Will this be the team that gets Arizona back to the Final Four for the first time in 25 years, and maybe go further? Who knows. But one thing is for certain, no Wildcats squad has had a better regular season than this one.
Colorado
Editorial: Threat of uranium mine in gated Colorado neighborhood drives home risk of split estates

South T Bar Ranch is a cautionary tale for Coloradans. Beware the split estate.
Colorado law allows for surface rights of land to be split from sub-surface mineral rights. Most commonly, conflict arises in Colorado’s natural gas-rich Denver-Julesburg Basin, where the Front Range sprawl north of Denver has landed subdivisions above mineral rights owned by major corporations planning or already using hydraulic fracturing to extract the gas.
South T Bar Ranch, located northwest of Cañon City, could become a nightmare situation for homeowners compared to the problems presented with hydraulic fracturing. Even modern uranium mining — known as ablation — causes a significant disruption to surface land, although companies claim it is safer and less problematic than pit mining.
Global Uranium and Enrichment, which owns the mineral rights below the 5,200-acre gated community, has received the necessary permits to begin exploratory drilling for uranium. If the company plans to proceed and extract deposits of uranium, landowners are legally required to provide the surface access necessary for the operation.
The blame for this scenario is twofold: a lack of due diligence by land buyers and a lack of disclosure from sellers, Realtors, and title companies.
The possibility of uranium mining on this land should have significantly reduced the value of these parcels from the outset. In other words, the land should have sold for a reduced price compared to other parcels in Fremont County where homeowners owned their mineral rights.
In this instance, it was homeowners in 2008 who gathered together their mineral rights and sold them to a company that was later purchased by Global Uranium and Enrichment. Subsequent landowners missed out on the windfall from that sale.
A simple disclosure could have avoided all this heartache. We’re not saying homeowners wouldn’t have still purchased the land, but at least they would feel less blindsided or would have had the knowledge needed to negotiate a better price on the land.
Colorado’s Contract to Buy and Sell Real Estate does include IN ALL CAPS an oil, gas, water and mineral disclosure. However, the disclosure only informs people about the risk of split estates; it doesn’t include specific information about whether the land being purchased is split from mineral rights. The clause merely encourages the buyer to “seek additional information.” Most buyers get the contract to buy and sell just before closing.
Title companies also do not trace the mineral rights separately, which really is an astounding lapse in the expensive services the title companies perform. Homeowners are on their own to research the ownership of mineral rights using county records or to hire an attorney to research the title and deed for them.
Where should the onus of due diligence fall?
The current system places too much of a burden on potential buyers. Colorado law already has strict rules for the disclosure of water rights and water sources, and the law should be updated so that disclosure of mineral rights is treated the same. Potential land buyers should be able to quickly see in the real estate listing whether land comes with water and minerals. The point of sale is too late to warn a potential buyer that the estate may or may not be split.
The website for the South T Bar Ranch now includes a disclosure about the split estate and the possibility of uranium mining. More homeowner’s associations, metropolitan districts and other entities should take similar steps to help potential buyers make informed decisions.
Unfortunately, it’s too late for the owners of South T Bar Ranch, who bought after the mineral rights deal in 2008 and failed to learn of the split estate through their Realtor, title company, or other investigations.
People who profited off selling the mineral rights feel vastly different about the potential for mining operations than those who purchased their property later and will not see a windfall from the operations. Some may have failed to negotiate for a reduced price, given the potential for mining.
Global Uranium and Enrichment is only seeking permits to drill wells exploring uranium deposits at this time. The possibility of an actual mining operation is still years away and will require a separate permitting process. It’s possible nothing will come of this exploration, and homeowners will be spared from having mining operations in their backyard (or nearby).
Coloradans can learn from this lesson, and those who learn they are already on a split estate, can make an offer to buy the mineral rights back before market conditions lead to exploration and extraction near their home.
Sign up for Sound Off to get a weekly roundup of our columns, editorials and more.
To send a letter to the editor about this article, submit online or check out our guidelines for how to submit by email or mail.

