Health
Domestic violence brain injuries likely outnumber head trauma from football players
NEWNow you can take heed to Fox Information articles!
Home violence victims probably undergo a better fee of mind trauma than soccer gamers and troopers, however the precise quantity is unknown as a result of many of those accidents, which overwhelmingly happen in ladies, are by no means recognized, in accordance with the New York Occasions.
“Individuals may suppose, somebody smacked her within the head or pushed her, no large deal,” says Dr. Eve M. Valera, affiliate professor of psychiatry at Harvard College and a number one skilled on traumatic mind accidents amongst home violence survivors.
In 1990, Dr. Gareth Roberts evaluated the mind of a 76-year-old lady who died after years of abuse from her husband who was reported to have develop into ‘demented’ in her last years, in accordance with the information outlet.
Dolak’s accidents included a cranium fracture, mind hemorrhaging, and everlasting harm to an optical nerve.
(North Information and Photos)
However he found on post-mortem that her mind was just like these sufferers with Alzheimer’s and appropriate “to a level” with boxers who suffered from continual traumatic encephalopathy, and the case turned the primary connection within the literature between neurogenerative illness and abused ladies, in accordance with the Occasions.
Intimate accomplice violence (IPV) contains bodily, sexual or psychological abuse in a romantic relationship that roughly one in 4 ladies or one in 10 males have skilled as sexual or bodily violence and/or stalking throughout their lifetime, in accordance with the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention.
Strangulation is outlined because the exterior obstruction of blood vessels and/or airflow within the neck leading to lack of oxygen, in accordance with The Coaching Institute on Strangulation Prevention.
INFLATION, WAR, COVID PANDEMIC PUSHING US STRESS LEVELS THROUGH THE ROOF, POLL SAYS
Roughly 68% of IPV victims expertise near-strangulation, however solely half have seen indicators of trauma with solely 15% of those that do present proof of accidents subsequently photographed to doc the abuse, per the Institute.
However lack of consciousness can happen inside seconds and dying can comply with inside minutes throughout strangulation, with the Institute noting the percentages improve by 750% for an IPV survivor of 1 strangulation to be killed in comparison with somebody who has not been strangulated.
The company’s choice on Brineura, which is manufactured by Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc, got here on Thursday and can profit sufferers recognized with CLN2, simply one of many 14 variations of Batten illness.
(iStock)
Frequent indicators of strangulation embody petechiae (small pink spots brought on by bleeding underneath the pores and skin) on the face, eyeballs and eyelids, swelling, scratch marks and abrasions across the neck, in accordance with a Strangulation in Intimate Associate Violence Truth Sheet.
The very fact sheet additionally notes victims might complain of reminiscence loss, dizziness, complications, a hoarse voice, problem swallowing or respiration.
Due to these signs, victims might have problem processing the occasion and infrequently don’t report it to the police, so many home assaults largely go unnoticed, per the Occasions.
The frequency and severity of the signs makes it ” … troublesome to suppose via or deal with the advanced, typically formidable organizational duties required for battered ladies to cease the violence, disengage from violent companions and/or set up unbiased lives,” stated the authors of a home abuse 2002 research, the place virtually all contributors had suffered head trauma with 40% dropping consciousness.
Despite the fact that a lot of the analysis relating to concussions and neurogenerative illness comes from learning male brains, among the analysis suggests ladies are extra inclined to concussions partly as a result of males have extra muscular necks to cushion a blow to the top and ladies have leaner nerve fibers, often called axons, that shear extra simply throughout trauma, in accordance with the Occasions.
However ladies additionally could also be extra weak to post-concussive signs due to intercourse hormones variations with analysis pointing to a progesterone disruption that happens presumably due to affect on the pituitary gland within the mind. A number of research counsel if a sufferer occurs to be in her menstrual cycle throughout the traumatic occasion, she will be able to undergo extra nervousness and despair afterward in comparison with males, per the Occasions.
WHO SAYS GLOBAL ANXIETY AND DEPRESSION INCREASED 25% DUE TO COVID-19 PANDEMIC
“A lot cash goes into investigating concussions in sports activities that these protocols and papers go on to form the way in which concussions generally are thought of,” stated Stephen Casper, professor of historical past of Clarkson College.
