Business
Who Are the Victims in the D.C. Plane Crash?

Sixty-four people were inside the American Airlines regional jet carving a path through the evening sky from Wichita, Kan., to Washington D.C., on Jan. 29.
A four-person flight crew. A lawyer eager to celebrate her 33rd birthday, seven hunting buddies and a Kansas farming couple visiting their daughter. Twenty-eight people returning from an elite figure skating camp, including skaters, their parents and coaches.
As the plane, Flight 5342, was preparing to land, it collided with an Army Black Hawk helicopter carrying three soldiers, creating a fireball above the Potomac River and killing all aboard both aircraft.
These are many of the victims of the crash, identified by The New York Times through interviews with their families, employers and friends, and official statements.
Asra Hussain, 26
via Columbia Public Health
Business Travelers
Work drew several of the passengers to Wichita, the largest city in Kansas and a Midwestern hub of manufacturing and aviation. Two analysts for Moody’s were on the plane, the company said.
Two women on the plane were colleagues from Wilkinson Stekloff, a Washington, D.C., law firm, and had traveled to Kansas for a deposition.
Ms. Keys, who turned 33 on the day of the crash, was worried their meetings would run long and force them to stay overnight. But things wrapped up, and they made their way to the Wichita airport that afternoon to catch their flight to Reagan National Airport.
“We were super excited she was able to take that flight back,” said David Seidman, Ms. Keys’s longtime partner. “She was coming home.”
They traded a last text before the flight took off: “Safe flight. I love you.”
The Kansans
The only nonstop flight each day between Wichita and the capital was Flight 5342, operated by American Eagle.
Bob Schrock, 58
Danielle Davidson, via DTN
The Schrocks regularly made the trip. Their roots and large farm were in Kiowa, Kan., but after their daughter, Ellie, moved east for college, the Schrocks bought a home in Maryland and began splitting their time between the Plains and the coast, friends said.
“They flew back a dozen times a year or so,” said Michael Simpson, who had known the Schrocks for 20 years.
He said the couple were devoted to their Catholic faith and to fitness. They were regulars at Sunday services and also at a local weight room, where they would pull up together in their turquoise Jeep for morning workouts.
“They loved the Lord,” Mr. Simpson said. “They loved their community.”
Grace Maxwell, 20
via Cedarville University
Ms. Duggins grew up and attended college in Wichita before heading east to Harvard Law School and starting a career as a civil rights lawyer. She returned to Kansas often to see her parents and visit old friends and professors, who remembered her as a “beacon of light” who was passionate about tackling inequalities and abuses in the criminal justice system.
“She was going to conquer the world,” said Dorothy Harpool, a senior marketing educator at the W. Frank Barton School of Business at Wichita State University, where Ms. Duggins earned undergraduate degrees in international business, economics and Spanish.
The Flight Crews
Flying was both a job and a passion for the two pilots and two crew members aboard the nonstop flight from Wichita that had been operating for just a year. The flight crew included:
Mr. Campos had wanted to fly since he was a toddler, said his aunt, Beverly Lane.
“I think he wanted to be free, and be able to fly and soar like a bird,” she said.
Mr. Lilley was engaged to be married in the fall.
“I was so proud when Sam became a pilot,” his father, Timothy Lilley, wrote on Facebook after the crash. “Now it hurts so bad I can’t even cry myself to sleep.”
The three aviators from the helicopter who were identified by the Army:
Skaters, Parents and Coaches
The plane carried talented and ambitious young skaters from around the country. They had been in Wichita for a development camp hosted by U.S. Figure Skating that followed last month’s national championships.
Many of the young skaters dreamed of competing at the Olympics, and Wichita was a place to make lasting impressions on coaches with U.S. Figure Skating. Edward Zhou, a high school junior from Fairfax, Va., had been on the cusp of qualifying for the U.S. national championships and both gleefully and masterfully performed routines at the camp, according to coaches there. Both his parents died in the crash.
