Lifestyle
One restaurant has a way to fight food waste: Making food out of 'trash'

Kayla Abe (pictured here) and her partner, chef David Murphy, co-founded Shuggie’s Trash Pie in 2022, in part to address the global problem of food waste. According to the food waste reduction nonprofit ReFED, 38% of the U.S. food supply goes uneaten.
Ryan Kellman/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ryan Kellman/NPR
Climate change is affecting our food, and our food is affecting the climate. NPR is dedicating a week to stories and conversations about the search for solutions.
No one, except maybe Sesame Street’s Oscar the Grouch, wants to consume food that most people think of as garbage.
But if everyone ate fare that might otherwise be thrown out — say, weird animal parts or milk that’s close to its sell-by date — we’d significantly reduce the impacts of human-caused climate change.
“Addressing food waste turns out to be one of the biggest climate solutions of them all,” said climate scientist Jonathan Foley, who serves as executive director of the climate solutions think tank Project Drawdown.
According to the food waste reduction nonprofit ReFED, 38% of the U.S. food supply goes uneaten.
All of the processes involved in making food, from clearing land and raising cattle to packaging and cooking ingredients, contribute to one-third of the world’s planet-warming pollution. The food waste that ends up rotting in landfills is particularly problematic.
“It causes methane to go into the atmosphere as well, and that’s a really potent greenhouse gas,” Foley said.
Methane traps more heat than carbon dioxide, which causes global warming. An estimated 60% of methane emissions are human-caused and come largely from agriculture, fossil fuels and food waste decomposing in landfills.
Restaurants are in an optimal position to help solve this problem.
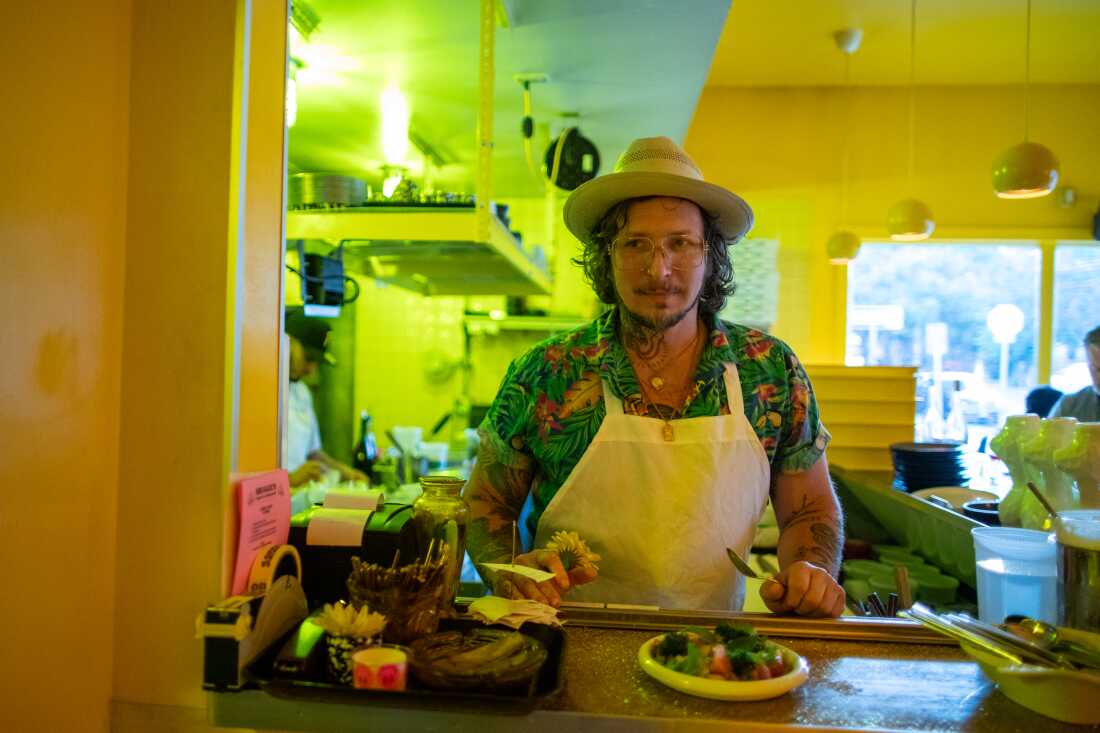

