy (RSVPreF3) was the first FDA-approved RSV vaccine, available for adults ages 60 and older.
Abrysvo (RSVpreF) is another vaccine that is available to adults ages 60 and older and certain pregnant women.
Beyfortus (nirsevimab) is a preventative medication that reduces the risk of serious lower respiratory tract disease caused by RSV in infants. One dose is recommended for all infants younger than 8 months old and some toddlers younger than 19 months old.
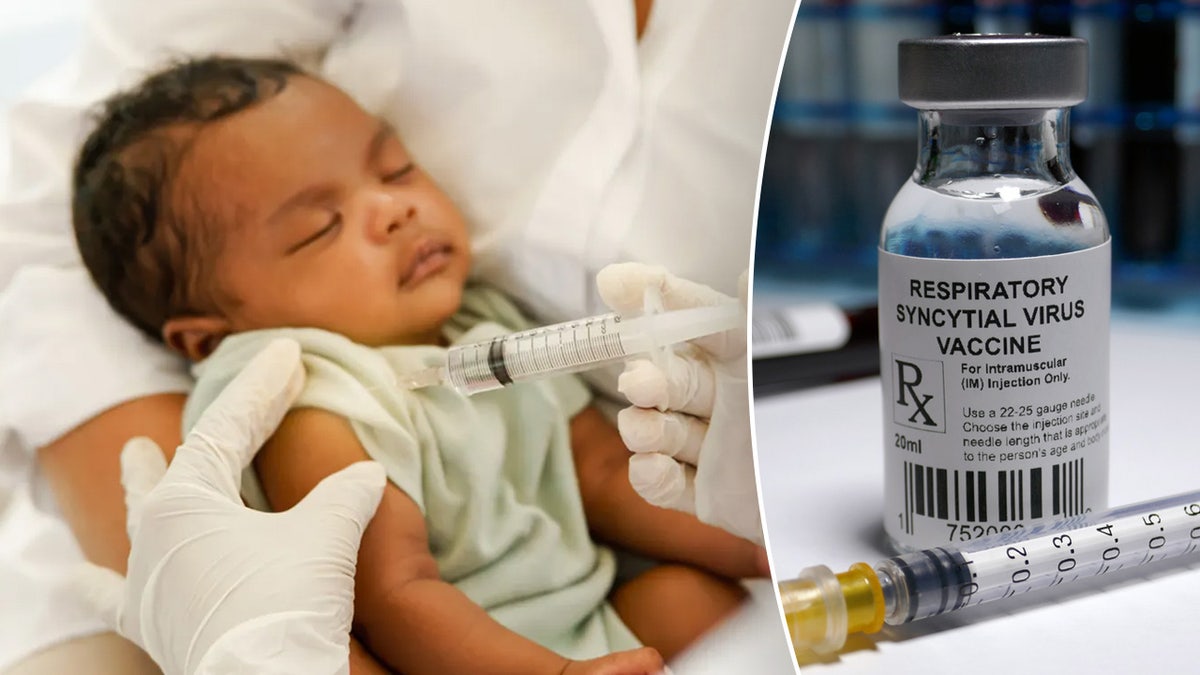
To help prevent RSV illness, the FDA approved three medications in 2023. (iStock)
“These approvals finally give us a way to prevent RSV complications in certain people, notably older adults, pregnant women and very young kids,” Joshua Murdock, PharmD, a pharmacy editor at GoodRx based in Arizona, said in a statement sent to Fox News Digital.
Murdock is one of the pharmacists who compiled the list of the most influential approvals.
“These are much needed because RSV is a contagious and potentially dangerous virus, and previously only certain babies could receive an RSV preventative medication,” he said.
3. Opill for contraception
Opill, the first over-the-counter (OTC) birth control pill, was approved by the FDA in July 2023.
The medication, called norgestrel, is expected to be available in early 2024.
HEALTH ALERT FOR WOMEN: EARLY USE OF BIRTH CONTROL PILLS LINKED TO HIGHER RATES OF DEPRESSION, STUDY FINDS
“Having an over-the-counter birth control pill is long overdue,” said Murdock. “Being able to walk into a local pharmacy or big-box retailer and purchase a birth control pill will likely make a big difference in the accessibility of contraception.”