Edward Zhou, 16, Kaiyan Mao, 52, and Yu Zhou, 60
Another teenager from Northern Virginia, Cory Haynos, nailed the triple axel in Wichita and was thrilled to show off his new jump. In December, he had landed that axel for the first time.
“I’d been watching him work on it all week, just fighting to do it,” said Mark Mitchell, one of the U.S. Figure Skating coaches at the camp. “So when I saw him, I just said, ‘Oh, my gosh! Cory just landed the triple axel!’ And he was so happy, just so happy.”
Cory’s parents were accompanying their son.
Olivia Eve Ter excelled on the ice. She was a powerful jumper and had started traveling out of state to compete, propelled by dreams of becoming an Olympian. Her mother, Olesya Taylor, was born in Ukraine and grew up in northern Russia, and believed in taking advantage of every opportunity available to her children in the United States, her husband, Andrey Ter, said. The mother and daughter were on the flight together, returning home to Virginia.
“My wife had no rest,” Mr. Ter said. “She moved so fast, and it all stopped on Wednesday.”
The Skating Club of Boston, in Norwood, Mass., confirmed that two of its coaches were killed in the crash, along with two of their skating students and the mothers of the skaters.
Yevgeniya Shishkova, 52, and Vadim Naumov, 55
Stewart Fraser/Colorsport, via Shutterstock
Jinna Han, 13
The Skating Club of Boston
Spencer Lane, 16
The Skating Club of Boston
Most of the young skaters on the plane had been in the top group at the camp. They were the “very best young skaters,” Sam Auxier, interim chief executive of U.S. Figure Skating, said, adding, “A key part of the young skating family is gone.” Among them were Sean Kay and Angela Yang, an ice dancing pair from Delaware that had been undefeated in the juvenile division this year. Both 11 and traveling with their mothers and their coach, they were two of the youngest passengers on the plane.
Sean Kay, 11, and Yulia Kay, 42
Sasha Kirsanov, 46
Stephen Dunn/Getty Images
Some of the athletes loved skating so much that their parents could hardly keep them off the ice. In addition to hours of training for U.S. Figure Skating events, the Livingston sisters, Everly and Alydia, performed for the public in outdoor events on some weekends and holidays. “Some competitors didn’t want to skate on outdoor rinks, but the girls were always up for having fun,” said Tara Modlin-Maurizi, a skating agent who produced some of those performances. The girls had traveled to Wichita with their parents, and the four were on their way home to Northern Virginia when the plane crashed.
Alydia Livingston, 11, and Everly Livingston, 14
Donna Smojice Livingston, 48, and Peter Livingston, 48
Brielle Beyer survived cancer when she was just a baby and grew into a tough skater, her coach, Kalle Strid, said. “Sometimes she would get mad at me if we didn’t try the more difficult things,” he said. “She was an extraordinary talent.”
Justyna Magdalena Beyer, 42
The Hunters
Duck hunting season was almost over in Kansas when the group from Southern Maryland arrived at Fowl Plains, a hunting outfitter that offers guided trips.
The men, many who worked in plumbing and steamfitting, were thrilled to be there, eager to hunt ducks and geese. Some had known each other since childhood, part of a tight-knit community south of Washington.
Mr. Stovall was a steamfitter by trade, a Baltimore Orioles fan and an avid outdoorsman, hunter and snowboarder. His Facebook page was full of photos from his adventures with his wife, son and friends.
Mr. Pitcher knew the men through work, his father, Jameson Pitcher, said.
The elder Mr. Pitcher said his son owned a plumbing business and had been married just over a year. Jesse Pitcher and his wife, Kylie, were in the process of building a new house.
“He was just getting started with life,” his father said.
From Abroad
The flight also carried passengers from other countries.
Pergentino Malabed Jr., 51
A colonel in the Philippines National Police, Mr. Malabed had been on a work trip to test out armored vests. His wife, Rio, recalled how their 3-year-old daughter had been crying as she held her father’s hand outside the Manila airport. His wife said he had kissed the girl and told her, “I’ll see you soon.”