David Murphy, chef and co-owner of Shuggie’s Trash Pie in San Francisco, a restaurant that focuses on imperfect and up-cycled ingredients, previously worked in high-end restaurants. “We always demanded the best. The most perfect little Brussels sprout,” he says.
Ryan Kellman/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ryan Kellman/NPR
According to research from the U.S. Department of Agriculture, people are spending more on eating out in this country than they are at home, and the restaurant industry was responsible for almost 10 million tons of leftover food in 2022, according to 2022 data from ReFED.
Restaurants can make practical tweaks, like reducing or customizing portion sizes. “That’s a big one,” said Roni Neff, an associate professor at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health who studies food systems and waste. “Seventy percent of the food that’s wasted in restaurants is happening after it’s served to people — on their plates.”
Neff said restaurants can also streamline their ordering processes so surplus food isn’t sitting around. And then there are the chefs.
“They can help to shape people’s views, expand our ideas of what’s good food. And they can also shift behaviors in more subtle ways,” he said.
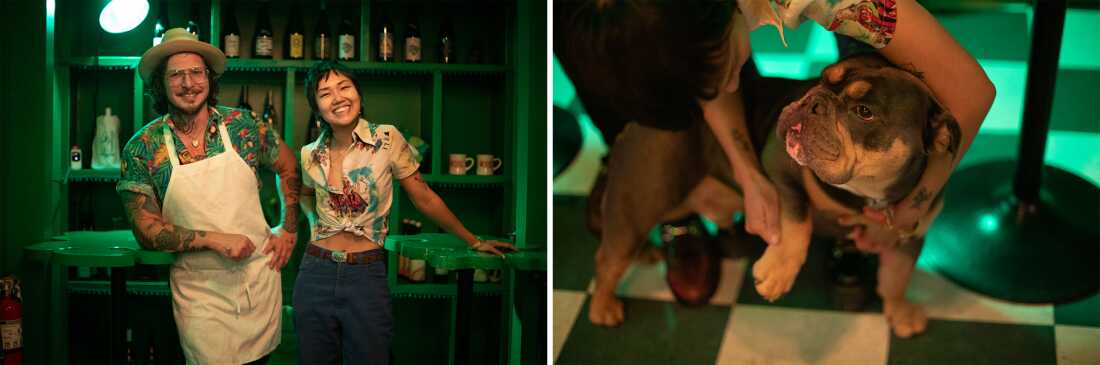
Shuggie’s co-owners David Murphy and Kayla Abe met at a farmers market in downtown San Francisco. They were united in their desire to help local farmers who were having trouble selling their extra produce. Pictured at right, Abe and Murphy’s dog, Beef.
Ryan Kellman/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ryan Kellman/NPR
That’s where restaurants like Shuggie’s Trash Pie come in.
Founded by chef David Murphy and his partner, Kayla Abe, in 2022, the San Francisco “climate solutions restaurant” works to get diners comfortable with imperfect ingredients usually discarded by the food system. According to Abe, Shuggie’s has saved 41,000 pounds of food waste from the trash can in the roughly 2 1/2 years since it opened.
“Our big goal is to change the way America’s eating,” said Abe. “And bring the idea to the mainstream that eating trash is cool.”

Shuggie’s menu features dishes made from imperfect and surplus ingredients — often sourced from local farmers who have too much of a particular produce to sell, or a produce that is past its prime. “I was constantly talking to them about their issues,” says Abe of her conversations with farmers. “And food waste was a recurring one.”
Ryan Kellman/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ryan Kellman/NPR
Like a few other sustainability-focused restaurants and chains in the U.S. (e.g. Emmer & Rye Hospitality Group in Austin and San Antonio, Texas, and Lighthouse in Brooklyn, New York) Shuggie’s sources food that local producers cannot sell because there’s a surplus, it looks irregular, or it’s past its prime.
“We do not dumpster dive,” said Murphy. “That is not something that we do.”
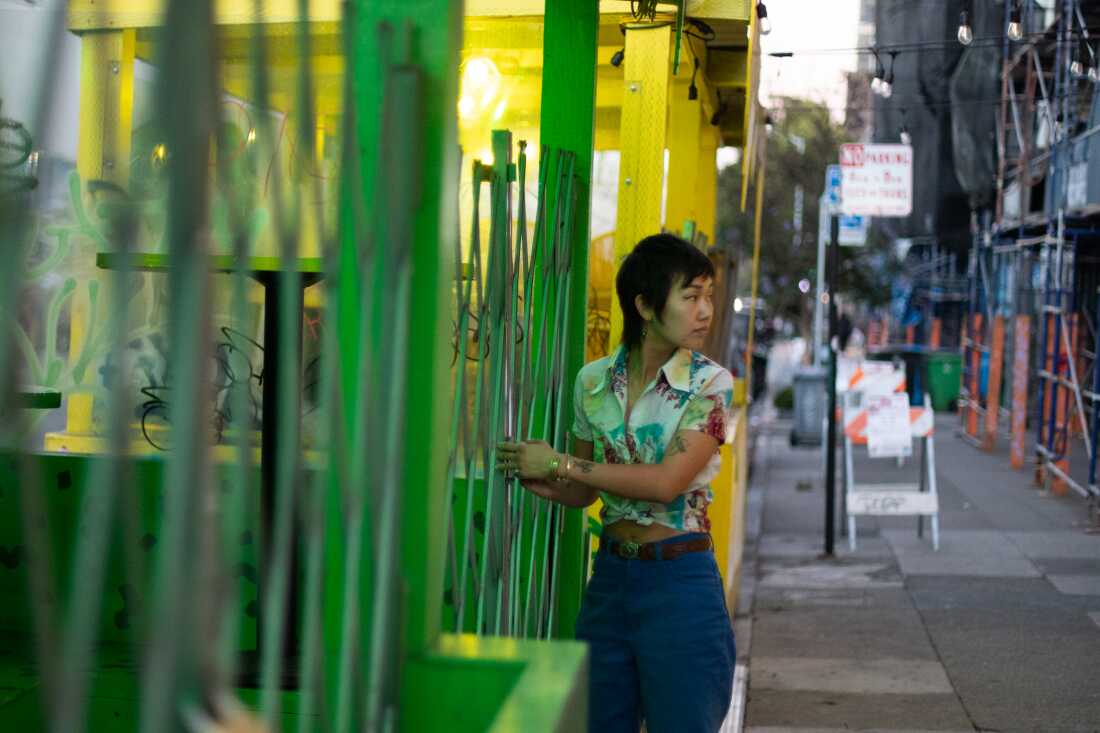

