Finance
Why You Have to ‘Date’ Your Financial Advisor to Find ‘the One’ | Entrepreneur

Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
Our money is very personal. We tend to be overly private about it and rarely open up and share our financial skeletons, mistakes, what keeps us up at night, how much we make, how much we have and so on. How many people do you really open up to about your money?
This is the challenge and opportunity. Most of us need help to understand and manage all aspects of our money, but we have one big roadblock that prevents us from getting help: a lack of trust. It’s scary to open up and let someone into your financial life, so we tend to not let others in and then suffer the consequences of not getting the professional help we need to get the outcomes we desire.
Connecting with a financial advisor is a lot like dating. Ever been on a first date that went poorly? Most of us have! We can learn a lot from the dating process when it comes to finding the right financial advisor for us. Here are three things you should consider when looking for and hiring a financial advisor so you can become the master of your money and take action to improve your finances.
Related: The Pros and Cons of Hiring a Financial Advisor
Where we find our financial advisor matters
When we are ready to commit to a serious long-term and trusting relationship, be that marriage or with a financial advisor, we tend to look to sources of credibility that instill confidence. I like to compare this to finding your life partner via eHarmony vs. Tinder. Both provide a service that people are looking for but the experience and outcomes are arguably very different.
When looking for a financial advisor we have a similar situation. Finding a financial advisor by getting served up an ad on Facebook and then getting bombarded with cold calls doesn’t quite feel right. It doesn’t exactly give us the confidence we need to open up about our money. Would you marry an advisor you found this way?
Instead, people should look in places where a community of advisors already exists, like the CFP Board’s LetsMakeAPlan service. Like dating, this helps us know we are looking in the right place to find that first date that we actually want to go on. But it creates another problem: How do we pick the right advisor for this first date when we have hundreds to choose from?
How we choose our financial advisor matters
Ever heard of the jelly conundrum? Basically, when we are given more than five or so jelly choices on the shelf at the grocery store, we shut down and don’t pick any of them. The same holds true when trying to figure out which advisor to pick. Serving up a list of hundreds of potential advisors is overwhelming, we simply won’t pick one at all. Imagine having to pick your first date from 100+ people, forget it!
The importance of advice engagement is becoming more and more important. It is essentially how well an advisor connects with and listens to us which in turn instills trust and confidence so we will take action. Connecting with a financial professional is of the utmost importance since getting help with our money requires us to open up and take action.
If we don’t connect with our advisor on a deep level of understanding, then chances are we won’t open up about our money, let alone take action on any recommendations they have for us, so the first step is finding and connecting with an advisor we can trust. We know from the paradox of choice that we won’t make a choice when we have too many options to pick from so we have to find a place or service that helps us narrow down the choices from hundreds to three or four.
Our brains can handle this. The challenge here is that most “refining” processes only let us refine via things like where we live or the type of credentials an advisor might have. Both are helpful, but we don’t connect with other human beings based solely on our ZIP code.
How to connect with a financial advisor matters
I love this quote from former President Theodore Roosevelt: “No one cares how much you know until they know how much you care.”
When dating to find and marry your life partner your first and second dates will cover topics like your interests, your background, what you went to school for, what you like to do for fun, etc. We talk about these things since we are wired to connect with other people like us based on a variety of shared commonalities, philosophies, interests, etc. But eventually, we get to the topics of money, employment, faults, quirks, family baggage and so on. In other words, once we know we like each other, we start to dig into the less glamorous yet equally important topics.
The same should happen when we’re looking for and trying to connect with a financial advisor. It’s important to get to know your advisor on a human level first. Do you like each other? Do you have share commonalities, etc.? Once you feel like you could work with a particular advisor you can then dig into asking more business-related questions.
People should look for ways to connect with their financial advisor like they would with someone they might date. Do you have shared commonalities, experiences, interests and philosophies? Connecting on these levels will set the stage for trust and opening up about your money. Trust is a byproduct of what I refer to as human dimensions. Once we connect on these dimensions, then it becomes very important that the advisor we’re considering has the experience and credentials to best help us — hence the above quote from Roosevelt.
Relationships matter. When it comes to finding the best financial advisor, consider these three tips. Getting help with your money is just as important as where and who you’re getting the help from.