The first over-the-counter (OTC) birth control pill, Opill (not pictured), was approved by the FDA in July 2023. (iStock)
Veronica Vernon, PharmD, assistant professor and vice chair of pharmacy practice at Butler University in Indiana, calls Opill a “tremendous step forward in terms of increasing access to contraception.”
Said Vernon in a statement to GoodRx, “A prescription for contraception can be a significant barrier for some patients due to the time and cost involved in having a visit.”
4. Zurzuvae for postpartum depression
Postpartum depression (PPD) affects up to 20% of women, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
The condition causes feelings of extreme sadness, anxiety and fatigue in the weeks after giving birth.
5 TIPS FOR MANAGING POSTPARTUM ISSUES FROM A NEW YORK-BASED FAMILY PHYSICIAN
In August 2023, the FDA approved Zurzuvae (zuranolone) as a treatment for PPD.
While traditional antidepressants can take weeks to show effectiveness, Zurzuvae has been shown to relieve symptoms in as little as three days.

Postpartum depression affects up to 20% of women, according to the National Institutes of Health. (iStock)
“Bringing Zurzuvae to the market as a fast-acting, oral option for postpartum depression is a huge step in providing greater access to care for women after childbirth,” Murdock told Fox News Digital.
“Up until this approval, women seeking an approved PPD treatment could only access a similar medication by an IV infusion given over 60 hours, making it challenging for many to receive adequate care.”
5. Leqembi for Alzheimer’s disease
Approved in July 2023, Leqembi (lecanemab) is the first Alzheimer’s medication to address the disease at its root cause rather than just addressing the symptoms.
NEW DEMENTIA DRUG ‘HAS GIVEN ME HOPE’: ALZHEIMER’S PATIENTS REVEAL THEIR STORIES
Leqembi (lecanemab) is a new advancement in Alzheimer’s research.
It’s the first clinically backed Alzheimer’s medication that targets the root cause of the condition.
Compared to a placebo, an infusion with no medication, Leqembi lowered the worsening of dementia symptom severity by an average of 27% over a 1.5-year period.
“Before this approval, existing Alzheimer’s treatments didn’t fully address the root cause of the condition,” said Murdock.
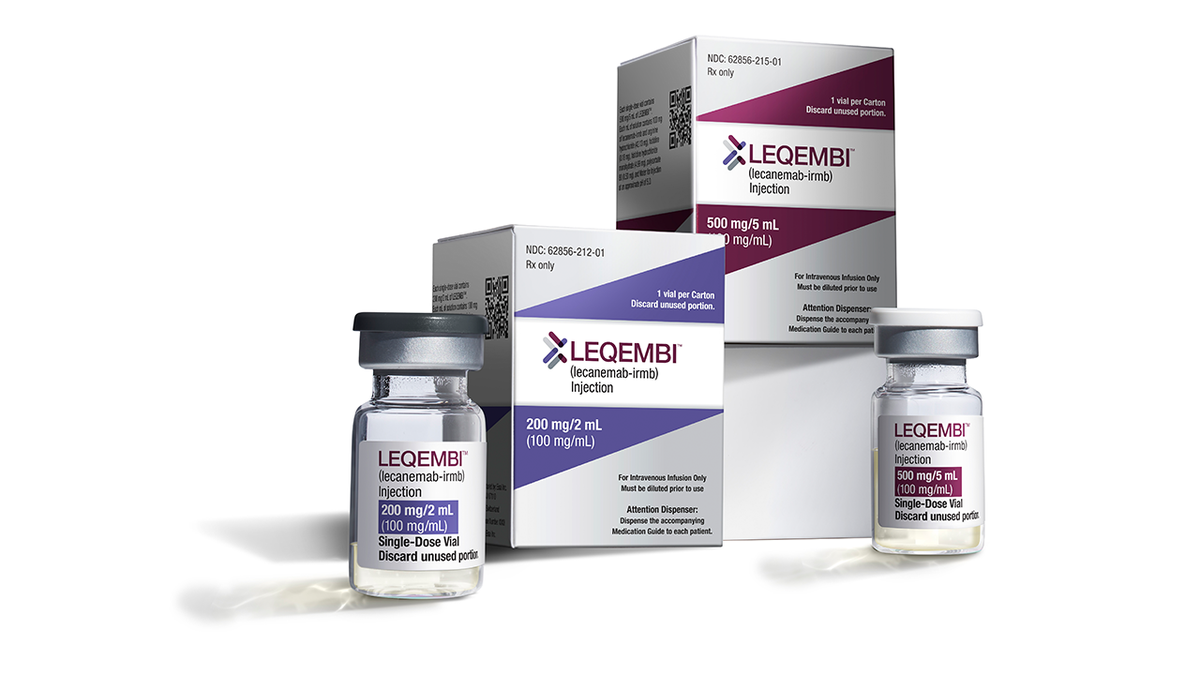
Leqembi (lecanemab) is a new advancement in Alzheimer’s research. It’s the first clinically backed Alzheimer’s medication targeting the root cause of the condition. (AP Photos)
“Leqembi is the first clinically backed medication that may slow disease progression in its early stages,” he went on.
