Business
Drugmakers are abandoning cheap generics, and now U.S. cancer patients can’t get meds
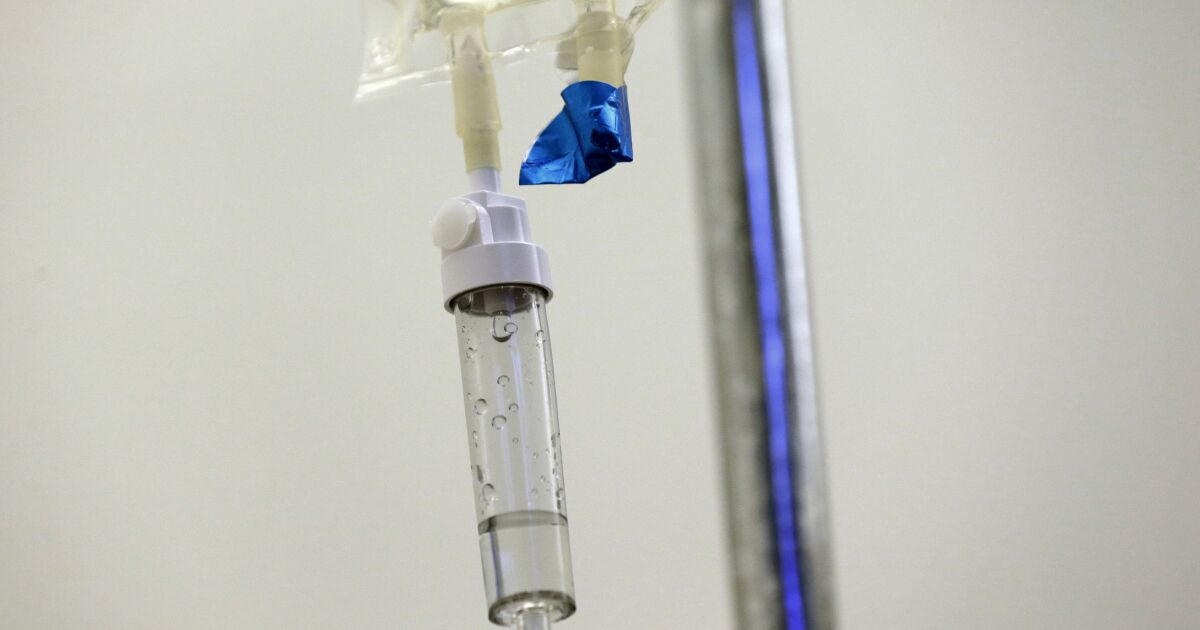
On Nov. 22, three inspectors from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration arrived at the sprawling Intas Pharmaceuticals plant south of Ahmedabad, India, and found hundreds of trash bags full of shredded documents tossed into a garbage truck. Over the next 10 days, the inspectors assessed what looked like a systematic effort to conceal quality problems at the plant, which provided more than half of the U.S. supply of generic cisplatin and carboplatin, two cheap drugs used to treat as many as 500,000 new cancer cases every year.
Seven months later, doctors and their patients are facing the unimaginable: In California, Virginia and everywhere in between, they are being forced into grim contemplation of untested rationing plans for breast, cervical, bladder, ovarian, lung, testicular and other cancers. Their decisions are likely to result in preventable deaths.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are among scores of drugs in shortage, including 12 other cancer drugs, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder pills, blood thinners and antibiotics. Supply chain issues left over from the COVID crisis and limited FDA oversight are part of the problem, but the main cause, experts agree, is the underlying weakness of the generic drug industry.
Made mostly overseas, these old but crucial drugs are often sold at a loss or for little profit. Domestic manufacturers have little interest in making them, setting their sights instead on high-priced drugs with plump profit margins.
The problem isn’t new, and that’s particularly infuriating to many clinicians. President Biden, whose son Beau died of an aggressive brain cancer, has focused his Cancer Moonshot on discovering cures — undoubtedly expensive ones. Indeed, existing brand-name cancer drugs often cost tens of thousands of dollars a year.
But what about the thousands of patients today who can’t get a drug like cisplatin, approved by the FDA in 1978 and costing as little as $6 a dose?
“It’s just insane,” said Dr. Mark Ratain, a cancer doctor and pharmacologist at the University of Chicago. “Your roof is caving in, but you want to build a basketball court in the backyard because your wife is pregnant with twin boys and you want them to be NBA stars when they grow up?”
“It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now,” said Dr. Stephen Divers, an oncologist in Hot Springs, Ark., who in recent weeks has had to delay or change treatment for numerous bladder, breast and ovarian cancer patients because his clinic cannot find enough cisplatin and carboplatin.
