Health
At Long Last, Can Malaria Be Eradicated?

All via childhood, Miriam Abdullah was shuttled out and in of hospitals, her skinny physique wracked with fever and ravaged by malaria. She was so sick so usually that her fixed remedies drained her mother and father, who additionally cared for her many siblings, each financially and emotionally.
“Sooner or later, even my mum gave up,” recalled Ms. Abdullah, now 35.
In Nyalenda, the poor neighborhood in Kisumu, Kenya, the place Ms. Abdullah lives, malaria is endemic and ubiquitous. A few of her buddies developed meningitis after turning into contaminated; one died. “Malaria has actually tormented us as a rustic,” she stated.
There are tens of hundreds of thousands of horror tales like Ms. Abdullah’s, handed down from era to era. However now change is within the air: Malaria is the uncommon international well being scourge about which consultants are sanguine — a lot in order that some have begun to speak about eradicating the illness.
“I believe there’s a lot room for optimism,” stated Philip Welkhoff, director for malaria applications on the Invoice and Melinda Gates Basis. “Later this decade, we may really launch a push that will get us all the way in which to zero.”
China and El Salvador had been licensed malaria-free final yr, and the six international locations within the Larger Mekong area, together with Vietnam and Thailand, have pushed down instances by about 90 %. About 25 international locations are anticipated to have eradicated malaria by 2025.
The majority of infections now happen in Africa. Even there, regardless of the restrictions imposed by the coronavirus pandemic, almost 12 million extra African youngsters acquired preventive malaria medicine in 2020 than in 2019.
However it’s the arrival of two new vaccines that portend a sea change. The primary, known as Mosquirix, was 35 years within the making. It was accredited by the World Well being Group simply final yr and could also be distributed as quickly as late subsequent yr.
A extra highly effective malaria vaccine, developed by the Oxford staff that created the AstraZeneca Covid vaccine, could also be only a yr or two away. Many consultants imagine it’s this formulation, which has proven an efficacy of as much as 80 % in scientific trials, that will rework the struggle towards malaria.
Nonetheless extra choices are on the horizon, together with an mRNA vaccine being developed by the German firm BioNTech; monoclonal antibodies that may stop malaria for six months or longer; mattress nets coated with long-lasting pesticides or with chemical substances that paralyze mosquitoes; in addition to new methods to lure and kill mosquitoes.
“It’s an thrilling time,” stated Dr. Rose Jalang’o, who led a pilot take a look at of the Mosquirix vaccine in Kenya, the place it was given to youngsters alongside different immunizations.
However attending to a malaria-free world would require greater than promising instruments. In lots of African international locations, distribution of vaccines, medicine and mattress nets requires overcoming myriad challenges, together with tough terrain, different pressing medical priorities and misinformation.
Whereas the funding for malaria applications is extra beneficiant than for a lot of different illnesses that plague the poorest nations, sources are nonetheless restricted. Cash devoted to 1 strategy usually leads funders to neglect others, fueling competitors and generally rancor.
Mosquirix price greater than $200 million to develop over greater than 30 years, however its efficacy is roughly half that of the Oxford vaccine, known as R21. The primary doses of Mosquirix won’t be delivered to African youngsters till late 2023 or early 2024. The availability can be severely constrained for plenty of causes, and is predicted to stay so for years.
In December, Gavi, a nongovernmental group that helps vaccinations worldwide, dedicated $156 million to distribute Mosquirix. And in August, Unicef granted the vaccine’s producer, GlaxoSmithKline, a $170 million contract, sufficient to supply 18 million doses over the following three years.
However that may be a far cry from the estimated 100 million doses that can be wanted every year.
