Science
Q&A: Why COVID-19 booster shots turned out to be more complicated than vaccines
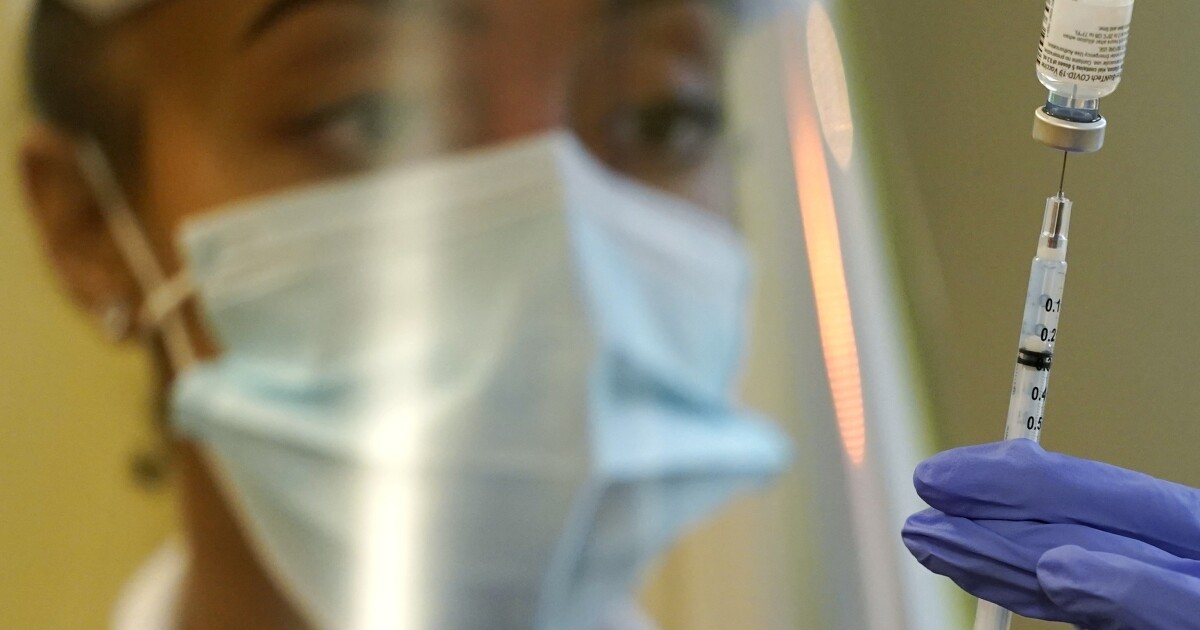
Just some months in the past, the safety provided by COVID-19 vaccines introduced Individuals pleasure and reduction, permitting the totally immunized to ditch their masks and return to a semblance of pre-pandemic life. Now that safety appears extra like an phantasm.
What occurred?
Has our vaccine-induced immune response actually fizzled? Is the Delta variant guilty for waning vaccine effectiveness? Is the resurgent dread of COVID-19 warranted? Will booster pictures restore our safety — and the hope that got here with it?
Each the Meals and Drug Administration and the Facilities for Illness Management and Safety grappled with these questions earlier than giving the go-ahead to boosters in sure populations. If that steering appeared disjointed or confused, it was largely as a result of the science remains to be rising.
E-newsletter
Get our free Coronavirus At this time e-newsletter
Join the newest information, finest tales and what they imply for you, plus solutions to your questions.
You might often obtain promotional content material from the Los Angeles Occasions.
Issue within the crosswinds of politics, worry, rampant misinformation and a vaccination marketing campaign that has misplaced its momentum, and issues change into much more fraught.
As an example, in declining to suggest {that a} third dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine be made out there to all who obtained their second dose a minimum of six months earlier, members of a CDC advisory panel made clear they didn’t wish to undermine public confidence in COVID-19 vaccines when so many haven’t even gotten their first dose.
How did we get right here?