Finance
Cop29: $250bn climate finance offer from rich world an insult, critics say

Developing countries have reacted angrily to an offer of $250bn in finance from the rich world – considerably less than they are demanding – to help them tackle the climate crisis.
The offer was contained in the draft text of an agreement published on Friday afternoon at the Cop29 climate summit in Azerbaijan, where talks are likely to carry on past a 6pm deadline.
Juan Carlos Monterrey Gómez, Panama’s climate envoy, told the Guardian: “This is definitely not enough. What we need is at least $5tn a year, but what we have asked for is just $1.3tn. That is 1% of global GDP. That should not be too much when you’re talking about saving the planet we all live on.”
He said $250bn divided among all the developing countries in need amounted to very little. “It comes to nothing when you split it. We have bills in the billions to pay after droughts and flooding. What the heck will $250bn do? It won’t put us on a path to 1.5C. More like 3C.”
According to the new text of a deal, developing countries would receive a total of at least $1.3tn a year in climate finance by 2035, which is in line with the demands most submitted before this two-week conference. That would be made up of the $250bn from developed countries, plus other sources of finance including private investment.
Poor nations wanted much more of the headline finance to come directly from rich countries, preferably in the form of grants rather than loans.
Civil society groups criticised the offer, variously describing it as “a joke”, “an embarrassment”, “an insult”, and the global north “playing poker with people’s lives”.
Mohamed Adow, a co-founder of Power Shift Africa, a thinktank, said: “Our expectations were low, but this is a slap in the face. No developing country will fall for this. It’s not clear what kind of trick the presidency is trying to pull. They’ve already disappointed everyone, but they have now angered and offended the developing world.”
The $250bn figure is significantly lower than the $300bn-a-year offer that some developed countries were mulling at the talks, to the Guardian’s knowledge.
The offer from developed countries, funded from their national budgets and overseas aid, is supposed to form the inner core of a “layered” finance settlement, accompanied by a middle layer of new forms of finance such as new taxes on fossil fuels and high-carbon activities, carbon trading and “innovative” forms of finance; and an outermost layer of investment from the private sector, into projects such as solar and windfarms.
These layers would add up to $1.3tn a year, which is the amount that economists have calculated is needed in external finance for developing countries to tackle the climate crisis. Many activists have demanded more: figures of $5tn or $7tn a year have been put forward by some groups, based on the historical responsibilities of developed countries for causing the climate crisis.
after newsletter promotion
This latest text is the second from an increasingly embattled Cop presidency. Azerbaijan was widely criticised for its first draft on Thursday.
There will now be further negotiations among countries and possibly a new or several new iterations of this draft text.
Avinash Persaud, a former adviser to the Barbados prime minister, Mia Mottley, and now an adviser to the president of the Inter-American Bank, said: “There is no deal to come out of Baku that will not leave a bad taste in everyone’s mouth, but we are within sight of a landing zone for the first time all year.”
Finance
US Treasury Selects BNY as Financial Agent for Direct Express Program | PYMNTS.com