“There’s no cash to be comprised of learning intimate-partner abuse.”

Alesha Dixon leads folks holding banners throughout an illustration in opposition to home violence
(AP2013)
The Authorities Accountability Workplace launched a report in 2020 concluding that IPV impacts over 30% of women and men in the US, however acknowledged as a result of the general prevalence information on these accidents is unknown, this has precipitated a lack of knowledge of the problem.
The Occasions compares extreme mind accidents to highly effective earthquakes, however as an alternative of bridges and buildings crumbling, our bones fracture as hemorrhages later erupt with uncooked painful facial wounds.
“However delicate mind accidents are smaller quakes: Books fall off cabinets; vases are damaged. It’s tougher to survey the harm and simple to overlook what’s damaged, however one thing is clearly unsuitable,” the paper stated.
CLICK HERE TO DOWNLOAD THE FOX NEWS APP
Name the Nationwide Home Violence Hotline at 1-800-799-SAFE or click on right here for extra sources in case you need assistance.

Health
Denise Austin’s Healthy Warm Weather Eating Tips to Help You Lose Weight

Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Health
Army unveils new fitness test with tougher standards — could you pass it?

“Army Strong” is more than just a tagline — for soldiers, it’s a requirement for duty.
The U.S. Army requires that all active-duty soldiers prove their physical prowess by passing a rigorous fitness test. There have been multiple versions of the test over the years — and the Army recently announced that a new version has been adopted.
On June 1, 2025, the military branch will roll out its new Army Fitness Test (ACFT) as a replacement for the current Army Combat Fitness Test (ACFT).
WALKING CERTAIN NUMBER OF STEPS DAILY REDUCES CANCER RISK, OXFORD STUDY FINDS
The new test — which is based on “18 months of data analysis and feedback from thousands of test iterations” — will introduce updated scoring standards that emphasize “readiness and combat effectiveness,” according to an Army press release.
Soldiers will have until Jan. 1, 2026, to meet the new AFT requirements without facing “adverse actions.”
The U.S. Army requires that all active-duty soldiers prove their physical prowess by passing a rigorous fitness test. (iStock)
AFT scores are recorded during basic training for soldiers and initial training for officers, the Army states on its website.
Active-duty soldiers are required to complete the test twice a year, while soldiers in the Army Reserve and Army National Guard must record scores once a year.
EXERCISE CAN PREVENT COGNITIVE DECLINE EVEN WHEN ENERGY LAGS, RESEARCHERS DISCOVER
“The AFT is designed to improve soldier readiness and ensure physical standards [and] prepare soldiers for the demands of modern warfare,” said Sgt. Maj. Christopher Mullinax, senior enlisted leader, deputy chief of staff for Operations, Army Headquarters, in the release.
“It emphasizes holistic fitness over event-specific training and is grounded in performance.”

Recruits undergo physical training in the training center of The Third Separate Assault Brigade on September 14, 2024, in Dnipro, Ukraine. (Getty Images)
Scoring requirements are more demanding for the new test, with soldiers in combat roles held to the highest standards.
“Combat standards are sex-neutral for the 21 direct combat roles, a change designed to ensure fairness and operational readiness,” the release states.
5 components of the test
The AFT consists of the following five events, as described on the Army’s website.
1. Three-repetition maximum deadlift
In this challenge, the soldier must lift the maximum weight possible three times using a 60-pound hex bar and plates.
This move assesses muscular strength, balance and flexibility.
“It’s doable — but only with smart, progressive training.”
“Deadlifts require a person to recruit glute and hamstring strength in order to lift a barbell off the ground to waist height,” said Miles Hill, a certified personal trainer and boxing instructor at Rumble in New York City. “It is the most effective technique for picking heavy weights off the ground.”
The deadlift can also be dangerous for civilians if they use improper form, warned Dr. Hooman Melamed, an orthopedic spine surgeon and sport medicine expert from Beverly Hills.

