Health
COVID-19 pandemic: How has it changed after two years?

NEWNow you can hearken to Fox Information articles!
How has the COVID-19 pandemic modified after two years?
Extra international locations are shifting towards a return to regular and studying to dwell with the virus. Secure, efficient vaccines have been developed and there is higher understanding of find out how to deal with individuals sickened by the virus.
REPUBLICANS DEMAND TSA ALLOW COVID MASK MANDATE TO EXPIRE
Two years after the pandemic started, questions stay in regards to the coronavirus. However specialists know much more about find out how to preserve it underneath management.
The virus primarily spreads via the air when an contaminated particular person exhales, talks, coughs or sneezes. It is why well being officers have inspired using masks and ventilating areas, as an alternative of specializing in recommendation to wipe down surfaces as they did early on.
FILE — Registered nurse Bryan Hofilena attaches a “COVID Affected person” sticker on a physique bag of a affected person who died of coronavirus at Windfall Holy Cross Medical Middle in Los Angeles, Tuesday, Dec. 14, 2021.
(AP Picture/Jae C. Hong, File)
Remedy has additionally advanced for individuals who get sick or must be hospitalized. Among the many choices are antivirals, such because the drug remdesivir, or newer capsules from Pfizer and Merck; anti-inflammatory medication together with steroids; and relying on what variant is circulating, lab-made antibodies to assault the virus.
HAWAII BECOMES LAST STATE TO LIFT MASK MANDATE, IDAHO ENDS COVID-19 DISASTER DECLARATION
“The world has watched us study in real-time find out how to deal with COVID-19,” says Neil J. Sehgal, an assistant professor of well being coverage and administration on the College of Maryland Faculty of Public Well being.
COVID-19 vaccines had been additionally developed in file time. As of early March, 10 vaccines have been cleared for emergency use by the World Well being Group.
Nonetheless, distribution of vaccines has been unequal regardless of a world effort to ship pictures extra pretty and misinformation has fueled hesitancy in regards to the pictures.
And there’s nonetheless a lot left to study. Research are underway to raised perceive lengthy COVID-19, which may persist for months after an preliminary an infection. And scientists are looking out for the subsequent fast-spreading variant.
“Finally each nation should study to dwell with COVID,” says Sehgal.

Health
