Colorado
New Colorado tax credit could lift 50,000 children out of poverty, is latest to tap TABOR surplus

Boasting that child poverty in Colorado would soon be cut nearly in half, Gov. Jared Polis on Friday signed a large new tax credit for low-income families into law.
The ceremony put an underline on a legislative session that featured state policymakers looking again and again to the state surplus to flatten inequalities. Lawmakers passed dozens of new tax credits this year that tapped into massive revenues the state couldn’t keep and otherwise would have to return through refund checks.
The new family affordability tax credit that received Polis’ signature is by far the largest individual tax credit in terms of cost. It is also, advocates say, among the most impactful.
They expect it to lift more than 50,000 children out of poverty.
The new law, passed as House Bill 1311, will use roughly $700 million per year that comes in over the state revenue growth limit set by the Taxpayer’s Bill of Rights, or TABOR. It will send the poorest Colorado families $3,200 per child younger than 6. The amount of the credit will scale down as children grow older and family incomes increase, eventually zeroing out at $85,000 per year for joint filers and once children turn 17.
“Kids don’t choose who their parents are or what their income level is — or how they grow up,” Polis said during the bill signing ceremony at a Denver preschool. “Making sure kids everywhere have food on the table (and) have the support that they need to grow up is a big deal.”
The child tax credit stacks atop others passed or expanded by the legislature this year, including an increase to the state’s match of the Earned Income Tax Credit. In all, the new policies tap billions of dollars from projected TABOR surpluses in coming years that would have to be returned to taxpayers one way or another.
Democratic lawmakers, often over dissents from Republicans, opted mostly for directed credits rather than the general refunds that long have been typical in the state’s boom years.
How the new tax credits work
The Colorado Fiscal Institute, a progressive think tank involved in crafting the legislation, predicts families will receive as much as $4,400 a year per child 5 and younger through an expanded child care tax credit and the new family affordability tax credit.
Throw in the Earned Income Tax Credit increase, which matches up to 50% of the federal EITC that sends money to low-income households, and Colorado families could see significant financial help. The state EITC match doubled this year, amounting to nearly $1,900 extra for very-low-income working families with three or more children.
The credits depend on consistent TABOR surpluses and will be scaled down in less robust economic times. Caroline Nutter, the legislative coordinator for the think tank, estimates the credit changes will reduce the number of children in poverty — about 133,000 kids — by 40% in years when the credits are fully funded.
“What we’re really trying to do there is make sure families, even those making more than the median household income in Colorado, are receiving help,” Nutter said. “Raising kids in this state is not cheap. Even if you’re making $100,000 a year, it’s still a big cost to bear.”
The credits, while stacking together, work differently:
- The EITC expansion is based on a federal tax credit worth between $600 (for individuals without children) and $7,430 (for families with three or more children). Qualification limits range from $17,640 per year in adjusted gross income for a single person up to $63,398 for joint filers. Colorado will match up to 50% of the federal credit if state growth is on a solid footing.
- The child care tax credit covers a percentage of child care costs, depending on household income. At most, the federal credit covers about $1,050 for one dependent child and up to $2,100 for two or more. The Colorado credit matches up to 70% of that for households with incomes of $60,000 or less.
- The new family tax credit scales down based on family income as well as the ages and number of children. Single filers making $15,000 or less per year in adjusted gross income — and joint filers making $25,000 or less — will receive up to $3,200 for each child younger than 6 and, for children ages 6 to 16, up to $2,400. The credit amounts decrease as incomes rise, with a cap of $75,000 for individual filers and $85,000 for joint filers.
Coloradans may benefit from other credits, too — notably a $1,500 credit for child care workers, home health care workers, personal care aides and certified nursing assistants making less than $75,000 per year that Polis also signed into law Friday. Earlier this week, he signed off on a new tax credit that covers two years of in-state college tuition for students whose families make $90,000 a year or less.
On hand at Friday’s ceremony was U.S. Sen. Michael Bennet, who has championed a short-lived federal child tax credit that he’s hoping to revive in Congress next year by leveraging the looming expiration of tax cuts. He praised the state’s new credit.
“The family affordability tax credit testifies to the idea that we don’t have to accept those levels of childhood poverty as a permanent state of our economy, or our democracy, or our society,” he said. “I think the national leadership you’ve shown here is something that we will carry back to Washington, D.C. — to be able to say that because of your leadership, governor, Colorado now has the best anti-poverty legislation of any state in America.”