Business
Video: The Web of Companies Owned by Elon Musk

new video loaded: The Web of Companies Owned by Elon Musk

By Kirsten Grind, Melanie Bencosme, James Surdam and Sean Havey
February 27, 2026
Business
Commentary: How Trump helped foreign markets outperform U.S. stocks during his first year in office
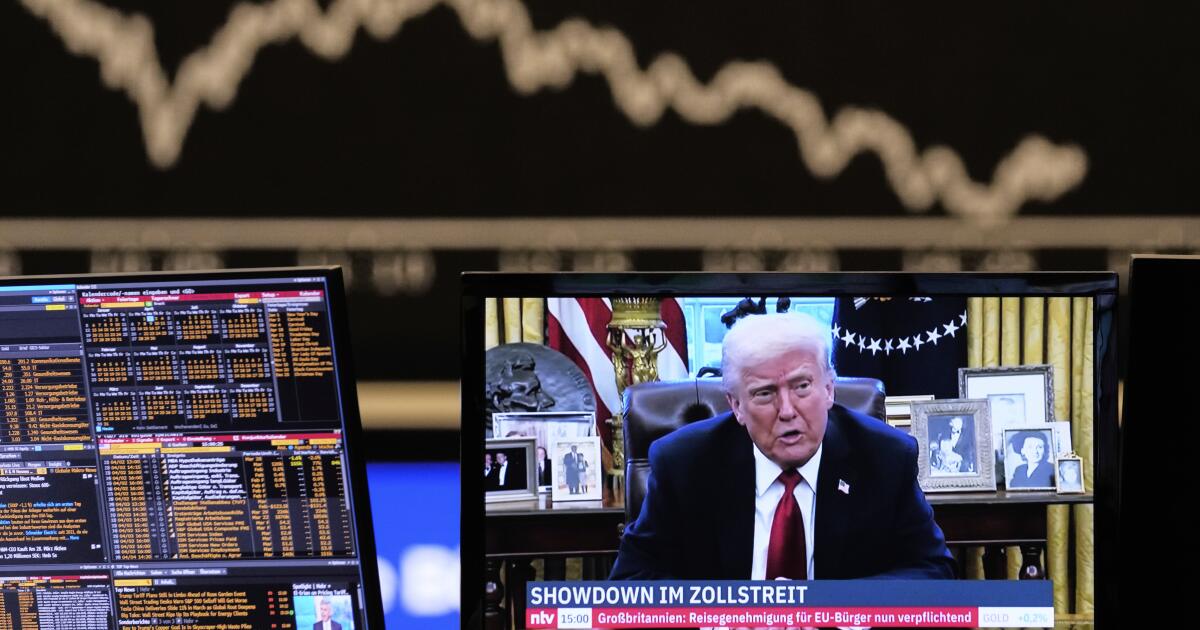
Trump has crowed about the gains in the U.S. stock market during his term, but in 2025 investors saw more opportunity in the rest of the world.
If you’re a stock market investor you might be feeling pretty good about how your portfolio of U.S. equities fared in the first year of President Trump’s term.
All the major market indices seemed to be firing on all cylinders, with the Standard & Poor’s 500 index gaining 17.9% through the full year.
But if you’re the type of investor who looks for things to regret, pay no attention to the rest of the world’s stock markets. That’s because overseas markets did better than the U.S. market in 2025 — a lot better. The MSCI World ex-USA index — that is, all the stock markets except the U.S. — gained more than 32% last year, nearly double the percentage gains of U.S. markets.
That’s a major departure from recent trends. Since 2013, the MSCI US index had bested the non-U.S. index every year except 2017 and 2022, sometimes by a wide margin — in 2024, for instance, the U.S. index gained 24.6%, while non-U.S. markets gained only 4.7%.
The Trump trade is dead. Long live the anti-Trump trade.
— Katie Martin, Financial Times
Broken down into individual country markets (also by MSCI indices), in 2025 the U.S. ranked 21st out of 23 developed markets, with only New Zealand and Denmark doing worse. Leading the pack were Austria and Spain, with 86% gains, but superior records were turned in by Finland, Ireland and Hong Kong, with gains of 50% or more; and the Netherlands, Norway, Britain and Japan, with gains of 40% or more.
Investment analysts cite several factors to explain this trend. Judging by traditional metrics such as price/earnings multiples, the U.S. markets have been much more expensive than those in the rest of the world. Indeed, they’re historically expensive. The Standard & Poor’s 500 index traded in 2025 at about 23 times expected corporate earnings; the historical average is 18 times earnings.
Investment managers also have become nervous about the concentration of market gains within the U.S. technology sector, especially in companies associated with artificial intelligence R&D. Fears that AI is an investment bubble that could take down the S&P’s highest fliers have investors looking elsewhere for returns.
But one factor recurs in almost all the market analyses tracking relative performance by U.S. and non-U.S. markets: Donald Trump.
Investors started 2025 with optimism about Trump’s influence on trading opportunities, given his apparent commitment to deregulation and his braggadocio about America’s dominant position in the world and his determination to preserve, even increase it.
That hasn’t been the case for months.
”The Trump trade is dead. Long live the anti-Trump trade,” Katie Martin of the Financial Times wrote this week. “Wherever you look in financial markets, you see signs that global investors are going out of their way to avoid Donald Trump’s America.”
Two Trump policy initiatives are commonly cited by wary investment experts. One, of course, is Trump’s on-and-off tariffs, which have left investors with little ability to assess international trade flows. The Supreme Court’s invalidation of most Trump tariffs and the bellicosity of his response, which included the immediate imposition of new 10% tariffs across the board and the threat to increase them to 15%, have done nothing to settle investors’ nerves.
Then there’s Trump’s driving down the value of the dollar through his agitation for lower interest rates, among other policies. For overseas investors, a weaker dollar makes U.S. assets more expensive relative to the outside world.
