Business
Two Big Ideas for Preventing Another Banking Crisis

No limits
Final yr, Marc Lasry, the proprietor of the Milwaukee Bucks basketball workforce, revealed that its star participant, Giannis Antetokounmpo, at one time had been placing his cash in 50 banks, with no single account holding greater than $250,000. Why? As a result of Antetokounmpo needed each cent to be insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance coverage Company. And $250,000 is the cap on insured deposits.
What Mr. Antetokounmpo apparently didn’t notice — however was pushed dwelling with the collapse of Silicon Valley Financial institution final week — is that the deposit insurance coverage cap’s days are over. True, the legislation says there’s a restrict, and the federal government has to invoke a “systemic danger exception” to again uninsured deposits. However when a financial institution is on the verge of failing, the specter of systemic danger at all times exists.
“Ever because the S.&L. disaster within the Eighties, everybody will get rescued,” mentioned Karen Petrou, a co-founder of Federal Monetary Analytics, referring to depositors.
Robert Hockett, a monetary regulation knowledgeable at Cornell College, believes it’s time to make the overarching assure express. And he’s not alone: Inside the subsequent few days, Consultant Ro Khanna, a California Democrat, is predicted to introduce a invoice that proposes elevating or eradicating the F.D.I.C.’s protection cap.
Mr. Hockett and others argue that insuring all deposits might enhance the banking system. They are saying it wouldn’t introduce ethical hazard, as a result of placing deposits in danger is just not what retains banks in test. As a substitute, what’s supposed to maintain bankers from appearing too recklessly is the data that if their financial institution fails, shareholders and bondholders can be worn out, executives can be investigated and, in lots of instances, the federal government will attempt to claw again compensation.
Deposit insurance coverage has lengthy been funded by the banks themselves. Since 2005, their contributions have been “risk-priced,” which means the extra danger a financial institution takes, the upper the premiums it pays. Bigger banks pay greater than smaller banks. Mr. Hockett’s scheme would clearly require bigger contributions — and tighter rules — however he envisions the same tiered system. He additionally envisions a return of measures like stress assessments, which Congress eradicated for midsize banks throughout the Trump administration.
Explicitly insuring all deposits, Mr. Hockett says, might forestall a run on a troubled financial institution, as a result of prospects would know forward of time that their cash was protected. It might additionally assist protect small and midsize banks. Though SVB plainly mismanaged its danger, the financial institution catered to a sector it understood nicely: enterprise capitalists and start-ups. Its mortgage portfolio was not the issue. Different smaller banks additionally focus on specific sectors and are prepared to make loans that the large behemoths won’t be. That must be inspired, Mr. Hockett says.
Not everybody thinks deposits ought to be freed from danger. Sheila Bair, who was the chair of the F.D.I.C. throughout the monetary disaster, virtually groaned after I introduced up the concept of insuring all deposits.
“These have been huge tech corporations like Roku whining and crying about their uninsured deposits,” she mentioned. “If a $200 billion financial institution can deliver down the banking system, then we don’t have a secure, resilient system.”
Ms. Bair went on to say that she thinks the banking system is “largely resilient” and that the actual drawback was that the regulators didn’t talk nicely sufficient to the general public that the disaster was restricted to a small group of banks.
Nonetheless, Hockett’s concept has some lawmakers on board. We’ll see if it flies. — Joe Nocera
IN CASE YOU MISSED IT
President Biden asks Congress for brand spanking new instruments to focus on executives of failed banks. One facet of the plan would broaden the F.D.I.C.’s capability to hunt the return of compensation from executives of failed banks, an influence at the moment restricted to the most important banks.
UBS is reportedly in talks to accumulate Credit score Suisse. The Swiss Nationwide Financial institution and the Swiss regulator FINMA organized the talks, in response to the Monetary Instances. Credit score Suisse mentioned on Thursday that it might borrow as a lot as $54 billion from the Swiss Nationwide Financial institution after its shares tumbled 24 % to a brand new low.
Goldman Sachs eyes an enormous payout. The Wall Avenue large tried to assist Silicon Valley Financial institution prepare a last-minute capital increase to reserve it. But it surely additionally had one other function: Goldman purchased $21.4 billion of debt from the failed financial institution (which the failed lender booked at a price of $1.8 billion), and is about to make greater than $100 million by promoting the bonds.
A Silicon Valley Financial institution buyer’s view of the collapse goes viral. Quite a lot of tweets by Alexander Torrenegra, founder and C.E.O. of a recruitment web site and an investor on the Colombian model of “Shark Tank,” revealed what it was wish to be reduce off because the financial institution imploded.