Do new credits undermine TABOR?
Together, Colorado’s new tax credits represent a reimagining of how state officials handle TABOR surpluses — while trying to stay within the constraints of the constitutional amendment passed by voters more than 30 years ago.
Traditionally, state revenue that’s over the cap would be returned to Coloradans largely through a six-tier system that gave higher-income households a bigger share under the idea they paid more in taxes. Nutter called that approach “wasteful” because it directs money to people who already have the most resources.
The Common Sense Institute, a nonpartisan, free enterprise-oriented think tank, noted that the money returned through tax credits still stays with Colorado taxpayers, versus going into government programs. But a CSI report on tax credits argues that the new approach “broadly undermines TABOR’s intent” by divorcing refunds from taxes paid.
In coming years, upwards of $1 billion per year that would typically be refunded through the six-tier system will instead go to targeted tax credits, according to its report.
Lang Sias, a former state representative and now a research fellow at the think tank, said the legislature “has effectively substituted its judgment on how those tax dollars should be spent over that of taxpayers who would otherwise see the refunds.”
“We’re moving away from a TABOR refund and toward a TABOR redistribution,” he said in an interview.
He didn’t weigh in on the merits of the new policies but questioned lawmakers’ decision to tie the new tax credits to the state’s surplus and, in some cases, to give them sunsets. Assuming they’re as beneficial as proponents say, both cases mean they may not be permanent policies.
The new tax credits also aren’t the only way state officials responded to a foreseeable future of $1 billion-plus surpluses. Polis fought for a $450 million income tax cut, which predominantly will benefit wealthier Coloradans, and a decrease in the state sales tax rate during economic booms.
Taxpayers can also continue to expect flat TABOR refunds when they file their taxes — albeit closer to the $115 range than the $700-plus amounts of recent years.
Nutter argued that while the shift will affect income brackets differently compared to the prior system, people across the spectrum still will see more money in their pockets — from the credits or, for wealthier people, through the tax cuts.
Stay up-to-date with Colorado Politics by signing up for our weekly newsletter, The Spot.

Colorado
Colorado Rockies spring training game no. 17 thread: Kyle Freeland vs. Jedisxson Paez

In his first spring training action of 2026, Kyle Freeland faced the daunting task of pitching against Team USA in an exhibition game on March 4. He gave up a solo homer to Aaron Judge in a two-hit, one-strikeout performance in one inning.
Today, Freeland and the Rockies (8-6-1) will take part in his first Cactus League action against the White Sox (10-7) at Camelback Ranch. The Rockies are 5-2 on the road this spring vs. 3-5-1, including the showdown vs. Team USA, at Salt River Fields.
Advertisement
Today’s game represents a rematch of a Feb. 23 showdown where the Rockies beat the White Sox 5-4. Chicago will send Jedisxson Paez to the mound to start the game. The 22-year-old RHP will be making his third spring appearance. He’s posted a 23.14 ERA in 2 1/3 innings over two starts with six earned runs, six hits, including one homer, three strikeouts and one walk. Former Rockie Drew Romo will be starting at catcher for the White Sox.
On Sunday, four pitchers combined to throw five scoreless innings and Kyle Karros and Tyler Freeman each had two-hit performances in the Rockies 4-4 tie with Cleveland. Even though it’s only spring training, the Rockies offense has been much improved thus far. The Rockies rank among all Major League teams this Spring in: on-base percentage (.381, T-1st), home runs (23, T-4th), average (.287, 3rd), HBP (14, T-2nd), slugging (.492, 3rd), OPS (.871, 3rd), runs scored (98, 5th), RBI (91, 6th) and total bases (254, 6th).
Earlier on Monday, the Rockies released a new motto for the 2026 campaign: “New era. At altitude. We are here for the climb.”
First Pitch: 2:05 p.m. MDT
Advertisement
TV: None
Radio: 850 AM/94.1 FM KOA Rockies Radio Network (1:55 p.m. pregame)
Lineups:
Colorado
Outraged over incentives for data centers that are no good for Colorado (Letters)

Data centers: What good are they for Colorado?
Re: “Dueling policies for data centers,” March 1 news story
The Denver Post article about two competing bills in the legislature regarding new data centers in Colorado seems to start with the presumption that we want the data centers.
