Business
Snapchat is nearing 1 billion monthly users. Why can’t it turn a profit?

Snapchat, an app whose disappearing messages and silly face filters made chatting with loved ones more casual, is close to a milestone that few social media platforms achieve: reaching 1 billion monthly users.
But Snap, the Santa Monica company behind the app, faces a crucial test. The 14-year-old tech company is still losing money and has seen its share price tumble as it barrels forward to popularize augmented reality glasses next year.
And even though more people in developing countries are using the app, Snapchat usage in markets where the company makes more revenue per user, including the United States and Europe, has dropped.
Snapchat has 943 million monthly active users globally, according to the company.
Growth in India, where TikTok is banned, and Pakistan have fueled Snapchat’s global user growth, data from market intelligence firm Sensor Tower show. In India, Snapchat monthly users have surpassed 250 million, making up more than a quarter of its user base, according to numbers Snap released in July.
At the same time, in the third quarter, Snapchat monthly active users declined by 4% in the U.S. and double digits in France, Italy, Germany and the United Kingdom, Sensor Tower said.
Snap Chief Executive Evan Spiegel wrote in a September note to employees the company is in a “crucible moment,” comparing it to a “middle child” wedged between larger tech giants and smaller rivals.
“This moment isn’t just about survival,” Spiegel wrote in the note. “It’s about proving that a different way of building technology, one that deepens friendships and inspires creativity, can succeed in a world that often rewards the opposite.”
The 35-year-old tech executive co-founded Snapchat — initially known as Picaboo — in 2011 with friends as part of a class project while attending Stanford University. Back then, texts and photos posted on social media such as Facebook and Instagram were more permanent.
Snapchat’s logo is a ghost and the app distinguished itself from its competitors by giving people a way to share photos and messages that disappeared once someone viewed it. Instead of a social media app that opens to a feed of content, Snapchat opens to a camera.
Rather than worry about whether they looked perfect, people leaned into quirky and creative ways to express themselves. They overlaid effects onto their selfies, transforming their faces into cute dogs and even puking rainbows. The app encouraged people to keep sending these disappearing messages known as “Snaps” to their loved ones at least once a day, keeping what’s known as a “streak” alive.
As Snapchat’s popularity soared, fueling the rise of vertical videos, bigger social media rivals took notice. Snapchat’s co-founders turned down Facebook’s multibillion-dollar offer to buy the company.
Facebook and its photo-sharing app Instagram copied Snapchat’s signature features including Stories, which allowed people to post images and videos that vanish after 24 hours. This prompted some Snapchat users to flock to its rival Instagram. Spiegel jokingly titled himself as the vice president of product at Meta, Facebook’s parent company, on LinkedIn, a nod to the social media giant’s cloning of Snapchat’s features.
Although Snapchat set itself apart from other social media, it also faced similar concerns tech platforms grappled with such as child safety and mental health. The app is popular among teenagers, prompting some users to question if they’re too old for Snapchat and should leave.
Alex Sirek started using Snapchat as a teen to chat and make plans with her friends, filling the app with high school and college memories.
But as she grew up, she realized there were downsides to being on the app. She constantly opened Snapchat to check her face, which made her feel bad about her skin. When friends posted about partying or going out, she felt the fear of missing out.
Last year, looking to free up storage on her smartphone, Sirek deleted Snapchat.
After about a year, the 24-year-old San Diego fitness influencer downloaded Snapchat again but rarely uses the app.
“I kept wanting to open it, but now I just don’t even think about it,” she said. “I forget that I have it on my phone.”
Investor confidence in the company has plummeted. In 2021, Snap’s stock peaked at more than $83 per share. Snap’s share price closed Tuesday at $7.64.
Competing with larger rivals such as Instagram, Facebook, YouTube and TikTok, for ad dollars has been challenging for Snapchat and it has struggled to consistently turn a profit. Apple’s privacy feature made it tougher for advertisers to track users across apps and websites, posing an extra hurdle for social networks.
Research firm eMarketer estimates that in 2025 Snapchat will claim 2.1% of U.S. social network ad spending, but said that share is dropping.
Snapchat’s initial focus on disappearing messages made it tougher for the company to rope in advertisers because people typically don’t want to see ads in the middle of a private conversation. But the company has been updating its ad tools and expanded the places where ads are shown, including between short videos.
Although Snapchat is popular among Gen Z and millennials, its audience might limit what businesses want to advertise on its platform.
“It definitely skews a lot younger and that naturally sort of limits advertiser interests in its audience,” said Max Willens, a senior analyst at eMarketer. If a business wants to advertise retirement planning, for example, they would probably go to Facebook instead of Snapchat.
On Snapchat, advertisers have also used augmented reality effects to promote their brands in quirky ways to a young audience. Snapchat users can transform themselves into a dancing McDonald’s McRib sandwich or snap selfies with digital animals from the Disney film “Zootopia 2.”
Snap has been looking at other ways to make money. The company offers subscription plans so users can customize the app’s wallpaper, personalize their digital avatars known as Bitmojis and see how often their friends view their content. It started to limit the amount of free storage it offers to 5 gigabytes. AI company Perplexity said it will pay Snap $400 million over one year so users can find answers from its “AI-powered answer engine.”
In the third quarter, Snap revenue reached $1.5 billion, up 10% compared with the same period last year. The company narrowed its net loss to $104 million, versus a net loss of $153 million during the year-earlier period.
This month, JP Morgan analysts raised Snap’s price target to $8 after the Perplexity deal but kept an underweight rating on the shares, meaning they expect the stock to underperform.
The firm said Snap has “a sizable market opportunity, an engaged user base, and a solid track record of innovation” but it’s also looking for “more consistent execution, improved user & revenue trends, & greater profitability.”
Snap has made bold and expensive bets on the future of computing by releasing a drone and glasses to capture photos and videos — though those products flopped. Now Snap plans to release augmented reality glasses in 2026 that let people interact with digital images overlaid onto the physical world. Instead of taking out your phone, people will be able to review documents, stream movies, play chess and more through glasses.
For now, analysts say it’s too early to tell if Snap’s bets will pay off or the company will end up in the social media graveyard like Myspace or Vine.
“There’s nothing written down that says you just get to be around forever if you’re a social media platform,” Willens said. “Although almost all of those still kind of trudge along in some state or another.”