Shuggie’s co-owner Kayla Abe gets ready for closing time. Before co-founding Shuggie’s with partner David Murphy in 2022, Kayla Abe worked for the organization that runs the farmers market at San Francisco’s Ferry Building. “The more we can grow this movement, we can actually start to make bigger change,” she says of advocating for food waste reduction as a restaurateur.
Ryan Kellman/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ryan Kellman/NPR
Instead, Murphy and Abe have built strong relationships with local produce farmers, as well as fish and meat distributors.
“To look at the ugly food or the imperfect food, that it doesn’t have to be the best of everything, is a relatively new way for people to look at their food,” said Jordan Bow, the founder of the distributor Royal Hawaiian Seafood, and Shuggie’s main seafood source for oft-discarded fish parts like halibut cheeks and various types of bycatch. “I’m counting on the chefs to be creative and not just do what everybody else does.”
It’s going to take many more restaurants doing this work, as well as a broader cultural change among customers, to really make a dent in the massive food waste problem. That’s true both for eating out and eating at home. And if that shift happens, it could mean less food waste in landfills and less planet-warming pollution, which makes reducing food waste a huge climate solution.
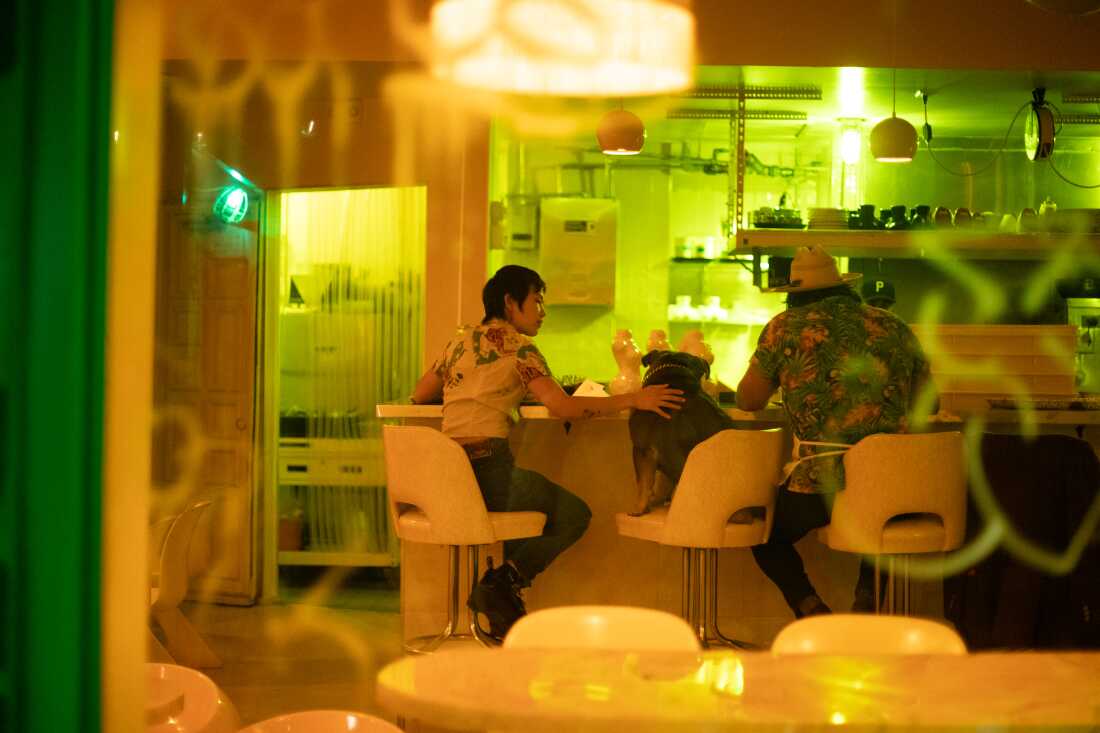