It’s just a travesty that this is the level of health care in the United States of America right now.
— Dr. Stephen Divers, an oncologist grappling with drug shortages
Results from a survey of academic cancer centers released this month found that 93% couldn’t find enough carboplatin and 70% had cisplatin shortages.
“All day, in between patients, we hold staff meetings trying to figure this out,” said Dr. Bonny Moore, an oncologist in Fredericksburg, Va. “It’s the most nauseous I’ve ever felt. Our office stayed open during COVID; we never had to stop treating patients. We got them vaccinated, kept them safe, and now I can’t get them a $10 drug.”
The 10 cancer clinicians KFF Health News interviewed for this story said that, given current shortages, they prioritize patients who can be cured over later-stage patients, in whom the drugs generally can only slow the disease, and for whom alternatives — though sometimes less effective and often with more side effects — are available. But some doctors are even rationing doses intended to cure.
Isabella McDonald, then a junior at Utah Valley University, was diagnosed in April with a rare, often fatal bone cancer, whose sole treatment for young adults includes the drug methotrexate. When Isabella’s second cycle of treatment began June 5, clinicians advised that she would be getting less than the full dose because of a methotrexate shortage, said her father, Brent.
Brent McDonald and his daughter Isabella, who was diagnosed with a rare, often fatal bone cancer. Clinicians said she would be getting less than the full dose of methotrexate because the drug is in shortage.
(Rachel McDonald)
“They don’t think it will have a negative impact on her treatment, but as far as I am aware, there isn’t any scientific basis to make that conclusion,” he said. “As you can imagine, when they gave us such low odds of her beating this cancer, it feels like we want to give it everything we can and not something short of the standard.”
Brent McDonald stressed that he didn’t blame the staffers at Intermountain Health who take care of Isabella. The family — his other daughter, Cate, made a TikTok video about her sister’s plight — were simply stunned at such a basic flaw in the healthcare system.
At Moore’s practice in Virginia, clinicians gave 60% of the optimal dose of carboplatin to some uterine cancer patients during the week of May 16, then shifted to 80% after a small shipment came in the following week. The doctors had to omit carboplatin from normal combination treatments for patients with recurrent disease, she said.
On June 2, Moore and her colleagues were glued to their drug distributor’s website, as anxious as teenagers waiting for Taylor Swift tickets to go on sale — only with mortal consequences at stake.
She later emailed KFF Health News: “Carboplatin did NOT come back in stock today. Neither did cisplatin.”
Doses remained at 80%, she said. Things hadn’t changed 10 days later.
Generics manufacturers are pulling out
The causes of shortages are well established. Everyone wants to pay less, and the middlemen who procure and distribute generics keep driving down wholesale prices. The average net price of generic drugs fell by more than half between 2016 and 2022, according to research by Anthony Sardella, a business professor at Washington University in St. Louis.
As generics manufacturers compete to win sales contracts with the big buyers, including wholesale purchasers Vizient and Premier, their profits sink. Some are going out of business. Akorn, which made 75 common generics, went bankrupt and closed in February.
Israeli generics giant Teva, which has a portfolio of 3,600 medicines, announced May 18 it was shifting to brand-name drugs and “high-value generics.” Lannett Co., with about 120 generics, announced a Chapter 11 reorganization amid declining revenue.
Other companies are in trouble too, said David Gaugh, interim chief executive of the Assn. for Accessible Medicines, the leading generics trade group.
The generics industry used to lose money on about a third of the drugs it produced, but now it’s more like half, Gaugh said. So when a company stops making a drug, others do not necessarily step up, he said.
Officials at Fresenius Kabi and Pfizer said they have increased their carboplatin production since March, but not enough to end the shortage. On June 2, FDA Commissioner Robert Califf announced the agency had given emergency authorization for Chinese-made cisplatin to enter the U.S. market, but the impact of the move wasn’t immediately clear.
Cisplatin and carboplatin are made in special production lines under sterile conditions, and expanding or changing the lines requires FDA approval. Bargain-basement prices have pushed production overseas, where it’s harder for the FDA to track adherence to quality standards. The Intas plant inspection was a relative rarity in India, where the FDA in 2022 reportedly inspected only 3% of sites that make drugs for the U.S. market.
Sardella, the Washington University professor, testified last month that a quarter of all U.S. drug prescriptions are filled by companies that received FDA warning letters in the past 26 months. And pharmaceutical product recalls are at their highest level in 18 years, reflecting fragile supply conditions.