Army soldiers must complete a timed two-mile run on a flat outdoor course in a test of aerobic endurance. (iStock)
“If your posture or form is off, the risk to your lower back and hips is high — it could be a career-ending injury for some,” he told Fox News Digital.
2. Hand-release push-up
The soldier must complete as many hand-release push-ups as possible in two minutes, using proper technique.
“Hand release push-ups require a person to drop all the way to the ground, lift their hands in the air for a second, and then push themselves back up to high plank,” said Hill, who is also a second-degree black belt in Taekwondo.
NYPD DETECTIVE SHARES GRUELING WORKOUTS TO MOTIVATE COPS TO GET IN SHAPE
Melamed noted that while hand-release push-ups are great for building upper body strength, if the person is not already strong, the sudden force can damage the shoulders.
The hand-release push-up tests muscular endurance and flexibility.
3. Sprint-drag-carry
With the sprint-drag-carry (SDC), the soldier is tasked with completing five 50-meter shuttles (sprint, drag, lateral, carry, sprint) as quickly as possible, using two 40-pound kettlebells and a 90-pound sled.
“The sprint-drag-carry is probably the toughest sequence here, since it requires explosive strength, muscular endurance and cardiovascular endurance,” Hill said.
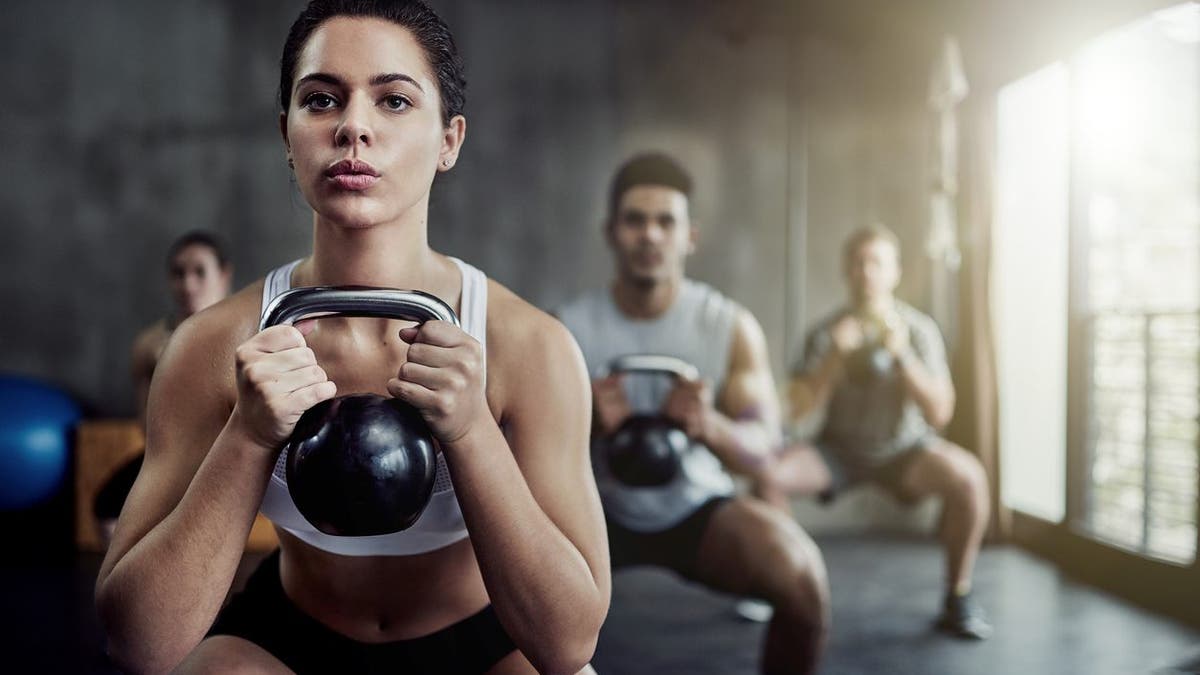

“Combat standards are sex-neutral for the 21 direct combat roles, a change designed to ensure fairness and operational readiness,” the Army’s release states. (Cecilie_Arcurs)
Melamed calls the SDC a “brutal test of speed and explosive power.”