Business
Versant launches, Comcast spins off E!, CNBC and MS NOW

Comcast has officially spun off its cable channels, including CNBC and MS NOW, into a separate company, Versant Media Group.
The transaction was completed late Friday. On Monday, Versant took a major tumble in its stock market debut — providing a key test of investors’ willingness to hold on to legacy cable channels.
The initial outlook wasn’t pretty, providing awkward moments for CNBC anchors reporting the story.
Versant fell 13% to $40.57 a share on its inaugural trading day. The stock opened Monday on Nasdaq at $45.17 per share.
Comcast opted to cast off the still-profitable cable channels, except for the perennially popular Bravo, as Wall Street has soured on the business, which has been contracting amid a consumer shift to streaming.
Versant’s market performance will be closely watched as Warner Bros. Discovery attempts to separate its cable channels, including CNN, TBS and Food Network, from Warner Bros. studios and HBO later this year. Warner Chief Executive David Zaslav’s plan, which is scheduled to take place in the summer, is being contested by the Ellison family’s Paramount, which has launched a hostile bid for all of Warner Bros. Discovery.
Warner Bros. Discovery has agreed to sell itself to Netflix in an $82.7-billion deal.
The market’s distaste for cable channels has been playing out in recent years. Paramount found itself on the auction block two years ago, in part because of the weight of its struggling cable channels, including Nickelodeon, Comedy Central and MTV.
Management of the New York-based Versant, including longtime NBCUniversal sports and television executive Mark Lazarus, has been bullish on the company’s balance sheet and its prospects for growth. Versant also includes USA Network, Golf Channel, Oxygen, E!, Syfy, Fandango, Rotten Tomatoes, GolfNow, GolfPass and SportsEngine.
“As a standalone company, we enter the market with the scale, strategy and leadership to grow and evolve our business model,” Lazarus, who is Versant’s chief executive, said Monday in a statement.
Through the spin-off, Comcast shareholders received one share of Versant Class A common stock or Versant Class B common stock for every 25 shares of Comcast Class A common stock or Comcast Class B common stock, respectively. The Versant shares were distributed after the close of Comcast trading Friday.
Comcast gained about 3% on Monday, trading around $28.50.
Comcast Chairman Brian Roberts holds 33% of Versant’s controlling shares.
Business
Ties between California and Venezuela go back more than a century with Chevron