“This extra time of independence for patients to go about their daily lives is a major milestone in Alzheimer’s treatments.”
Rebecca M. Edelmayer, PhD, senior director of scientific engagement at the Alzheimer’s Association in Chicago, told GoodRx that Leqembi is now covered by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) and many other insurers due to its full traditional approval.
In clinical trials, Leqembi slowed the progression of dementia symptoms by an average of 27% over a 1.5-year period, GoodRx noted.
6. OTC naloxone for opioid overdoses
Over 97,600 people die of drug overdoses each year, according to data from the National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics.
Seven out of every 10 of those deaths are caused by opioids, which are powerful prescription pain medications.

Prior to 2023, naloxone, which reverses opioid overdoses, was only available with a prescription. In March 2023, the FDA approved Narcan, the first OTC nasal spray. (iStock)
In March 2023, the FDA approved Narcan, the first OTC nasal spray.
In July 2023, RiVive, another nasal spray, also acquired FDA approval.
Anita Jacobson, PharmD, a clinical professor at the University of Rhode Island College of Pharmacy and the director of the Community First Responder Program, told GoodRx that these approvals helped to reduce the stigma surrounding overdose medications.
WHAT IS KETAMINE, THE DRUG THAT KILLED MATTHEW PERRY ON OCTOBER 28?
“The fact that people now see this as an OTC product, like ibuprofen, cough medicine or any other product that they can buy, can really help to remove fear,” said Jacobson, adding that the approvals “also allow us to distribute naloxone across state lines in a way that we could not do when it was prescription only.”
Murdock noted that naloxone is a “life-saving medication, capable of reversing overdoses from opioids like fentanyl, heroin, hydrocodone and more.”
He also told Fox News Digital, “Greater accessibility to naloxone is critical in combating opioid overdose deaths.”
7. Zepbound for chronic weight management
The newest medication for chronic weight loss management, Eli Lilly’s Zepbound contains tirzepatide, the same active ingredient in Mounjaro, the popular type 2 diabetes drug.
Administered as a weekly injection, Zepbound works by reducing appetite. In clinical trials, it helped participants lose an average of 34 to 48 pounds after 72 weeks, GoodRx noted.

The newest medication for chronic weight loss management, Eli Lilly’s Zepbound contains tirzepatide, the same active ingredient in Mounjaro, the popular type 2 diabetes drug. (iStock)
On Nov. 8, the FDA approved Zepbound for adults who are considered obese (BMI of 30 or higher), as well as those who are overweight (BMI of 27 or higher) and have another weight-related health condition.
“There are a number of chronic weight management medications available on the market, but none are quite as effective as this new long-term option,” Murdock told Fox News Digital.
OZEMPIC AND WEGOVY WEIGHT LOSS DRUGS COULD HELP REDUCE ALCOHOL USE DISORDER SYMPTOMS, STUDY SUGGESTS
Minisha Sood, M.D., an assistant professor at the Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in New York, told GoodRx that one of Zepbound’s benefits is how well it’s tolerated by patients.
“It’s thus potentially useful for patients who do not respond well to semaglutide (Wegovy) or liraglutide (Saxenda),” she said.
“In the current climate of medication shortages, it also affords those who have been struggling with lack of access to semaglutide or liraglutide an opportunity to receive incretin-based treatment for obesity,” Sood added.