Young vaper who required double lung transplant shares warnings as e-cigarette sales rise
MINNEAPOLIS – E-cigarette sales are climbing — and it’s primarily young people who are getting hooked.
Those between the ages of 18 and 24 vape the most, but 9% of youth between 11 and 15 years old say they’re regular vapors, according to data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
One of them, 22-year-old Jackson Allard of North Dakota, almost lost his life due to his vaping habit — and now he’s warning others of the dangers.
SMOKING CIGARETTES CAN DESTROY LUNGS, BUT SHOCKING NEW STUDY REVEALS WHY VAPING CAN HARM THE HEART
Besides leading to addiction, vaping can cause permanent lung damage, according to the CDC.
Last October, Allard developed parainfluenza, which led to pneumonia and then acute respiratory distress syndrome. His lungs were full of fluid.
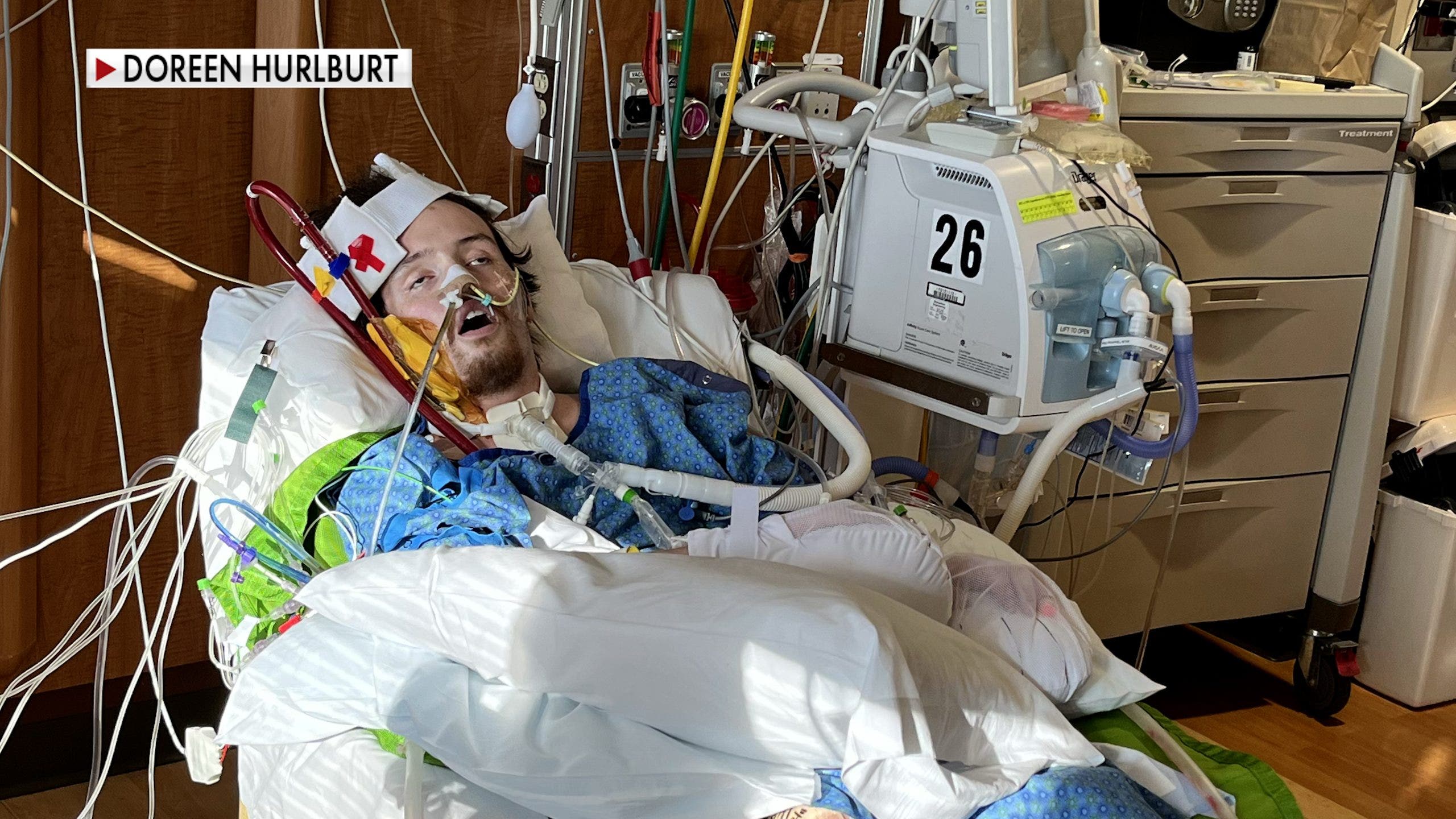
Jackson Allard, pictured, was in the hospital for three months before he was healthy enough to qualify as a transplant recipient. Now he meets weekly with other lung transplant recipients for rehab. “I’m the youngest person by far, so it’s a little weird,” Allard said. (Doreen Hurlburt )
“I was really sick, barely able to sleep, puking constantly,” Allard told Fox News.
The young man was on ECMO, a form of life support, for 70 days.
“I had a 1% chance to live,” Allard said.
His lungs were damaged so badly that in Jan. 2024, he received a double lung transplant — a rare procedure for someone his age.
SMOKING SHRINKS THE BRAIN AND DRIVES UP ALZHEIMER’S RISK, NEW STUDY FINDS
“The first thing that went through my head was, ‘Can I live a normal life after this?’” Allard said.
Allard and his family live in Fargo, North Dakota, but they’re renting an apartment in Minneapolis while he recovers from his transplant.
Twice a week, he attends rehabilitation and gets weekly bloodwork. He also gets his PICC line, a tube connected to his veins for long-term medication, cleaned each week. Allard takes 30 pills a day and his family is responsible for giving him his IV medication.
“I had a 1% chance to live.”
Based on his doctors’ input, Allard and his grandmother, Doreen Hurlburt, believe vaping is to blame for his lung failure.
“When I first started vaping, I was probably 14. I was pretty much non-stop doing it,” Allard said. He later started using a weed vape as well.
“I told my friend who smokes weed, I was like, ‘Be careful with that,’” Allard said, suggesting that people use marijuana gummies instead of vapes.