Let’s begin by acknowledging that vaccines had been by no means excellent
Even in medical trials, the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine was reported to be 95% efficient at stopping circumstances of COVID-19. Meaning the chance of changing into sick after getting the pictures was small however not zero — and it doesn’t say something concerning the vaccine’s capability to thwart a coronavirus an infection within the first place.
Furthermore, that lofty determine was unlikely to carry underneath real-world situations. In the US, shut to three% of adults are immune-compromised and subsequently unlikely to mount a robust protecting response to a vaccine. Plus, new viral variants are regularly being incubated domestically or imported from overseas.
Random mutations to the coronavirus’ genome may alter it in ways in which may make it extra transmissible, or improve its capability to make individuals severely in poor health. One other fear is that mutations might change the virus in ways in which stop vaccine-induced antibodies from recognizing it.
The rise of the Delta variant exhibits that scientists are proper to be frightened. In chart after chart, FDA and the CDC specialists cited analysis suggesting that the now-dominant pressure has helped erode vaccines’ effectiveness in myriad methods.
Vaccines have an effect on the immune system in complicated, and mysterious, methods
The primary months following immunization are the heyday for antibodies: They’re plentiful, not too long ago skilled to acknowledge their goal virus, and diversified sufficient to acknowledge a number of of its options. A virus trying to invade is unlikely to sneak previous.
However as that preliminary spate of antibodies decays, the immune system can depend on its reminiscence banks — the legions of white blood cells through which resides the battle plan for preventing a brand new an infection. The looks of a virus ought to immediate these specialised cells to swing into motion. Helper T cells stimulate B cells to provide a contemporary crop of antibodies. In addition they immediate different T cells to search out cells which were contaminated and kill them.
However this course of isn’t instantaneous, and if the coronavirus can set up itself within the nostril and mouth rapidly sufficient, the immune system might not reply quick sufficient to bar the gates. An infection occurs.
For most individuals — however clearly not all — the cavalry will arrive in time to blunt an all-out invasion and head off extreme illness. That will clarify why researchers have discovered that the longer the time since vaccination, the higher the chances that inoculated individuals take a look at constructive for a coronavirus an infection, despite the fact that the speed at which they’re being hospitalized for COVID-19 has risen a lot much less steeply.
This sample has been noticed in Israel, Qatar and the US. In a single examine that targeted on New York, the three out there vaccines’ mixed capability to stop an infection fell from 92% in early Might to about 77% in late August, and the decline was seen in all age teams. But throughout the identical interval, when age was taken into consideration, the vaccines’ effectiveness in stopping hospitalization held regular. (By mid-June, nonetheless, hospitalization charges amongst vaccinated adults over 65 did start to climb.)
In the case of immunity, age issues
Immunity typically weakens as we become old, and so does our response to vaccines. Each of these information have been key within the present pandemic.
Earlier than vaccines turned out there, individuals 65 and older had been by far probably to die of COVID-19. In order that they had been among the many first Individuals to get vaccine — and notably the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, which turned out there first.
That makes senior residents the age group furthest out from vaccination. And with clear proof that they’re as soon as once more susceptible to extreme COVID-19, advisors to the FDA and CDC agreed that these 65 and up who obtained their second dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine a minimum of six months earlier ought to have a booster shot of that vaccine made out there to them.
A examine by the CDC suggests this group is amongst these most in want of booster pictures. For these 65 and over within the U.S. who obtained the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, the safety in opposition to being hospitalized for COVID-19 fell from 86% between January and Might to 73% between June and August.
Older Individuals who obtained the Moderna vaccine fared higher: Their safety declined from 91% to 86%, a distinction too small to be statistically important.
For probably the most half, the Moderna vaccine held up higher than the Pfizer-BioNTech one among age teams, although all the adjustments had been sufficiently small that they may have been because of probability.
The reason for this pattern is under no circumstances clear. It may replicate the significance of age, the size of time since vaccination, or the actual vaccine they obtained.