The Bank of New York Mellon (BNY) will serve as the financial agent for the Direct Express program, which provides 3.4 million Americans with a prepaid debit card to receive monthly federal benefits.
The U.S. Department of the Treasury’s Bureau of the Fiscal Service said in a Thursday (Nov. 21) press release that it selected BNY for this role after evaluating proposals from multiple financial institutions and seeing the bank’s offering of features and customer service options.
The new agreement will begin Jan. 3 and will last five years, according to the release.
“Since 2008, the Direct Express program has paid federal beneficiaries seamlessly, inclusively and securely, while sparing taxpayers and customers the costs and risk associated with cashing paper checks,” Fiscal Service Commissioner Tim Gribben said in the release. “This new agreement will further our goals of delivering a modern customer experience and strengthening Treasury’s commitment to paying the right person, in the right amount, at the right time.”
With this agreement, BNY will add to the cardholder experience features like online/digital funds access, bill pay, cardless ATM access, omnichannel chat and text customer service, online dispute filing and in-person authentication options, the bank said in a Thursday press release.
“Drawing on our leading platform capabilities, we look forward to advancing the program’s goal of providing high-quality financial services to individuals and communities throughout the U.S.,” Jennifer Barker, global head of treasury services and depositary receipts at BNY, said in the release.
Seventy-seven percent of the recipients of disbursements opt for instant payments when given the option, according to the PYMNTS Intelligence and Ingo Payments collaboration, “Measuring Consumers’ Growing Interest in Instant Payouts.”
That’s because consumers looking for disbursements — paychecks, government payments, insurance settlements, investment earnings — want their money quickly, the report found.
In October, the Treasury Department credited the Office of Payment Integrity, within the Bureau of the Fiscal Service, with enhancing its fraud prevention capabilities and expanding offerings to new and existing customers.
The department said its “technology and data-driven” approach allowed it to prevent and recover more than $4 billion in fraud and improper payments, up from $652 million in 2023.
Finance
Islamic finance: a powerful solution for climate action – Greenpeace International
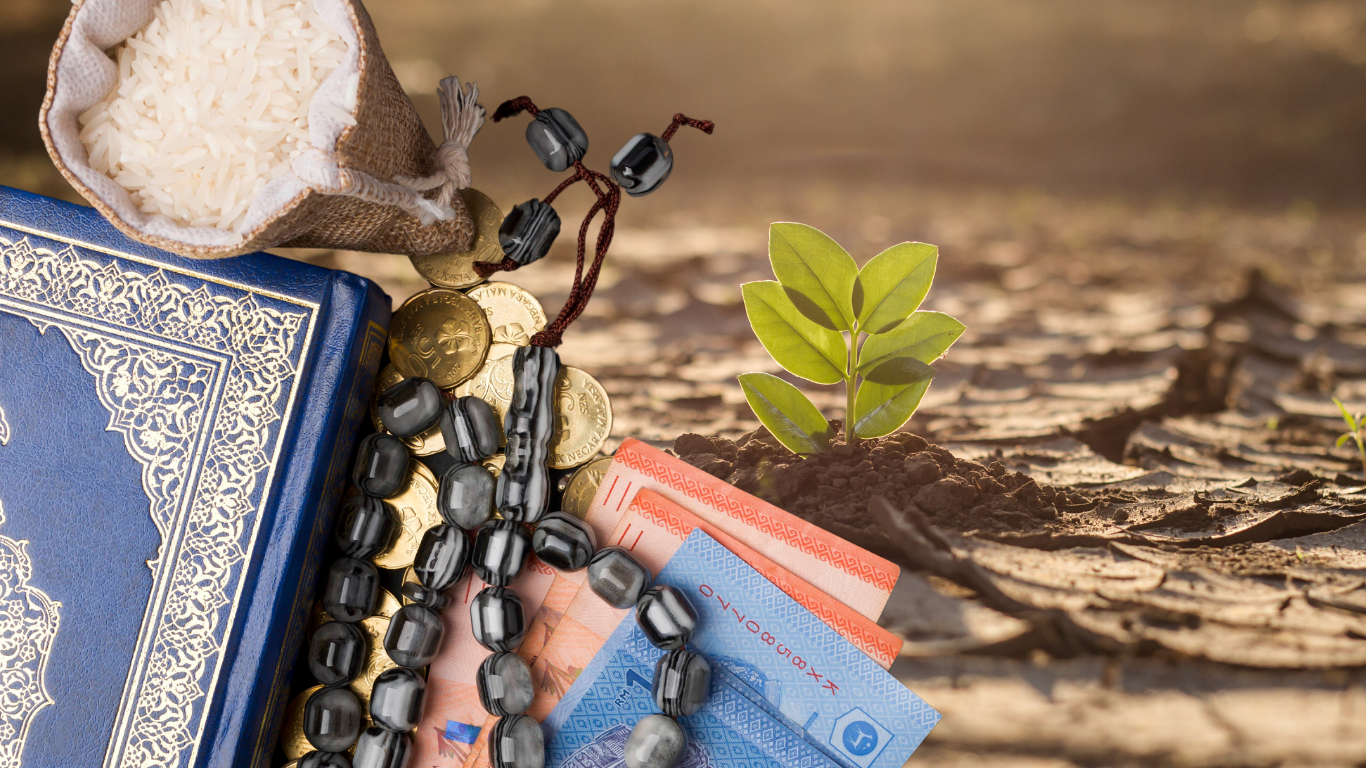

Across the globe, Muslim communities find themselves disproportionately affected by climate change, with extreme weather events, rising food insecurity, and other climate impacts taking a toll on their livelihoods, cultural practices, and spiritual life.
In the last few years, devastating floods swept through Pakistan, affecting millions, displacing thousands, and leaving entire communities struggling to rebuild. In Indonesia, one of the world’s most populous Muslim-majority countries, rising sea levels threaten to submerge coastal villages and erode vital agricultural lands. Meanwhile, in parts of the Middle East and North Africa, persistent droughts and water scarcity are increasing pressures on already fragile ecosystems and economies.
The climate crisis is having a profound impact on the daily lives and religious practices of millions of people
These climate pressures extend beyond immediate threats to survival. Climate change has also begun affecting food security in Muslim-majority regions, especially during Ramadan, a holy month where fasting is practised from dawn until dusk. In communities already grappling with the impacts of droughts or floods, maintaining food stocks for Ramadan can become a significant challenge. In Somalia, where cycles of drought and flash floods have eroded food systems, many families are forced to navigate long-standing shortages, with climate-induced shocks compounding existing vulnerabilities.
Food insecurity is a worsening crisis as global warming affects harvests, disrupts fisheries, and drives up food prices, making the observance of Ramadan particularly strenuous, both physically and economically. This brings climate change into the daily lives and religious practices of millions in profound ways, reminding us that the climate crisis is as much a social and economic issue as it is an environmental one.
Islamic finance: a financial system grounded in ethical responsibility
Islamic finance has been operating in the global financial system for decades, providing an ethical foundation rooted in Islamic principles that promote fairness, social responsibility, and environmental stewardship.

