Business
Original ‘Star Trek’ Enterprise model was lost and found decades later. Now it's the subject of a lawsuit
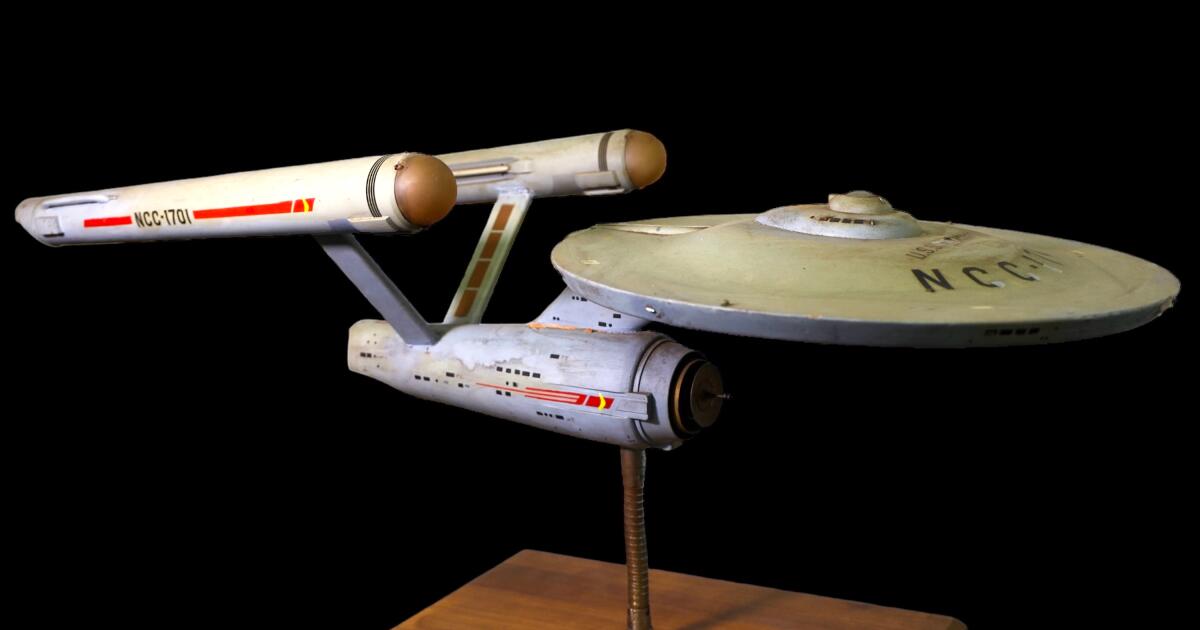