Do we’d like a brand new sort of financial institution?
The dialog in Washington about find out how to regulate banks within the wake of Silicon Valley Financial institution’s collapse is nicely underway, with disagreements about find out how to bail out failed lenders and forestall one other disaster.
However to Lowell Bryan, a former head of McKinsey & Firm’s banking follow, the reply lies in a debate that was held three a long time in the past. His proposal: Create a brand new sort of low-risk financial institution.
U.S. banking ought to be divided by ranges of riskiness, Mr. Bryan argued within the Nineteen Nineties. Deposits at “core banks” could be insured by the federal government, however these lenders could be allowed to take part solely in low-risk companies.
Wholesale banks would draw funding from non-public traders however wouldn’t be protected by the federal government. In the event that they made deadly missteps, the federal government would intervene to forestall widespread panic, however the corporations would fail and traders could be punished. (Mr. Bryan has argued that huge monetary corporations might personal each sorts of banks — as long as the depository lender was adequately shielded from its wholesale counterpart.)
The attraction of this technique, Mr. Bryan instructed DealBook in an interview, is that it essentially limits the dangers within the banking trade in a method that advanced necessities for liquidity and capital measures don’t.
“The central challenge is, if you happen to give a federal assure, you need to put actual limits on the flexibility to lift deposits,” he mentioned.
Take into account what occurred at banks which have failed not too long ago. Silicon Valley Financial institution elevated its deposit base to $175 billion, whereas investing that cash in a bond portfolio that was susceptible to rising rates of interest. It additionally prolonged $74 billion in loans to largely one dangerous sector, tech start-ups.
In the meantime, Silicon Valley Financial institution pushed onerous for regulatory exemptions that allowed it to pursue doubtlessly profitable, however harmful, monetary bets.
Mr. Bryan’s concept has been examined earlier than. At McKinsey within the Eighties and Nineteen Nineties, he was a distinguished proponent of the core financial institution idea, writing books and testifying earlier than Congress on the matter. He assembled an uncommon coalition, together with Consultant Chuck Schumer, Democrat of New York and now the Senate majority chief; NationsBank, a predecessor of Financial institution of America; J.P. Morgan, earlier than it merged with Chase Manhattan; and Goldman Sachs.
Opposing them was a gaggle that included Jay Powell, a Treasury Division official within the George H.W. Bush administration who’s now the Federal Reserve chair, and Sandy Weill, the architect of what turned Citigroup. They argued that American lenders benefited from relaxed rules that allowed them to diversify their companies, and so they received. Rewrites of U.S. banking guidelines allowed the creation of each monumental common banks and smaller lenders that would nonetheless tackle dangers.
Defending depositors ensures religion within the total banking system, Mr. Bryan mentioned. However banks can’t be allowed to function with an primarily limitless safety in opposition to the implications of danger. He contends that what he’s calling for is obvious and slender, succesful at this level of successful bipartisan assist.
“There’s not a have to rewrite every thing,” he mentioned.
‘If I dominated as off-limits something I’d labored on after I was in Congress, I suppose I’d be a monk.’
— Barney Frank, the previous liberal congressman and an architect of the landmark Dodd-Frank act to reform monetary regulation, defending his determination to serve on the board of Signature Financial institution. Regulators closed the New York-based lender final weekend after many depositors withdrew their cash following the collapse of Silicon Valley Financial institution.
On our radar: ‘Age of Straightforward Cash’
There’s a brief rationalization of what precipitated the collapse of Silicon Valley Financial institution: When Moody’s knowledgeable the financial institution’s chief government this month that its bonds have been at risk of being downgraded to junk, a failed try to lift cash incited panic and a run on deposits. However “Age of Straightforward Cash,” a PBS documentary launched this week, particulars a for much longer reply that begins with the monetary disaster in 2008. The “Frontline” correspondent James Jacoby particulars how the Fed’s rescue interventions after the disaster, and later throughout the pandemic, fueled the longest bull market in historical past — and the underlying situations for SVB’s failure.
Sarah Kessler contributed reporting.
We’d like your suggestions. Please electronic mail ideas and recommendations to dealbook@nytimes.com.

Business
Paramount's board approves bid by David Ellison's Skydance Media in sweeping Hollywood deal

Tech scion David Ellison’s months-long quest to win control of Paramount Global moved closer to the finish line Sunday, in a deal that marks a new chapter for the long-struggling media company and parent of one of Hollywood’s oldest movie studios.
