Alaska
Crammed with tourists, Alaska’s capital wonders what will happen as its magnificent glacier recedes – WTOP News
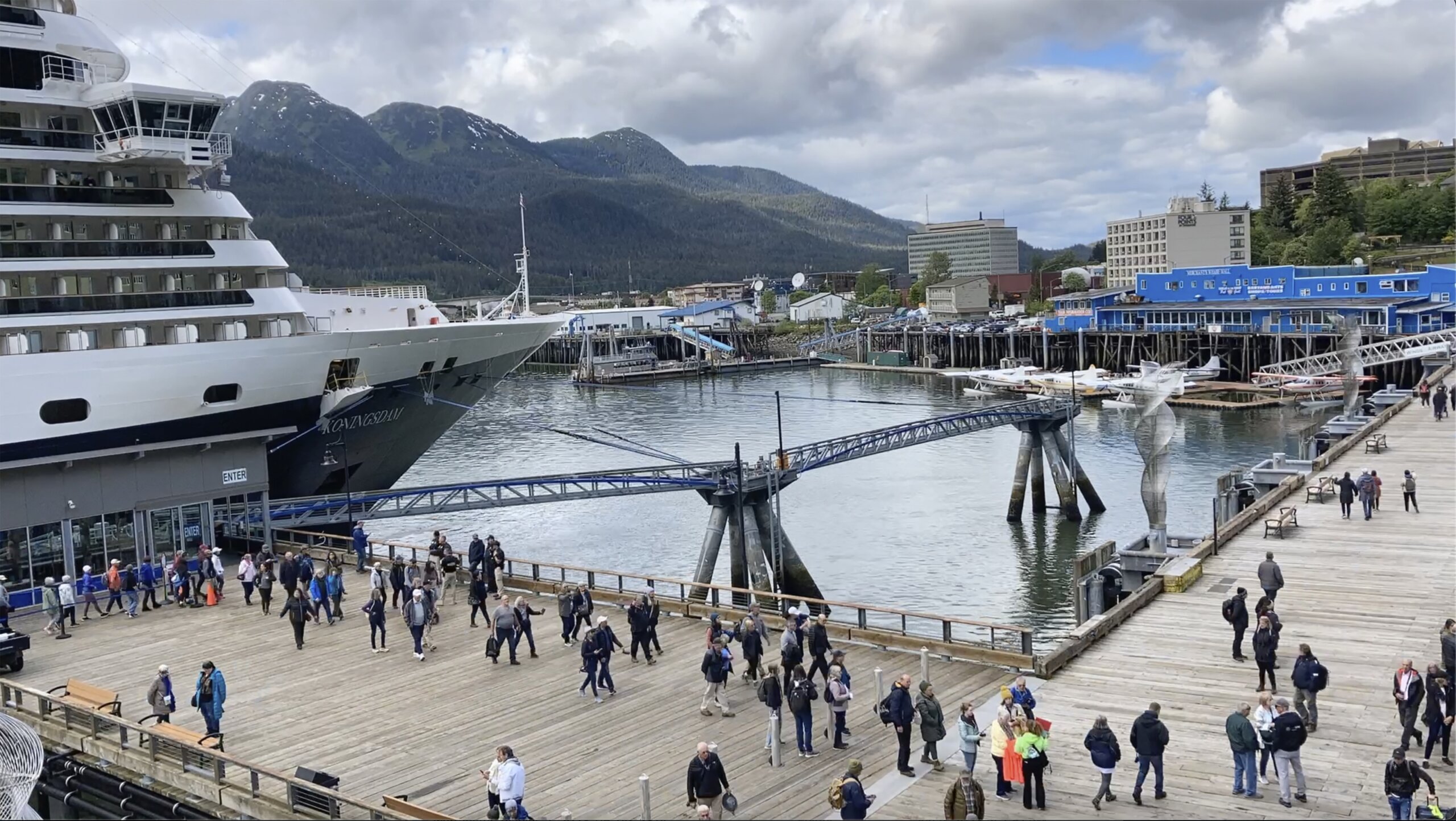