In April, Heritage Auctions heralded the discovery of the original model of the U.S.S. Enterprise, the iconic starship that whooshed through the stars in the opening credits of the 1960s TV series “Star Trek” but had mysteriously disappeared around 45 years ago.
The auction house, known for its dazzling sales of movie and television props and memorabilia, announced that it was returning the 33-inch model to Eugene “Rod” Roddenberry Jr., son of series creator Gene Roddenberry. The model was kept at Heritage’s Beverly Hills office for “safekeeping,” the house proclaimed in a statement, shortly after an individual discovered it and brought it to Heritage for authentication.
“After a long journey, she’s home,” Roddenberry’s son posted on X, (formerly Twitter).
Heritage Auctions Executive Vice President Joe Maddalena, left, with Eugene “Rod” Roddenberry Jr., son of “Star Trek” creator Gene Rodenberry, with the first model of the starship Enterprise.
(Heritage Auctions / HA.com)
But the journey has been far from smooth. The starship model and its celebrated return is now the subject of a lawsuit alleging fraud, negligence and deceptive trade practice, highlighting the enduring value of memorabilia from the iconic sci-fi TV series.
The case was brought by Dustin Riach and Jason Rivas, longtime friends and self-described storage unit entrepreneurs who discovered the model among a stash of items they bought “sight unseen” from a lien sale at a storage locker in Van Nuys last October.
“It’s an unfortunate misunderstanding. We have a seller on one side and a buyer on the other side and Heritage is in the middle, and we are aligning the parties on both sides to get the transaction complete,” said Armen Vartian, an attorney representing the Dallas-based auction house, adding that the allegations against his client were “unfounded.”
The pair claimed that once the model was authenticated and given a value of $800,000, they agreed to consign it to an auction sale with Heritage planned for July 2024, according to the lawsuit. However, following their agreement, they allege the auction house falsely questioned their title to the model and then convinced them, instead of taking it to auction, to sell it for a low-ball $500,000 to Roddenberry Entertainment Inc. According to the suit, Eugene Roddenberry, the company’s CEO, had shown great interest in the model and could potentially provide a pipeline of memorabilia to the auction house in the future.