Paramount Global board members on Sunday approved the bid by Ellison’s Skydance Media and its backers to buy the Redstone family’s Massachusetts holding firm, National Amusements Inc., said two sources close to the deal who were not authorized to comment.
A spokesperson for Paramount declined to comment.
The Redstones’ voting stock in Paramount would be transferred to Skydance, giving Ellison, son of billionaire Oracle Corp. co-founder Larry Ellison — a key backer of the deal — control of a media operation that includes Paramount Pictures, broadcast network CBS and cable channels MTV, Comedy Central and Nickelodeon.
The proposed $8.4 billion multipronged transaction also includes merging Ellison’s production company into the storied media company, giving it more heft to compete in today’s media environment.
The agreement, which mints Ellison as a Hollywood mogul, came together during the last two weeks as Ellison and his financing partners renewed their efforts to win over the Redstone family and Paramount’s independent board members.
Shari Redstone has long preferred Ellison’s bid over other those of potential suitors, believing the 41-year-old entrepreneur possesses the ambition, experience and financial heft to lift Paramount from its doldrums.
But, in early June, Redstone got cold feet and abruptly walked away from the Ellison deal — a move that stunned industry observers and Paramount insiders because it was Redstone who had orchestrated the auction.
Within about a week, Ellison renewed his outreach to Redstone. Ellison ultimately persuaded her to let go of the entertainment company her family has controlled for nearly four decades. The sweetened deal also paid the Redstone family about $50 million more than what had been proposed in early June. On Sunday Paramount’s full board, including special committee of independent directors, had signed off on the deal, the sources said.
Under terms of the deal, Skydance and its financial partners RedBird Capital Partners and private equity firm KKR have agreed to provide a $1.5-billion cash infusion to help Paramount pay down debt. The deal sets aside $4.5 billion to buy shares of Paramount’s Class B shareholders who are eager to exit.
The Redstone family would receive $1.75-billion for National Amusements, a company that holds the family’s Paramount shares and a regional movie theater chain founded during the Great Depression, after the firm’s considerable debts are paid off.
The proposed handoff signals the end of the Redstone family’s nearly 40-year reign as one of America’s most famous and fractious media dynasties. The late Sumner Redstone’s National Amusements was once valued at nearly $10 billion, but pandemic-related theater closures, last year’s Hollywood labor strikes and a heavy debt burden sent its fortunes spiraling.
In the last five years, the New York-based company has lost two-thirds of its value. Its shares are now worth $8.2 billion based on Friday’s closing price of $11.81 a share.
The struggles in many ways prompted Shari Redstone to part with her beloved family heirloom. Additionally, National Amusements was struggling to cover its debts, and the high interest rates worsened the outlook for the Redstone family.
Paramount boasts some of the most historic brands in entertainment, including the 112-year-old Paramount Pictures movie studio, known for landmark films such as “The Godfather” and “Chinatown.” The company owns television stations including KCAL-TV (Channel 9) and KCBS-TV (Channel 2). Its once-vibrant cable channels such as Nickelodeon, TV Land, BET, MTV and Comedy Central have been losing viewers.
The handover requires the approval of federal regulators, a process that could take months.
In May, Paramount’s independent board committee said it would entertain a competing $26-billion offer from Sony Pictures Entertainment and Apollo Global Management. The bid would have retired all shareholders and paid off Paramount’s debt, but Sony executives grew increasingly wary of taking over a company that relies on traditional TV channels.
Earlier this year, Warner Bros. Discovery expressed interest in a merger or buying CBS. However, that company has struggled with nearly $40 billion in debt from previous deals and is in similar straits as Paramount. Media mogul Byron Allen has also shown interest.