JUNEAU, Alaska (AP) — Thousands of tourists spill onto a boardwalk in Alaska’s capital city every day from cruise ships…
JUNEAU, Alaska (AP) — Thousands of tourists spill onto a boardwalk in Alaska’s capital city every day from cruise ships towering over downtown. Vendors hawk shoreside trips and rows of buses stand ready to whisk visitors away, with many headed for the area’s crown jewel: the Mendenhall Glacier.
A craggy expanse of gray, white and blue, the glacier gets swarmed by sightseeing helicopters and attracts visitors by kayak, canoe and foot. So many come to see the glacier and Juneau’s other wonders that the city’s immediate concern is how to manage them all as a record number are expected this year. Some residents flee to quieter places during the summer, and a deal between the city and cruise industry will limit how many ships arrive next year.
But climate change is melting the Mendenhall Glacier. It is receding so quickly that by 2050, it might no longer be visible from the visitor center it once loomed outside.
That’s prompted another question Juneau is only now starting to contemplate: What happens then?
“We need to be thinking about our glaciers and the ability to view glaciers as they recede,” said Alexandra Pierce, the city’s tourism manager. There also needs to be a focus on reducing environmental impacts, she said. “People come to Alaska to see what they consider to be a pristine environment and it’s our responsibility to preserve that for residents and visitors.”
The glacier pours from rocky terrain between mountains into a lake dotted by stray icebergs. Its face retreated eight football fields between 2007 and 2021, according to estimates from University of Alaska Southeast researchers. Trail markers memorialize the glacier’s backward march, showing where the ice once stood. Thickets of vegetation have grown in its wake.
While massive chunks have broken off, most ice loss has come from the thinning due to warming temperatures, said Eran Hood, a University of Alaska Southeast professor of environmental science. The Mendenhall has now largely receded from the lake that bears its name.
Scientists are trying to understand what the changes might mean for the ecosystem, including salmon habitat.
There are uncertainties for tourism, too.
Most people enjoy the glacier from trails across Mendenhall Lake near the visitor center. Caves of dizzying blues that drew crowds several years ago have collapsed and pools of water now stand where one could once step from the rocks onto the ice.
Manoj Pillai, a cruise ship worker from India, took pictures from a popular overlook on a recent day off.
“If the glacier is so beautiful now, how would it be, like, 10 or 20 years before? I just imagine that,” he said.
Officials with the Tongass National Forest, under which the Mendenhall Glacier Recreation Area falls, are bracing for more visitors over the next 30 years even as they contemplate a future when the glacier slips from casual view.
The agency is proposing new trails and parking areas, an additional visitor center and public use cabins at a lakeside campground. Researchers do not expect the glacier to disappear completely for at least a century.
“We did talk about, ‘Is it worth the investment in the facilities if the glacier does go out of sight?’” said Tristan Fluharty, the forest’s Juneau district ranger. “Would we still get the same amount of visitation?”
A thundering waterfall that is a popular place for selfies, salmon runs, black bears and trails could continue attracting tourists when the glacier is not visible from the visitor center, but “the glacier is the big draw,” he said.
Around 700,000 people are expected to visit this year, with about 1 million projected by 2050.
Other sites offer a cautionary tale. Annual visitation peaked in the 1990s at around 400,000 to the Begich, Boggs Visitor Center, southeast of Anchorage, with the Portage Glacier serving as a draw. But now, on clear days, a sliver of the glacier remains visible from the center, which was visited by about 30,000 people last year, said Brandon Raile, a spokesperson with the Chugach National Forest, which manages the site. Officials are discussing the center’s future, he said.
“Where do we go with the Begich, Boggs Visitor Center?” Raile said. “How do we keep it relevant as we go forward when the original reason for it being put there is not really relevant anymore?”
At the Mendenhall, rangers talk to visitors about climate change. They aim to “inspire wonder and awe but also to inspire hope and action,” said Laura Buchheit, the forest’s Juneau deputy district ranger.
After pandemic-stunted seasons, about 1.6 million cruise passengers are expected in Juneau this year, during a season stretching from April through October.
The city, nestled in a rainforest, is one stop on what are generally week-long cruises to Alaska beginning in Seattle or Vancouver, British Columbia. Tourists can leave the docks and move up the side of a mountain in minutes via a popular tram, see bald eagles perch on light posts and enjoy a vibrant Alaska Native arts community.
On the busiest days, about 20,000 people, equal to two-thirds of the city’s population, pour from the boats.
City leaders and major cruise lines agreed to a daily five-ship limit for next year. But critics worry that won’t ease congestion if the vessels keep getting bigger. Some residents would like one day a week without ships. As many as seven ships a day have arrived this year.
Juneau Tours and Whale Watch is one of about two dozen companies with permits for services like transportation or guiding at the glacier. Serene Hutchinson, the company’s general manager, said demand has been so high that she neared her allotment halfway through the season. Shuttle service to the glacier had to be suspended, but her business still offers limited tours that include the glacier, she said.
Other bus operators are reaching their limits, and tourism officials are encouraging visitors to see other sites or get to the glacier by different means.
Limits on visitation can benefit tour companies by improving the experience rather than having tourists “shoehorned” at the glacier, said Hutchinson, who doesn’t worry about Juneau losing its luster as the glacier recedes.
“Alaska does the work for us, right?” she said. “All we have to do is just kind of get out of the way and let people look around and smell and breathe.”
Pierce, Juneau’s tourism manager, said discussions are just beginning around what a sustainable southeast Alaska tourism industry should look like.
In Sitka, home to a slumbering volcano, the number of cruise passengers on a day earlier this summer exceeded the town’s population of 8,400, overwhelming businesses, dragging down internet speeds and prompting officials to question how much tourism is too much.
Juneau plans to conduct a survey that could guide future growth, such as building trails for tourism companies.
Kerry Kirkpatrick, a Juneau resident of nearly 30 years, recalls when the Mendenhall’s face was “long across the water and high above our heads.” She called the glacier a national treasure for its accessibility and noted an irony in carbon-emitting helicopters and cruise ships chasing a melting glacier. She worries the current level of tourism isn’t sustainable.
As the Mendenhall recedes, plants and animals will need time to adjust, she said.
So will humans.
“There’s too many people on the planet wanting to do the same things,” Kirkpatrick said. “You don’t want to be the person who closes the door and says, you know, ‘I’m the last one in and you can’t come in.’ But we do have to have the ability to say, ‘No, no more.’”
Copyright
© 2023 The Associated Press. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, written or redistributed.