As a stunned world processes the U.S. government’s sudden intervention in Venezuela — debating its legality, guessing who the ultimate winners and losers will be — a company founded in California with deep ties to the Golden State could be among the prime beneficiaries.
Venezuela has the largest proven oil reserves on the planet. Chevron, the international petroleum conglomerate with a massive refinery in El Segundo and headquartered, until recently, in San Ramon, is the only foreign oil company that has continued operating there through decades of revolution.
Other major oil companies, including ConocoPhillips and Exxon Mobil, pulled out of Venezuela in 2007 when then-President Hugo Chávez required them to surrender majority ownership of their operations to the country’s state-controlled oil company, PDVSA.
But Chevron remained, playing the “long game,” according to industry analysts, hoping to someday resume reaping big profits from the investments the company started making there almost a century ago.
Looks like that bet might finally pay off.
In his news conference Saturday, after U.S. Special Forces snatched Venezuelan President Nicolás Maduro and his wife in Caracas and extradited them to face drug-trafficking charges in New York, President Trump said the U.S. would “run” Venezuela and open more of its massive oil reserves to American corporations.
“We’re going to have our very large U.S. oil companies, the biggest anywhere in the world, go in, spend billions of dollars, fix the badly broken infrastructure, the oil infrastructure, and start making money for the country,” Trump said during a news conference Saturday.
While oil industry analysts temper expectations by warning it could take years to start extracting significant profits given Venezuela’s long-neglected, dilapidated infrastructure, and everyday Venezuelans worry about the proceeds flowing out of the country and into the pockets of U.S. investors, there’s one group who could be forgiven for jumping with unreserved joy: Chevron insiders who championed the decision to remain in Venezuela all these years.
But the company’s official response to the stunning turn of events has been poker-faced.
“Chevron remains focused on the safety and well-being of our employees, as well as the integrity of our assets,” spokesman Bill Turenne emailed The Times on Sunday, the same statement the company sent to news outlets all weekend. “We continue to operate in full compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.”
Turenne did not respond to questions about the possible financial rewards for the company stemming from this weekend’s U.S. military action.
Chevron, which is a direct descendant of a small oil company founded in Southern California in the 1870s, has grown into a $300-billion global corporation. It was headquartered in San Ramon, just outside of San Francisco, until executives announced in August 2024 that they were fleeing high-cost California for Houston.
Texas’ relatively low taxes and light regulation have been a beacon for many California companies, and most of Chevron’s competitors are based there.
Chevron began exploring in Venezuela in the early 1920s, according to the company’s website, and ramped up operations after discovering the massive Boscan oil field in the 1940s. Over the decades, it grew into Venezuela’s largest foreign investor.
The company held on over the decades as Venezuela’s government moved steadily to the left; it began to nationalize the oil industry by creating a state-owned petroleum company in 1976, and then demanded majority ownership of foreign oil assets in 2007, under then-President Hugo Chávez.
Venezuela has the world’s largest proven crude oil reserves — meaning they’re economical to tap — about 303 billion barrels, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