Why do we want them and who wants them? Is it the politicians wanting bragging rights about our state becoming another Silicon Valley? Perhaps they want more businesses so they can collect more taxes from the new residents. Alternatively, they just want more power in Washington by increasing our population. Has anyone stopped to ask why we want to attract more people to our state?
Colorado is in a fight with other Western states to obtain more water for our growing population. Our wildlife is being crowded out by the increased urbanization. The roads are so crowded that it is not uncommon to come to a complete stop on our interchanges during rush hour. We have a serious housing shortage. The air is being polluted by the increased number of cars. These are all the result of a growing population. Did anyone stop to ask why we want more people?
During my 53 years living in Colorado, I have never heard anyone (other than politicians) say, “We need more people.” On the contrary, the conversation is more often about how we are becoming overcrowded. I would like the politicians to explain why we need more businesses and more people in our state. It should not be a presumption that more is better! Are our elected representatives truly reflecting the wishes of their constituents?
Doug Hurst, Parker
Anger and disbelief were our reactions when we read about House Bill 1030, which is under consideration at the statehouse. This outrageous corporate welfare bill would provide some of the world’s wealthiest corporations with massive state tax reductions to build monstrous resource-thirsty data centers. Analysts projected a $92.5 million tax loss in just three years if a bunch of these data centers are built. Just one 160-megawatt facility would gobble up as much power as 176,000 homes once completed. Consider for comparison that the entire DIA airport uses around 45 megawatts of power!
As the state legislature grapples with bone-deep budget cuts, we cannot afford to exempt data centers from paying their own way nor allow their unregulated construction. Taxpayer-funded corporate handouts would entail massive hits to tax revenue that should be used for our schools, roads, infrastructure, and valid state needs. What essential services will potentially be cut or axed to cover the lost revenue to the state from this corporate giveaway?
These data centers also demand massive amounts of our water. A CoreSite data center in Denver alone will use approximately 805,000 gallons of water per day to air-condition its computers. That is the same as the average daily indoor water use of 16,100 Denver homes.
I pray our state legislature will condemn HB-1030 to the corporate welfare hell where it belongs in. Instead, they should support Senate Bill 102 that will hopefully properly regulate these tax-eating, water-wasting, and electricity-gobbling monstrosities.
Terry Talbot, Grand Junction
As a pediatrician, I’ve noticed one key issue missing from the data center debate: public health.
Data centers are extraordinarily energy- and water-intensive. Nationally, they already consume about 4% of U.S. electricity — a figure expected to more than double by 2030. Much of that power still comes from burning fossil fuels. Without strong safeguards, that growth means more air pollution. In my clinical practice, I see firsthand how health is shaped by the air we breathe. More pollution means more asthma attacks, heart disease, and premature deaths, especially in communities already burdened by poor air quality.
Water use is another concern. Large data centers can use enormous amounts of water for cooling. In a drought-prone state like Colorado, this raises serious questions about long-term drinking water reliability and heat resilience.
Energy affordability is also a health issue. When infrastructure is built to serve massive corporate users, costs can shift to households. I see the effects of energy insecurity in families forced to choose between cooling their homes, buying medication, or putting food on the table.
Colorado has an opportunity to get this right. Senate Bill 102 would establish guardrails to protect ratepayers, limit pollution, and ensure large electricity users pay their full infrastructure costs. Other states, including Michigan and Virginia, are reconsidering generous tax incentives after seeing how quickly public costs can outpace public benefit.
Colorado can welcome innovation without sacrificing clean air, clean water, affordable energy, and community health. Public health must be a priority, not an afterthought.
Clare Burchenal, Denver
As the story makes clear, data centers in our communities have real impacts on our health, our pocketbooks and our quality of life. I’m a mom of two small children who are counting on the adults in the room to make responsible decisions that impact their futures. It’s dizzying to see the pace of data centers sweeping the country and confusing as to why leaders are rushing to accommodate them without taking into consideration all of the impacts these massive industrial complexes have on communities.
It’s critical that data centers are powered by clean-burning renewable energy, not fossil fuels. We are in a no-snow winter in Colorado, and we have no safeguards in place against data center water use. Energy infrastructure should be paid for by the billion-dollar big tech companies that will profit from it, not by unfair rate increases for our families and small businesses.