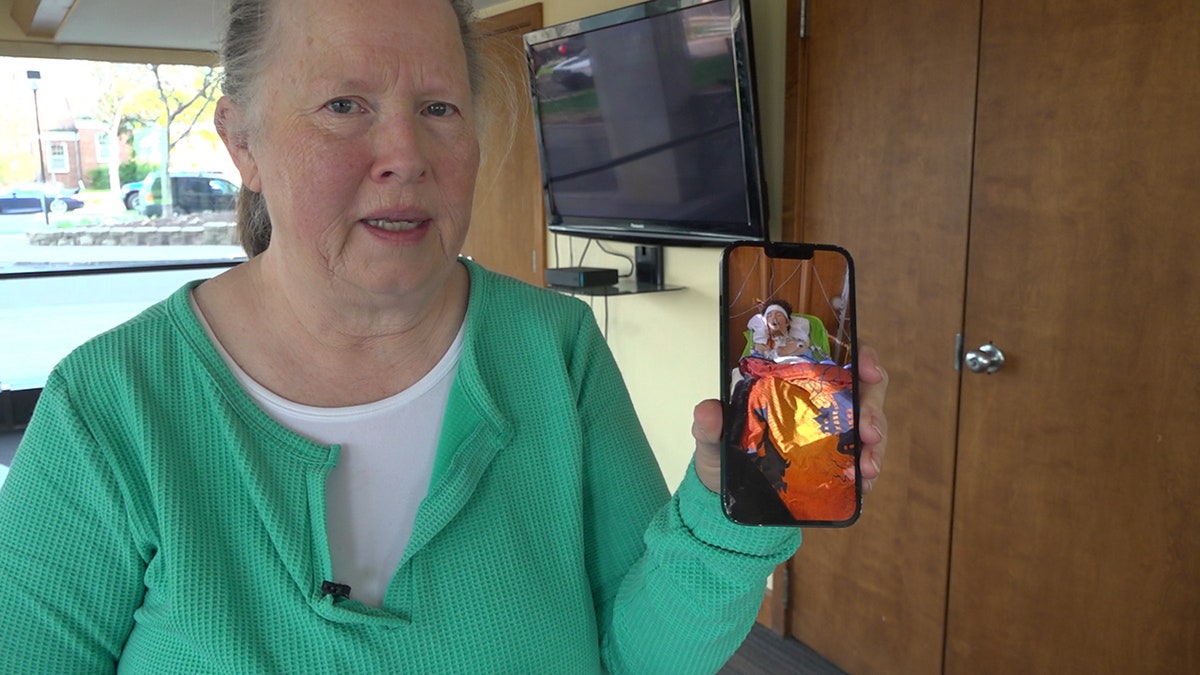

“It’s just scary to know that we can make a misstep and cause something bad to happen,” said Doreen Hurlburt, Jackson’s grandmother, pictured here. (Mills Hayes/Fox News)
His grandmother, Doreen Hurlburt, said she complained daily about Jackson’s vaping habits.
“Multiple doctors said, ‘If you smoke cigarettes for 50 years, we’ll see you with lung cancer, and if you vape for five years, we’ll see you with permanent lung damage,’” Hurlburt told Fox News.
Allard can’t drink alcohol or smoke, and his weakened immune system means he has to avoid big crowds.
FIRST NEW ‘QUIT-SMOKING’ DRUG IN 20 YEARS SHOWS PROMISING RESULTS IN US TRIAL: ‘HOPE AND EXCITEMENT’
Dr. Brooke Moore, a pediatric pulmonologist at Children’s Minnesota, did not treat Allard but often sees patients with vaping-related lung injuries.
“We’ve seen kids who have been vaping for short periods of time, and not necessarily with heavy use, come in with pretty significant lung injury from that,” Moore told Fox News.
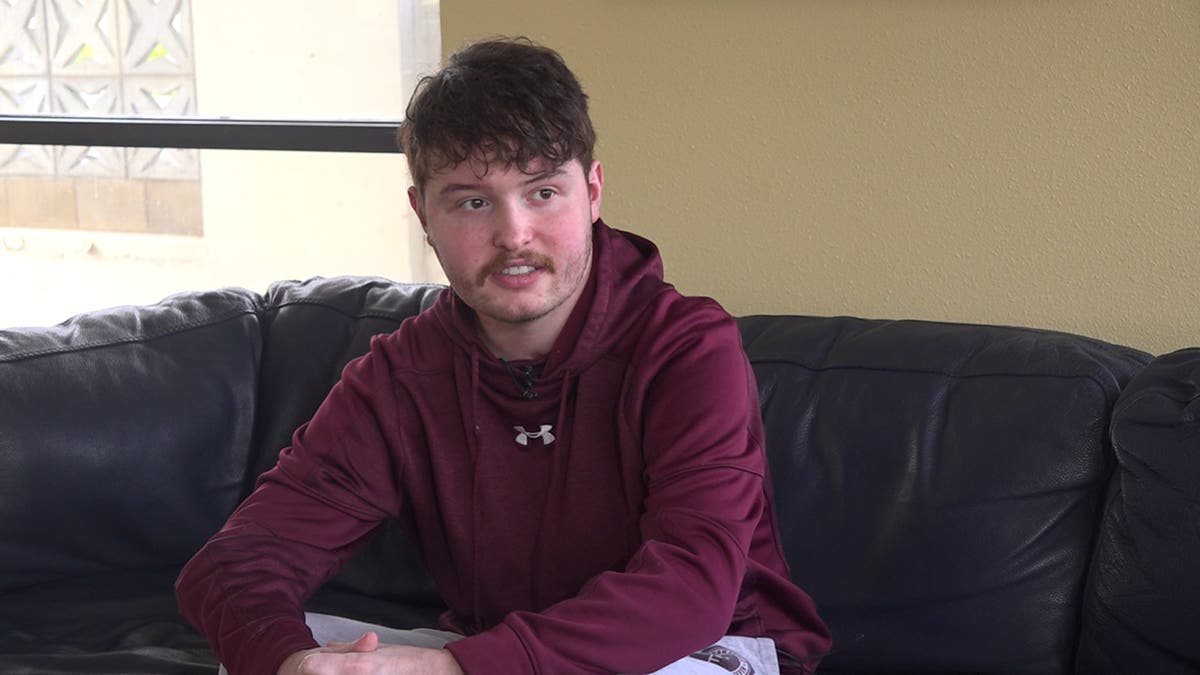

Most of Allard’s friends just turned 21 and all go out to the bars — but after his double lung transplant, he’s not allowed to drink or be in crowded places. “It’s the social aspect that I’m kind of worried about,” he told Fox News. (Mills Hayes/Fox News)
The majority of the patients Moore sees with vaping-related issues are between 16 and 19 years old.