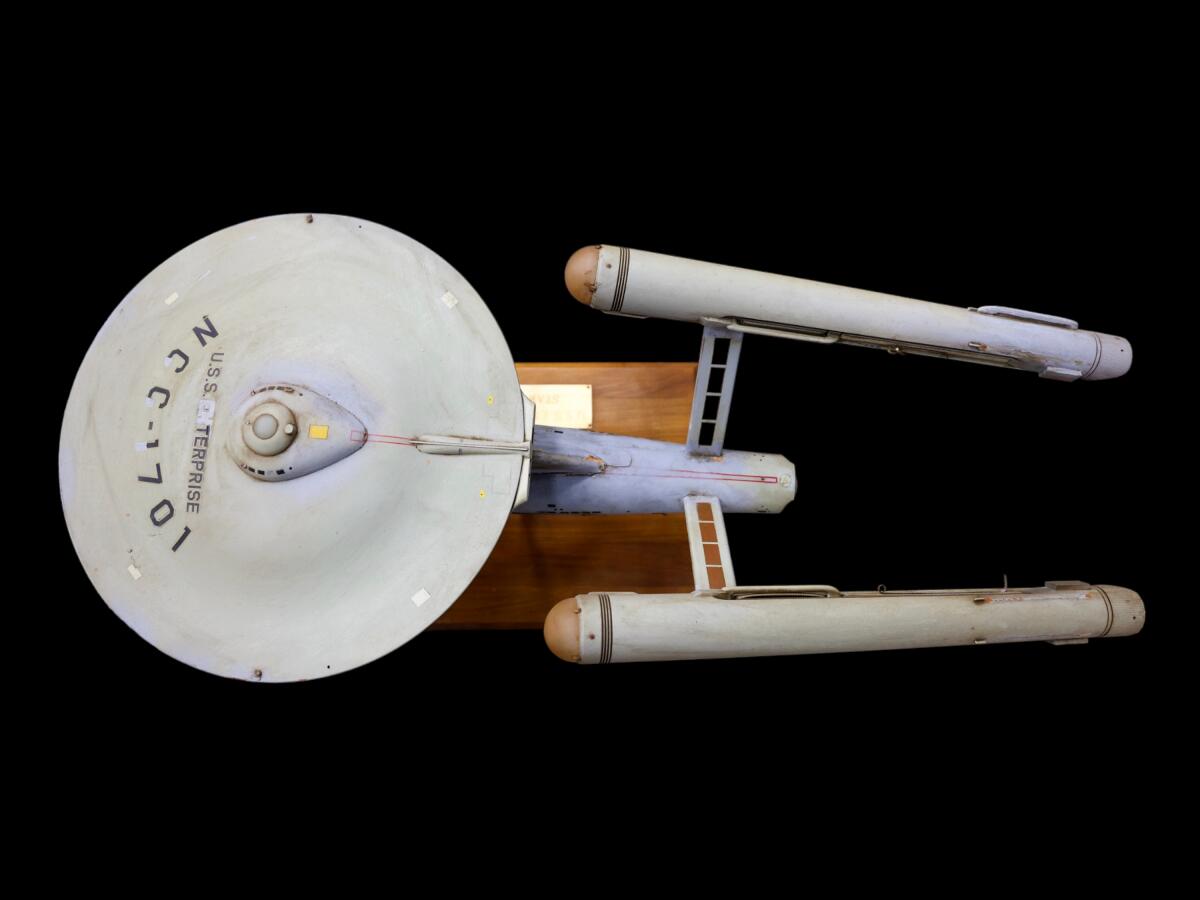
The model had gone missing for 45 years.
(Heritage Auctions / HA.com)
“They think we have a disagreement with Roddenberry,” said Dale Washington, Riach and Rivas’ attorney. “We don’t. We think they violated property law in the discharge of their fiduciary duties.”
The two men allege they have yet to receive the $500,000 payment.
A surprise discovery in a Van Nuys storage unit
For years, Riach and Rivas have made a living buying repossessed storage lockers and selling the contents online, at auction and at flea markets. In fact, Riach has appeared on the reality TV series “Storage Wars.”
“It’s a roll of dice in the dark,” Riach said of his profession bidding on storage lockers. “Sometimes you are buying a picture of a unit. When a unit goes to lien, what you see is what you get and the rest is a surprise. At a live auction you can shine a flashlight, smell and look inside to get a gauge. But online is a gamble, it’s only as good as the photo.”
Last fall, Riach said he saw a picture of a large locker in an online sale. It was 10 feet by 30 feet, and “I saw boxes hiding in the back, it was dirty, dusty, there were cobwebs and what looked like a bunch of broken furniture,” he said.
Something about it, he said, “looked interesting,” and he called Rivas and told him they should bid on it. Riach declined to say how much they paid.
There were tins of old photographs and negatives of nitrate film reels from the 1800s and 1900s. When Rivas unwrapped a trash bag that was sitting on top of furniture, he pulled out a model of a spaceship. The business card of its maker, Richard C. Datin, was affixed to the bottom of the base.
A Google search turned up that Datin had made “Star Trek” models, although the two men didn’t make the connection to the TV series.
“We buy lots of units and see models all of the time,” Riach said. He thought they would find a buyer and decided to list it on eBay with a starting price of $1,000.
At once, they were deluged with inquiries. Among Trekkies, the long-lost first starship model had attained a mythical status.
The original “Star Trek’’ debuted in 1966 and aired for three seasons. Although its original run was brief, the show has generated numerous films and television spinoffs and is one of the most lucrative entertainment franchises, with an enormous fan base.
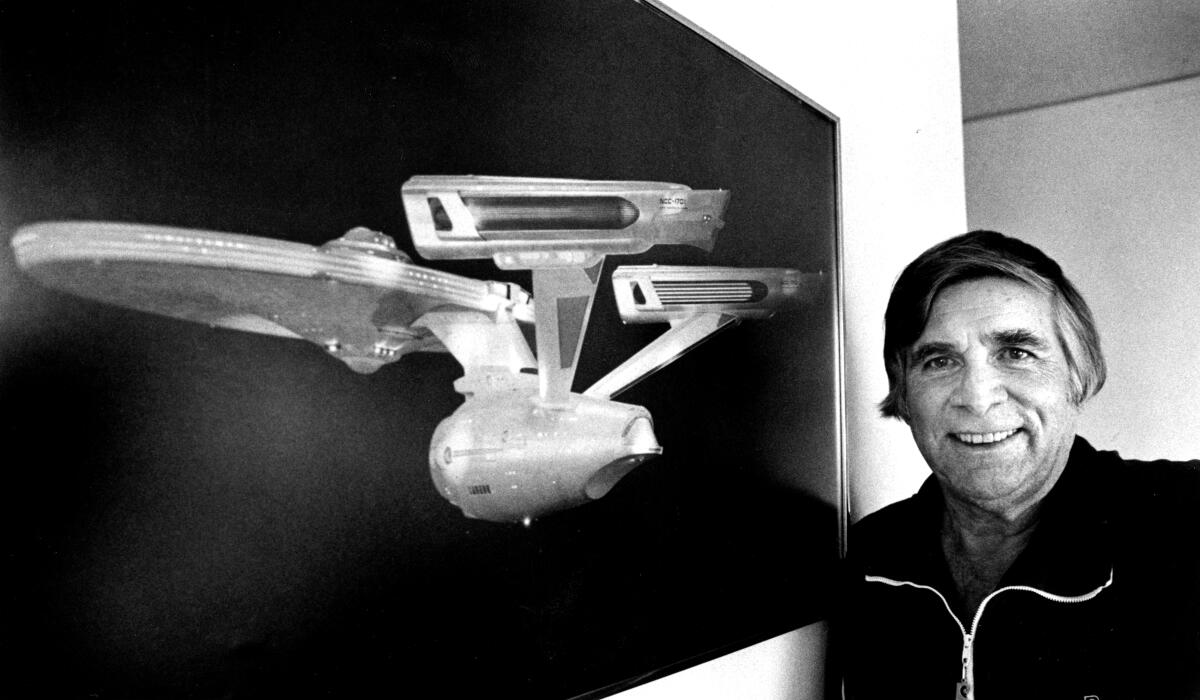