The FDA listed 137 drugs in shortage as of June 13, including many essential medicines made by few companies.
Intas voluntarily shut down its Ahmedabad plant after the FDA inspection, and the agency posted its shocking inspection report in January. Accord Healthcare, the U.S. subsidiary of Intas, said in mid-June it had no date for restarting production.
Asked why it waited two months after its inspection to announce the cisplatin shortage, given that Intas supplied more than half the U.S. market for the drug, the FDA said via email that it doesn’t list a drug in shortage until it has “confirmed that overall market demand is not being met.”
Prices for carboplatin, cisplatin, and other drugs have skyrocketed on the so-called gray market, where speculators sell medicines they snapped up in anticipation of shortages. A 600-milligram bottle of carboplatin, normally available for $30, was going for $185 in early May and $345 a week later, said Richard Scanlon, the pharmacist at Moore’s clinic.
“It’s hard to have these conversations with patients — ‘I have your dose for this cycle, but not sure about next cycle,’” said Dr. Mark Einstein, chair of the Department of Obstetrics, Gynecology and Reproductive Health at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School.
Should government step in?
Despite a drug shortage task force and numerous congressional hearings, progress has been slow at best. The 2020 CARES Act gave the FDA the power to require companies to have contingency plans enabling them to respond to shortages, but the agency has not yet implemented guidance to enforce the provisions.
As a result, neither Accord nor other cisplatin makers had a response plan in place when Intas’ plant was shut down, said Soumi Saha, senior vice president of government affairs for Premier, which arranges wholesale drug purchases for more than 4,400 hospitals and health systems.
Premier understood in December that the shutdown endangered the U.S. supply of cisplatin and carboplatin, but it also didn’t issue an immediate alarm, she said. “It’s a fine balance,” she said. “You don’t want to create panic. buying or hoarding.”
More lasting solutions are under discussion. Sardella and others have proposed government subsidies to get U.S. generics plants running full time. Their capacity is now half-idle. If federal agencies like the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services paid more for more safely and efficiently produced drugs, it would promote a more stable supply chain, he said.
“At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs,” said Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx, a nonprofit funded by health systems, foundations and the federal government that provides about 80 drugs to hospitals in its network. Civica is building a $140-million factory near Petersburg, Va., that will produce dozens more, Coukell said.
At a certain point the system needs to recognize there’s a high cost to low-cost drugs.
— Allan Coukell, senior vice president for public policy at Civica Rx
Ratain and his University of Chicago colleague Dr. Satyajit Kosuri recently called for the creation of a strategic inventory buffer for generic medications, something like the Strategic Petroleum Reserve, set up in 1975 in response to the OPEC oil crisis.
In fact, Ratain reckons, selling a quarter-million barrels of oil would probably generate enough cash to make and store two years’ worth of carboplatin and cisplatin.
“It would almost literally be a drop in the bucket.”
This article was produced by KFF Health News, formerly known as Kaiser Health News, a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues.

Business
On TikTok, Users Thumb Their Noses at Looming Ban

Over the last week, the videos started appearing on TikTok from users across the United States.
They all made fun of the same thing: how the app’s ties to China made it a national security threat. Many implied that their TikTok accounts had each been assigned an agent of the Chinese government to spy on them through the app — and that the users would miss their personal spies.
“May we meet again in another life,” one user wrote in a video goodbye set to Whitney Houston’s cover of Dolly Parton’s “I Will Always Love You.” The video included an A.I.-generated image of a Chinese military officer.
The videos were just one way that some of TikTok’s 170 million monthly U.S. users were reacting as they prepared for the app to disappear from the country as soon as Sunday.
The Supreme Court is set to rule on a federal law that required TikTok’s Chinese owner, ByteDance, to sell the app by Jan. 19 or face a ban in the United States. U.S. officials have said China could use TikTok to harvest Americans’ private data and spread covert disinformation. TikTok, which has said a sale is impossible and challenged the law, is now awaiting the Supreme Court’s response.
The possibility that the justices will uphold the law has set off a palpable sense of grief and dark humor across the app. Some users have posted videos suggesting ways to circumvent a ban with technological workarounds. Others have downloaded another Chinese app, Xiaohongshu, also known as “Red Note,” to thumb their noses at the U.S. government’s concerns about TikTok’s ties to China.
The videos highlight the collision taking place online between the law, which Congress passed with wide support last year, and everyday users of TikTok, who are dismayed that the app may soon disappear.
“Much of my TikTok feed now is TikTokers ridiculing the U.S. government, TikTokers thanking their Chinese spy as a form of ridicule,” said Anupam Chander, a professor of law and technology at Georgetown University and an expert on the global regulation of new technologies. “TikTokers recognize that they are not likely to be manipulated by anyone. They are actually quite sophisticated about the information they’re receiving.”