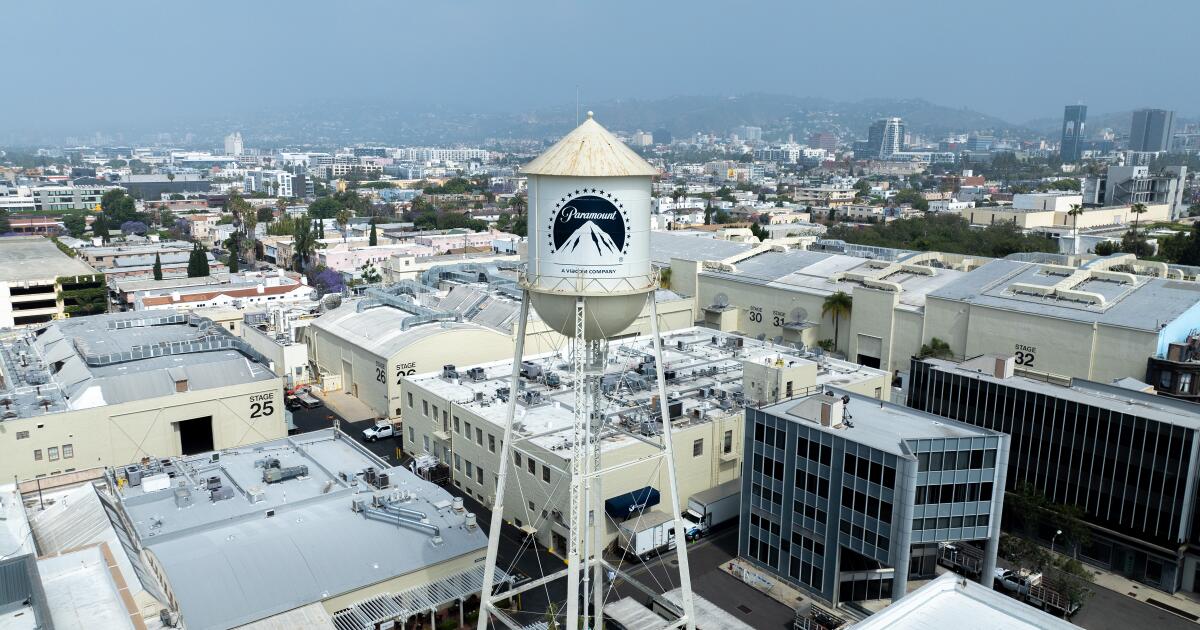
Skydance Media founder and Chief Executive David Ellison prevailed in his bid for Paramount.
(Evan Agostini/Invision/Associated Press)
Many in Hollywood — film producers, writers and agents — have been rooting for the Skydance takeover, believing it represents the best chance to preserve Paramount as an independent company. Apollo and Sony were expected to break up the enterprise, with Sony absorbing the movie studio into its Culver City operation.
The second phase of the transaction will be for Paramount to absorb Ellison’s Santa Monica-based Skydance Media, which has sports, animation and gaming as well as television and film production.
Ellison is expected to run Paramount as its chief executive. Former NBCUniversal CEO Jeff Shell, who’s now a RedBird executive, could help manage the operation. It’s unclear whether the Skydance team will keep on the three division heads who are now running Paramount: Paramount Pictures CEO Brian Robbins, CBS head George Cheeks and Showtime/MTV Entertainment Studios chief Chris McCarthy.
Skydance has an existing relationship with Paramount. It co-produced each film in the “Mission: Impossible” franchise since 2011’s “Mission: Impossible — Ghost Protocol,” starring Tom Cruise. It also backed the 2022 Cruise mega-hit “Top Gun: Maverick.”
Ellison first approached Redstone about making a deal last summer, and talks became known in December.
Redstone long viewed Ellison as a preferred buyer because the deal paid a premium to her family for their exit. She also was impressed by the media mogul , believing he could become a next-generation leader who could take the company her father built to a higher level, according to people knowledgeable of her thinking.
Larry Ellison is said to be contributing funding to the deal.
David Ellison was attracted to the deal because of his past collaborations with Paramount Pictures and the allure of combining their intellectual properties as well as the cachet of owning a historic studio, analysts said. Paramount’s rich history contains popular franchises including “Transformers,” “Star Trek,” “South Park” and “Paw Patrol.”
“Paramount is one of the major historic Hollywood studios with a massive base of [intellectual property], and so it seems to us that it’s more about using the capital that Ellison has and what he’s built at Skydance and leveraging that into owning a major Hollywood studio,” Brent Penter, senior research associate at Raymond James, said prior to the deal. “Not to mention the networks and everything else that Paramount has.”
The agreement prepares to close the books on the Redstone family’s 37-year tenure at the company formerly known as Viacom, beginning with Sumner Redstone’s hostile takeover in 1987.
Seven years later, Redstone clinched control of Paramount, after merging Viacom with eventually doomed video rental chain Blockbuster to secure enough cash for the $10-billion deal. Redstone long viewed Paramount as the crown jewel, a belief that took root a half-century ago when he wheeled-and-dealed over theatrical exhibition terms for Paramount’s prestigious films to screen at his regional theater chain.
Under Redstone’s control, Paramount won Academy Awards in the ’90s for “Forrest Gump” and “Saving Private Ryan.”