Gene Roddenberry, creator of “Star Trek,” with an image of the starship Enterprise in 1984.
(Ken Lubas / Los Angeles Times)
In 2022, at a Heritage auction of 75 props and items, a Starfleet Communicator from the 1990s series “Star Trek: Deep Space Nine” sold for $27,500 while a pair of Spock’s prosthetic Vulcan ear tips from the original series went for $11,875, more than twice the amount they brought when they were sold in 2017 for $5,100.
The starship’s design was crucial to the series’ success. “If you didn’t believe you were in a vehicle traveling through space, a vehicle that made sense, whose layout and design made sense, then you wouldn’t believe in the series,” Gene Roddenberry said in the 1968 book “The Making of Star Trek,” according to the auction house.
For years, the show’s creator had kept the 33-inch model on his desk. It became the prototype for the 11-foot model used in subsequent episodes. That version was later donated to the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum. But that first model disappeared around 1978 when the makers of “Star Trek: The Motion Picture” borrowed it.
A missing starship model
In 1979, Roddenberry wrote to then Paramount executive Jeffrey Katzenberg stating that he had “loaned” the model to the studio more than a year earlier.
“My problem is simply that of getting my model back,” Roddenberry wrote, according to a copy provided by Washington. “It is a fairly expensive piece of model making but its real value to me is what it represents.” He added that no one he had spoken with “had the slightest hint as to who got it or what happened to it.”
Roddenberry died in 1991.
After the massive interest sparked by the eBay listing, Riach and Rivas pulled the sale and began researching the model more intently. They discovered the connection between Datin and the TV series but also learned that the original model was the same size as the one they had found and it had gone missing. “I said wow, do we have something here?” said Riach, and then reached out to Heritage.
Riach admitted that “Star Trek” wasn’t really on his radar. He was a die-hard “Star Wars” fan, having collected vintage memorabilia from the space films since he was 8 years old.
But given the treasure he unearthed, he now says, “I love ‘Star Trek.’
“There are people buying storage units for 20 years and you will never find anything this great,” he said. “It’s like buying a lottery ticket. It was a very great find.”
Things took an unexpected twist, Riach said. In March, he and Rivas signed an agreement to sell the model for $500,000 after it was pulled from the planned auction and they were told Roddenberry Entertainment had a “strong claim” to the model’s title and “would tie them up with its ‘powerful legal team.’” But then they were given a new transfer agreement to sign with a new set of terms. Riach declined and, instead, he and Rivas called Washington.
Heritage “moved the goalposts,” said their attorney. Under the new agreement, Riach and Rivas would be paid a “finder’s fee,” which Washington called a “reward,” converting it from a transactional payment to a potentially voluntary payment.
They claimed that by April, when Heritage announced the model had resurfaced, the pair came to believe the house failed to disclose the item’s value was much greater than they had been told.
Joe Maddalena, Heritage’s executive vice president, made public statements calling it “priceless.” “It could sell for any amount and I wouldn’t be surprised because of what it is,” he told the AP. “It is truly a cultural icon.”
They also had not been paid.
On April 28, 10 days after Heritage announced it had returned the model to Roddenberry, Riach and Rivas’ lawyer sent a letter to the auction house’s attorney outlining their claims and asking for the payment promised; they also proposed mediation.
Vartian, the lawyer representing Heritage, said that Riach and Rivas became “impatient” about getting the transaction done, and disputes the house had a fiduciary duty to them.
“This is an arm’s-length business relationship,” Vartian said. “They bring something to the auction house and are trying to get the most possible amount as quickly as possible, that is [Heritage’s] position and what they did.”
Still, Vartian is confident that they will soon conclude the transaction, saying, “Various things including scheduling have taken longer than it would.”
For his part, Riach says this experience is much like that of the crew of the U.S.S. Enterprise — “a strange new world.”
“I’ve never experienced anything like this. I’ve sold fine art at auction and other places, I got my check and went on. I’ve never had this roller coaster.
“Storage is a hard game. Sometimes you win and sometimes you lose,” he added. “We’ve bought a $10,000 unit and everything was complete garbage. But if you play long enough, you can get lucky.”