Abe and Murphy work long hours at Shuggie’s. Prepping imperfect ingredients to restaurant standards creates additional work, and margins are tight. It can be challenging to persuade consumers to pay restaurant prices for what they perceive as waste. After closing for the night, Abe and Murphy, along with their dog Beef, sit down for a meal.
Ryan Kellman/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Ryan Kellman/NPR
There are simple ways to use leftover food in your refrigerator. To help you get started, NPR asked Shuggie’s chef Murphy to share some ideas. Below you’ll find three of his creative yet simple recipes that make use of commonly leftover items.
Carrot Top Chimichurri
Chef’s note: “This sauce is the base for so many of our dishes. For example, it gets incorporated into a pesto after we add cheese and nuts to it.”
Ingredients
2 cups carrot tops or beet tops, or wilting fridge greens
3 cloves garlic, minced
2 tablespoons vinegar (apple cider preferably)
1 cup extra virgin olive oil or grapeseed oil
1½ tablespoons chili flakes
salt, to taste
Method
In a blender, mix all the ingredients together on high for 30 seconds or until all the leaves have been incorporated well.
Season with salt.
So good you’ll want to use this chimi on everything!
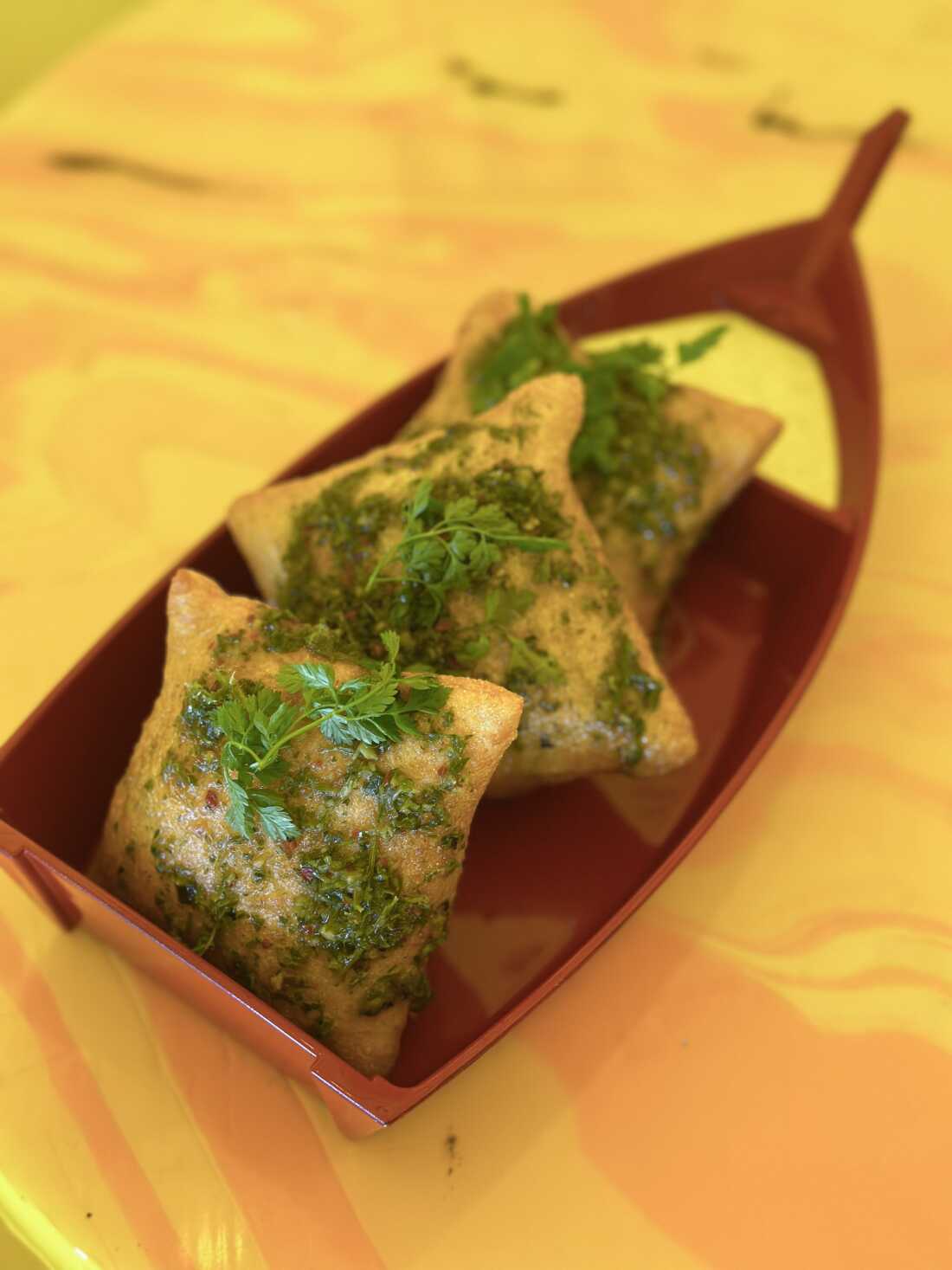