Ethical banking is a core pillar of Islamic finance. Through principles like zakat (charity) and waqf (endowment for public good), Islamic finance encourages financial activity that uplifts communities, supports sustainable projects, and avoids investments in industries harmful to people and the planet.
Many Islamic financial institutions in countries like Malaysia, the United Arab Emirates, and Saudi Arabia already support projects aimed at protecting the environment and enhancing social welfare. Success stories are already emerging. Malaysia’s green sukuk initiative has mobilised billions for renewable energy projects, while the UAE’s recent US$3.9 billion in green sukuk issuance demonstrates growing momentum. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 has allocated US$50 billion for renewable initiatives, targeting an emissions reduction of 278 million tons by 2030.
A US$400 billion opportunity for climate action
While Islamic finance principles already provide a framework that aligns well with sustainability, there is still much room to strengthen its role in addressing the climate crisis, enhancing resilience in vulnerable communities, and shifting investments towards clean, renewable energy.
A new report by Greenpeace Middle East & North Africa (MENA) (as part of the Ummah For Earth Alliance) and the Global Ethical Finance Initiative (GEFI), highlights the transformative potential of Islamic finance in accelerating the global transition to renewable energy and addressing the triple planetary crisis: climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss.
The report shows that the Islamic finance industry continues its robust expansion, with assets projected to reach USD$ 6.7 trillion by 2027, and that a strategic allocation of just 5% toward renewable energy and energy efficiency initiatives could mobilise approximately USD$ 400 billion by 2030 – a transformative sum for climate-vulnerable regions.

Islamic finance can help foster climate-resilient infrastructure, restore and protect biodiversity, and finance climate adaptation projects in at-risk communities. By explicitly directing funds away from fossil fuels and into green energy projects, Islamic financial institutions like the Islamic Development Bank (IsDB) can lead by example, especially in regions that are both vulnerable to climate impacts and hold significant influence in the global fossil fuel market. These institutions must accelerate their commitment to renewable energy investments.
As climate impacts intensify, Islamic finance offers a bridge between faith-based values and practical climate solutions. The convergence of Islamic finance and climate action represents more than a financial opportunity – it’s a moral imperative aligned with Islamic principles of environmental stewardship (khalifah) and balance (mizan).
Islamic finance, grounded in ethical principles and community responsibility, has a unique role to play in the global climate movement, particularly in the Global South. For millions across the globe, this form of finance offers a culturally relevant and powerful instrument to not only protect their communities from the worsening climate crisis but to promote environmental and economic sustainability in ways that align with their beliefs. Islamic finance offers a bridge between economic strength and ethical stewardship, creating pathways toward a more equitable and sustainable world for all.
Your voice can transform Islamic fiance
Ask your Islamic bank to support increasing investments in renewable energy!
Take action
-
Business1 week ago
Column: OpenAI just scored a huge victory in a copyright case … or did it?
-
 Health1 week ago
Health1 week agoBird flu leaves teen in critical condition after country's first reported case
-

 Business6 days ago
Business6 days agoColumn: Molly White's message for journalists going freelance — be ready for the pitfalls
-
World1 week ago
Sarah Palin, NY Times Have Explored Settlement, as Judge Sets Defamation Retrial
-

 Science3 days ago
Science3 days agoTrump nominates Dr. Oz to head Medicare and Medicaid and help take on 'illness industrial complex'
-

 Politics5 days ago
Politics5 days agoTrump taps FCC member Brendan Carr to lead agency: 'Warrior for Free Speech'
-
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25739950/247386_Elon_Musk_Open_AI_CVirginia.jpg)
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25739950/247386_Elon_Musk_Open_AI_CVirginia.jpg) Technology4 days ago
Technology4 days agoInside Elon Musk’s messy breakup with OpenAI
-

 Lifestyle5 days ago
Lifestyle5 days agoSome in the U.S. farm industry are alarmed by Trump's embrace of RFK Jr. and tariffs




