Alaska
Federal funds will help DOT study wildlife crashes on Glenn Highway

New federal funds will help Alaska’s Department of Transportation develop a plan to reduce vehicle collisions with wildlife on one of the state’s busiest highways.
The U.S. Transportation Department gave the state a $626,659 grant in December to conduct a wildlife-vehicle collision study along the Glenn Highway corridor stretching between Anchorage’s Airport Heights neighborhood to the Glenn-Parks Highway interchange.
Over 30,000 residents drive the highway each way daily.
Mark Eisenman, the Anchorage area planner for the department, hopes the study will help generate new ideas to reduce wildlife crashes on the Glenn Highway.
“That’s one of the things we’re hoping to get out of this is to also have the study look at what’s been done, not just nationwide, but maybe worldwide,” Eisenman said. “Maybe where the best spot for a wildlife crossing would be, or is a wildlife crossing even the right mitigation strategy for these crashes?”
Eisenman said the most common wildlife collisions are with moose. There were nine fatal moose-vehicle crashes on the highway between 2018 and 2023. DOT estimates Alaska experiences about 765 animal-vehicle collisions annually.
In the late 1980s, DOT lengthened and raised a downtown Anchorage bridge to allow moose and wildlife to pass underneath, instead of on the roadway. But Eisenman said it wasn’t built tall enough for the moose to comfortably pass through, so many avoid it.
DOT also installed fencing along high-risk areas of the highway in an effort to prevent moose from traveling onto the highway.
Moose typically die in collisions, he said, and can also cause significant damage to vehicles. There are several signs along the Glenn Highway that tally fatal moose collisions, and he said they’re the primary signal to drivers to watch for wildlife.
“The big thing is, the Glenn Highway is 65 (miles per hour) for most of that stretch, and reaction time to stop when you’re going that fast for an animal jumping onto the road is almost impossible to avoid,” he said.
The city estimates 1,600 moose live in the Anchorage Bowl.
Alaska
Flight attendant sacked for twerking on the job: ‘What’s wrong with a little twerk before work’