R21, the second vaccine, seems to be extra highly effective, cheaper and simpler to fabricate. And the Serum Institute of India is ready to supply greater than 200 million doses of R21 per yr.
Some malaria consultants observe that given the pressing want, the world wants each possibility it could possibly get. However others fear that each greenback directed to Mosquirix now’s a greenback much less for creating different instruments.
“Current malaria management measures are already underfunded,” stated Dr. Javier Guzman, director for international well being coverage on the Middle for World Improvement in Washington. “I don’t wish to be unfavorable, however a brand new software with out further funding principally means sacrifices and means a possibility price.”
‘It Simply Progresses Too Quick’
Malaria is among the many oldest infectious illnesses and one of many deadliest. Years of fast progress stalled a few decade in the past, leaving the toll in 2019 at a staggering 229 million new infections and 558,000 deaths.
Whereas the Covid pandemic didn’t ship malaria infections skyrocketing, as occurred with tuberculosis, the pandemic reversed a sluggish downward pattern in malaria deaths, which ratcheted as much as 627,000 in 2020.
Almost the entire lives misplaced to malaria are in sub-Saharan Africa, the place about 80 % of the deaths are in youngsters youthful than 5.
Many methods to struggle malaria are dated, but nonetheless inaccessible to hundreds of thousands. Solely about half of African youngsters sleep beneath insecticide-treated mattress nets, as an example, and even fewer obtain seasonal medicine that stop the an infection.
Malaria compounds social inequities. It robs youngsters of the power to struggle different pathogens, overwhelms well being care techniques and devastates complete communities. One untreated particular person with malaria can stay unwell for six months, giving mosquitoes the chance to unfold the parasite to as many as 100 different folks.
Designing a vaccine towards a parasite has proved far more difficult than creating one towards a virus or bacterium. Plasmodium falciparum, the organism that causes malaria in Africa, quickly cycles via a number of life levels, morphing into a brand new kind every time.
The physique struggles to acknowledge and defend itself towards this shape-shifter, leaving folks susceptible to repeated bouts of illness.
A mosquito chew delivers solely about 10 “sporozoites,” the type of the parasite that may be transmitted. However inside half-hour of an infection, the sporozoites invade the liver, and start multiply into an unbeatable military of 1000’s. Mosquirix and R21 goal sporozoites within the couple of minutes earlier than they enter the liver.
The parasite wrecks the physique so rapidly that by the point youngsters are taken to the hospital, many are in dire want of a blood transfusion. However blood is usually in brief provide in sub-Saharan Africa, and utilizing a bag for a small baby can imply that half or extra can be discarded, stated Dr. Mary Hamel, who leads the W.H.O.’s malaria vaccine implementation program.
“You see a baby who’s so pale and floppy and respiration so quickly, and so they’re simply splayed on the cot — and there’s nothing you are able to do,” she stated.
“You’ve bought to stop malaria — it simply progresses too quick,” she added.
Mosquirix, the primary vaccine towards any parasite, is a technical triumph. However its efficacy, at about 40 %, is far decrease than scientists had hoped.
Ideally, the vaccine could be deployed alongside present controls, like insecticide-treated mattress nets and preventive medicine, based mostly on knowledge indicating the place the instruments are most wanted and delivered by a sturdy well being care work power.
“In case you mix with the fitting software, you will get a a lot, a lot greater affect,” stated Dr. Thomas Breuer, chief international well being officer at GlaxoSmithKline, which manufactures Mosquirix.
The vaccine, which may be refrigerated, was examined in Kenya, Ghana and Malawi in youngsters youthful than 2 years — and extra simply than some consultants had feared. “It’s extra deliverable in rural, distant settings than many different vaccines have been,” stated Prashant Yadav, an knowledgeable in well being care provide chains on the Middle for World Improvement.