8. Roctavian for hemophilia A
In June 2023, the FDA approved Roctavian (valoctocogene roxaparvovec) to treat severe hemophilia A, a genetic bleeding disorder.
It’s the first gene therapy to combat uncontrolled and prolonged bleeding associated with this condition, according to GoodRx.
Roctavian, administered as a one-time infusion for people with hemophilia, has been shown to reduce the number of bleeding episodes by 50% each year. (iStock)
The drug, administered as a one-time infusion, has been shown to reduce the number of bleeding episodes by 50% each year.
Leonard Valentino, M.D., a hematologist and president/CEO of the National Bleeding Disorders Foundation in New York, told GoodRx that Roctavian marks a “groundbreaking leap” in hemophilia A treatment, but noted that more research is needed into its long-term effects.

Each year, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approves hundreds of new drugs and therapeutic products for use by the American public. (iStock)
“Considering gene therapy is a significant decision, and continuous discussion with medical professionals and family members is crucial to weigh the potential pros and cons,” he said.
GoodRx’s Murdock told Fox News Digital that Roctavian shows “a lot of promise” in reducing bleeding without the need to receive routine treatments, but agreed that the long-term effects are not yet fully understood.
9. Casgevy and Lyfgenia for sickle cell disease
The most common inherited blood disorder in the United States, sickle cell disease affects an estimated 100,000 people in the country, as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) noted on its website.
The disease disproportionately affects people of Black or African ancestry.
‘REMARKABLE’ GENE-EDITING TREATMENT FOR SICKLE CELL DISEASE IS APPROVED BY FDA
Patients with sickle cell disease have an inherited gene mutation that produces abnormal hemoglobin, which makes it more difficult for the cells to move through the bloodstream, per the NIH.
The diseased cells eventually get stuck in blood vessels, blocking blood flow. This can lead to painful episodes called sickle cell crises, infection, acute chest syndrome or stroke, per the CDC.
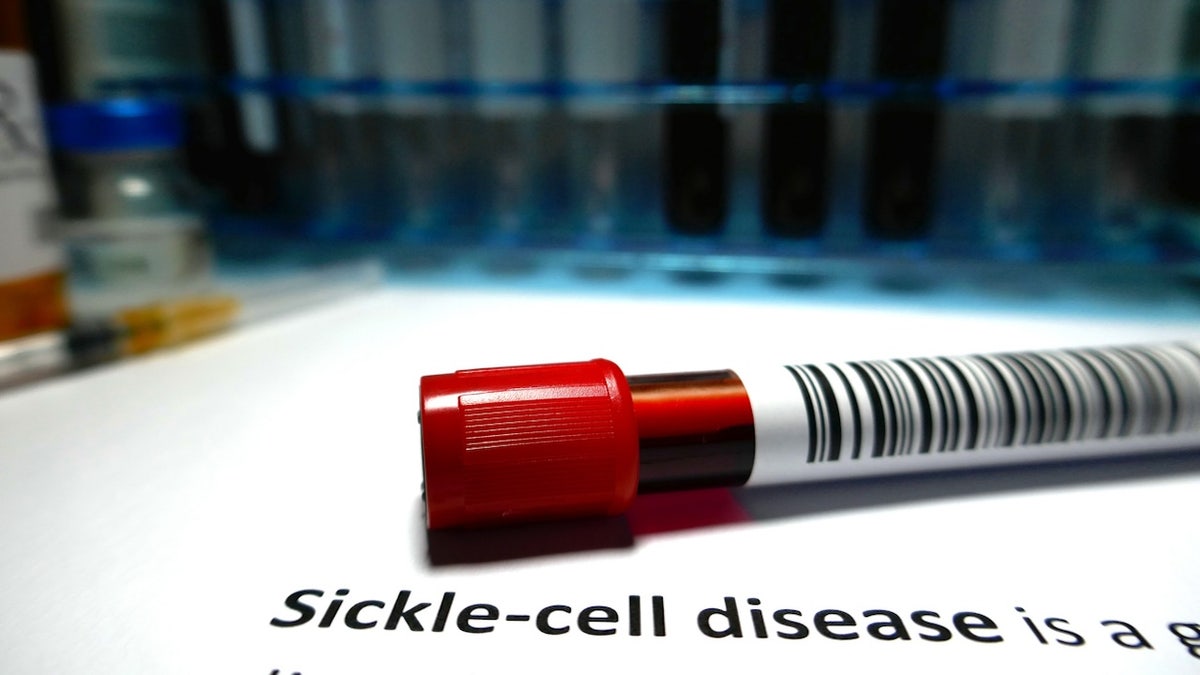
Patients with sickle cell disease have an inherited gene mutation that produces abnormal hemoglobin, which makes it more difficult for the cells to move through the bloodstream. (iStock)
On Dec. 8, the FDA approved two gene therapies for sickle cell disease, Casgevy (also called exagamglogene autotemcel, or “exa-cel”) and Lyfgenia (lovotibeglogene autotemcel, or “lovo-cel”).