He pioneered the idea of treating films as an investment portfolio and hedging bets on some productions by taking on financial partners — a strategy now widely used throughout the industry.
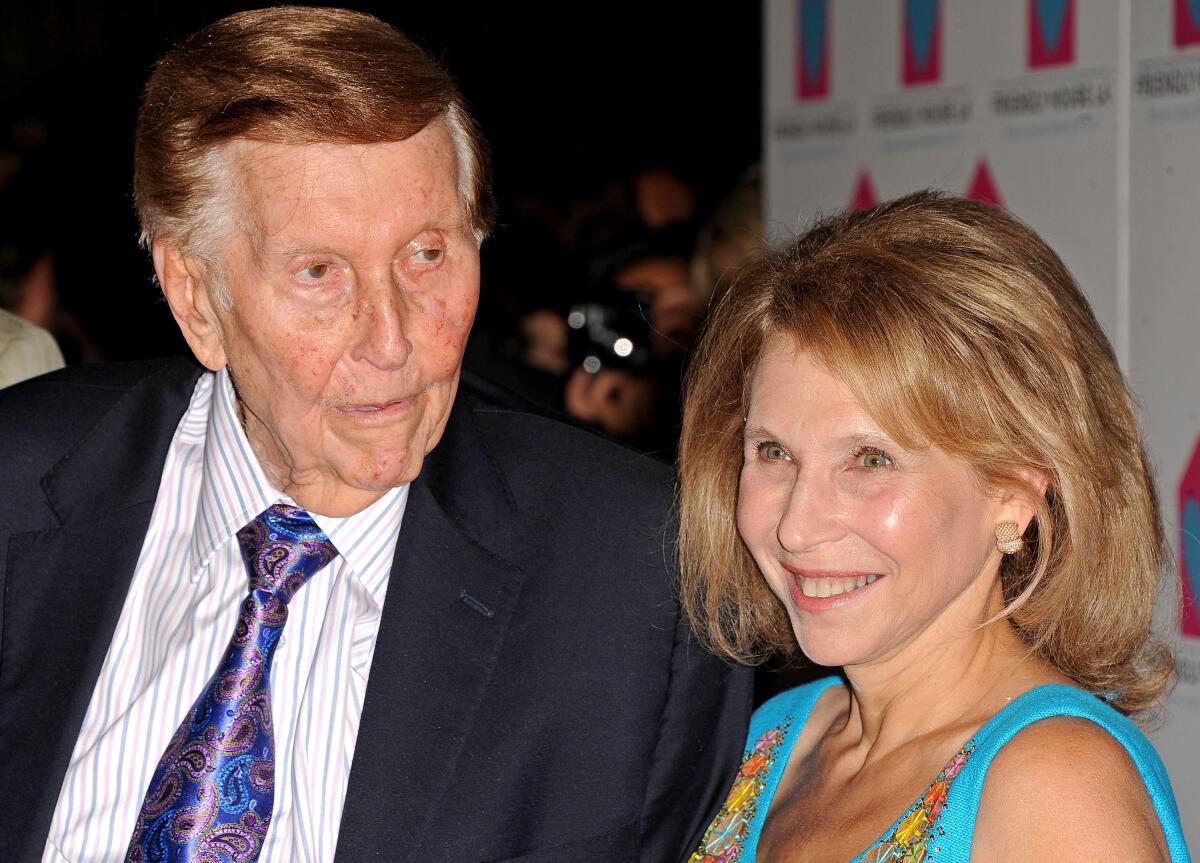

The late Sumner Redstone and his daughter Shari Redstone have owned a controlling interest in Viacom, which was rebranded as Paramount, through their family holding company, National Amusements Inc., since 1987.
(Katy Winn/Invision/Associated Press)
In 2000, Redstone expanded his media empire again by acquiring CBS, a move that made Viacom one of the most muscular media companies of the time, rivaling Walt Disney Co. and Time Warner Inc. Just six years later, Redstone broke it up into separate, sibling companies, convinced that Viacom was more precious to advertisers because of its younger audience. Redstone also wanted to reap dividends from two companies.
After years of mismanagement at Viacom, which coincided with the elder Redstone’s declining health, and boardroom turmoil, his daughter stepped in to oust Viacom top management and members of the board. Three years later, following an executive misconduct scandal at CBS, Shari Redstone achieved her goal by reuniting CBS and Viacom in a nearly $12-billion deal.
The combined company, then called ViacomCBS and valued at more than $25 billion, was supposed to be a TV juggernaut, commanding a major percentage of TV advertising revenue through the dominance of CBS and more than two dozen cable channels.