Group well being employees went door-to-door to publicize Mosquirix, and governments unfold the phrase by way of native tv and radio exhibits. Regardless of misinformation that circulated on WhatsApp and social media, uptake of the vaccine was akin to that of routine immunizations.
However in lots of African international locations, distrust of vaccines is excessive. In a single survey, about half of individuals in Niger and the Democratic Republic of Congo stated they’d not belief a malaria vaccine.
Furthermore, Mosquirix have to be given in 4 doses, the primary at 5 months of age and the fourth after 18 months of age. However few different vaccines are given to youngsters older than 18 months, and lots of mother and father in Africa face monumental logistical hurdles in taking youngsters to a clinic.
Mother and father may wrongly assume that the primary three doses of Mosquirix are protecting sufficient, researchers stated. (In contrast, R21 has an efficacy of 70 % after three doses given earlier than 17 months of age. A booster given a yr later maintains and even enhances its efficiency.)
“It might be simpler if the final shot was at 18 months,” Dr. Kwame Amponsa-Achiano, a doctor and epidemiologist who leads the vaccine program at Ghana’s ministry of well being, stated of Mosquirix.
In comparison with the billions of {dollars} poured into Covid vaccines, the funds for malaria are a pittance. The Gates Basis spends about $270 million a yr preventing the illness, not counting its contributions to the World Fund to Struggle AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria.
The shortage of sources signifies that folks — and organizations — find yourself choosing favourite methods. Some preserve that controlling mosquitoes is the logical path, whereas others push vaccines. Nonetheless others say monoclonal antibodies are the way in which ahead.
In such a extremely aggressive enviornment, Mosquirix doesn’t emerge as the apparent winner.
“Deploying a software which is pricey, and never that efficient, with a brief length of motion, will not be the factor that you just wish to result in first,” stated Dr. Scott Filler, head of malaria applications for the World Fund, which helps greater than half of malaria applications worldwide.
The cash could be higher spent growing use of mattress nets, or making certain that individuals have entry to fundamental main well being companies, together with testing, treating and monitoring for malaria, Dr. Filler stated.
Even the Gates Basis, which has poured greater than $200 million into the event of Mosquirix, is now lukewarm on the vaccine and is focusing as an alternative on dashing newer instruments to Africa.
“A few of this different stuff within the portfolio goes to be higher, cheaper, simpler to deploy and simpler to scale up,” Dr. Welkhoff stated.
However different consultants imagine that given malaria’s devastation, a vaccine with low efficacy is healthier than none.
“Now we have this vaccine that has been examined very, very extensively — greater than any vaccine previous to approval,” stated Michael Anderson, a former director common of Britain’s Division for Worldwide Improvement who now heads MedAccess, a nonprofit group financed by the British authorities.
R21 has price lower than $100 million to develop. If regulators are as quick and nimble as they had been with Covid vaccines, it might be approved just a few months after the researchers submit ultimate knowledge on the finish of this yr.
The 2 vaccines will not be essentially in competitors, stated Dr. Adrian Hill, R21’s architect and director of the Jenner Institute on the College of Oxford.
The most important downside with Mosquirix “is there isn’t sufficient of it,” Dr. Hill stated. Nonetheless, R21 could be easier to ship as a result of it’s “a extra fashionable product,” he added. “It was designed in 2012, not within the Eighties and Nineteen Nineties.”
For a lot of mother and father in Africa, a vaccine can not come quickly sufficient. In Kisumu, Ms. Abdullah is anxious to immunize her 2-year-old daughter, who has already had malaria as soon as, towards the sickness that marred her personal childhood.
“I’d go for it instantly,” she stated. “In reality, I’d go for it earlier than I even go for the Covid-19 vaccine.”