Chef David Murphy’s Carrot Top Chimichurri sauce, showcased here on Shuggie’s Pizza Puffs.
Kayla Abe
hide caption
toggle caption
Kayla Abe
Shuggie’s Dream Beans
Chef’s note: “Use this wholesome bean dish as a dumpster for all sorts of leftovers sitting in the fridge. I’ve added squid, octopus, numerous different veggies, tired greens, fennel … anything!”
Ingredients
3 cups great northern beans, soaked, cooked in a flavorful vegetable stock. (You can sub with cannellini, gigante, or your favorite soup bean.)
½ cup chopped garlic
½ cup sundried tomatoes in oil, chopped
1 tin Spanish anchovies in oil
1 cup herb stems, chopped
4 cups tired greens (kale, collards, arugula, or any other thing left in the crisper), chopped into 1-inch pieces
1 stick dry cured Spanish chorizo, chopped into ⅛-inch cubes
4 quarts flavorful vegetable or chicken stock
3 tablespoons smoked paprika
1 teaspoon cayenne pepper
2 tablespoons black pepper
1 large yellow onion, medium dice
Method
Cook beans until tender, strain.
In another pot with a bit of grapeseed oil in the pan, cook all veggies and chorizo, deglaze with stock, add dry spices, anchovy and sundried tomato.
Add salt to taste.
Ladle into bowls, top with croutons made from day old bread, and add carrot top chimi!

Shuggie’s Dream Beans
Kayla Abe
hide caption
toggle caption
Kayla Abe
Ricotta Fluff
Chef’s note: “Throw this creamy topping on waffles, or insert it in place of mozzarella on your favorite pizza … super sexy!”
Ingredients
1 gallon milk (close to or even past its expiration date!)
¼ cup white vinegar
2 cups heavy cream
Salt to taste
Honey or other sweetener of your choice
Method
Whip heavy cream to soft peaks.
Heat milk to a simmer over low heat.
Pour in vinegar, stir gently, then strain.
Let curds cool.
Fold in heavy cream and season with salt.
Slather the mixture on toasted bread with olive oil.
Sweeten to taste.
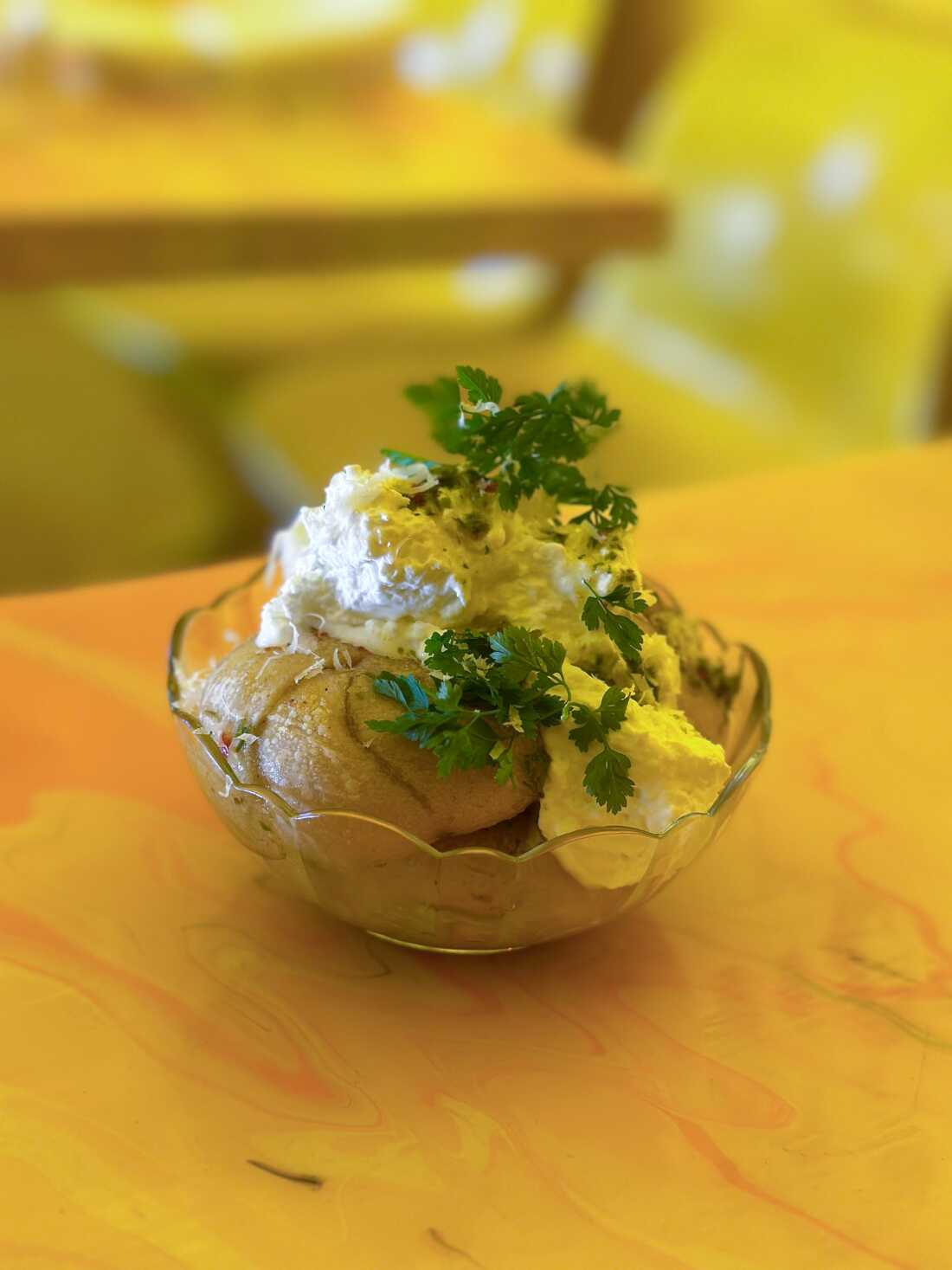