The single-dose infusions are approved for patients 12 years of age and older to prevent pain crises and health complications caused by sickle cell disease.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“We at the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America Inc. have tremendous hope in [Casgevy], a potential cure for people living with sickle cell disease that could change their lives for the better,” Lewis Hsu, M.D., the Chicago-based chief medical officer of the Sickle Cell Disease Association of America, told GoodRx.
The list of influential medications was selected by Alyssa Billingsley, PharmD, Missouri-based director of pharmacy content at GoodRx, and pharmacy editor Stacia Woodcock, PharmD, in New York City — in addition to Murdock.
Shiv Sudhakar contributed reporting.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.

Health
Mom’s Gripes About Sister-in-Law Put Daughter in a Bind

My mother is hypercritical of my brother’s wife, to the point that she blames my sister-in-law for my brother’s “failings” (not getting a better job, not taking better care of his health, etc.). It has gotten worse now that there are grandchildren. My mother constantly criticizes how my sister-in-law is raising the kids, who are lovely and adore their grandparents.
Although my mother will occasionally raise criticisms with my sister-in-law and brother, I am mostly her audience.
I have a great relationship with my sister-in-law, and when my mother goes off on one of her rants, I defend her. I tell my mother how lucky she is to have such wonderful grandchildren, and point out that my brother is an adult who makes his own decisions. This just leads to an argument between my mother and me.
When I finally told my mother how much it hurts me to hear her say these things about my sister-in-law, she said that she needed to air her frustrations with someone. I want to be there for my mother, but I don’t like being put in this position. How do I navigate this?
From the Therapist: The short answer to your question is that you can navigate this by no longer engaging in these conversations. But I imagine you already know this. What you might be less aware of is that you aren’t being “put in this position” of supportive daughter, protective sister-in-law and unwilling confidante. You’ve chosen it, and it’s worth examining why you’ve signed up for a job you don’t want — and what makes it hard to resign.
Usually when we find ourselves repeatedly engaging in uncomfortable family patterns, it’s because they echo familiar roles from our childhood. It sounds as if you’re struggling with enmeshment, a relationship pattern in which boundaries between family members become blurred or are nonexistent.
Think of enmeshment as being like two trees that have grown so close together that their branches have become intertwined. While this might look like closeness, it actually prevents either tree from growing in a healthy way. In your case, your mother’s emotions and grievances have become so entangled with your own emotional life that it’s hard to distinguish where her feelings end and yours begin.
You mention wanting to “be there” for your mom even though these conversations hurt you. Many adult children who struggle to say no to their parents grew up serving as their parents’ emotional support system, or absorbing their parents’ feelings, even at the expense of their own. When you told your mother how much her venting hurt you, she responded not by acknowledging your feelings, but by asserting her need to “air her frustrations.” Her response reveals something important: She sees you as a vessel for her emotional overflow rather than as someone with valid feelings of your own. And yet, despite your hurt, you’re still more concerned about her feelings than yours.
You’re asking how to navigate this situation, but I think the deeper question is: How can you begin to value your own emotional needs?
You can start by reframing what it means to make a reasonable request, which is essentially what setting a boundary is. A boundary isn’t about pushing someone away. Instead, it’s about making a bid for connection. It’s saying: “I want to feel good being close to you, but when you do X, it makes me want to avoid you. Help me come closer.”