Health
This Tropical Fruit May Improve Your Skin, Heart Health and More

Use left and right arrow keys to navigate between menu items.
Use escape to exit the menu.
Sign Up
Create a free account to access exclusive content, play games, solve puzzles, test your pop-culture knowledge and receive special offers.
Already have an account? Login
Health
FDA approves first twice-yearly injection that prevents HIV infection

FDA authorizes AI tool to predict breast cancer risk
Senior medical analyst Dr. Marc Siegel discusses advancements in artificial intelligence aimed at predicting an individual’s future risk of breast cancer and the increased health risks from cannabis as users age.
NEWYou can now listen to Fox News articles!
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved a new, twice-yearly shot — the first and only of its kind — to prevent HIV, the creator of the drug, Gilead Sciences, announced on Wednesday.
Sold under the name Yeztugo, the company’s injectable HIV-1 capsid inhibitor (lenacapavir) reduces the risk of sexually acquired HIV in adults and adolescents.
“This is a historic day in the decades-long fight against HIV,” said Daniel O’Day, chairman and CEO of California-based Gilead Sciences, in a press release.
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE COULD BE PREVENTED BY ANTIVIRAL DRUG ALREADY ON MARKET
The medicine, which only needs to be administered twice a year, has shown “remarkable outcomes in clinical studies,” as Gilead claims it could transform HIV prevention.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has approved a new, twice-yearly shot, Yeztugo, to prevent HIV, the creator of the drug announced on Wednesday. (Gilead Sciences via AP)
The drug is given as an injectable under the skin that the body then slowly absorbs. Individuals must have a negative HIV-1 test prior to starting the treatment.
In large trials last year, the drug was not only nearly 100% effective in its prevention of HIV, but proved superior to once-daily oral medication like Truvada, another drug by Gilead.
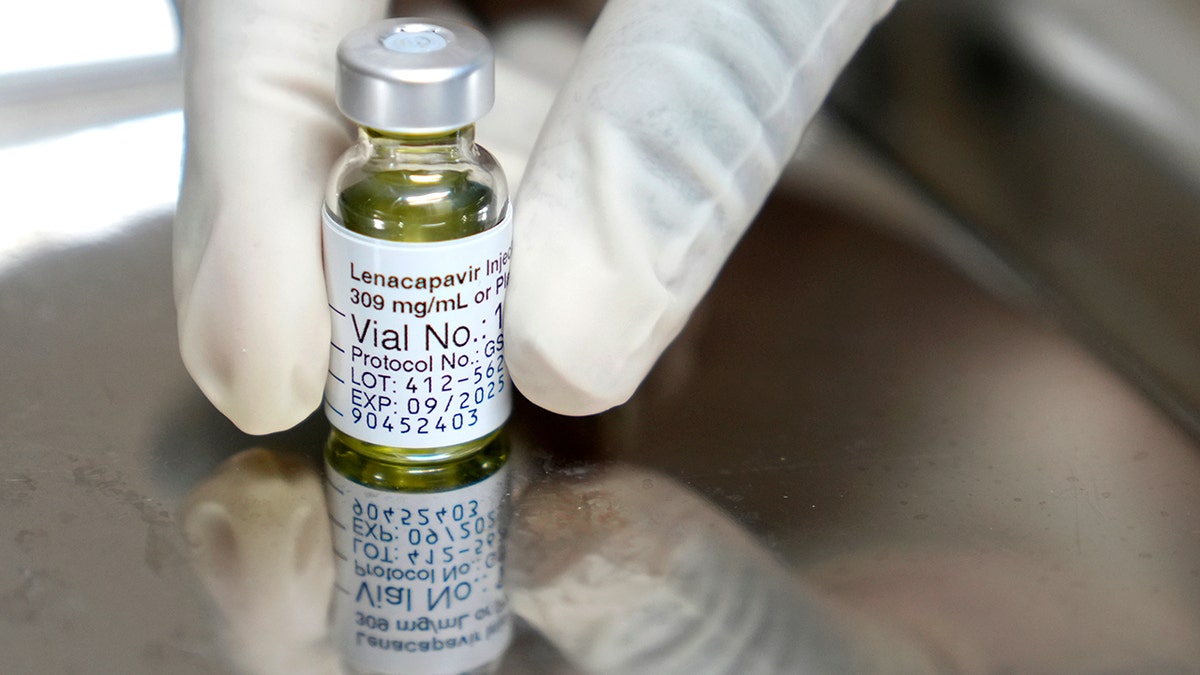
The drug is given as an injectable under the skin that the body then slowly absorbs. Individuals must have a negative HIV-1 test prior to starting the treatment. (AP Photo/Nardus Engelbrecht)
The journal Science named lenacapavir its 2024 “Breakthrough of the Year.”
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
Lenacapavir uses a multi-stage approach that distinguishes it from other approved antiviral medications.