TikTok declined to comment on the users’ references to its ties to China.
Some users are not willing to give up the app — or their supposed spies — so easily.
Hundreds of TikTok videos over the last week have cataloged how teenagers could keep using the app in the United States, according to a review by The New York Times. One of the most popular methods described is the use of a VPN, or a virtual private network, which can mask a user’s location and make it appear that the person is elsewhere.
“They can’t actually ban TikTok in the U.S. because VPNs are not banned,” Sasha Casey, a TikTok user, said in a recent video that was liked over 60,000 times. “Use a VPN. And send a picture to Congress while you do it, because that’s what I’ll be doing.”
While VPNs can make it appear that a phone, a laptop or another electronic device is in a remote location, it is not clear if the technology can circumvent the ban. A device’s real location is stored in many places, including in the app store that was used to download TikTok.
TikTok fans also seem to be behind the sudden surge in popularity for Xiaohongshu, the most downloaded free app on Tuesday and Wednesday in the U.S. Apple Store. Hundreds of millions of people in China use the app, which, like TikTok, features short videos and text-based posts. Xiaohongshu means “little red book” in Mandarin.
Mr. Chander anticipates that the Supreme Court will uphold the ban law this week, though he believes that TikTok has the winning case. He said the downloads of Red Note and the Chinese spy memes showed that many Americans did not agree with their government’s security concerns, particularly at the expense of free speech.
“When the United States shutters a massive free expression service, which our democratic allies have not shuttered, it will make us the censor and put us in the unusual position of silencing expression,” Mr. Chander said. “It will make Americans who use TikTok really distrustful of the U.S. government as carrying their best interests.”
Business
Edison stock turns volatile as growing blame for wildfires lands on the power company

Southern California’s catastrophic fires have rocked the stock of Edison International, the parent company of Southern California Edison, as accusations and lawsuits about the utility’s potential role in starting the fires mount.
Shares of Edison International closed up 5% at $61.30 on Wednesday after plunging 23% this month, making it one of the worst performers on the Standard & Poor’s 500. The rebound came after Ladenburg Thalmann analysts upgraded their rating of the stock to neutral from sell, saying that their target price of $56.50 a share reflected worst-case outcomes associated with the current wildfires.
“At this time, it is too early to discern what the outcomes will be with respect to the impact of the fires on the California Wildfire Insurance Fund solvency and/or the future earnings of Edison International,” the analysts wrote, according to Barron’s. “An initial assessment of SCE’s role in the start of the fires will likely not occur until the summer of 2025 at the earliest.”
State lawmakers established the wildfire fund in the wake of wildfires several years ago after Wall Street investors lost confidence and ratings agencies threatened to downgrade California’s investor-owned utilities.
Market analyst Zacks downgraded Edison International stock from outperform to neutral after the fires started last week. Zacks predicted Edison’s operating revenue would increase during 2025 and 2026, while acknowledging that “the company has been incurring significant wildfire-related costs” and that “higher-than-expected decommissioning costs could materially impact the company’s operating results.”
RBC Capital Markets, another analyst, had a loftier view of Edison as recently as October when it called the utility “a high quality operator, with investor confidence around wildfire risk improving from best in class mitigation efforts.”
The fallout from the fires is an abrupt disruption for a company that had been surging in recent months. In its most recent quarterly report, the company posted a profit of $516 million, or $1.33 per share, compared with $155 million, or 40 cent per share, in the third quarter of last year.
“Our team has achieved remarkable success over the last several years managing unprecedented climate challenges, making our operations more resilient and positioning us strongly for the growth ahead,” President Pedro J. Pizarro said in the report.
Fire agencies are investigating whether downed Southern California Edison utility equipment played a role in igniting the 800-acre Hurst fire near Sylmar, company officials have acknowledged.
The company issued a report Friday saying that a downed conductor was discovered at a tower in the vicinity of the Hurst fire, but that it “does not know whether the damage observed occurred before or after the start of the fire.” The fire is nearly fully contained, according to the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection.
SCE is also under scrutiny for possibly being involved in sparking the Eaton fire that has burned 14,000 acres and destroyed thousands of structures, wiping out whole swaths of Altadena, where at least 16 people died in the blaze.
On Tuesday the Newport Beach law firm of Bridgford, Gleason & Artinian filed a mass action complaint in Los Angeles Superior Court against SCE regarding the Eaton fire on behalf of victims including Jeremy Gursey, whose Altadena property was destroyed in the fire.