Establishing a boundary consists of three steps:
-
State the issue and the desire to come closer (what will make this possible): “Mom, I love you and want to support you, but these conversations about my sister-in-law put me in an impossible position and make me want to avoid talking with you, which I know isn’t what either of us wants. I’m happy to talk about other things together, but in order to keep our relationship strong, I need this topic to be off limits.”
-
Set the boundary (what you will do): “If you’re struggling with their choices, I’m happy to support you in finding a therapist who can help you work through these feelings. But if you bring up these frustrations with me, I’m going to end the conversation and we can talk another time about other things.”
-
Hold the boundary (do what you say): A boundary isn’t about what the other person will or won’t do. A boundary is a contract with yourself. If you say you’ll end the conversation when your mom brings up your sister-in-law, you need to hold that boundary every single time. If you end the conversation only 90 percent of the time, then why would the other person honor your request when 10 percent of the time, you can’t honor it yourself? Honoring your request might sound like: “Mom, I’m going to end the conversation now because I’m not comfortable talking about my sister-in-law. I love you, and we’ll talk later.”
If you start to feel guilty, remember that just because someone sends you guilt doesn’t mean you have to accept delivery. Remind yourself that when you become your mother’s outlet for criticism of your sister-in-law, you’re participating in a cycle that strains loyalties and causes you personal distress. And keep in mind that being a good daughter means setting boundaries that encourage our parents to grow, rather than enabling patterns that harm our family relationships.
Want to Ask the Therapist? If you have a question, email askthetherapist@nytimes.com. By submitting a query, you agree to our reader submission terms. This column is not a substitute for professional medical advice.
Health
Cancer death rates decline yet new diagnoses spike for some groups, says report

Alcohol linked to 7 types of cancer
Dr. Nicole Saphier joins ‘America’s Newsroom’ to discuss the surgeon general pushing for cancer warning labels on alcohol and the CDC warning of norovirus cases surging in parts of the U.S.
A major annual cancer report has revealed a mix of good news and points of concern.
Cancer diagnoses are expected to exceed two million in 2025, with approximately 618,120 deaths predicted, according to the American Cancer Society’s annual cancer trends report, which was published today in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
ACS researchers compiled data from central cancer registries and from the National Center for Health Statistics.
ALCOHOL LINKED TO CANCER RISK IN US SURGEON GENERAL’S NEW ADVISORY
While mortality rates have declined, certain groups are seeing a spike in diagnoses, the report noted.
Cancer diagnoses are expected to exceed two million in 2025, with approximately 618,120 deaths predicted. (iStock)
“Continued reductions in cancer mortality because of drops in smoking, better treatment and earlier detection is certainly great news,” said lead author Rebecca Siegel, senior scientific director of surveillance research at the ACS in Georgia, in a press release.
“However, this progress is tempered by rising incidences in young and middle-aged women, who are often the family caregivers, and a shifting cancer burden from men to women, harkening back to the early 1900s, when cancer was more common in women.”
Overall decline in death rates
Cancer death rates dropped 34% between 1991 and 2022, according to the ACS report.
That equates to approximately 4.5 million deaths avoided due to early detection, reductions in smoking, and improvements in treatment, the report stated.
Cancer death rates dropped 34% between 1991 and 2022.
Several factors likely contributed to this decline, noted John D. Carpten, Ph.D., chief scientific officer at City of Hope, a national cancer research and treatment organization in California.
“I think a big one is smoking cessation and the battle against lung cancer, which has always been the most common form of cancer and is tied to tobacco use,” Carpten told Fox News Digital in an on-camera interview.
“Screening programs are a critical component of early detection, and expanding access to these services will save countless lives.” (iStock)
“But without a doubt, I think new and better methods for early detection, and screening for colorectal cancer and other forms of the disease, have also allowed us to see a decrease.”
Lifestyle improvements have also helped to decrease mortality, he said, along with the development of new and better therapies for cancer.
LIVER CANCER PATIENT GIVEN 6 MONTHS TO LIVE LOSES 76 POUNDS EATING SPECIFIC FOODS
Despite overall declines in mortality, the report revealed that death rates are rising for cancers of the oral cavity, pancreas, uterine corpus and liver (for females).
Some common cancers have also seen an increase in diagnoses, including breast (female), prostate, pancreatic, uterine corpus, melanoma (female), liver (female) and oral cancers associated with the human papillomavirus, the report stated.