Some patients have lung injury and others have milder respiratory symptoms.
“We’ve done a very good job of educating youth about not starting to smoke traditional tobacco-based cigarettes,” Moore said.
“With vaping products, we don’t have as much long-term data, but in the short term, the risk seems to be as high as cigarettes — and I would argue in some cases worse.”
US SCHOOLS INVEST MILLIONS IN SURVEILLANCE TECHNOLOGY TO COMBAT TEEN VAPING EPIDEMIC
Moore said her patients typically vape THC and nicotine.
“It doesn’t seem to be that vaping just nicotine or just THC is less of a risk for lung disease than one or the other,” she said.
Most vaping patients have some underlying mental health concerns, such as anxiety, depression or a combination of those, the doctor noted.
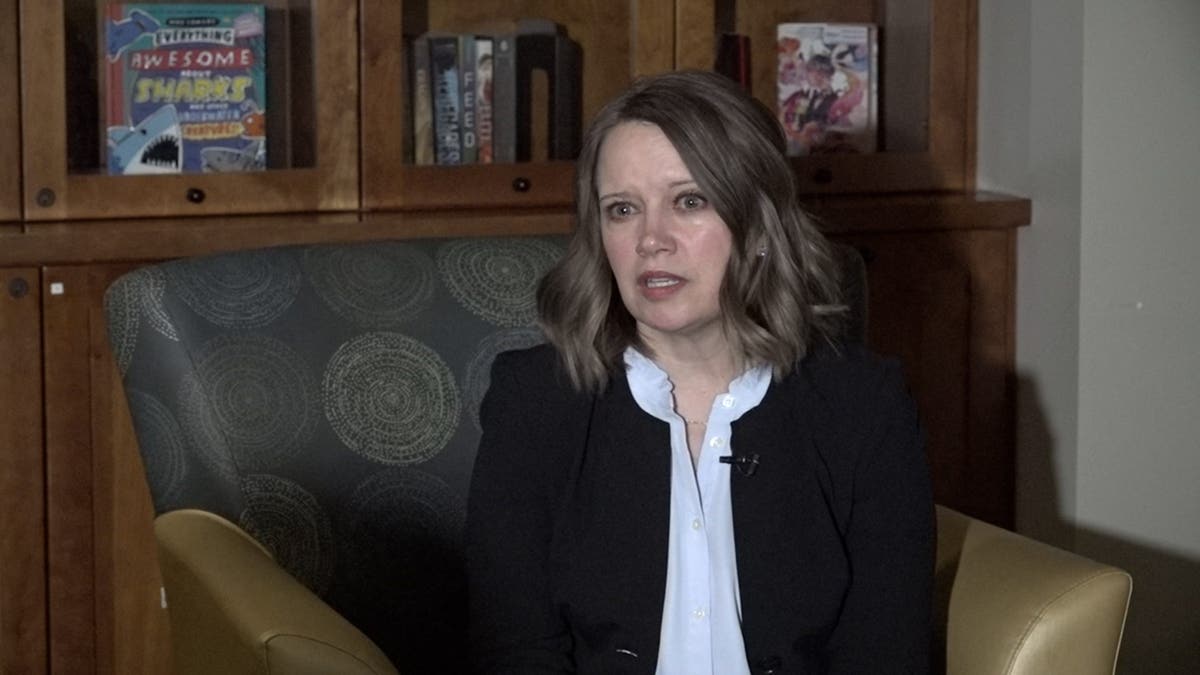

Dr. Brook Moore, pictured here, said patients will come in with a cough and shortness of breath due to vaping. “They’ve created flavors and advertising that mimics a lot of the things that kids, teenagers and young adults like to use,” she said about the manufacturers. (Mills Hayes/Fox News)
“They’re using their vape products to self-medicate,” Moore said. “It shows there is a much bigger issue at play than just people vaping to vape.”