But changes in the TV landscape took a toll.
As consumer cord-cutting became more widespread and TV advertising revenue declined, ViacomCBS’ biggest asset became a serious liability.
The company was late to enter the streaming wars and then spent heavily on its Paramount+ streaming service to try to catch up with Netflix and even Disney. (In early 2022, the company was renamed Paramount Global in a nod to its moviemaking past and to tie in with its streaming platform of the same name.)
The company’s eroding linear TV business and the decline of TV ad revenue, as well as its struggles trying to make streaming profitable, will be major challenges for Ellison as he takes over Paramount. Though traditional TV is declining, it still brings in cash for Paramount.
And streaming is a whole different economic proposition from television, one that offers slimmer profits. Meanwhile, the company also faces larger industry questions about when — if ever — box office revenue will return to pre-pandemic levels.
“This is a company that is floating on hope,” said Stephen Galloway, dean of Chapman University’s Dodge College of Film and Media Arts. “And hope isn’t a great business strategy.”
Business
Missing the paperwork on your IRAs? All is not lost

Dear Liz: I have four daughters, now in their late 30s and early 40s. When they were very young, I started investing for them. As they began to earn their own money, I started Roth IRAs for them as well.
A decade ago, due to an unexpected divorce, a 30-day escrow and a move, I lost the paperwork for their accounts. After the investment company was acquired by another in 2015, I forwarded the new company’s contact information to my daughters. One transferred her account to another investment company, while her sisters left theirs in place.
Recently I found the old investment paperwork. The company has changed hands again, but the new company says it has no information about my three other daughters’ accounts. Can anything be done?
Answer: Since the latest company can’t find the accounts, your daughters should contact the escheat office of the state where you lived before your move.
Perhaps you didn’t update your address with the original company when you moved and the account statements or other mail were returned as undeliverable. If the company and its successor couldn’t find you — and some companies don’t look very hard — the accounts would be considered unclaimed and would have to be turned over to the state.
Links to state escheat offices can be found online at unclaimed.org, the website for the National Assn.
of Unclaimed Property Administrators.
The good news is that there’s no time limit for claiming previously unclaimed property.
The bad news is that some states will liquidate stocks and other investments after escheatment. If that’s the case, then the three daughters who didn’t move their accounts will have missed out on nearly a decade of investment returns.
Dear Liz: Is it common for a brokerage agreement to say the firm can close my account for any reason and without any notice? The agreement goes on to say that the brokerage can liquidate the investments in my account if it’s closed and that the brokerage is not responsible for any investment losses that result.
Answer: The short answer is yes — brokerage accounts can be closed at any time by the firm or by the client.
Such agreements often specify certain actions that can trigger a closure, such as failing to maintain a minimum required balance. But the agreements also typically have language that allows the brokerage to close your account at any time and for any reason.
Brokerages don’t commonly close customer accounts. If yours does, however, move quickly to transfer your investments to another firm.
Failure to act could result in your investments being liquidated, and you would owe capital gains taxes on any appreciation in their value.
Dear Liz: You have written that non-spouse beneficiaries are now required to drain their inherited IRAs within 10 years. Is this requirement retroactive?
I inherited an IRA from my mother in 2015. I have been taking out the minimum required each year. If I must drain the account within 10 years, will the increase in yearly income affect my Social Security benefits?
Answer: The 10-year requirement applies only to accounts inherited from people who died after Dec. 31, 2019.
IRA distributions don’t affect Social Security benefits, but could affect Medicare premiums if the withdrawal is large enough. Taxable income above certain limits triggers a Medicare surcharge known as an income-related monthly adjustment amount, or IRMAA.
Dear Liz: My husband passed away 10 months ago. I applied for widow benefits.
The Social Security Administration sent me a letter that said they cannot pay because my Social Security benefit would equal two-thirds of the amount of my pension. Please help me with this.
Answer: This is known as the government pension offset, and it applies to people who receive a pension from a job that didn’t pay into Social Security. Any survivor or spousal benefits you might receive are reduced by two-thirds of the pension amount. In your case, your entire benefit was offset.
People are understandably upset to learn they don’t qualify for survivor or spousal benefits through Social Security. But since your pension is large enough to offset any benefit, you’re financially better off with the pension than without it.
For more information, see the government pension offset pamphlet, available online at SSA.gov/pubs or by calling the Social Security Administration toll-free at (800) 772-1213.
Business
California’s workplace violence prevention law is now in effect. Here's how it changes things

Beginning this month, California businesses will be required to have plans in place to prevent violence in the workplace.