It would be one thing if trade flows and the dollar’s value reflected economic conditions that investors could themselves parse in creating a picture of investment opportunities. That’s not the case just now. “The current uncertainty is entirely man-made (largely by one orange-hued man in particular) but could well continue at least until the US mid-term elections in November,” Sam Burns of Mill Street Research wrote on Dec. 29.
Trump hasn’t been shy about trumpeting U.S. stock market gains as emblems of his policy wisdom. “The stock market has set 53 all-time record highs since the election,” he said in his State of the Union address Tuesday. “Think of that, one year, boosting pensions, 401(k)s and retirement accounts for the millions and the millions of Americans.”
Trump asserted: “Since I took office, the typical 401(k) balance is up by at least $30,000. That’s a lot of money. … Because the stock market has done so well, setting all those records, your 401(k)s are way up.”
Trump’s figure doesn’t conform to findings by retirement professionals such as the 401(k) overseers at Bank of America. They reported that the average account balance grew by only about $13,000 in 2025. I asked the White House for the source of Trump’s claim, but haven’t heard back.
Interpreting stock market returns as snapshots of the economy is a mug’s game. Despite that, at her recent appearance before a House committee, Atty. Gen. Pam Bondi tried to deflect questions about her handling of the Jeffrey Epstein records by crowing about it.
“The Dow is over 50,000 right now, she declared. “Americans’ 401(k)s and retirement savings are booming. That’s what we should be talking about.”
I predicted that the administration would use the Dow industrial average’s break above 50,000 to assert that “the overall economy is firing on all cylinders, thanks to his policies.” The Dow reached that mark on Feb. 6. But Feb. 11, the day of Bondi’s testimony, was the last day the index closed above 50,000. On Thursday, it closed at 49,499.50, or about 1.4% below its Feb. 10 peak close of 50,188.14.
To use a metric suggested by economist Justin Wolfers of the University of Michigan, if you invested $48,488 in the Dow on the day Trump took office last year, when the Dow closed at 48,448 points, you would have had $50,000 on Feb. 6. That’s a gain of about 3.2%. But if you had invested the same amount in the global stock market not including the U.S. (based on the MSCI World ex-USA index), on that same day you would have had nearly $60,000. That’s a gain of nearly 24%.
Broader market indices tell essentially the same story. From Jan. 17, 2025, the last day before Trump’s inauguration, through Thursday’s close, the MSCI US stock index gained a cumulative 16.3%. But the world index minus the U.S. gained nearly 42%.
The gulf between U.S. and non-U.S. performance has continued into the current year. The S&P 500 has gained about 0.74% this year through Wednesday, while the MSCI World ex-USA index has gained about 8.9%. That’s “the best start for a calendar year for global stocks relative to the S&P 500 going back to at least 1996,” Morningstar reports.
It wouldn’t be unusual for the discrepancy between the U.S. and global markets to shrink or even reverse itself over the course of this year.
That’s what happened in 2017, when overseas markets as tracked by MSCI beat the U.S. by more than three percentage points, and 2022, when global markets lost money but U.S. markets underperformed the rest of the world by more than five percentage points.
Economic conditions change, and often the stock markets march to their own drummers. The one thing less likely to change is that Trump is set to remain president until Jan. 20, 2029. Make your investment bets accordingly.
Business
How the S&P 500 Stock Index Became So Skewed to Tech and A.I.