Ricotta Fluff sits atop Shuggie’s Garlic Knots, with a dash of Carrot Top Chimi. The fluff can also be used in desserts.
Kayla Abe
hide caption
toggle caption
Kayla Abe
Audio and digital stories edited by Jennifer Vanasco and Sadie Babits. Audio story mixed by Isabella Gomez-Sarmiento.

Lifestyle
Mundane, magic, maybe both — a new book explores ‘The Writer’s Room’

There’s a three-story house in Baltimore that looks a bit imposing. You walk up the stone steps before even getting up to the porch, and then you enter the door and you’re greeted with a glass case of literary awards. It’s The Clifton House, formerly home of Lucille Clifton.
The National Book Award-winning poet lived there with her husband, Fred, starting in 1967 until the bank foreclosed on the house in 1980. Clifton’s daughter, Sidney Clifton, has since revived the house and turned it into a cultural hub, hosting artists, readings, workshops and more. But even during a February visit, in the mid-afternoon with no organized events on, the house feels full.

The corner of Lucille Clifton’s bedroom, where she would wake up and write in the mornings
Andrew Limbong/NPR
hide caption
toggle caption
Andrew Limbong/NPR
“There’s a presence here,” Clifton House Executive Director Joël Díaz told me. “There’s a presence here that sits at attention.”
Sometimes, rooms where famous writers worked can be places of ineffable magic. Other times, they can just be rooms.

Princeton University Press
Katie da Cunha Lewin is the author of the new book, The Writer’s Room: The Hidden Worlds That Shape the Books We Love, which explores the appeal of these rooms. Lewin is a big Virginia Woolf fan, and the very first place Lewin visited working on the book was Monk’s House — Woolf’s summer home in Sussex, England. On the way there, there were dreams of seeing Woolf’s desk, of retracing Woolf’s steps and imagining what her creative process would feel like. It turned out to be a bit of a disappointment for Lewin — everything interesting was behind glass, she said. Still, in the book Lewin writes about how she took a picture of the room and saved it on her phone, going back to check it and re-check it, “in the hope it would allow me some of its magic.”
Let’s be real, writing is a little boring. Unlike a band on fire in the recording studio, or a painter possessed in their studio, the visual image of a writer sitting at a desk click-clacking away at a keyboard or scribbling on a piece of paper isn’t particularly exciting. And yet, the myth of the writer’s room continues to enrapture us. You can head to Massachusetts to see where Louisa May Alcott wrote Little Women. Or go down to Florida to visit the home of Zora Neale Hurston. Or book a stay at the Scott & Zelda Fitzgerald Museum in Alabama, where the famous couple lived for a time. But what, exactly, is the draw?