Business
What soaring gas prices mean for California’s EV market

It has been a bumpy road for the electric vehicle market as declining federal support and plateauing public interest have eaten away at sales.
But EV sellers could soon receive a boost from an unexpected source: The war in Iran is pushing up gas prices.
As Americans look to save money at the pump, more will consider switching to an electric or hybrid vehicle. Average gas prices in the U.S. have risen nearly 17% since Feb. 28 to reach $3.48 per gallon. In California, the average is $5.20 per gallon.
Electric vehicles are pricier than gasoline-powered cars and charging them isn’t cheap with current electricity prices, but sky-high gas prices can tip the scales for consumers deciding which kind of vehicle to buy next.
“We probably will see an uptick in EV adoption and particularly hybrid adoption” if gas prices stay high, said Sam Abuelsamid, an auto analyst at Telemetry Agency. “The last time we had oil prices top $100 per barrel was early 2022 and that’s when we saw EV sales really start to pick up in the U.S.”
In a 2022 AAA survey, 77% of respondents said saving money on gas was their primary motivator for purchasing an electric vehicle. That year, 25% of survey respondents said they were likely or very likely to purchase an EV.
As oil prices cooled, the number fell to16% in 2025.
In California, annual sales of new light-duty zero-emission vehicles jumped 43% in 2022, according to the state’s Energy Commission. The market share of zero-emission vehicles among all light-duty vehicles sold rose from 12% in 2021 to 19% in 2022.
“Prior to 2022, we didn’t really have EVs available when we had oil price shocks,” Abuelsamid said. “But every time we did, it coincided with a move toward more fuel-efficient vehicles.”
Dealers are anticipating a windfall.
Brian Maas, president of the California New Car Dealers Assn., predicted enthusiasm for EVs will rebound across California if oil prices don’t come down.
“If prior gasoline price spikes are any indication, you tend to see interest in more fuel-efficient vehicles,” he said.
Rising gas prices could be a lifeline for EV makers at a time when federal support for green cars has been declining.
Under President Trump, a federal $7,500 tax incentive for new electric vehicles was eliminated in September, along with a $4,000 incentive for used electric vehicles.
In California, the zero-emission vehicle share of the total new-vehicle market was 22% through the first 10 months of 2025, then dropped sharply to 12% in the last two months of the year, according to the California Auto Outlook.
Meanwhile Tesla, the most popular EV brand in the country, has grappled with an implosion of its reputation with some consumers after its chief executive, Elon Musk, became one of Trump’s most vocal supporters and helped run the controversial Department of Government Efficiency.
Over the last several months, Ford, General Motors and Stellantis have pared back EV ambitions.
Other automakers, including Nissan, announced plans to stop producing their more affordable electric models.
The Trump administration has moved to roll back federal fuel economy standards and revoked California’s permission to implement a ban on new gas-powered car sales by 2035.
David Reichmuth, a researcher with the Clean Transportation program in the Union of Concerned Scientists, said the shift in production plans will affect EV availability, even if demand surges.
That could keep people from switching to cleaner vehicles regardless of higher gas prices.
“This is a transition that we need to make for both public health and to try to slow the damage from global warming, whether or not the price of gasoline is $3 or $5 or $6 a gallon,” he said.
According to Cox Automotive, new EV sales nationally were down 41% in November from a year earlier. Used EV sales were down 14% year over year that month.
To be sure, oil prices can fluctuate wildly in times of uncertainty. It will take time for consumers to decide on new purchases.
Brian Kim, who manages used car sales at Ford of Downtown LA, said he has yet to see a jump in the number of people interested in EVs, hybrids or more fuel-efficient gas-powered engines.
Still, if the price at the pump stays stuck above its current level, it could happen soon.
“Once the gas prices hit six [dollars per gallon] or more and people feel it in their pocket, maybe things will start to change,” he said.
Business
Nearly 60 gigawatts of U.S. clean power stalled, trade group finds