In 2019, there was an outbreak of e-cigarette or vaping product use-associated lung injury, or EVALI. Those cases were linked to vitamin E acetate in vaping products.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
As of Feb. 2020, more than 2,800 patients had been admitted to various hospitals in the U.S. due to EVALI, with 68 deaths reported.
But in 2020, the CDC stopped tracking EVALI cases.
That’s when Johns Hopkins Children’s Center Dr. Christy Sadreameli started to pay more attention.

Many of the vape products commonly sold are “kind of on the market illegally,” a doctor warned. (iStock)
“If you were to ask me how many cases of EVALI happen every year in the U.S., we don’t know that anymore,” Sadreameli told Fox News Digital.
“It’s definitely still out there. And I’m still concerned about it.”
Many of the vape products commonly sold are “kind of on the market illegally,” Sadreameli added.
“They’re on the market without approval and without undergoing review.”
“They haven’t gone through the FDA review or approval process, and it’s hard to enforce something like that. These things were already being sold,” she continued.
“They’re kind of on the market without approval and without undergoing review. So that’s kind of messed up.”
Symptoms of vaping-related lung injury include coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever or gastrointestinal symptoms, according to WebMD.
If people who often vape are experiencing a combination of those symptoms, they should see a doctor as soon as possible, experts advise.
Patients who want to quit can work with their doctor to make a plan.
There are also cessation support groups and programs available.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
CDC, WebMD give update on current bird flu outbreak: ‘Be alert, not alarmed’
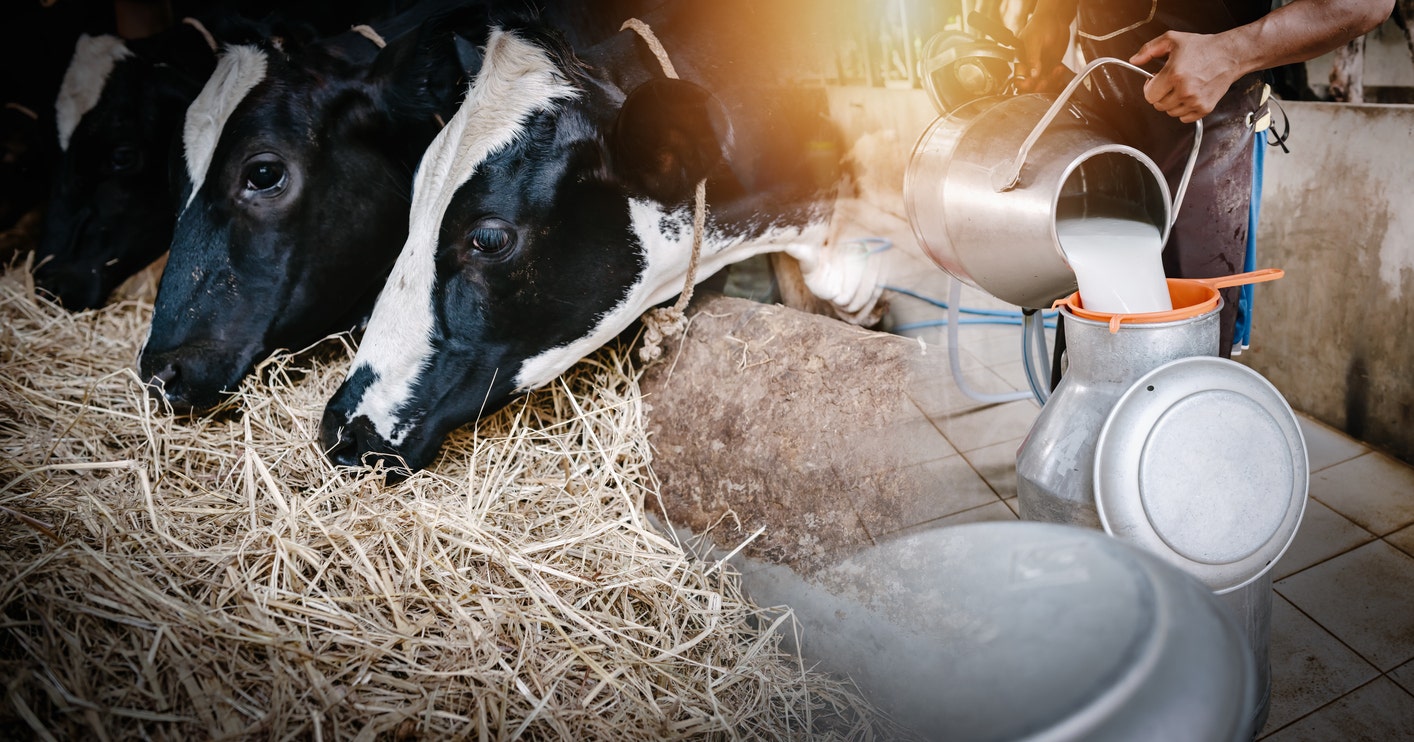

As bird flu continues to spread among cattle in the U.S., WebMD and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) joined forces on Thursday to present a live-streamed briefing on the status of the outbreak.