There is a way to do this right. Senate Bill 102 has some important protections for our families and communities while still allowing for the responsible construction and operation of data centers built in appropriate places in our state. It is unacceptable that our leaders do nothing to protect us from big tech excesses. SB-102 will protect all Colorado kids – and their parents and communities. Join me in urging our legislators to pass this important bill.
Sara Kuntzler, Arvada
U.S. women’s hockey players above the game and politics
Re: “Trump tore athletes down on the world’s stage,” March 1 commentary
Dear Megan Schrader,
Thank you for your column on how the president disrespected the U.S. women’s Olympic hockey team. Your excellent commentary hit and sent the puck into the back of the net, so to speak.
To take it a step further, I believe the women’s choice not to visit the White House was more than meets the eye. Ostensibly, they declined the invitation because of the timing, specifically the resumption of play in the professional women’s hockey league.
Yet, I would like to believe it was more an expression of contempt for the president and his policies.
The women were smarter and braver and truer to their values than were the men’s Olympic hockey team, who, with the same timing issues, chose to accept the invitation to the White House. That visit and the visit to the State of the Union Address only helped bolster the president’s optics. An exception was the Colorado Avalanche’s own Brock Nelson, who declined to accompany the men’s team because he valued his family time more than a public charade.
In sports — as in life — we need more people like the women hockey players who will elevate their values above the games and politics.
Bill Allegar, Denver
Backing up to park for safety?
Re: “Do you back into a parking spot or back out?” March 1 feature story
I read this with slight amusement. For someone who has traveled a bit, and especially in Asia (Japan in particular), backing into a parking space is a very common practice (not a new trend) and has been for decades. On my first trip to Japan, around 1992, I was told it was what most people did.
As for the company Imminent Threat Solutions recommending “tactical parking” because they should “prevail against all threats,” seems like marketing hype of the biggest kind, building fear into your daily life of running errands and going to work. Has there been bad behaviour, shootings, and whatnot in a parking lot? Sure, but let’s not build fear for something that happens rarely to the average individual.
Randy DeBoer, Denver
To add to the parking procedures article in Sunday’s paper, there is another option, one that I use and recommend; it’s the “drive-through” to an open space.
After having been hit and having a rental car damaged (a three-month hassle to resolve) by a driver who backed out of an opposite space without looking, I don’t drive into a parking space if I can help it. What I do instead is find an open space where I can drive in straight and continue to a back-to-back adjoining space where I can park and then drive ahead to depart. These parking spots are typically a longer walk to my destination, and I benefit from the additional steps.
G. E. Cole, Centennial
I enjoyed your article on discussing whether to back in or pull straight into parking spaces. Our oldest son is a backer-inner, and I am starting to be one too. What is missing from your analysis, though, is the grocery store, much less Costco or Home Depot. Almost nobody is a backer-inner in these places, since you’re typically loading stuff in your backseat, hatch, or pickup bed. I guess the backer-inners are just not going to be able to escape as quickly once they’ve picked up 50 pounds of dog food, 25 rolls of paper towels, or five sheets of 4′ x 8′ plywood. Hope they survive.
Tim Hickisch, Highlands Ranch
You can support immigrants and the law
Re: “Faith communities show support for immigrants,” Feb. 22 news story
Faith communities do show support for immigrants. I don’t agree with those who stand against the law and ICE. While we may support all people made in the image of God, we should not be for illegal immigrants. They have broken the law, and some are doing great harm while living here. Legal immigrants, please come. Illegal immigrants, please go home and come here legally.
Deanna R Walworth, Brighton
Sign up for Sound Off to get a weekly roundup of our columns, editorials and more.
To send a letter to the editor about this article, submit online or check out our guidelines for how to submit by email or mail.