Colorado
Outraged over incentives for data centers that are no good for Colorado (Letters)

Data centers: What good are they for Colorado?
Re: “Dueling policies for data centers,” March 1 news story
The Denver Post article about two competing bills in the legislature regarding new data centers in Colorado seems to start with the presumption that we want the data centers.
Why do we want them and who wants them? Is it the politicians wanting bragging rights about our state becoming another Silicon Valley? Perhaps they want more businesses so they can collect more taxes from the new residents. Alternatively, they just want more power in Washington by increasing our population. Has anyone stopped to ask why we want to attract more people to our state?
Colorado is in a fight with other Western states to obtain more water for our growing population. Our wildlife is being crowded out by the increased urbanization. The roads are so crowded that it is not uncommon to come to a complete stop on our interchanges during rush hour. We have a serious housing shortage. The air is being polluted by the increased number of cars. These are all the result of a growing population. Did anyone stop to ask why we want more people?
During my 53 years living in Colorado, I have never heard anyone (other than politicians) say, “We need more people.” On the contrary, the conversation is more often about how we are becoming overcrowded. I would like the politicians to explain why we need more businesses and more people in our state. It should not be a presumption that more is better! Are our elected representatives truly reflecting the wishes of their constituents?
Doug Hurst, Parker
Anger and disbelief were our reactions when we read about House Bill 1030, which is under consideration at the statehouse. This outrageous corporate welfare bill would provide some of the world’s wealthiest corporations with massive state tax reductions to build monstrous resource-thirsty data centers. Analysts projected a $92.5 million tax loss in just three years if a bunch of these data centers are built. Just one 160-megawatt facility would gobble up as much power as 176,000 homes once completed. Consider for comparison that the entire DIA airport uses around 45 megawatts of power!
As the state legislature grapples with bone-deep budget cuts, we cannot afford to exempt data centers from paying their own way nor allow their unregulated construction. Taxpayer-funded corporate handouts would entail massive hits to tax revenue that should be used for our schools, roads, infrastructure, and valid state needs. What essential services will potentially be cut or axed to cover the lost revenue to the state from this corporate giveaway?
These data centers also demand massive amounts of our water. A CoreSite data center in Denver alone will use approximately 805,000 gallons of water per day to air-condition its computers. That is the same as the average daily indoor water use of 16,100 Denver homes.
I pray our state legislature will condemn HB-1030 to the corporate welfare hell where it belongs in. Instead, they should support Senate Bill 102 that will hopefully properly regulate these tax-eating, water-wasting, and electricity-gobbling monstrosities.
Terry Talbot, Grand Junction
As a pediatrician, I’ve noticed one key issue missing from the data center debate: public health.
Data centers are extraordinarily energy- and water-intensive. Nationally, they already consume about 4% of U.S. electricity — a figure expected to more than double by 2030. Much of that power still comes from burning fossil fuels. Without strong safeguards, that growth means more air pollution. In my clinical practice, I see firsthand how health is shaped by the air we breathe. More pollution means more asthma attacks, heart disease, and premature deaths, especially in communities already burdened by poor air quality.
Water use is another concern. Large data centers can use enormous amounts of water for cooling. In a drought-prone state like Colorado, this raises serious questions about long-term drinking water reliability and heat resilience.
Energy affordability is also a health issue. When infrastructure is built to serve massive corporate users, costs can shift to households. I see the effects of energy insecurity in families forced to choose between cooling their homes, buying medication, or putting food on the table.
Colorado has an opportunity to get this right. Senate Bill 102 would establish guardrails to protect ratepayers, limit pollution, and ensure large electricity users pay their full infrastructure costs. Other states, including Michigan and Virginia, are reconsidering generous tax incentives after seeing how quickly public costs can outpace public benefit.
Colorado can welcome innovation without sacrificing clean air, clean water, affordable energy, and community health. Public health must be a priority, not an afterthought.
Clare Burchenal, Denver
As the story makes clear, data centers in our communities have real impacts on our health, our pocketbooks and our quality of life. I’m a mom of two small children who are counting on the adults in the room to make responsible decisions that impact their futures. It’s dizzying to see the pace of data centers sweeping the country and confusing as to why leaders are rushing to accommodate them without taking into consideration all of the impacts these massive industrial complexes have on communities.