Nvidia, the chipmaker that became the world’s most valuable public company two years ago, was alone worth more than $4.75 trillion as of Thursday morning. Its value, or market capitalization, is more than double the combined worth of all the companies in the energy sector, including oil giants like Exxon Mobil and Chevron.
The chipmaker’s market cap has swelled so much recently, it is now 20 percent greater than the sum of all of the companies in the materials, utilities and real estate sectors combined.
What unifies these giant tech companies is artificial intelligence. Nvidia makes the hardware that powers it; Microsoft, Apple and others have been making big bets on products that people can use in their everyday lives.
But as worries grow over lavish spending on A.I., as well as the technology’s potential to disrupt large swaths of the economy, the outsize influence that these companies exert over markets has raised alarms. They can mask underlying risks in other parts of the index. And if a handful of these giants falter, it could mean widespread damage to investors’ portfolios and retirement funds in ways that could ripple more broadly across the economy.
The dynamic has drawn comparisons to past crises, notably the dot-com bubble. Tech companies also made up a large share of the stock index then — though not as much as today, and many were not nearly as profitable, if they made money at all.
How the current moment compares with past pre-crisis moments
To understand how abnormal and worrisome this moment might be, The New York Times analyzed data from S&P Dow Jones Indices that compiled the market values of the companies in the S&P 500 in December 1999 and August 2007. Each date was chosen roughly three months before a downturn to capture the weighted breakdown of the index before crises fully took hold and values fell.
The companies that make up the index have periodically cycled in and out, and the sectors were reclassified over the last two decades. But even after factoring in those changes, the picture that emerges is a market that is becoming increasingly one-sided.
In December 1999, the tech sector made up 26 percent of the total.
In August 2007, just before the Great Recession, it was only 14 percent.
Today, tech is worth a third of the market, as other vital sectors, such as energy and those that include manufacturing, have shrunk.
Since then, the huge growth of the internet, social media and other technologies propelled the economy.
Now, never has so much of the market been concentrated in so few companies. The top 10 make up almost 40 percent of the S&P 500.
How much of the S&P 500 is occupied by the top 10 companies
With greater concentration of wealth comes greater risk. When so much money has accumulated in just a handful of companies, stock trading can be more volatile and susceptible to large swings. One day after Nvidia posted a huge profit for its most recent quarter, its stock price paradoxically fell by 5.5 percent. So far in 2026, more than a fifth of the stocks in the S&P 500 have moved by 20 percent or more. Companies and industries that are seen as particularly prone to disruption by A.I. have been hard hit.
The volatility can be compounded as everyone reorients their businesses around A.I, or in response to it.
The artificial intelligence boom has touched every corner of the economy. As data centers proliferate to support massive computation, the utilities sector has seen huge growth, fueled by the energy demands of the grid. In 2025, companies like NextEra and Exelon saw their valuations surge.
The industrials sector, too, has undergone a notable shift. General Electric was its undisputed heavyweight in 1999 and 2007, but the recent explosion in data center construction has evened out growth in the sector. GE still leads today, but Caterpillar is a very close second. Caterpillar, which is often associated with construction, has seen a spike in sales of its turbines and power-generation equipment, which are used in data centers.
One large difference between the big tech companies now and their counterparts during the dot-com boom is that many now earn money. A lot of the well-known names in the late 1990s, including Pets.com, had soaring valuations and little revenue, which meant that when the bubble popped, many companies quickly collapsed.
Nvidia, Apple, Alphabet and others generate hundreds of billions of dollars in revenue each year.
And many of the biggest players in artificial intelligence these days are private companies. OpenAI, Anthropic and SpaceX are expected to go public later this year, which could further tilt the market dynamic toward tech and A.I.
Methodology
Sector values reflect the GICS code classification system of companies in the S&P 500. As changes to the GICS system took place from 1999 to now, The New York Times reclassified all companies in the index in 1999 and 2007 with current sector values. All monetary figures from 1999 and 2007 have been adjusted for inflation.
-

 World2 days ago
World2 days agoExclusive: DeepSeek withholds latest AI model from US chipmakers including Nvidia, sources say
-

 Massachusetts2 days ago
Massachusetts2 days agoMother and daughter injured in Taunton house explosion
-

 Montana1 week ago
Montana1 week ago2026 MHSA Montana Wrestling State Championship Brackets And Results – FloWrestling
-

 Oklahoma1 week ago
Oklahoma1 week agoWildfires rage in Oklahoma as thousands urged to evacuate a small city
-

 Louisiana5 days ago
Louisiana5 days agoWildfire near Gum Swamp Road in Livingston Parish now under control; more than 200 acres burned
-

 Denver, CO2 days ago
Denver, CO2 days ago10 acres charred, 5 injured in Thornton grass fire, evacuation orders lifted
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoYouTube TV billing scam emails are hitting inboxes
-

 Technology6 days ago
Technology6 days agoStellantis is in a crisis of its own making
