Dose most likely issues too
Different variables possible play a job in a vaccine’s longevity, although scientists nonetheless have a lot to be taught. As an example, does the variety of occasions a vaccinated particular person is uncovered to the coronavirus have an effect on his or her danger of an infection? Does the quantity of virus matter? Do these (or different) components affect the chance of changing into severely in poor health?
The solutions are of important curiosity to healthcare employees and others with important jobs who’re in frequent contact with individuals who might carry the virus. If vaccine safety may be overwhelmed by frequent or excessive doses of the virus, these employees may need periodic refreshers so long as the pandemic continues.
The uncertainty was mirrored in final week’s regulatory actions concerning booster pictures.
On Wednesday, the FDA amended its emergency authorization for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine to permit the usage of a booster in adults “whose frequent institutional or occupational publicity to SARS-CoV-2 places them at excessive danger of significant problems” of COVID-19.
The next day, the CDC’s Advisory Panel on Immunization Practices voted in opposition to an equivalent proposal after a number of panel members argued there was not sufficient proof these employees would profit. However inside hours, CDC Director Dr. Rochelle Walensky put aside that recommendation and signed off on offering these employees entry to boosters.
What’s true for the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine will not be true for others
Three vaccines defend Individuals, and so they’re every distinctive.
Those made by Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna use mRNA to instruct cells to make a bit of the coronavirus that’s sufficiently big to coach the immune system to acknowledge it, however far too small to do any injury.
Past that, the 2 vaccines are formulated otherwise. The Pfizer product incorporates 30 micrograms of vaccine, an quantity that’s the identical for all three doses. Moderna’s first and second pictures have 100 micrograms of vaccine, however its booster dose incorporates 50 micrograms.
The timing of pictures additionally differs. Pfizer’s first two doses are given three weeks aside, and Moderna’s are spaced 4 weeks aside.
Vaccine specialists have begun to counsel that giving the immune system extra time to reply to an preliminary dose earlier than giving the second may make for stronger, and presumably extra sturdy, immunity. The extra week between Moderna doses could be an essential cause for that vaccine’s comparatively higher endurance.
Both manner, a interval of six months between the second and third pictures could also be even higher for inducing lasting immunity.
The only-dose Johnson & Johnson vaccine makes use of a extra conventional vaccine design — a innocent chilly virus with a payload that introduces the immune system to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.
In its opening days, the vaccine was discovered to scale back the chance of symptomatic an infection by 66%, and a later examine reported that it decreased the chance of extreme illness in individuals over 50 by 68%.
There’s some proof that the Delta variant has decreased its effectiveness, though a examine sponsored by J&J confirmed {that a} single jab decreased the chance of COVID-19 by 79% with none decline because the Delta variant rose to prominence. A big examine revealed by the CDC discovered that safety in opposition to hospitalization fell to 60% after Delta turned dominant within the U.S.
Final week, J&J launched preliminary findings of a giant examine that examined the worth of including a second jab. None of those that obtained a booster shot 56 days after their preliminary dose developed a extreme or important case of COVID-19. Amongst examine individuals in the US, the booster decreased the chance of reasonable illness by 94%.

Science
Newsom's podcast sidekick: a single-use plastic water bottle

Johnny had Ed. Conan had Andy. And Gov. Gavin Newsom? A single-use plastic water bottle.
In most of the YouTube video recordings of Newsom’s new podcast, “This is Gavin Newsom,” a single-use plastic water bottle lurks on a table nearby.
Sometimes, it is accompanied by a single-use coffee cup. Other times, it stands alone.
Typically, such product placement would raise nary an eyebrow. But in recent weeks, environmentalists, waste advocates, lawmakers and others have been battling with the governor and his administration over a landmark single-use plastic law that Newsom signed in 2022, but which he has since worked to defang — reducing the number of packaged single-use products the law was designed to target and potentially opening the door for polluting forms of recycling.
Anti-plastic advocates say it’s an abrupt and disappointing pivot from the governor, who in June 2022, decried plastic pollution and the plague of single-use plastic on the environment.