It’s critical that data centers are powered by clean-burning renewable energy, not fossil fuels. We are in a no-snow winter in Colorado, and we have no safeguards in place against data center water use. Energy infrastructure should be paid for by the billion-dollar big tech companies that will profit from it, not by unfair rate increases for our families and small businesses.
There is a way to do this right. Senate Bill 102 has some important protections for our families and communities while still allowing for the responsible construction and operation of data centers built in appropriate places in our state. It is unacceptable that our leaders do nothing to protect us from big tech excesses. SB-102 will protect all Colorado kids – and their parents and communities. Join me in urging our legislators to pass this important bill.
Sara Kuntzler, Arvada
U.S. women’s hockey players above the game and politics
Re: “Trump tore athletes down on the world’s stage,” March 1 commentary
Dear Megan Schrader,
Thank you for your column on how the president disrespected the U.S. women’s Olympic hockey team. Your excellent commentary hit and sent the puck into the back of the net, so to speak.
To take it a step further, I believe the women’s choice not to visit the White House was more than meets the eye. Ostensibly, they declined the invitation because of the timing, specifically the resumption of play in the professional women’s hockey league.
Yet, I would like to believe it was more an expression of contempt for the president and his policies.
The women were smarter and braver and truer to their values than were the men’s Olympic hockey team, who, with the same timing issues, chose to accept the invitation to the White House. That visit and the visit to the State of the Union Address only helped bolster the president’s optics. An exception was the Colorado Avalanche’s own Brock Nelson, who declined to accompany the men’s team because he valued his family time more than a public charade.
In sports — as in life — we need more people like the women hockey players who will elevate their values above the games and politics.
Bill Allegar, Denver
Backing up to park for safety?
Re: “Do you back into a parking spot or back out?” March 1 feature story
I read this with slight amusement. For someone who has traveled a bit, and especially in Asia (Japan in particular), backing into a parking space is a very common practice (not a new trend) and has been for decades. On my first trip to Japan, around 1992, I was told it was what most people did.
As for the company Imminent Threat Solutions recommending “tactical parking” because they should “prevail against all threats,” seems like marketing hype of the biggest kind, building fear into your daily life of running errands and going to work. Has there been bad behaviour, shootings, and whatnot in a parking lot? Sure, but let’s not build fear for something that happens rarely to the average individual.
Randy DeBoer, Denver
To add to the parking procedures article in Sunday’s paper, there is another option, one that I use and recommend; it’s the “drive-through” to an open space.
After having been hit and having a rental car damaged (a three-month hassle to resolve) by a driver who backed out of an opposite space without looking, I don’t drive into a parking space if I can help it. What I do instead is find an open space where I can drive in straight and continue to a back-to-back adjoining space where I can park and then drive ahead to depart. These parking spots are typically a longer walk to my destination, and I benefit from the additional steps.
G. E. Cole, Centennial
I enjoyed your article on discussing whether to back in or pull straight into parking spaces. Our oldest son is a backer-inner, and I am starting to be one too. What is missing from your analysis, though, is the grocery store, much less Costco or Home Depot. Almost nobody is a backer-inner in these places, since you’re typically loading stuff in your backseat, hatch, or pickup bed. I guess the backer-inners are just not going to be able to escape as quickly once they’ve picked up 50 pounds of dog food, 25 rolls of paper towels, or five sheets of 4′ x 8′ plywood. Hope they survive.
Tim Hickisch, Highlands Ranch
You can support immigrants and the law
Re: “Faith communities show support for immigrants,” Feb. 22 news story
Faith communities do show support for immigrants. I don’t agree with those who stand against the law and ICE. While we may support all people made in the image of God, we should not be for illegal immigrants. They have broken the law, and some are doing great harm while living here. Legal immigrants, please come. Illegal immigrants, please go home and come here legally.
Deanna R Walworth, Brighton
Sign up for Sound Off to get a weekly roundup of our columns, editorials and more.
To send a letter to the editor about this article, submit online or check out our guidelines for how to submit by email or mail.
Colorado
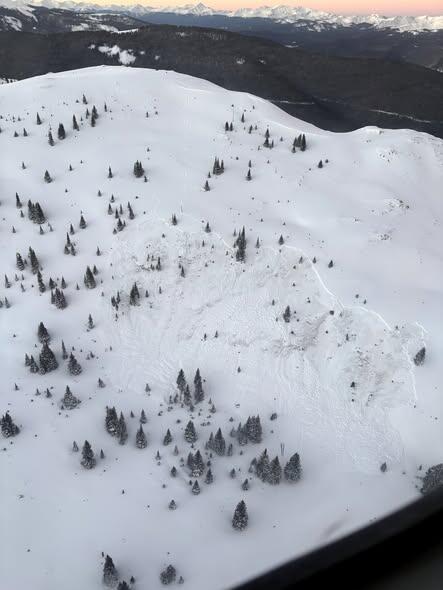
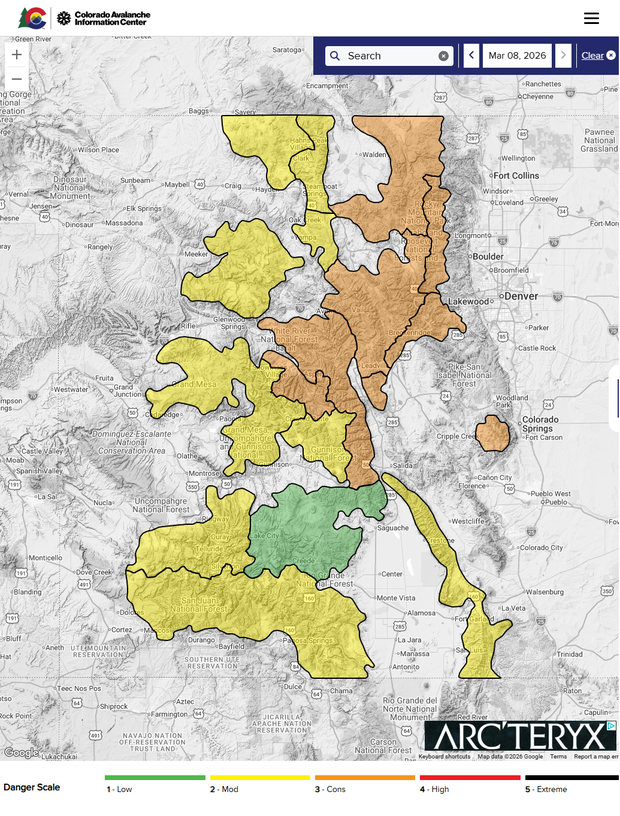
Skier killed in avalanche in Colorado’s Boss Basin, first ski death of the season