Senate Bill 553, signed by Gov. Gavin Newsom last fall, requires that employers develop plans to protect workplaces from foreseeable threats of violence, which can range from bullying and harassment to active shooter and hostage situations. Under the law, employers were to have these comprehensive plans in place by July 1.
Here’s what you should know about the new law:
Who pushed for the workplace violence prevention law, and why?
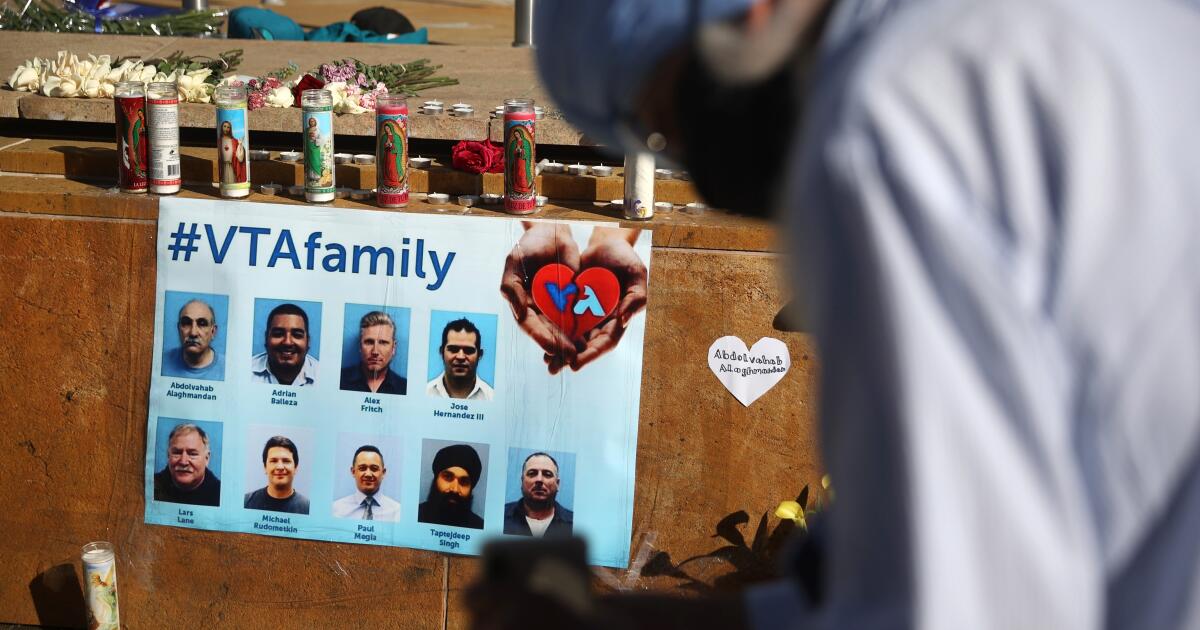
State Sen. Dave Cortese (D-San Jose), who wrote the legislation, said he began looking into regulating workplace violence after a major shooting in 2021 at a light-rail yard roiled his district. In the incident, an employee killed nine colleagues at the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority before taking his own life.
Surveying the scene soon after the shooting, Cortese said he felt there could have been a clear plan for how workers might respond in such a situation. “It would have saved lives,” he said.
Cortese said the requirements outlined by the law took cues from a regulation the California Division of Occupational Safety and Health had been in the process of developing. Their safety standard, however, given their lengthy rule-making process and bureaucratic delays, probably would have taken several more years to get final approval.
More than half of such shootings in 2021 occurred in places of commerce, including grocery stores and manufacturing sites, according to the FBI.
SB 553 was backed by several unions, among them the United Food and Commercial Workers Western States Council. The union sought a law that would help address what it described as a rash of violent attacks at grocery stores and pharmacies, as workers were being pressured by their employers to crack down on shoplifting.
Grocery and other retail workers who interact with the public have long worried about violence in the workplace. Notably, they faced harassment and at times assault from customers who refused to comply with mask mandates in the early years of the COVID-19 pandemic. Fast-food workers also have complained of violent and dangerous customers.
Did anyone oppose the legislation? If so, why?
Industry groups such as the National Retail Assn. had vehemently opposed SB 553, arguing the paperwork would be overly burdensome for businesses.
They also took issue with a provision the bill had in its early stages that prohibited businesses from requiring nonsecurity employees to confront shoplifters and active shooters. That language was later removed. Eventually, the trade groups dropped their opposition.
What exactly is required under the law?