“It’s like that whole French Laundry thing all over again,” said one anti-plastic advocate, who didn’t want to be identified for fear of angering the governor. Newsom was infamously caught dining without a mask at the wine country restaurant during the COVID-19 lockdown.
Newsom’s efforts to scale back SB 54, the state’s single-use plastic recycling law, has dismayed environmentalists who have long considered Newsom one of their staunchest allies.
“Our kids deserve a future free of plastic waste and all its dangerous impacts … No more,” Newsom said in 2022, when he signed SB 54. “California won’t tolerate plastic waste that’s filling our waterways and making it harder to breathe. We’re holding polluters responsible and cutting plastics at the source.”
Asked about the presence of the plastic water bottle, Daniel Villaseñor, the governor’s deputy director of communications, had this response:
“Are you really writing a story this baseless or should we highlight this video for your editor?” Villaseñor said via email, attaching a video clip showing this reporter seated near a plastic water bottle at last year’s Los Angeles Times’ Climate Summit. (The bottles were placed near chairs for all the panelists; this particular one was never touched.)
After this story was first published, the governor’s office said the plastic water bottles seen on the podcast were placed there by staff or production teams and not at Newsom’s request, and that the governor remains committed to seeing SB 54 implemented.
More than a half-dozen environmentalists and waste advocates asked to comment for this story declined to speak on the record, citing concerns including possible retribution from the governor’s office and appearing to look like scolds as negotiations over implementing SB 54 continue.
Dianna Cohen, the co-founder and chief executive of Plastic Pollution Coalition, said that while she wouldn’t comment on the governor and his plastic sidekick, she noted that plastic pollution is an “urgent global crisis” that requires strong policies and regulations.
“Individuals — especially those in the public eye — can help shift culture by modeling these solutions. We must all work to embrace the values we want to see and co-create a healthier world,” she said in a statement.
On Thursday, Newsom dropped a new episode of “This is Gavin Newsom” with independent journalist Aaron Parnas. In the video, there wasn’t a plastic bottle in sight.
Science
In Southern California, many are skipping healthcare out of fear of ICE operations

Missed childhood vaccinations. Skipped blood sugar checks. Medications abandoned at the pharmacy.
These are among the healthcare disruptions providers have noticed since Immigration and Customs Enforcement operations began in Southern California earlier this month.
Across the region, once-busy parks, shops and businesses have emptied as undocumented residents and their families hole up at home in fear. As rumors of immigration arrests have swirled around clinics and hospitals, many patients are also opting to skip chronic-care management visits as well as routine childhood check-ups.
In response, local federally qualified health centers — institutions that receive federal funds and are required by law to provide primary care regardless of ability to pay — have been scrambling to organize virtual appointments, house calls and pharmacy deliveries to patients who no longer feel safe going out in public.
“We’re just seeing a very frightening and chaotic environment that’s making it extremely difficult to provide for the healthcare needs of our patients,” said Jim Mangia, president of St. John’s Community Health, which offers medical, dental and mental health care to more than 100,000 low-income patients annually in Southern California.
Prior to the raids, the system’s network of clinics logged about a 9% no-show rate, Mangia said. In recent weeks, more than 30% of patients have canceled or failed to show. In response, the organization has launched a program called Healthcare Without Fear to provide virtual and home visits to patients concerned about the prospect of arrest.
“When we call patients back who missed their appointment and didn’t call in, overwhelmingly, they’re telling us they’re not coming out because of ICE,” said Mangia, who estimates that 25% of the clinic’s patient population is undocumented. “People are missing some pretty substantial healthcare appointments.”
A recent survey of patient no-shows at nonprofit health clinics across Los Angeles County found no universal trends across the 118 members of the Community Clinic Assn. of L.A. County, President Louise McCarthy said. Some clinics have seen a jump in missed appointments, while others have observed no change. The data do not indicate how many patients opted to convert scheduled in-person visits to telehealth so they wouldn’t have to leave home, she noted.