Colorado
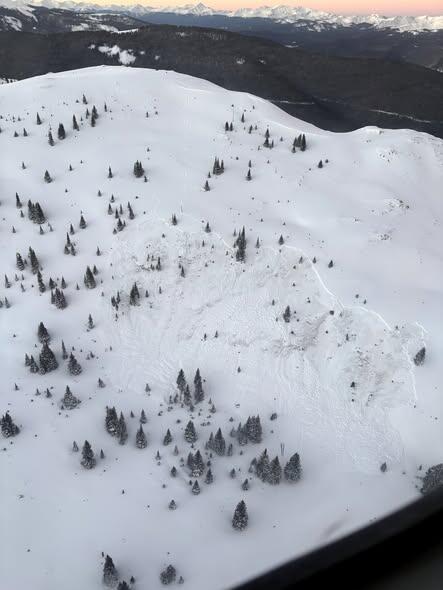
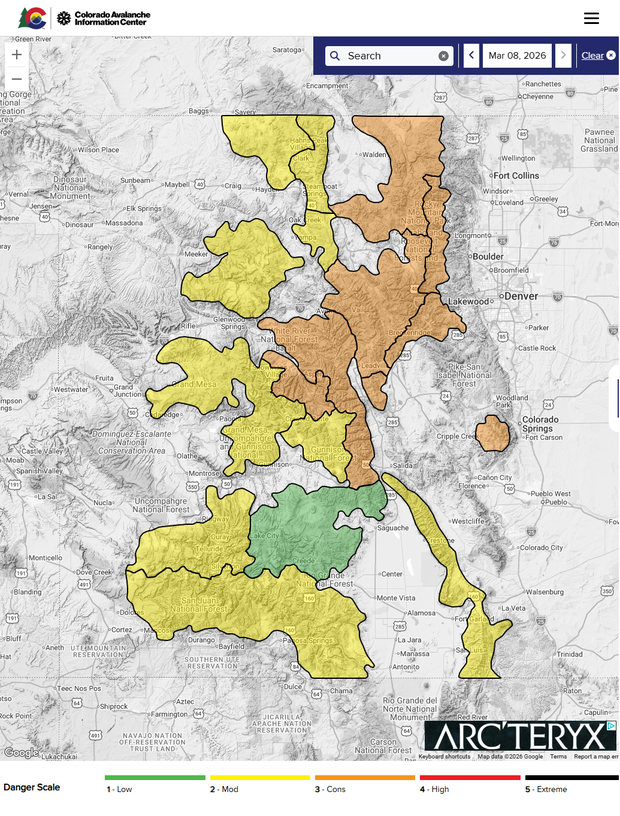
Skier killed in avalanche in Colorado’s Boss Basin, first ski death of the season

Early Sunday morning, Colorado rescue crews found the body of a missing skier who was killed in a recent avalanche.
The skier was reported missing in the Boss Basin area in the upper portion of Resolution Creek on March 7.
Summit County Rescue Group, Vail Mountain Rescue and the Summit and Eagle County Sheriff’s Offices began searching the area and discovered the site of the avalanche. They noticed that nearby ski and snowmobile tracks led up to where it occurred.
The Colorado Avalanche Information Center says Flight for Life helped with the search. They found the body of the missing skier in the avalanche debris on Sunday, around sunrise.
CAIC staff said the avalanche started near the treeline on a northeast-facing slope and was about two feet deep. The slope angles ranged from 33 to 36 degrees.
According to CAIC data, this is the first person killed in an avalanche during the 2025-2026 ski season.
Avalanche danger in some parts of the high country is considerable, particularly on north- and east-facing slopes and on large open slopes just below ridgelines.
The CAIC Forecast for Sunday says:
“The avalanche danger will stay at CONSIDERABLE (3of5) on Sunday for the places that picked up the most snow in this last storm (Elk and Sawatch Ranges). Areas that received less than 8 inches will go back to MODERATE danger, but this may vary significantly from drainage to drainage and with elevation. Assume a higher danger if you find a foot or more of new snow. Across the region, wind-drifted slopes will remain the most dangerous regardless of the danger. In the shallower areas (Elks and Sawatch), we’re more concerned about avalanches in motion breaking deeper, failing in buried facet layers.
On Sunday, as the sun pops out, remember that a strong spring sun can make sunny slopes unstable rather quickly. Keep an eye out for roller balls as an indication of a forthcoming shed cycle of loose avalanches.”
-

 Wisconsin1 week ago
Wisconsin1 week agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Massachusetts7 days ago
Massachusetts7 days agoMassachusetts man awaits word from family in Iran after attacks
-

 Maryland1 week ago
Maryland1 week agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Florida1 week ago
Florida1 week agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Pennsylvania4 days ago
Pennsylvania4 days agoPa. man found guilty of raping teen girl who he took to Mexico
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week ago2 Survivors Describe the Terror and Tragedy of the Tahoe Avalanche
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoKeith Olbermann under fire for calling Lou Holtz a ‘scumbag’ after legendary coach’s death
-

 Virginia5 days ago
Virginia5 days agoGiants will hold 2026 training camp in West Virginia