“If you’re not conditioned, tearing a hamstring or pulling something mid-run can happen,” he said.
4. Plank
The soldier must maintain a proper plank position for as long as possible, testing muscular endurance and balance.
“A plank is an ultimate test of core strength and endurance, as it requires a person to hold their body weight for as long as they can,” said Hill. “It can be challenging, but it is the time requirement that determines the challenge.”
CRUNCHES BY AGE: HERE’S HOW MANY YOU SHOULD BE ABLE TO DO
Melamed noted that while this move looks simple, holding a proper plank for time is extremely challenging. “It exposes weaknesses in the back, core and shoulder girdle.”
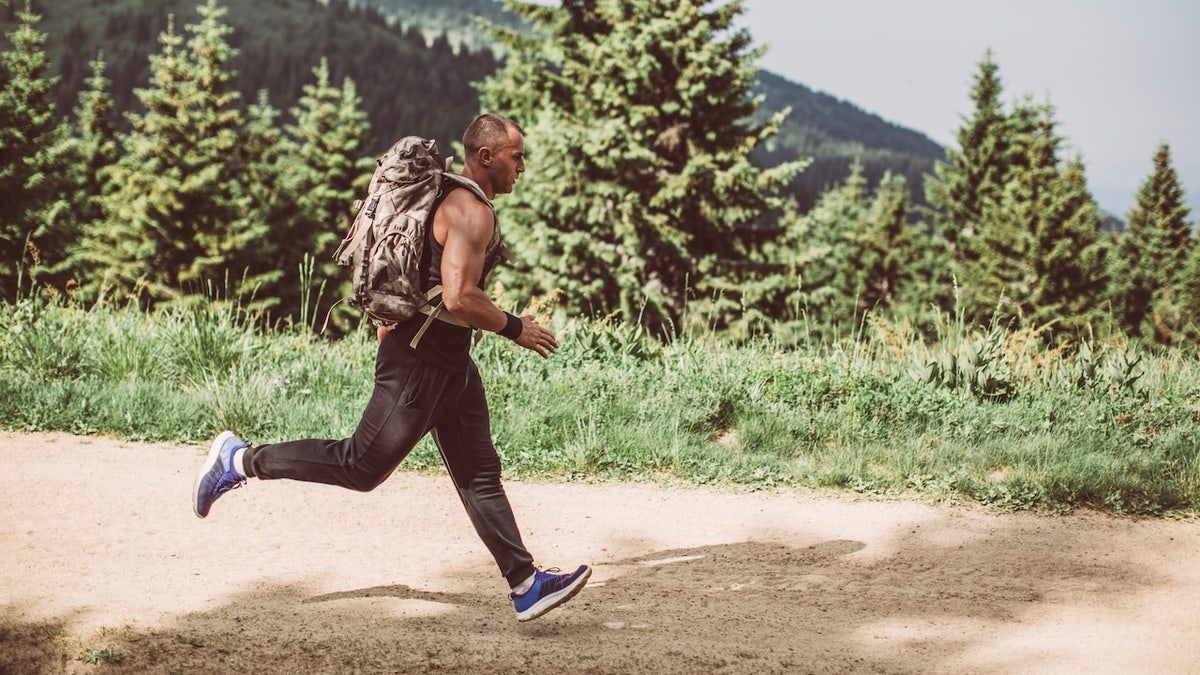
5. Two-mile run
The soldier must complete a timed two-mile run on a flat outdoor course in a test of aerobic endurance.
“Two-mile runs are relatively easy for any able-bodied human — however, the time constraints are what makes it challenging,” Hill said.