Patients have also expressed concerns that any usage of health services could make them targets. Earlier this month, the Associated Press reported that the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services shared the personal data of Medicaid enrollees with the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, including their immigration status. No specific enforcement actions have been directly linked to the data.
“The level of uncertainty and anxiety that is happening now is beyond the pale,” McCarthy said, for patients and staff alike.
County-run L.A. General Medical Center issued a statement on Thursday refuting reports that federal authorities had carried out enforcement operations at the downtown trauma center. While no immigration-related arrests have been reported at county health facilities, “the mere threat of immigration enforcement near any medical facility undermines public trust and jeopardizes community health,” the department said in a statement.
Los Angeles County is among the providers working to extend in-home care options such as medication delivery and a nurse advice line for people reluctant to come in person.
“However, not all medical appointments or conditions can be addressed remotely,” a spokesperson said. “We urge anyone in need of care not to delay.”
Providers expressed concern that missing preventative care appointments could lead to emergencies that both threaten patients’ lives and further stress public resources. Preventative care “keeps our community at large healthy and benefits really everyone in Los Angeles,” said a staff member at a group of L.A. area clinics. He asked that his employer not be named for fear of drawing attention to their patient population.
Neglecting care now, he said, “is going to cost everybody more money in the long run.”
A patient with hypertension who skips blood pressure monitoring appointments now may be more likely to be brought into an emergency room with a heart attack in the future, said Dr. Bukola Olusanya, a medical director at St. John’s.
“If [people] can’t get their medications, they can’t do follow-ups. That means a chronic condition that has been managed and well-controlled is just going to deteriorate,” she said. “We will see patients going to the ER more than they should be, rather than coming to primary care.”
Providers are already seeing that shift. When a health team visited one diabetic patient recently at home, they found her blood sugar levels sky-high, Mangia said. She told the team she’d consumed nothing but tortillas and coffee in the previous five days rather than risk a trip to the grocery store.
Science
At Chile’s Vera Rubin Observatory, Earth’s Largest Camera Surveys the Sky

At the heart of the new Vera C. Rubin Observatory in Chile is the world’s largest digital camera. About the size of a small car, it will create an unparalleled map of the night sky.
The observatory’s first public images of the sky are expected to be released on June 23. Here’s how its camera works.
When Times reporters visited the observatory on top of an 8,800-foot-high mountain in May, the telescope was undergoing calibration to measure minute differences in the sensitivity of the camera’s pixels. The camera is expected to have a life of more than 10 years.
A single Rubin image contains roughly as much data as all the words that The New York Times has published since 1851. The observatory will produce about 20 terabytes of data every night, which will be transferred and processed at facilities in California, France and Britain.
Specialized software will compare each new image with a template assembled from previous data, revealing changes in brightness or position in the sky. The observatory is expected to detect up to 10 million changes every night.
Some changes will be artificial. Simulations suggest that roughly one in 10 Rubin images will contain at least one bright streak or glint from the thousands of SpaceX Starlink and other satellites orbiting Earth.
Despite streaks, clouds, maintenance and other interruptions over the next decade, the Rubin Observatory is expected to catalog 20 billion galaxies and 17 billion stars across the Southern sky.
-

 Arizona3 days ago
Arizona3 days agoSuspect in Arizona Rangers' death killed by Missouri troopers
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoGoogle is shutting down Android Instant Apps over ‘low’ usage
-

 Education1 week ago
Education1 week agoOpinion | Artificial intelligence, Trump and the Future: 13 Gen Z-ers Discuss
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoSlow and Steady, Kay Ryan’s “Turtle” Poem Will Win Your Heart
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week ago‘No Kings’ demonstrators to gather across Greater Cincinnati in opposition to Trump
-

 News6 days ago
News6 days agoAt Least 4 Dead and 4 Missing in West Virginia Flash Flooding
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFate of Trump's $9.4 billion spending cut package hangs on House GOP moderates
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoHow Many Law Enforcement Agencies Are Involved in LA Immigration Protests?