Increased diagnoses among certain groups
Diagnoses for many cancer types are increasing among certain groups.
Cancer rates for women 50 to 64 years of age have surpassed those for men, the report revealed. For women under 50, rates are 82% higher than males in that age group.

The report revealed that diagnoses of colorectal cancer in men and women under 65 and cervical cancer in women between 30 and 44 years of age has increased. (iStock)
As far as what is influencing the “disconcerting trend” in women’s cancers, Carpten said it is likely “highly nuanced” and will require additional research.
“The decrease in fertility and increases in obesity that we’ve seen are risk factors for breast cancer, especially in postmenopausal middle-aged women,” he said.
“But there could be other modifiable risk factors at play, like alcohol and physical activity.”
Cancer rates for women 50 to 64 years of age have surpassed those for men.
Another trend in the increase in early cancers is occurring in individuals under the age of 50, Carpten noted.
In particular, the report revealed that diagnoses of colorectal cancer in men and women under 65 and cervical cancer in women between 30 and 44 years of age has increased.

Some common cancers have also seen an increase in diagnoses, including breast (female), prostate, pancreatic, uterine corpus, melanoma (female), liver (female) and oral cancers associated with the human papillomavirus. (iStock)
The report also discusses inequities in cancer rates among certain ethnic groups, with Native American and Black people experiencing higher diagnoses of some cancer types.
“Progress against cancer continues to be hampered by striking, wide static disparities for many racial and ethnic groups,” said senior author Dr. Ahmedin Jemal, senior vice president of surveillance and health equity science at the ACS, in the release.
AI DETECTS OVARIAN CANCER BETTER THAN HUMAN EXPERTS IN NEW STUDY
The report shows mixed trends for children, with diagnoses declining in recent years for patients 14 years of age and younger, but rising for adolescents between 15 and 19.
“Mortality rates have dropped by 70% in children and by 63% in adolescents since 1970, largely because of improved treatment for leukemia,” the ACS stated in the release.
Pancreatic cancer a growing concern
The ACS report also warns about “lagging progress” against pancreatic cancer, the third-leading cause of cancer death in the U.S.
The ACS report also warns about “lagging progress” against pancreatic cancer, the third-leading cause of cancer death in the U.S. (iStock)
Rates of diagnoses and deaths from the disease type are on the rise.
“Pancreatic is an incredibly deadly form of cancer,” Carpten said.
One of the main issues with pancreatic cancer, he said, is that it sometimes can grow in an individual for up to 10 years before it’s detected.
“If we can identify those cancers when they’re at at a curable stage, we can improve outcomes.”
One of the best opportunities for beating pancreatic cancer is early detection, Carpten said.
“By the time those cancers have advanced, they’ve spread to the liver or other organs, and they’re almost impossible to cure at that stage,” he said.
“If we can identify those cancers when they’re at a curable stage, we can improve outcomes.”
‘It takes a village’
Making progress in fighting cancer “takes a village,” Carpten told Fox News Digital.
“It will require partnerships between the community, the health care system, cancer researchers, government, industry — we all have to work together if we want to continue to see a decrease and an ultimate increase in cures,” he said.

“We all have to work together if we want to continue to see a decrease and an ultimate increase in cures,” a cancer researcher said. (iStock)
Dr. Wayne A. I. Frederick, interim chief executive officer of the American Cancer Society and the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network (ACS CAN), stated that the report highlights the need to “increase investment in both cancer treatment and care, including equitable screening programs.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“Screening programs are a critical component of early detection, and expanding access to these services will save countless lives,” he said in the release.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“We also must address these shifts in cancer incidence, mainly among women. A concerted effort between health care providers, policymakers and communities needs to be prioritized to assess where and why mortality rates are rising.”
Fox News Digital reached out to the ACS for further comment.
Health
FDA Moves Forward With Last-Minute Push to Cut Nicotine Levels in Cigarettes

The Biden administration unveiled a proposal on Wednesday to cut the level of nicotine in cigarettes, a last-minute push on a plan that could meaningfully cut cancer rates nationwide and extend the lives of millions of cigarette smokers.