Early Sunday morning, Colorado rescue crews found the body of a missing skier who was killed in a recent avalanche.
The skier was reported missing in the Boss Basin area in the upper portion of Resolution Creek on March 7.
Summit County Rescue Group, Vail Mountain Rescue and the Summit and Eagle County Sheriff’s Offices began searching the area and discovered the site of the avalanche. They noticed that nearby ski and snowmobile tracks led up to where it occurred.
The Colorado Avalanche Information Center says Flight for Life helped with the search. They found the body of the missing skier in the avalanche debris on Sunday, around sunrise.
CAIC staff said the avalanche started near the treeline on a northeast-facing slope and was about two feet deep. The slope angles ranged from 33 to 36 degrees.
According to CAIC data, this is the first person killed in an avalanche during the 2025-2026 ski season.
Avalanche danger in some parts of the high country is considerable, particularly on north- and east-facing slopes and on large open slopes just below ridgelines.
The CAIC Forecast for Sunday says:
“The avalanche danger will stay at CONSIDERABLE (3of5) on Sunday for the places that picked up the most snow in this last storm (Elk and Sawatch Ranges). Areas that received less than 8 inches will go back to MODERATE danger, but this may vary significantly from drainage to drainage and with elevation. Assume a higher danger if you find a foot or more of new snow. Across the region, wind-drifted slopes will remain the most dangerous regardless of the danger. In the shallower areas (Elks and Sawatch), we’re more concerned about avalanches in motion breaking deeper, failing in buried facet layers.
On Sunday, as the sun pops out, remember that a strong spring sun can make sunny slopes unstable rather quickly. Keep an eye out for roller balls as an indication of a forthcoming shed cycle of loose avalanches.”
Colorado
Arizona men’s basketball shakes off poor start to win at Colorado in regular season finale