“Based upon our investigation, our discussions with various consultants, the public statements of SCE, and the video evidence of the fire’s origin, we believe that the Eaton Fire was ignited because of SCE’s failure to de-energize its overhead wires which traverse Eaton Canyon—despite a red flag PDS wind warning issued by the national weather service the day before the ignition of the fire,” lawyer Richard Bridgford said in a statement.
The firm said it has represented more than 10,000 California fire victims in past suits against Pacific Gas & Electric Co. and SCE. Bridgford told Yahoo Finance that his inbox is full of Southern California residents seeking to participate in the Eaton fire lawsuit and that he anticipates “there’ll be hundreds joining.”
The most extreme level of a red flag fire warning, a “particularly dangerous situation,” returned to parts of Los Angeles and Ventura counties Wednesday morning, heightening concerns about the potential for new fires.
“The danger has not yet passed,” Los Angeles Fire Department Chief Kristin Crowley said during a news conference Wednesday. “So please prioritize your safety.”
Business
Albania Gives Jared Kushner Hotel Project a Nod as Trump Returns

The government of Albania has given preliminary approval to a plan proposed by Jared Kushner, Donald J. Trump’s son-in-law, to build a $1.4 billion luxury hotel complex on a small abandoned military base off the coast of Albania.
The project is one of several involving Mr. Trump and his extended family that directly involve foreign government entities that will be moving ahead even while Mr. Trump will be in charge of foreign policy related to these same nations.
The approval by Albania’s Strategic Investment Committee — which is led by Prime Minister Edi Rama — gives Mr. Kushner and his business partners the right to move ahead with accelerated negotiations to build the luxury resort on a 111-acre section of the 2.2-square-mile island of Sazan that will be connected by ferry to the mainland.
Mr. Kushner and the Albanian government did not respond Wednesday to requests for comment. But when previously asked about this project, both have said that the evaluation is not being influenced by Mr. Kushner’s ties to Mr. Trump or any effort to try to seek favors from the U.S. government.
“The fact that such a renowned American entrepreneur shows his interest on investing in Albania makes us very proud and happy,” a spokesman for Mr. Rama said last year in a statement to The New York Times when asked about the projects.
Mr. Kushner’s Affinity Partners, a private equity company backed with about $4.6 billion in money mostly from Saudi Arabia and other Middle East sovereign wealth funds, is pursuing the Albania project along with Asher Abehsera, a real-estate executive that Mr. Kushner has previously teamed up with to build projects in Brooklyn, N.Y.
The Albanian government, according to an official document recently posted online, will now work with their American partners to clear the proposed hotel site of any potential buried munitions and to examine any other environmental or legal concerns that need to be resolved before the project can move ahead.
The document, dated Dec. 30, notes that the government “has the right to revoke the decision,” depending on the final project negotiations.
Mr. Kushner’s firm has said the plan is to build a five-star “eco-resort community” on the island by turning a “former military base into a vibrant international destination for hospitality and wellness.”
Ivanka Trump, Mr. Trump’s daughter, has said she is helping with the project as well. “We will execute on it,” she said about the project, during a podcast last year.
This project is just one of two major real-estate deals that Mr. Kushner is pursuing along with Mr. Abehsera that involve foreign governments.
Separately, the partnership received preliminary approval last year to build a luxury hotel complex in Belgrade, Serbia, in the former ministry of defense building, which has sat empty for decades after it was bombed by NATO in 1999 during a war there.
Serbia and Albania have foreign policy matters pending with the United States, as both countries seek continued U.S. support for their long-stalled efforts to join the European Union, and officials in Washington are trying to convince Serbia to tighten ties with the United States, instead of Russia.
Virginia Canter, who served as White House ethics lawyer during the Obama and Clinton administrations and also an ethics adviser to the International Monetary Fund, said even if there was no attempt to gain influence with Mr. Trump, any government deal involving his family creates that impression.
“It all looks like favoritism, like they are providing access to Kushner because they want to be on the good side of Trump,” Ms. Canter said, now with State Democracy Defenders Fund, a group that tracks federal government corruption and ethics issues.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science5 days ago
Science5 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago‘How to Make Millions Before Grandma Dies’ Review: Thai Oscar Entry Is a Disarmingly Sentimental Tear-Jerker
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoMichael J. Fox honored with Presidential Medal of Freedom for Parkinson’s research efforts
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: Millennials try to buy-in or opt-out of the “American Meltdown”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoMeta Drops Rules Protecting LGBTQ Community as Part of Content Moderation Overhaul