Sold under the name Yeztugo, the company’s injectable HIV-1 capsid inhibitor (lenacapavir) reduces the risk of sexually acquired HIV in adults and adolescents. (iStock)
“While most antivirals act on just one stage of viral replication, lenacapavir is designed to inhibit HIV at multiple stages of its lifecycle,” states the press release from Gilead.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
“Yeztugo is one of the most important scientific breakthroughs of our time and offers a very real opportunity to help end the HIV epidemic,” O’Day said in the press release.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions during clinical trials included injection site reactions, headache and nausea, according to the company.
Health
Video: What Happens if Vaccines Aren’t Recommended?

In recent extraordinary moves, Health Secretary Robert F. Kennedy Jr. has fired and replaced a team that makes vaccine recommendations for the country. Apoorva Mandavilli, a science and global health reporter at The New York Times, explains how this change could impact vaccine accessibility.
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoYale’s Endowment Selling Private Equity Stakes as Trump Targets Ivies
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoBarbara Holdridge, Whose Record Label Foretold Audiobooks, Dies at 95
-

 Science1 week ago
Science1 week agoIn Taxicab Geometry, Pi Equals 4 and Circles Aren’t Round
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoYosemite Bans Large Flags From El Capitan, Criminalizing Protests
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoA Murdered Journalist’s Unfinished Book About the Amazon Gets Completed and Published
-

 Culture1 week ago
Culture1 week agoHow Many Memorable Lines Can You Match Up With Their Novels?
-
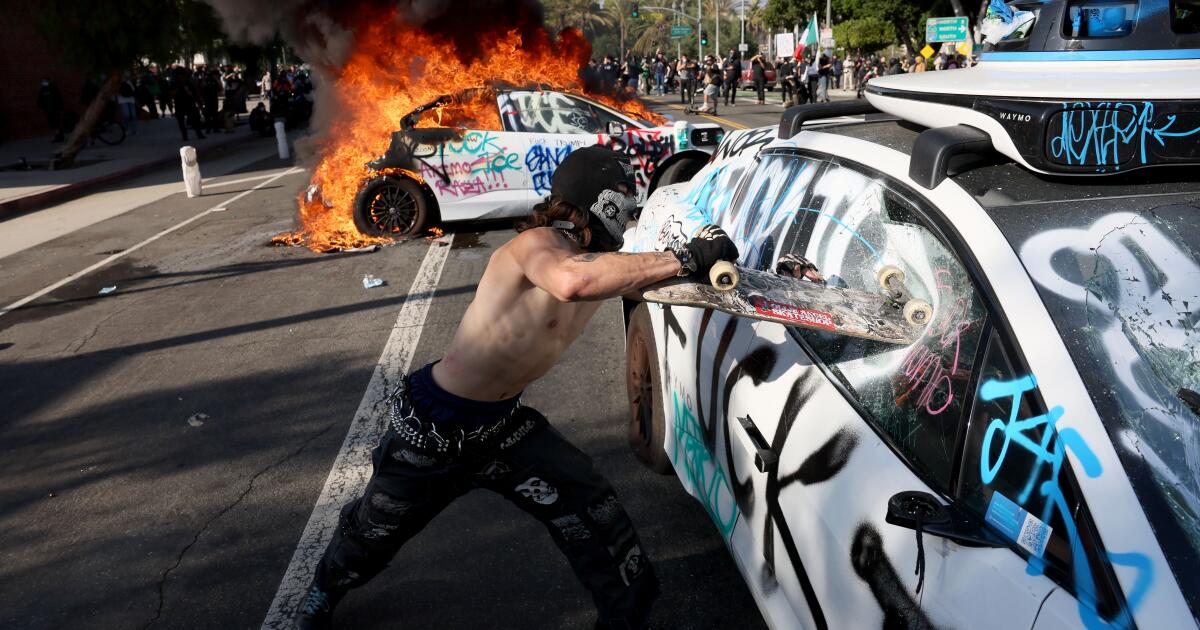

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoWaymo halts service in downtown Los Angeles amid ICE protests
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week agoFox News Politics Newsletter: Hillary ‘Can’t Handle the Ratio'