Second-ranked Arizona rallied from down 11 late in the first half to win 89-79 at Colorado on Saturday night, putting the finishing touches on its first Big 12 title. The 29 victories are the most in school history during the regular season, breaking a mark done four previous times including in 2021-22 in Tommy Lloyd’s first year running the program.
Brayden Burries had a career-high 31 points, 22 coming in the second half, while Koa Peat scored 19 of his 25 in the first half. The freshmen combined to make 21 of 31 shots and Burries added an 11-of-12 performance at the foul line, and Burries added seven rebounds, five steals and an assist.
Tobe Awaka, Ivan Kharchenkov and Motiejus Krivas each had 10 for Arizona, which shot 70.4 percent in the second half and 55.9 percent for the game. The Wildcats had a 54-26 edge on points in the paint and finished plus-5 on the boards after being down four at the half.
Jaden Bradley went scoreless for the first time this season, missing all three of his shots, but he made up for it with six of the UA’s 22 assists.
Colorado (17-14) got 28 points from Isaiah Johnson, who set the school freshman season scoring record. The Buffaloes shot 40.6 percent and made 7 of 22 from 3 but only hit one triple after halftime.
The UA trailed 38-36 at halftime, only the fourth time this season it has been down after 20 minutes, after being down 11 late in the first half. A Burries 3 tied it at 44, thenKharchenkov gave the Wildcats their first lead at 48-46 with 16:59 remaining.
Arizona got the lead up to five before Colorado fought back. Six straight by Bangot Dak put the Buffaloes ahead 54-52 but then Dak picked up his fourth foul and had to sit.
That began a 4-minute stretch with 10 lead changes before Arizona got a stop and Burries drained a 3 on the other end to put the UA up 66-62 with 9:17 left. The Wildcats made six straight shots, including back-to-back baskets inside byAwaka to make it 73-64 with 7:15 remaining.
A 3 from Kharchenkov put Arizona up 10 with 5:48 to go. The Buffaloes got within six before Peat dunked through a zone defense, and a Burries layup again got the lead to double digits.
Peat had 12 of Arizona’s first 14 points in the first seven minutes, but none put the Wildcats in the lead. The Buffaloes never trailed in the first half, jumping out to an 8-point edge with 8:08 left before halftime and extending that to 36-25 with 4:21 to go in the half, both on 3s by Johnson.
Colorado hit six 3-pointers in the first half, three by Johnson, while Arizona was 0 for 6 from deep
A 9-0 run, capped by a 3-point play by Burries, got the UA within two in the final minute, setting the stage for the second half.
Arizona now gets a few days off before heading to the Big 12 Tournament in Kansas City. As the No. 1 seed it has a double bye into Thursday’s quarterfinals, where it will face either No. 8 UCF, No. 9 Cincinnati or No. 16 Utah. They beat those teams this season by seven, 26 and 19 points, respectively.
2026 Big 12 Tournament schedule
No. 12 ASU (16-15) vs. No. 13 Baylor (16-15), 9:30 a.m. (ESPN+)
No. 9 Cincinnati (17-14) vs. No. 16 Utah (10-21), 12 p.m. (ESPN+)
No. 10 BYU (21-10) vs. No. 15 Kansas State (12-19), 4 p.m. (ESPN+)
No. 11 Colorado (17-14) vs. No. 14 Oklahoma State (18-13), 6:30 p.m. (ESPN+)
ASU/Baylor winner vs. No. 5 Iowa State (25-6), 9:30 a.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
Cincinnati/Utah winner vs. No. 8 UCF (20-10), 12 p.m. (ESPNU)
BYU/Kansas State winner vs. No. 7 West Virginia (18-13), 4 p.m. (ESPNU)
Colorado/Oklahoma State winner vs. No. 6 TCU (21-10), 6:30 p.m. (ESPN2/ESPNU)
ASU/Baylor-Iowa State winner vs. No. 4 Texas Tech (22-9), 9:30 a.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
Cincinnati/Utah-UCF winner vs. No. 1 Arizona (29-2), 12 p.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
BYU/Kansas State-West Virginia winner vs. No. 2 Houston (26-5), 4 p.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
Colorado/Oklahoma State-TCU winner vs. No. 3 Kansas (22-9), 6:30 p.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
Quarterfinal 1 winner vs. Quarterfinal 2 winner, 4 p.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
Quarterfinal 3 winner vs. Quarterfinal 4 winner, 6:30 p.m. (ESPN/ESPN2)
Semifinal winners, 3 p.m. (ESPN)
-

 Wisconsin1 week ago
Wisconsin1 week agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Massachusetts6 days ago
Massachusetts6 days agoMassachusetts man awaits word from family in Iran after attacks
-

 Maryland1 week ago
Maryland1 week agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Florida1 week ago
Florida1 week agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Pennsylvania4 days ago
Pennsylvania4 days agoPa. man found guilty of raping teen girl who he took to Mexico
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week ago2 Survivors Describe the Terror and Tragedy of the Tahoe Avalanche
-

 Sports5 days ago
Sports5 days agoKeith Olbermann under fire for calling Lou Holtz a ‘scumbag’ after legendary coach’s death
-

 Virginia5 days ago
Virginia5 days agoGiants will hold 2026 training camp in West Virginia