A total of 59 gigawatts of U.S. clean energy projects are facing delays at a time when demand for power from AI data centers is surging, according to a trade group study.
Developers are seeing an average delay of 19 months over issues such as long interconnection times, supply constraints and regulatory barriers, the American Clean Power Assn. said in a quarterly market report.
The backlog is happening despite the growing need for power on grids that are being taxed by energy-hungry data centers and increased manufacturing. The Trump administration has implemented a slew of policies to slow the build-out of solar and wind projects, including delaying approvals on federal lands.
The potential energy generation facing delays is the equivalent of 59 traditional nuclear reactors, enough to power more than 44 million homes simultaneously.
“Current policy instability is beginning to impact investor confidence and negatively impact project timelines at a time when demand is surging,” American Clean Power Chief Policy Officer JC Sandberg said in a statement.
Despite the hurdles, developers were able to bring more than 50 gigawatts of wind, solar and batteries online in 2025, accounting for more than 90% of all new power capacity in the U.S., the report found. Clean power purchase agreements declined 36% in 2025 compared with 2024, signaling that the build-out of clean power in the U.S. could be lower in the 2028 to 2030 time period, according to the report.
Chediak writes for Bloomberg.
Business
Feud between Vegas gambler and Paramount exec sparks $150-million fraud lawsuit