If finalized, the proposal would require cigarette makers to significantly reduce the levels of nicotine in their products in an effort to make smoking less addictive and less satisfying. Research has suggested that the move would result in fewer people taking up the habit and would help the nation’s roughly 30 million smokers quit or switch to less harmful alternatives like e-cigarettes.
The policy is a centerpiece of antismoking initiatives by Dr. Robert Califf, commissioner of the Food and Drug Administration, who has recounted treating cardiology patients ravaged by smoking during his medical career.
“It’s the biggest thing I’ve ever seen in terms of societal benefit, cost saving and lives saved, and strokes prevented and cancers prevented,” Dr. Califf said.
The policy’s companion effort to ban menthol cigarettes has been set aside indefinitely after vehement opposition from cigarette makers and other opponents, including convenience store retailers.
Whether the nicotine reduction plan would survive the incoming administration of President-elect Donald J. Trump is unclear. Mr. Trump has traditionally been industry friendly and opposed to heavily regulating businesses. In addition, he has had the support of tobacco companies, including Reynolds American, which contributed at least $8 million to Mr. Trump’s main super PAC during the presidential campaign. Reynolds has already expressed its opposition to the proposed requirement.
Mr. Trump’s campaign co-chair and incoming chief of staff, Susie Wiles, is a former lobbyist for Swisher, a company that makes cigars. The rule applies to cigarettes, roll-your-own tobacco, pipe tobacco and cigars (though not premium cigars).
Some public health advocates are holding out hope that the Trump administration will allow the proposal to move forward, given that a previous version was considered by the F.D.A. during his first term. At minimum, officials could continue to allow the public to comment on the initiative without killing it or putting it into effect.
The F.D.A.’s proposal includes projections that by 2100, the nicotine reduction measure would prevent an estimated 48 million young people from starting to smoke. By 2060, the agency also estimates that 1.8 million tobacco-related deaths would be prevented, and that $30 trillion in benefits would accrue over 40 years, mostly from the generation that would not begin smoking.
“We do have an extremely toxic and addictive product with cigarettes that remain on the marketplace, that still kills almost a half a million people a year,” said Dorothy Hatsukami, a tobacco researcher from the University of Minnesota who has studied low-nicotine cigarettes for about 15 years. “So it’s really kind of an unfortunate situation that we haven’t really done anything dramatically about it.”
In 2022, Dr. Califf released an updated proposal to lower nicotine levels, and opposition began to grow almost immediately.
Tobacco companies have viewed the initiative as a major threat to their business. Luis Pinto, a spokesman for Reynolds American, said the proposal would “effectively eliminate legal cigarettes and fuel an already massive illicit nicotine market.”
“These actions would also have a significant negative economic impact on farmers, retailers and others,” he added.
Convenience store retailers have also opposed earlier versions of the proposal, saying they would sustain substantial losses in revenue from a projected decline in cigarette sales.
Congressional Republicans have also tried to thwart restrictions on nicotine levels. In 2023, members of an influential House subcommittee passed a measure that would have prevented the F.D.A. from spending any money to advance limits on nicotine, with nearly all of the supporting votes by Republicans. The Senate did not include the provision in a final budget package.
Still, supporters of the plan point to signs that incoming public health officials may be receptive to it, including to the popularity of Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s pledge to tackle chronic diseases and improve the health of Americans if he is confirmed to lead the nation’s top health agency. Mr. Trump himself has said that he is personally opposed to cigarette smoking.
“Given these enormous benefits, we urge the incoming Trump administration to move forward in finalizing and implementing this rule,” Yolonda C. Richardson, the president of Campaign for Tobacco-Free Kids, said in a statement. “Few actions would do more to fight chronic diseases such as cancer and cardiovascular disease that greatly undermine health in the United States, and that the incoming administration has indicated should be a priority to address.”
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science5 days ago
Science5 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago‘How to Make Millions Before Grandma Dies’ Review: Thai Oscar Entry Is a Disarmingly Sentimental Tear-Jerker
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoMichael J. Fox honored with Presidential Medal of Freedom for Parkinson’s research efforts
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: Millennials try to buy-in or opt-out of the “American Meltdown”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoMeta Drops Rules Protecting LGBTQ Community as Part of Content Moderation Overhaul