Lewin said in an interview that whenever she was at a book event or an author reading, an audience question about the writer’s writing space came up. And yes, some of this is basic fan-driven curiosity. But also “it started to occur to me that it was a central mystery about writing, as if writing is a magic thing that just happens rather than actually labor,” she said.
In a lot of ways, the book is a debunking of the myths we’re presented about writers in their rooms. She writes about the types of writers who couldn’t lock themselves in an office for hours on end, and instead had to find moments in-between to work on their art. She covers the writers who make a big show of their rooms, as a way to seem more writerly. She writes about writers who have had their homes and rooms preserved, versus the ones whose rooms have been lost to time and new real estate developments. The central argument of the book is that there is no magic formula to writing — that there is no daily to-do list to follow, no just-right office chair to buy in order to become a writer. You just have to write.
Lifestyle
Bruce Johnston Retiring From The Beach Boys After 61 Years

Bruce Johnston
I’m Riding My Last Wave With The Beach Boys
Published
Bruce Johnston is riding off into the California sunset … at least for now.
The Beach Boys legend announced Wednesday he’s stepping away from touring after six decades with the iconic band. The 83-year-old revealed in a statement to Rolling Stone he’s hanging up his touring hat to focus on what he calls part three of his long music career.
“It’s time for Part Three of my lengthy musical career!” Johnston said. “I can write songs forever, and wait until you hear what’s coming!!! As my major talent beyond singing is songwriting, now is the time to get serious again.”
Johnston famously stepped in for co-founder Brian Wilson in 1965 for live performances, becoming a staple of the Beach Boys’ touring lineup ever since. Now, he says he’s shifting gears toward songwriting and even some speaking engagements … with occasional touring member John Stamos helping him craft what he’ll talk about onstage.
“I might even sing ‘Disney Girls’ & ‘I Write The Songs!!’” he teased.
But don’t call it a full-on farewell tour just yet. Johnston made it clear he’s not shutting the door completely, saying he’s excited to reunite with the band for special occasions, including their upcoming July 2-4 shows at the Hollywood Bowl as part of the Beach Boys’ 2026 tour. The run celebrates both the 60th anniversary of “Pet Sounds” and America’s 250th birthday.
“This isn’t goodbye, it’s see you soon,” he wrote. “I am forever grateful to be a part of the Beach Boys musical legacy.”
Lifestyle
On the brink of death, a woman is saved by a stranger and his family
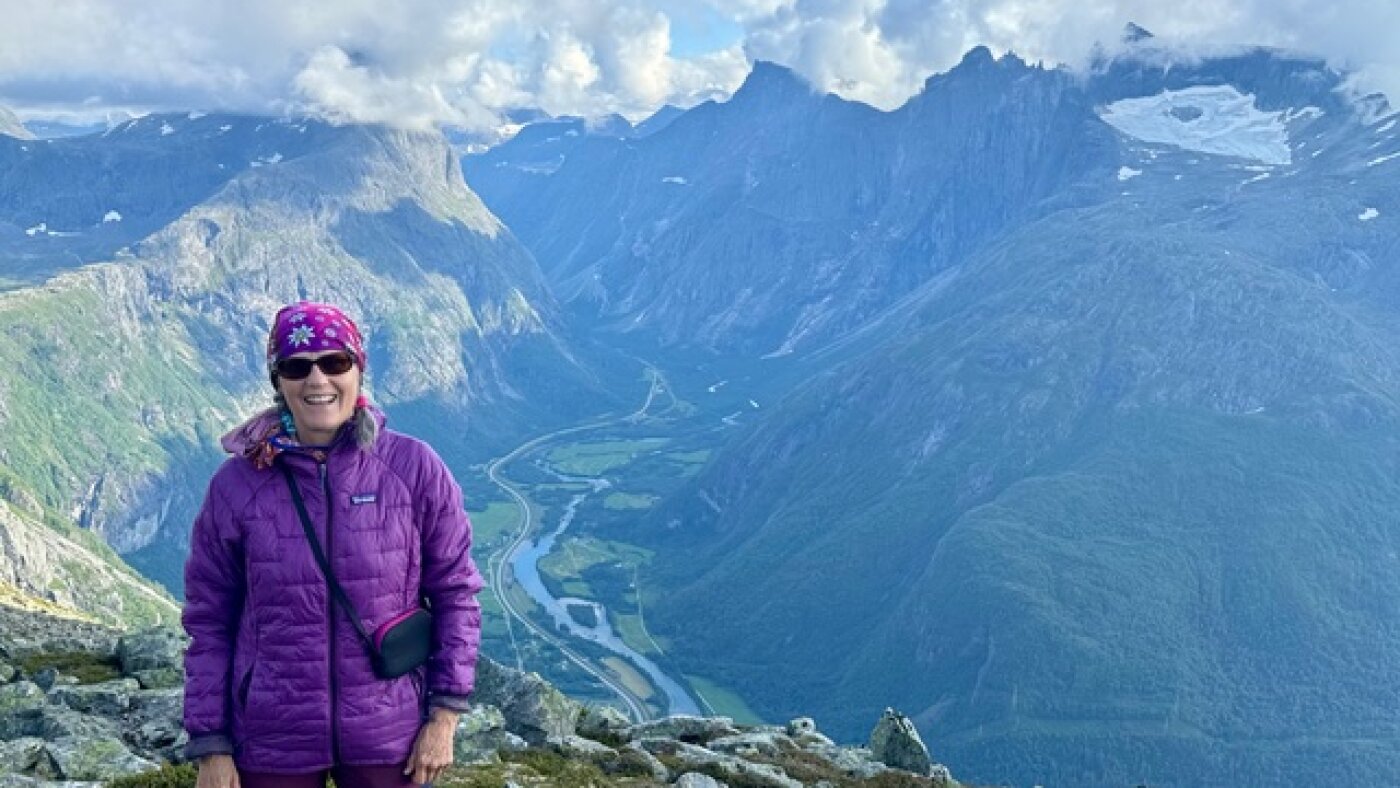