The high-stakes feud between Paramount Skydance President Jeff Shell and Las Vegas gambler and self-professed “fixer” Robert James “R.J.” Cipriani spilled into court on Monday.
Cipriani filed a lawsuit against Shell on claims of fraud and eight other counts, alleging that he reneged on an oral agreement to develop an English-language version of a Spanish music show that streams on Roku TV.
He is seeking $150 million in damages.
In the 67-page lawsuit, filed in Los Angeles County Superior Court, Cipriani claims that in exchange for providing “sophisticated, high-value crisis communications services, entirely without compensation” over 18 months, Shell had agreed to develop the show “Serenata De Las Estrellas,” (Star Serenade), but failed to do so. Cipriani and his wife were to be named as co-executive producers.
“This case arises from the oldest form of fraud: a powerful man took everything a less powerful man had to offer, promised to repay him, lied to him when he asked about it, and then refused to compensate him at all,” states the complaint.
Cipriani — who has producer credits on a 2020 documentary about Vegas, “Money Machine: Behind the Lies,” and the 2015 movie “Wild Card” — intended to make “Serenata” as a “lasting legacy for his mother,” Regina, saying the effort “has been the driving force and the most important thing consuming [Cipriani’s] entire life of almost sixty-five years,” according to the suit.
The show was inspired by a song that the Philadelphia-born Cipriani used to sing to his late mother when he was growing up.
The litigation is the latest twist in a simmering behind-the-scenes scandal that has left much of Hollywood slack-jawed.
For weeks, Cipriani had threatened to file a lawsuit against Shell, with the potential to derail his comeback at Paramount, three years after he lost his job as NBCUniversal’s chief executive over an inappropriate relationship with an underling.
Cipriani’s suit alleges Shell wasdesperate for help in quelling negative stories about him.
It also portrays him as someone who was indiscreet, allegedly sharing sensitive information during the period when the Ellison family, through Skydance Media, was preparing to close its deal to acquire Paramount and then was actively pursuing Warner Bros. Discovery to add to its growing entertainment and media empire.
The eventual rift between the unlikely pair began in August 2024. Patty Glaser, the high-powered entertainment litigator, convened a meeting between the two men.
During the meeting with Shell, the executive expressed to Cipriani his concern that emails and texts between him and Hadley Gamble, the CNBC anchor Shell had been involved with, would come out, saying “that would absolutely destroy me,” according to the suit.
Cipriani claims in his lawsuit Shell was facing “catastrophic personal exposure arising from his conduct toward yet another woman in the media industry,” similar to what had prompted his ouster from NBCUniversal and that he “solicited” his “crisis communications services.”
According to the suit, Cipriani was in a position to help him, having engaged in a “longstanding practice of exposing misconduct in the entertainment and media industries.”
Robert James “R.J.” Cipriani in Amazon Prime Video’s 2025 series “Cocaine Quarterback.”
(Courtesy of Prime)
A high-rolling blackjack player, Cipriani’s colorful résumé includes aiding the FBI in the arrest and conviction of USC athlete-turned global drug kingpin Owen Hanson, who was sentenced to 21 years in federal prison, and filing a RICO suit against Resorts World Las Vegas.
Leveraging his “unique media relationships and industry influence,” Cipriani said in his complaint that he provided Shell with “ongoing threat-monitoring and intelligence services,” and “took proactive steps to suppress, redirect, or neutralize” negative coverage against Shell before publication.
Cipriani said Shell expressed “effusive gratitude” to him after he planted a story about another entertainment industry figure “in order to divert media attention” away from Shell. “Thank you thank you thank you,” Shell wrote in a text to Cipriani, according to the lawsuit, which included a copy of the text.
During tense negotiations over Paramount’s streaming rights for the highly successful “South Park” franchise last summer, Shell allegedly asked to talk to Cipriani about the matter. Cipriani then “orchestrat[ed] the placement of a highly favorable news article,” that was “devastating to Shell’s and Paramount’s adversaries in the dispute,” the suit states.
After a story published in a Hollywood trade, Cipriani wrote to Shell on WhatsApp, “I’m the one that put the article out for you!!!” and “I didn’t want to tell you till it hit so you have plausible deniability.”
According to a message cited in the lawsuit, Shell responded, “I love you!!!! …Thank you Rj,” adding “I owe you dinner at least!”
Despite those boasts, Paramount ultimately paid “South Park” creators millions more than Skydance had intended. To remove obstacles from Skydance’s path to buy Paramount, the media company agreed to two blockbuster deals that include paying the “South Park” production company more than $1.25 billion to continue the cartoon — making it one of the richest deals in television history.
During the course of their relationship, Cipriani further alleges that Shell alerted him to a then-pending $7.7-billion Paramount deal for the rights to UFC fights, while Netflix “believed” it had a “handshake deal” for the same rights, according to the suit.
Cipriani disclosed in his lawsuit that he filed a whistleblower complaint with the Securities and Exchange Commission over the disclosure of material information, claiming that Shell told him that not even UFC President Dana White knew of the transaction. In a WhatsApp message cited in the lawsuit, Shell told Cipriani that the deal was “very hush, hush until we sign.”
While the gambler continued to provide his services to Shell gratis, their relationship began to sour.
Cipriani became enraged that Shell did not uphold his end of the alleged deal to help him with the TV show, viewing it as a slap to him and his mother.
In February, the pair met to resolve their growing dispute. According to the lawsuit, also in attendance was an unidentified entertainment attorney who had represented both men in separate matters.
Patty Glaser has been widely reported as having represented Shell and Cipriani. She introduced them in summer 2024, as The Times reported Saturday.
“We were presented with a draft complaint riddled with clear errors of fact and law,” Glaser said in a statement last week. “We will strongly respond.”
The February meeting did not go well.
Shell not only “refused to compensate” Cipriani, but also told him that he could not “assist” him “in obtaining a television show or other entertainment industry opportunity.”
Cipriani further alleged in his lawsuit that during their “failed summit,” Shell revealed his “disdain” for David Zaslav, the Warner Bros. Discovery CEO, and disclosed that Paramount intended to “sweeten” its pending hostile offer for the studio to fend off Netflix prior to announcing its intention to do so publicly.
After the meeting, Cipriani stated in his complaint that Shell’s attorney privately offered Cipriani a “$150,000 personal loan” to resolve the dispute.
-

 Wisconsin1 week ago
Wisconsin1 week agoSetting sail on iceboats across a frozen lake in Wisconsin
-

 Massachusetts1 week ago
Massachusetts1 week agoMassachusetts man awaits word from family in Iran after attacks
-

 Maryland1 week ago
Maryland1 week agoAM showers Sunday in Maryland
-

 Pennsylvania5 days ago
Pennsylvania5 days agoPa. man found guilty of raping teen girl who he took to Mexico
-

 Florida1 week ago
Florida1 week agoFlorida man rescued after being stuck in shoulder-deep mud for days
-

 Sports6 days ago
Sports6 days agoKeith Olbermann under fire for calling Lou Holtz a ‘scumbag’ after legendary coach’s death
-

 Detroit, MI4 days ago
Detroit, MI4 days agoU.S. Postal Service could run out of money within a year
-

 Miami, FL6 days ago
Miami, FL6 days agoCity of Miami celebrates reopening of Flagler Street as part of beautification project



