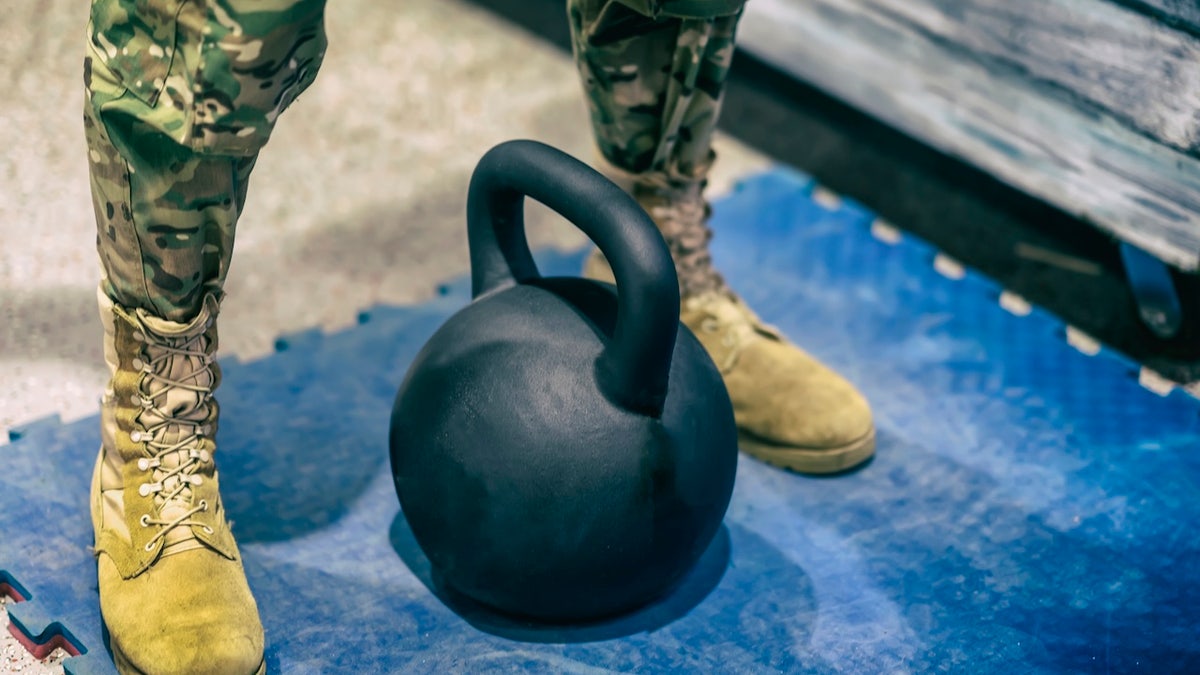

With the sprint-drag-carry (SDC), the soldier is tasked with completing five 50-meter shuttles (sprint, drag, lateral, carry, sprint) as quickly as possible, using two 40-pound kettlebells and a 90-pound sled. (iStock)
The standing power throw event, which was part of the previous version of the test, is no longer included as a requirement.
“We eliminated the standing power throw because it wasn’t effectively promoting fitness and readiness as well as we would like,” Mullinax said.
“Furthermore, it presented an elevated risk of overuse injury and encouraged soldiers to focus on technique rather than demonstrating true power.”
How tough is it?
The toughness of a workout or fitness test is relative to the overall fitness of an individual, according to Dr. Jason Perry, M.D., primary care sports medicine physician with Baptist Health Orthopedic Care in Deerfield Beach, Florida.
STAY FIT IN YOUR 40S AND BEYOND WITH THESE SMART WORKOUT TIPS
“Generally speaking, the AFT is challenging, but not impossible for the average person with a basic fitness foundation,” Perry, who is unaffiliated with the Army, told Fox News Digital.
“It’s designed to test full-body strength, muscular endurance, speed, agility and cardiovascular stamina — all elements essential for combat readiness, but also relevant to functional fitness for civilians.”
Compared to a typical gym workout, the AFT is more demanding because it combines different physical domains into one test, he said.
“Compared to elite athletic training, it’s moderate — but not easy,” Perry added.