The presentation, called “WebMD and CDC Presents, 2024 Bird Flu: What You Need to Know,” was moderated by Neha Pathak, M.D., chief physician editor for WebMD in Atlanta, Georgia.
The first reports of sick dairy cows came to the USDA in early March, according to Eric Deeble, deputy assistant secretary for the Office of Congressional Relations at the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) in Washington, D.C.
AMID BIRD FLU SPREAD, EXPERTS REVEAL IF IT’S SAFE TO DRINK MILK
Testing revealed that the cows had contracted H5N1, more commonly known as avian influenza, or bird flu.
“Any new disease of cattle is a great concern to us,” Deeble said during the briefing.
As bird flu continues to spread among cattle in the U.S., WebMD and the CDC issued an update on Thursday. (Getty Images)
“The H5N1 in cattle is a relatively mild disease. They generally recover after supportive care” within two to three weeks, he said.
“Their milk volume returns to normal, and they appear healthy and continue to feed as they did before they became sick.”
“Any new disease of cattle is a great concern to us.”
So far, the USDA has detected H5N1 in 49 dairy herds in nine states, Deeble stated.
“To put that into perspective, that’s around 1% of dairy farms in the affected states and about 1/10th of 1% nationally,” he said.
On April 29, a federal order from the USDA took effect, limiting the movement of lactating dairy cattle in an effort to monitor and compile H5N1 test results.
TEXAS CATS DIE ON DAIRY FARM AFTER DRINKING RAW MILK CONTAMINATED WITH BIRD FLU, CDC WARNS
“Under this order, dairy farmers are required to test their cows before moving them across state lines so that we know those cows are H5N1-free and don’t pose a risk to any new herd,” Deeble said.
The order also requires that any test results that detect the presence of H5N1 are reported to USDA labs.
No current food risk, experts say
Deeble assured those tuning in on Thursday that there is no risk with consuming milk and meat.
“I can say without reservation that our commercial milk and meat supplies are safe,” he said. “At no time were animals that are sick from H5N1 or any other animal disease permitted to enter into our food supply.”
He added, “USDA has never detected H5N1 in meat sold at retail.”
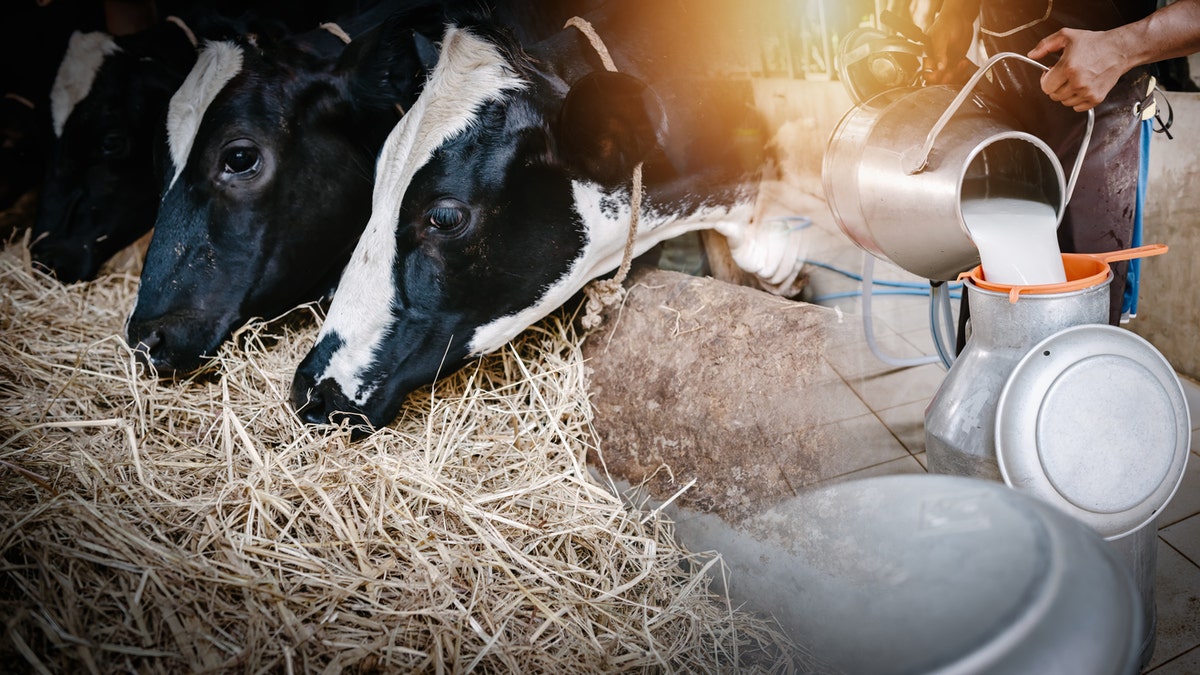

The first reports of sick dairy cows came to the USDA in early March, health officials said. (iStock)
Tests have confirmed that cooking meat to an internal temperature of 155 or above is sufficient to eliminate all traces of the virus, Deeble noted.