But even with those massive reserves, Venezuela has been producing less than 1% of the world’s crude oil supply. Production has steadily declined from the 3.5 million barrels per day pumped in 1999 to just over 1 million barrels per day now.
Currently, Chevron’s operations in Venezuela employ about 3,000 people and produce between 250,000 and 300,000 barrels of oil per day, according to published reports.
That’s less than 10% of the roughly 3 million barrels the company produces from holdings scattered across the globe, from the Gulf of Mexico to Kazakhstan and Australia.
But some analysts are optimistic that Venezuela could double or triple its current output relatively quickly — which could lead to a windfall for Chevron.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
Business
‘Stranger Things’ finale turns box office downside up pulling in an estimated $25 million
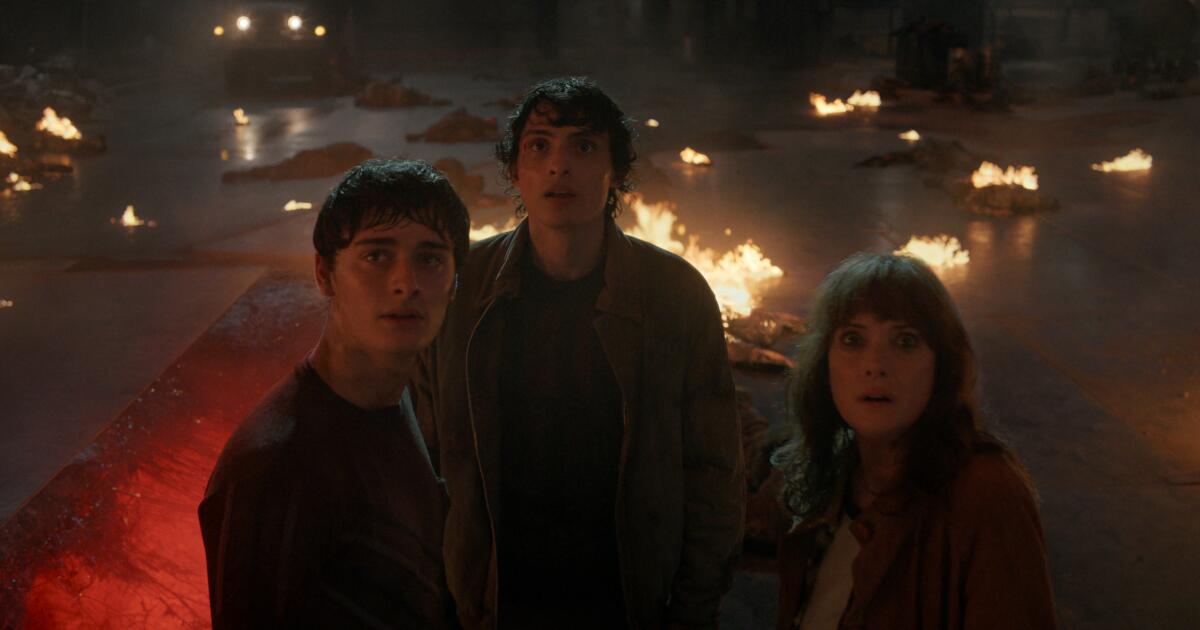
The finale of Netflix’s blockbuster series “Stranger Things” gave movie theaters a much needed jolt, generating an estimated $20 to $25 million at the box office, according to multiple reports.
Matt and Ross Duffer’s supernatural thriller debuted simultaneously on the streaming platform and some 600 cinemas on New Year’s Eve and held encore showings all through New Year’s Day.
Owing to the cast’s contractual terms for residuals, theaters could not charge for tickets. Instead, fans reserved seats for performances directly from theaters, paying for mandatory food and beverage vouchers. AMC and Cinemark Theatres charged $20 for the concession vouchers while Regal Cinemas charged $11 — in homage to the show’s lead character, Eleven, played by Millie Bobby Brown.
AMC Theatres, the world’s largest theater chain, played the finale at 231 of its theaters across the U.S. — which accounted for one-third of all theaters that held screenings over the holiday.
The chain said that more than 753,000 viewers attended a performance at one of its cinemas over two days, bringing in more than $15 million.
Expectations for the theater showing was high.
“Our year ends on a high: Netflix’s Strangers Things series finale to show in many AMC theatres this week. Two days only New Year’s Eve and Jan 1.,” tweeted AMC’s CEO Adam Aron on Dec. 30. “Theatres are packed. Many sellouts but seats still available. How many Stranger Things tickets do you think AMC will sell?”
It was a rare win for the lagging domestic box office.
In 2025, revenue in the U.S. and Canada was expected to reach $8.87 billion, which was marginally better than 2024 and only 20% more than pre-pandemic levels, according to movie data firm Comscore.
With few exceptions, moviegoers have stayed home. As of Dec. 25., only an estimated 760 million tickets were sold, according to media and entertainment data firm EntTelligence, compared with 2024, during which total ticket sales exceeded 800 million.
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoHamas builds new terror regime in Gaza, recruiting teens amid problematic election
-

 Indianapolis, IN1 week ago
Indianapolis, IN1 week agoIndianapolis Colts playoffs: Updated elimination scenario, AFC standings, playoff picture for Week 17
-

 News1 week ago
News1 week agoFor those who help the poor, 2025 goes down as a year of chaos
-

 World1 week ago
World1 week agoPodcast: The 2025 EU-US relationship explained simply
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoInstacart ends AI pricing test that charged shoppers different prices for the same items
-

 Business1 week ago
Business1 week agoApple, Google and others tell some foreign employees to avoid traveling out of the country
-

 Politics1 week ago
Politics1 week ago‘Unlucky’ Honduran woman arrested after allegedly running red light and crashing into ICE vehicle
-

 Technology1 week ago
Technology1 week agoChatGPT’s GPT-5.2 is here, and it feels rushed