In 1982, Jean Muenchrath was injured in a mountaineering accident and on the brink of death when a stranger and his family went out of their way to save her life.
Jean Muenchrath
hide caption
toggle caption
Jean Muenchrath
In early May 1982, Jean Muenchrath and her boyfriend set out on a mountaineering trip in the Sierra Nevada, a mountain range in California. They had done many backcountry trips in the area before, so the terrain was somewhat familiar to both of them. But after they reached one of the summits, a violent storm swept in. It began to snow heavily, and soon the pair was engulfed in a blizzard, with thunder and lightning reverberating around them.
“Getting struck and killed by lightning was a real possibility since we were the highest thing around for miles and lightning was striking all around us,” Muenchrath said.
To reach safer ground, they decided to abandon their plan of taking a trail back. Instead, using their ice axes, they climbed down the face of the mountain through steep and icy snow chutes.
They were both skilled at this type of descent, but at one particularly difficult part of the route, Muenchrath slipped and tumbled over 100 feet down the rocky mountain face. She barely survived the fall and suffered life-threatening injuries.

This was before cellular or satellite phones, so calling for help wasn’t an option. The couple was forced to hike through deep snow back to the trailhead. Once they arrived, Muenchrath collapsed in the parking lot. It had been five days since she’d fallen.
”My clothes were bloody. I had multiple fractures in my spine and pelvis, a head injury and gangrene from a deep wound,” Muenchrath said.
Not long after they reached the trailhead parking lot, a car pulled in. A man was driving, with his wife in the passenger seat and their baby in the back. As soon as the man saw Muenchrath’s condition, he ran over to help.
”He gently stroked my head, and he held my face [and] reassured me by saying something like, ‘You’re going to be OK now. I’ll be right back to get you,’” Muenchrath remembered.
For the first time in days, her panic began to lift.
“My unsung hero gave me hope that I’d reach a hospital and I’d survive. He took away my fears.”
Within a few minutes, the man had unpacked his car. His wife agreed to stay back in the parking lot with their baby in order to make room for Muenchrath, her boyfriend and their backpacks.
The man drove them to a nearby town so that the couple could get medical treatment.
“I remember looking into the eyes of my unsung hero as he carried me into the emergency room in Lone Pine, California. I was so weak, I couldn’t find the words to express the gratitude I felt in my heart.”

The gratitude she felt that day only grew. Now, nearly 45 years later, she still thinks about the man and his family.
”He gave me the gift of allowing me to live my life and my dreams,” Muenchrath said.
At some point along the way, the man gave Muenchrath his contact information. But in the chaos of the day, she lost it and has never been able to find him.
”If I knew where my unsung hero was today, I would fly across the country to meet him again. I’d hug him, buy him a meal and tell him how much he continues to mean to me by saving my life. Wherever you are, I say thank you from the depths of my being.”
My Unsung Hero is also a podcast — new episodes are released every Tuesday. To share the story of your unsung hero with the Hidden Brain team, record a voice memo on your phone and send it to myunsunghero@hiddenbrain.org.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts1 week ago
Massachusetts1 week agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Wisconsin3 days ago
Wisconsin3 days agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Denver, CO1 week ago
Denver, CO1 week ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Maryland4 days ago
Maryland4 days agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Louisiana1 week ago
Louisiana1 week agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Florida4 days ago
Florida4 days agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Oregon5 days ago
Oregon5 days ago2026 OSAA Oregon Wrestling State Championship Results And Brackets – FloWrestling

