For milk, the pasteurization process ensures it is safe to drink, he said.
“Our milk is cleared to a high temperature for a brief period of time, inactivating H5N1, as well as other bacteria and viruses that could make someone sick,” he said.
Risk of transmission to humans
The overall risk to the public from bird flu is low, according to Dr. Nirav D. Shah, M.D., principal deputy director of the CDC in Atlanta.
“That is in part because it’s rare for people to get infected with bird flu viruses — but it has happened,” he said during the briefing.
“If and when it does happen, it’s most often through direct unprotected contact with infected animals — for example, not wearing gloves, face masks or eye protection.”
COULD A BIRD FLU PANDEMIC SPREAD TO HUMANS? HERE’S WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
In April, the CDC reported one human case of bird flu in a dairy worker in Texas, Shah said.
“This person’s only symptom was eye redness, or conjunctivitis,” he said. “After testing positive, this person was provided [with] an antiviral medicine and thankfully made a full recovery. There have been no new or additional human cases since this individual in Texas.”
Other symptoms to watch for include cough, fever, muscle aches and fatigue, according to Shah.
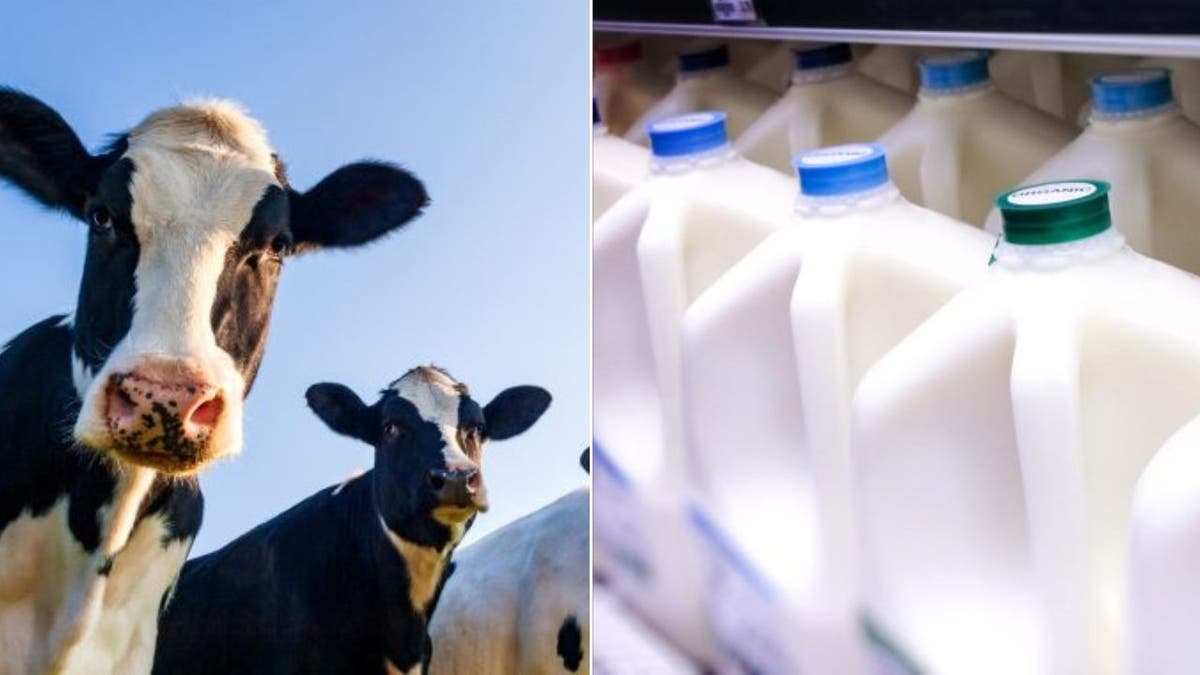

Experts said there is no risk associated with drinking milk purchased commercially. (iStock)
Although the overall risk to humans is low, the CDC is taking “aggressive steps” to make sure Americans stay well and informed, Shah said.