They deemed the stunt not-safe-for-twerk.
An Alaska Airlines flight attendant who was sacked for twerking on camera has created a GoFundMe to support her while she seeks a new berth.
The crewmember, named Nelle Diala, had filmed the viral booty-shaking TikTok video on the plane while waiting two hours for the captain to arrive, A View From the Wing reported.
She captioned the clip, which also blew up on Instagram, “ghetto bih till i D-I-E, don’t let the uniform fool you.”
Diala was reportedly doing a victory dance to celebrate the end of her new hire probationary period.
Unfortunately, her jubilation was short-lived as Alaska Airlines nipped her employment in the bum just six months into her contract.
The fanny-wagging flight attendant feels that she didn’t do anything wrong.
Diala has since reposted the twerking clip with the new caption: “Can’t even be yourself anymore, without the world being so sensitive. What’s wrong with a little twerk before work, people act like they never did that before.”
The new footage was hashtagged #discriminationisreal.
The disgraced stewardess even set up a GoFundMe page to help support the so-called “wrongfully fired” flight attendant until she can land a new flight attendant gig.
“I never thought a single moment would cost me everything,” wrote the ex-crewmember. “Losing my job was devastating.”
She claimed that the gig had allowed her to meet new people and see the world, among other perks.
While air hostessing was ostensibly a “dream job,” Diala admitted that she used the income to help fund her “blossoming lingerie and dessert businesses,” which she runs under the Instagram handles @cakezncake (which doesn’t appear to have any content?) and @figure8.lingerie.
As of Wednesday morning, the crowdfunding campaign has raised just $182 of its $12,000 goal.
Diala was ripped online for twerking on the job as well as her subsequent GoFundMe efforts.
“You don’t respect the uniform, you don’t respect your job then,” declared one critic on the popular aviation-focused Instagram page The Crew Lounge. “Terms and Conditions apply.”
“‘Support for wrongly fired flight attendant??’” mocked another. “Her GoFund title says it all. She still thinks she was wrongly fired. Girl you weren’t wrongly fired. Go apply for a new job and probably stop twerking in your uniform.”
“The fact that you don’t respect your job is one thing but doing it while in uniform and at work speaks volumes,” scoffed a third. “You’re the brand ambassador and it’s not a good look.”
Alaska
As Alaska sees a spike in Flu cases — another virus is on the rise in the U.S.
FAIRBANKS, Alaska (KTUU) – Alaska has recently seen a rise in both influenza and respiratory syncytial virus, better known as RSV. Amidst the spike in both illnesses, norovirus has also been on the rise in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) says it’s highly contagious and hand sanitizers don’t work well against it.
Current data for Alaska shows 449 influenza cases and 262 RSV cases for the week of Jan. 4. Influenza predominantly impacts the Kenai area, the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta, and the Northwest regions of the state. RSV is also seeing significant activity in the Yukon-Kuskokwim Delta and Anchorage.
Both are respiratory viruses that are treatable, but norovirus — which behaves like the stomach flu according to the CDC — is seeing a surge at the national level. It “causes acute gastroenteritis, an inflammation of the stomach or intestines,” as stated on the CDC webpage.
This virus is spread through close contact with infected people and surfaces, particularly food.
“Basically any place that people aggregate in close quarters, they’re going to be especially at risk,” said Dr. Sanjay Gupta, CNN’s Chief Medical Correspondent.
Preventing infection is possible but does require diligence. Just using hand sanitizer “does not work well against norovirus,” according to the CDC. Instead, the CDC advises washing your hands with soap and hot water for at least 20 seconds. When preparing food or cleaning fabrics — the virus “can survive temperatures as high as 145°F,” as stated by the CDC.
According to Dr. Gupta, its proteins make it difficult to kill, leaving many cleaning methods ineffective. To ensure a given product can kill the virus, he advises checking the label to see if it claims it can kill norovirus. Gupta said you can also make your own “by mixing bleach with water, 3/4 of a cup of bleach per gallon of water.”
For fabrics, it’s best to clean with water temperatures set to hot or steam cleaning at 175°F for five minutes.
As for foods, it’s best to throw out any items that might have norovirus. As a protective measure, it’s best to cook oysters and shellfish to a temperature greater than 145°F.
Based on Alaska Department of Health data, reported COVID-19 cases are significantly lower than this time last year.
See a spelling or grammatical error? Report it to web@ktuu.com
Copyright 2025 KTVF. All rights reserved.
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25822586/STK169_ZUCKERBERG_MAGA_STKS491_CVIRGINIA_A.jpg) Technology7 days ago
Technology7 days agoMeta is highlighting a splintering global approach to online speech
-

 Science4 days ago
Science4 days agoMetro will offer free rides in L.A. through Sunday due to fires
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25821992/videoframe_720397.png) Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoLas Vegas police release ChatGPT logs from the suspect in the Cybertruck explosion
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week ago‘How to Make Millions Before Grandma Dies’ Review: Thai Oscar Entry Is a Disarmingly Sentimental Tear-Jerker
-

 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoMichael J. Fox honored with Presidential Medal of Freedom for Parkinson’s research efforts
-

 Movie Reviews1 week ago
Movie Reviews1 week agoMovie Review: Millennials try to buy-in or opt-out of the “American Meltdown”
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoPhotos: Pacific Palisades Wildfire Engulfs Homes in an L.A. Neighborhood
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoTrial Starts for Nicolas Sarkozy in Libya Election Case