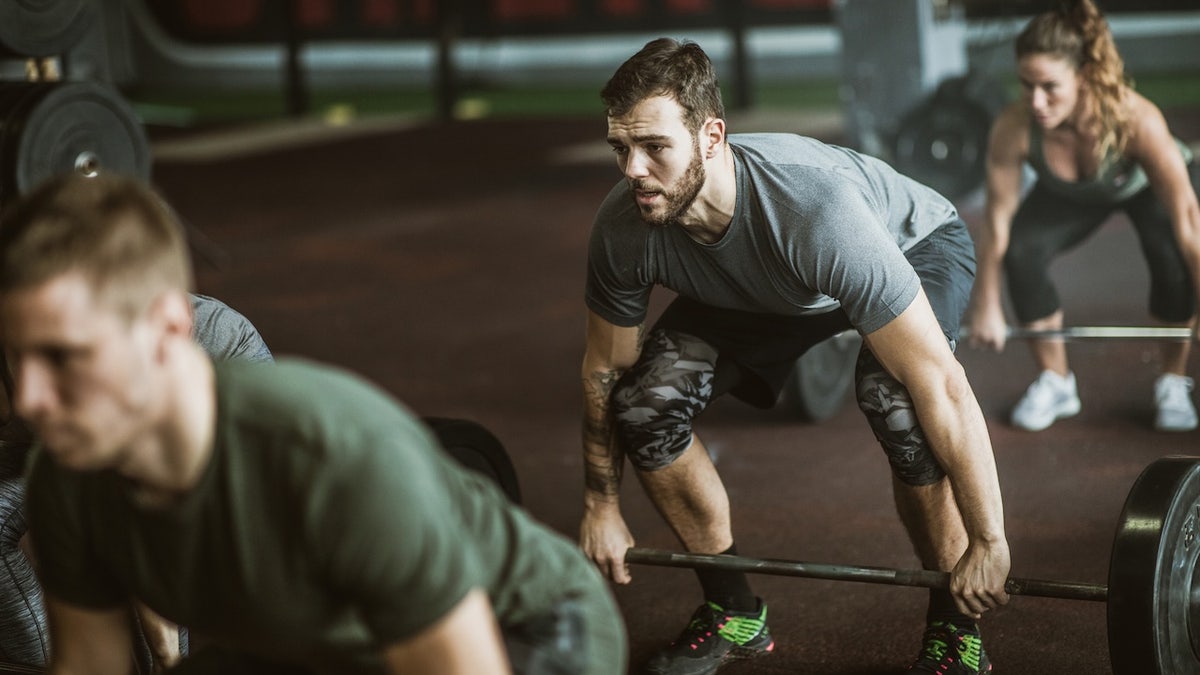

In the three-repetition maximum deadliftIn this challenge, the soldier must lift the maximum weight possible three times using a 60-pound hex bar and plates. (iStock)
For civilians who regularly strength train, run or do functional workouts (like CrossFit or HIIT), this test is well within reach, he said.
For a civilian who exercises three to four times a week, the AFT is “realistically achievable” with focused training over an eight- to 12-week period.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“About 30 to 50% of healthy, recreationally active adults could likely pass it with little to moderate training,” he predicted. “Sedentary adults or those with chronic conditions would have a harder time and would likely need a focused eight- to 12-week (or possibly longer) conditioning plan to pass.”
Melamed wasn’t quite as optimistic, estimating that less than 5% of civilians could pass the AFT.
“If you try this unprepared, you could get seriously hurt.”
“These aren’t weekend-warrior workouts — this is military-level conditioning,” he told Fox News Digital. “You have to work your way up to this level of intensity training.”
The expert also noted that there is a mental component to the test, but said mindset alone isn’t enough.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“If you try this unprepared, you could get seriously hurt,” he cautioned. “It’s doable — but only with smart, progressive training. You have to work up to it gradually.”
“And this test is as much about strategy and recovery as it is about raw strength.”
Health
Big Mac Salad For Weight Loss: How to Get The Benefis | Woman's World
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoBook Review: ‘Original Sin,’ by Jake Tapper and Alex Thompson
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoA $5 Billion Federal School Voucher Proposal Advances in Congress
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoVideo: Opinion | We Study Fascism, and We’re Leaving the U.S.
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLove, Death, and Robots keeps a good thing going in volume 4
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoAs Harvard Battles Trump, Its President Will Take a 25% Pay Cut
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta’s beef with the press flares at its antitrust trial
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMenendez Brothers Resentenced to Life With Parole, Paving Way for Freedom
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRepublicans say they're 'out of the loop' on Trump's $400M Qatari plane deal