“Right now, one of our top areas of focus is around farm worker safety and protection — specifically making sure that workers have access to personal protective equipment … like gloves, goggles or face masks, which can help reduce their risk of exposure if they happen to be working around affected cows.”
MAINE WILDLIFE AUTHORITIES FIND 6 DEAD WILD DUCKS THAT TESTED POSITIVE FOR BIRD FLU
The CDC is also working with local health departments to ensure that sick farmers are tested for bird flu and to monitor their status.
“In addition to that, scientists in our laboratories here at CDC are looking closely at the bird flu viruses to see if there are any changes in their DNA that might tell us if these viruses are able to spread more easily to people, between people, and, importantly, whether they might be causing more serious illness,” Shah added.
Although the overall risk to humans is low, the CDC is taking “aggressive steps” to make sure Americans stay well and informed, a doctor said. (REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration/File Photo)
Although the risk to the public “remains low” currently, the doctor offered guidance for certain groups that may be at a higher risk.
“If you happen to work around animals, whether it’s chickens, whether it’s cattle, or whether it’s pigs, and you develop signs and symptoms that might otherwise be the flu, it’s important to make sure you call a health care provider and have a conversation with them.”
Not another COVID, experts say
The current situation with bird flu is different from the early days of COVID-19, Shah said during the briefing.
“We are in a much different place because of over two decades of investment in planning and preparing for things like influenza,” he said.
CDC WARNS OF INVASIVE BACTERIAL OUTBREAK AMID SPIKE IN CASES AND FATALITY RATES: ‘RARE BUT SEVERE’
“As a result of that extensive planning and preparedness, there are medicines in place.”
If those medications are given early, they can reduce the severity and duration of illness, as was the case with the farmer in Texas, Shah noted.
“This is just one of many ways in which … influenza and bird flu differs from what many of us remember from four years ago,” he added.
Vaccines and prevention
The traditional influenza vaccine doesn’t provide much protection against avian flu, the experts noted.
“Even though they are … basically the same virus, they differ just enough to where the flu shot — which we hope everyone gets — doesn’t do a great job at protecting you,” said Shah.
“It might do a little bit of work, but it’s not enough to take you to the bank.”
“We’re not at a spot where vaccination is recommended for anyone,” a doctor said in the briefing on Thursday. (Julian Stratenschulte/dpa)
David Boucher, PhD, director of Infectious Diseases Preparedness and Response at ASPR in Washington, D.C., spoke during the Thursday briefing about the potential need for a bird flu vaccine.
“We’re not at a spot where vaccination is recommended for anyone,” he said.
Through the National Influenza Vaccine Program, the ASPR works with health partners to identify influenza viruses that are “just a little bit different from the things that we’ve seen in the past,” Boucher said.
WITH WHOOPING COUGH CASES ON THE RISE, DO YOU NEED A BOOSTER VACCINE?
For a novel virus, the team develops “building blocks” of a vaccine, he noted.
“The good news here is that this system has worked the way we hoped it would, and we have an initial supply of the building blocks we would need if we needed vaccines for the [H5N1] virus,” he said.
To monitor potential spread, the CDC is on the lookout for an increase in emergency department visits or laboratory tests that might signal a “cluster of cases,” a doctor said. (REUTERS/Dado Ruvic/Illustration)
In that scenario, Boucher said, the ASPR could partner with manufacturers of seasonal influenza vaccines for “large-scale” production.
Boucher also emphasized the importance of personal protective equipment (PPE) — such as gloves, goggles, face shields and N95 masks — for agricultural workers who may be close to infected animals.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
To monitor potential spread, the CDC is on the lookout for an increase in emergency department visits or laboratory tests that might signal a “cluster of cases,” Shah said.
“We’re also more recently looking at wastewater to see if there are changes there,” he said.
People can stay up to date on the latest bird flu developments from the CDC, the USDA, the FDA and other trusted sources of information, Shah added.
“We should be alert, not alarmed.”
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health.
Health
The Atkins Diet: Behind the Staple Weight Loss Plan | Woman's World

Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Forgot your password?
Get back to the Sign In
Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago'You need to stop': Gov. Noem lashes out during heated interview over book anecdote about killing dog
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoMan, 75, confesses to killing wife in hospital because he couldn’t afford her care, court documents say
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoRFK Jr said a worm ate part of his brain and died in his head
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPentagon chief confirms US pause on weapons shipment to Israel
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoHere's what GOP rebels want from Johnson amid threats to oust him from speakership
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPro-Palestine protests: How some universities reached deals with students
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoConvicted MEP's expense claims must be published: EU court
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoCalifornia Gov Gavin Newsom roasted over video promoting state's ‘record’ tourism: ‘Smoke and mirrors’