Legal experts said many companies had already started loosely addressing workplace violence concerns as mass shootings and other violent incidents dominated headlines over the years. The law helps to clarify employers’ obligations in this arena, experts said.
The law defines four types of workplace violence employers should try to prevent: violent action by a third-party person with no real reason to be at the worksite — essentially, a stranger showing up and harming an employee; violence by parties that are entitled to be there, such as customers, clients, patients or other authorized visitors; violence committed against employees by another employee; and violence by a third party who has a romantic or other personal relationship with an employee.
Under the law, most California businesses with at least 10 employees are required to have a policy document identifying potential violence and plans to deal with it — either as a standalone document, or as part of an existing injury and illness prevention policy.
They must also make workers aware of the violence prevention plan through annual training, and maintain a log of incidents of violence over a minimum of five years.
What else should I know about the law?
The law makes it easier for employees — or the unions that represent them — to get temporary restraining orders if they are threatened by a coworker or someone else in the workplace.
“That’s a big thing — most employees don’t get to choose who they work with or what happens at work,” said Ian A. Wright, a labor and employment attorney at Alston & Bird. “It gives employees an additional form of protection that they can go and seek themselves.”
Noncompliance could be met with civil penalties, and businesses that haven’t yet implemented the law are already several days past the deadline.
“My advice would be to get it done as soon as possible,” Wright said.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTension and stand-offs as South Africa struggles to launch coalition gov’t
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week ago4 killed, 9 injured after vehicle crashes into Long Island nail salon
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoSupreme Court denies Steve Bannon's plea to stay free while he appeals
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoVideo: How Blast Waves Can Injure the Brain
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoTrump says 'biggest problem' not Biden's age, 'decline,' but his policies in first appearance since debate
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie review: A Quiet Place, quivering since Day One
-
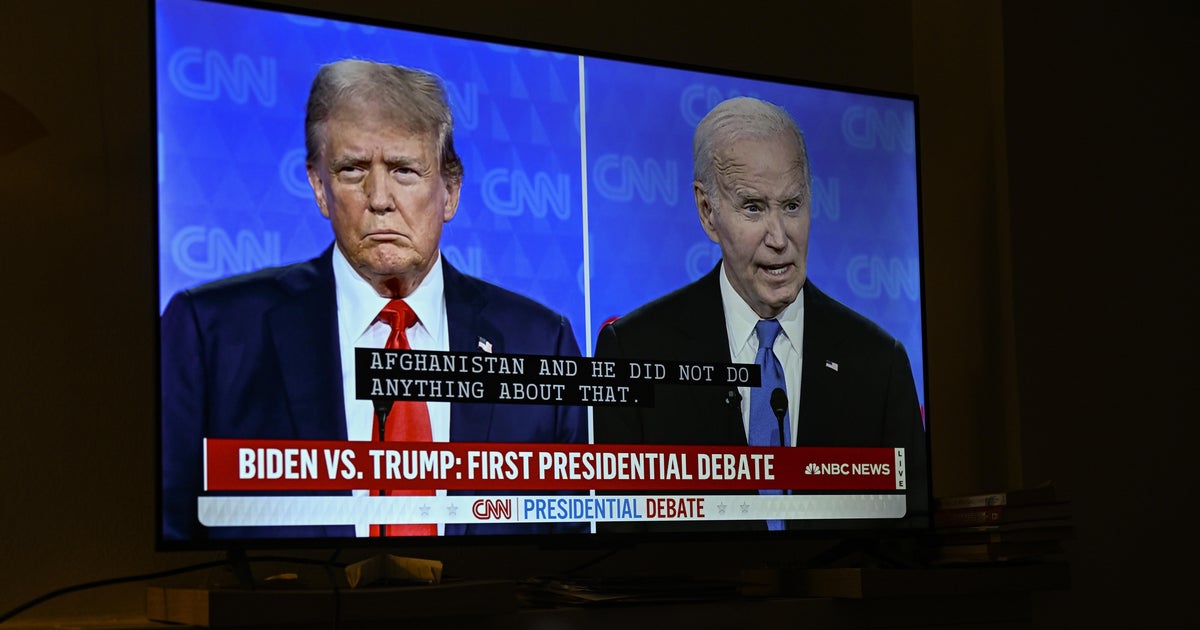
 News1 week ago
News1 week agoIncreasing numbers of voters don’t think Biden should be running after debate with Trump — CBS News poll
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoCaribbean braces for ‘very dangerous’ Hurricane Beryl















